Unix环境高级编程(十九)终端I/O
终端I/O应用很广泛,用于终端、计算机之间的直接连线、调制解调器以及打印机等等。终端I/O有两种不同的工作模式:
(1)规范模式输入处理:终端输入以行为单位进行处理,对于每个读要求,终端驱动程序最多返回一行。(默认模式)
(2)非规范模式输入处理:输入字符并不组成行。
终端设备是由一般位于内核的终端驱动程序控制的,每个终端设备有一个输入队列和一个输出队列。如下图: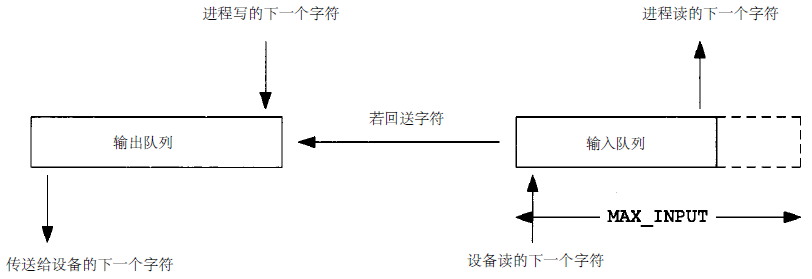
写个程序,更改特殊字符,禁用中断字符和更改文件结束符。程序如下:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <termios.h>
4 #include <errno.h>
5 #include <unistd.h>
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 struct termios term;
10 long vdisable;
11 //判断标准输入是否是终端设备
12 if(isatty(STDIN_FILENO) == 0)
13 {
14 printf("Standard input is not a terminal device.\n");
15 exit(-1);
16 }
17 if((vdisable = fpathconf(STDIN_FILENO,_PC_VDISABLE))<0)
18 {
19 perror("fpathconf eeror or _POSIX_VDISABLE not in effect");
20 exit(-1);
21 }
22 //获取termios结构
23 if(tcgetattr(STDIN_FILENO,&term) < 0)
24 {
25 perror("tcgetattr error");
26 exit(-1);
27 }
28
29 term.c_cc[VINTR] = vdisable;
30 term.c_cc[VEOF] = 2;
31 //设置termios结构
32 if(tcsetattr(STDIN_FILENO,TCSAFLUSH,&term) < 0)
33 {
34 perror("tcsetattr error");
35 exit(-1);
36 }
37 return 0;
38 }
获取和设置终端属性函数:
int tcgetattr(int fd, struct termios *termios_p);
int tcsetattr(int fd, int optional_actions,const struct termios *termios_p);
调用以上函数屏蔽标志取或设置一个值,程序如下:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <termios.h>
4 #include <errno.h>
5 #include <unistd.h>
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 struct termios term;
10 //获取termios结构
11 if(tcgetattr(STDIN_FILENO,&term) < 0)
12 {
13 perror("tcgetattr error");
14 exit(-1);
15 }
16 switch(term.c_cflag & CSIZE)
17 {
18 case CS5:
19 printf("5 bits/byte\n");
20 break;
21 case CS6:
22 printf("6 bits/byte\n");
23 break;
24 case CS7:
25 printf("7 bits/byte\n");
26 break;
27 case CS8:
28 printf("8 bits/byte\n");
29 break;
30 default:
31 printf("Unknown bityes/byte\n");
32 }
33 term.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE; //字符长度清0
34 term.c_cflag |= CS5; //设置为8 bites/byte
35 if(tcsetattr(STDIN_FILENO,TCSANOW,&term) < 0)
36 {
37 perror("tcsetattr error");
38 exit(-1);
39 }
40 return 0;
41 }
stty命令:在终端中输入stty -a命令显示终端的所有选项,执行命令结果如下: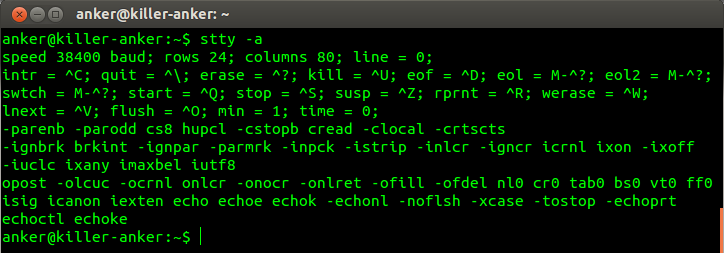
终端标识:在大多数UNIXi系统中,控制终端的名字是/dev/tty。
char *ctermid(char *s); //获取终端控制名字
int isatty(int fd); //判断fd是否为终端设备
char *ttyname(int fd); // 获取终端设备的路径名
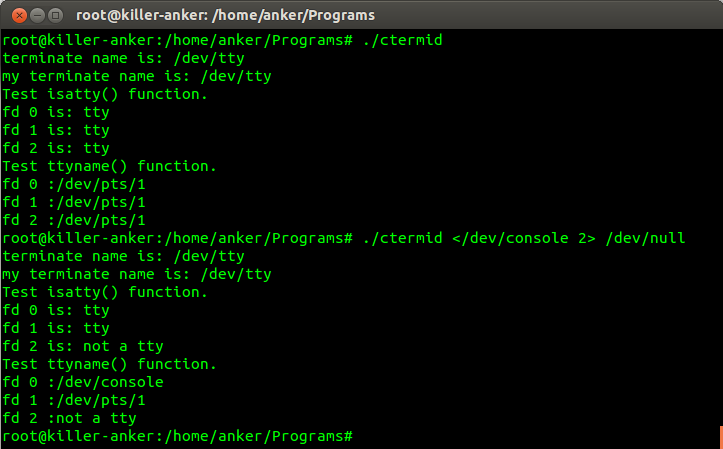
