Servlet基础
定义:实现了servlet接口的Java程序叫做servlet
1、新建maven项目,导入servlet依赖
<dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>4.0.1</version> </dependency> <!-- servlet依赖的jar包start --> <!-- jsp依赖jar包start --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.3.3</version> </dependency>
2、新建HelloServlet类,实现servlet接口,直接继承HttpServlet
//实现Servlet接口 public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("进入doget方法");
PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter(); writer.print("Hello,Servlet"); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(req,resp); } }
3、编写Hello.jsp,在WEB-INF目录下新建一个jsp的文件夹,新建hello.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Alan</title> </head> <body> ${msg} </body> </html>
4、在web.xml中注册Servlet,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.alan.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/user</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
5、配置Tomcat,并启动测试
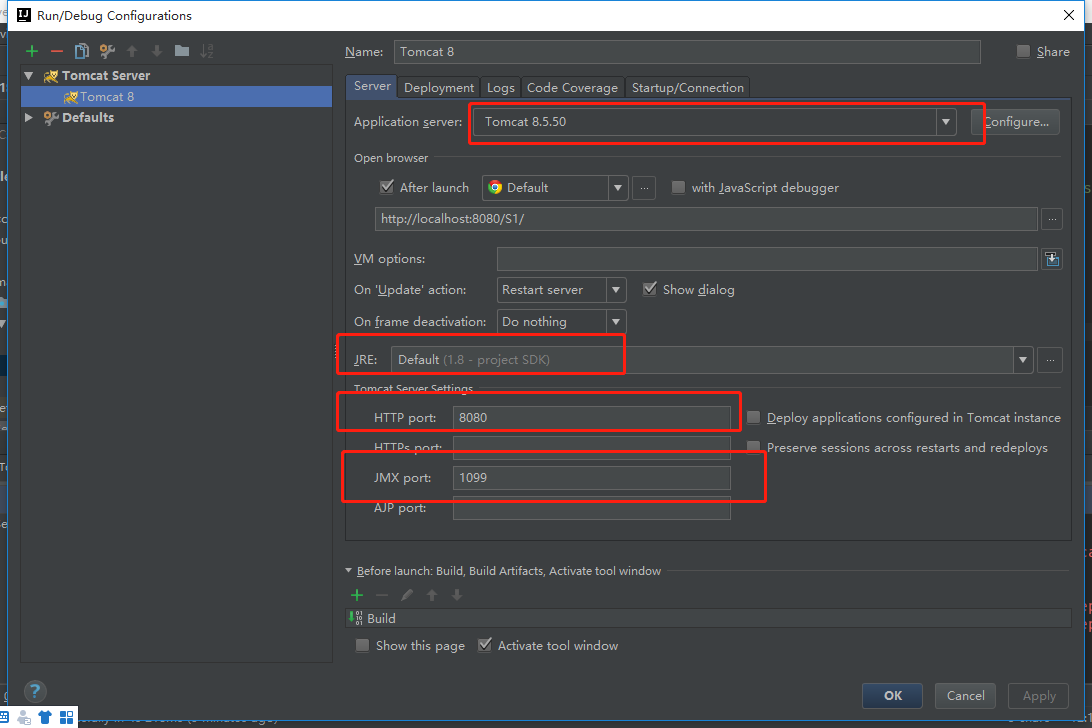
新增Artifact,选择war,右侧可自定义项目运行路径
启动tomcat
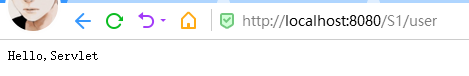
小结:
servlet的映射过程,浏览器连接web服务,web服务通过已注册的信息找到对应的servlet进行访问

新增ErrorServlet类
public class ErrorServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { resp.setContentType("text/html"); resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter(); writer.print("<h1>404</h1>"); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(req,resp); } }
web.xml注册ErrorServlet
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ErrorServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.alan.servlet.ErrorServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ErrorServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
启动tomcat测试
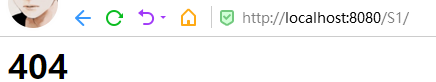

结论:指定了固有的映射路径优先级最高,如果找不到就会走默认
ServletContext
web服务启动时都会创建一个ServletContext,代表当前web应用,是Servlet池
不同的Servlet可以通过ServletContext共享数据
设置一个set和一个get,测试实现结果
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); context.setAttribute("username","alan");
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); String username = (String)context.getAttribute("username");
获取web.xml中的初始化参数
<!-- 配置一些web应用初始化参数--> <context-param> <param-name>url</param-name> <param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis</param-value> </context-param>
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); String url = context.getInitPatamter("url");
指定路径转发请求
//配置转发路径
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher=context.getRequestDispatcher("/user"); //forward实现转发 requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);
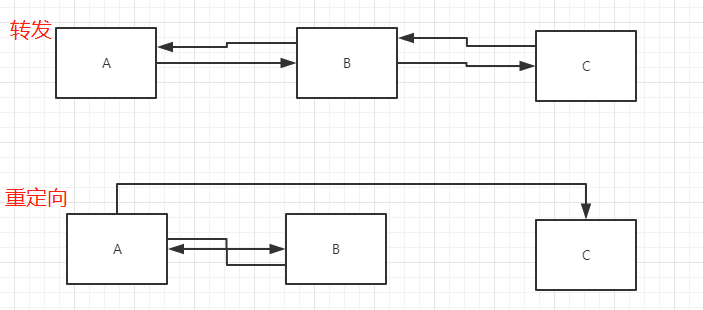
转发和重定向的概念
转发:A需要资源,只能去找B,B再去找C,再向A返回资源
重定向:A需要资源,A找到B,B告知A资源在C,A找C获得资源
异同:页面都实现跳转,请求转发URL不发生变化,重定向URL发生变化
读取资源文件
//db.properties
username=xxxx
password=xxxx
InputStream inputStream = this.getServletContext().getResourcesAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/db.properties"); Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(inputStream); String username = prop.getProperty("username");