写个程序输出控制终端的标识符信息,程序如下:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <termios.h>
4 #include <unistd.h>
5 #include <string.h>
6 static char ctermid_name[L_ctermid];
7 char* my_ctermid(char *str)
8 {
9 if(str == NULL)
10 str = ctermid_name;
11 return (strcpy(str,"/dev/tty"));
12 }
13 int main()
14 {
15 char tername[50];
16 char *name;
17 ctermid(tername);
18 printf("terminate name is: %s\n",tername);
19 my_ctermid(tername);
20 printf("my terminate name is: %s\n",tername);
21 printf("Test isatty() function.\n");
22 printf("fd 0 is: %s\n",isatty(0)? "tty" : "not a tty");
23 printf("fd 1 is: %s\n",isatty(1)? "tty" : "not a tty");
24 printf("fd 2 is: %s\n",isatty(2)? "tty" : "not a tty");
25 printf("Test ttyname() function.\n");
26 if(isatty(0))
27 {
28 name = ttyname(0);
29 if(name == NULL)
30 name ="undefined";
31 }
32 else
33 name = "not a tty";
34 printf("fd 0 :%s\n",name);
35 if(isatty(1))
36 {
37 name = ttyname(1);
38 if(name == NULL)
39 name ="undefined";
40 }
41 else
42 name = "not a tty";
43 printf("fd 1 :%s\n",name);
44 if(isatty(2))
45 {
46 name = ttyname(2);
47 if(name == NULL)
48 name ="undefined";
49 }
50 else
51 name = "not a tty";
52 printf("fd 2 :%s\n",name);
53 exit(0);
54 }
程序执行结果如下:
终端的窗口大小:内核为每个终端和伪终端保存了一个窗口大小结构winszie,用ioctl函数的TIOCGWINSZ命令可以获取此结构的当前值。
struct winsize {
unsigned short ws_row;
unsigned short ws_col;
unsigned short ws_xpixel; /* unused */
unsigned short ws_ypixel; /* unused */
};
写个程序打印终端窗口大小,程序如下:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <termios.h>
4 #include <unistd.h>
5 #include <string.h>
6 #include <sys/ioctl.h>
7 #include <signal.h>
8 #include <errno.h>
9
10 static void pr_winsize(int fd)
11 {
12 struct winsize size;
13 if(ioctl(fd,TIOCGWINSZ,(char *)&size) < 0)
14 {
15 perror("ioctl() error");
16 exit(-1);
17 }
18 printf("%d rows,%d columns\n",size.ws_row,size.ws_col);
19 }
20 static void sig_winch(int signo)
21 {
22 printf("SIGWINCH received\n");
23 pr_winsize(STDIN_FILENO);
24 }
25 int main()
26 {
27 if(isatty(STDIN_FILENO) == 0)
28 {
29 printf("STDIN_FILENO is not terminate device.\n");
30 exit(1);
31 }
32 if(signal(SIGWINCH,sig_winch) == SIG_ERR)
33 {
34 perror("signal() error");
35 exit(-1);
36 }
37 pr_winsize(STDIN_FILENO);
38 for( ; ;)
39 pause();
40 }
程序执行结果如下:

总结:本章介绍了终端,涉及到很多系统底层的知识,很多参数。看的时候只是了解了一些基本的终端操作,还要很多地方不懂,关键是不知道终端用在什么地方,以后用到了需要回头好好学习一下。





