Docker 与 K8S学习笔记(二十三)—— Kubernetes集群搭建
小伙伴们,好久不见,这几个月实在太忙,所以一直没有更新,今天刚好有空,咱们继续k8s的学习,由于我们后面需要深入学习Pod的调度,所以我们原先使用MiniKube搭建的实验环境就不能满足我们的需求了,我们这一节将使用kubeadm搭建Kubernets集群。
一、虚拟机创建
我们的集群包含三个节点kubevm1、kubevm2、kubevm3,其中kubevm1作为Master
我们首先需要使用Virtualbox创建一个虚拟机,步骤如下:
1、新建虚拟机
我们设置内存2G,硬盘20G,CPU 2核,在光驱设置中选择已经下好的Centos镜像。
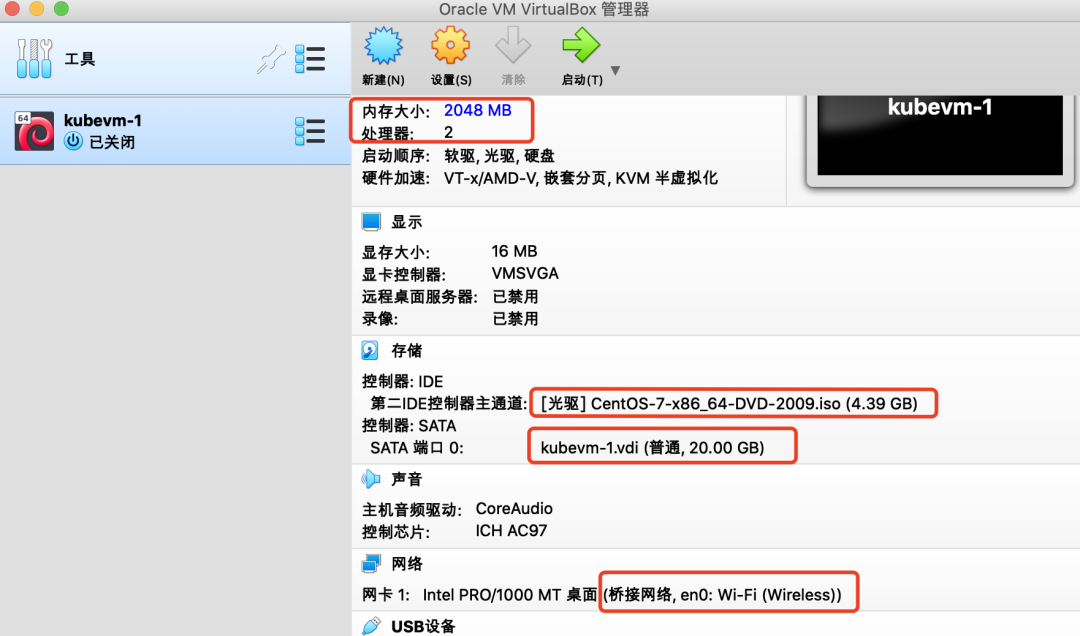
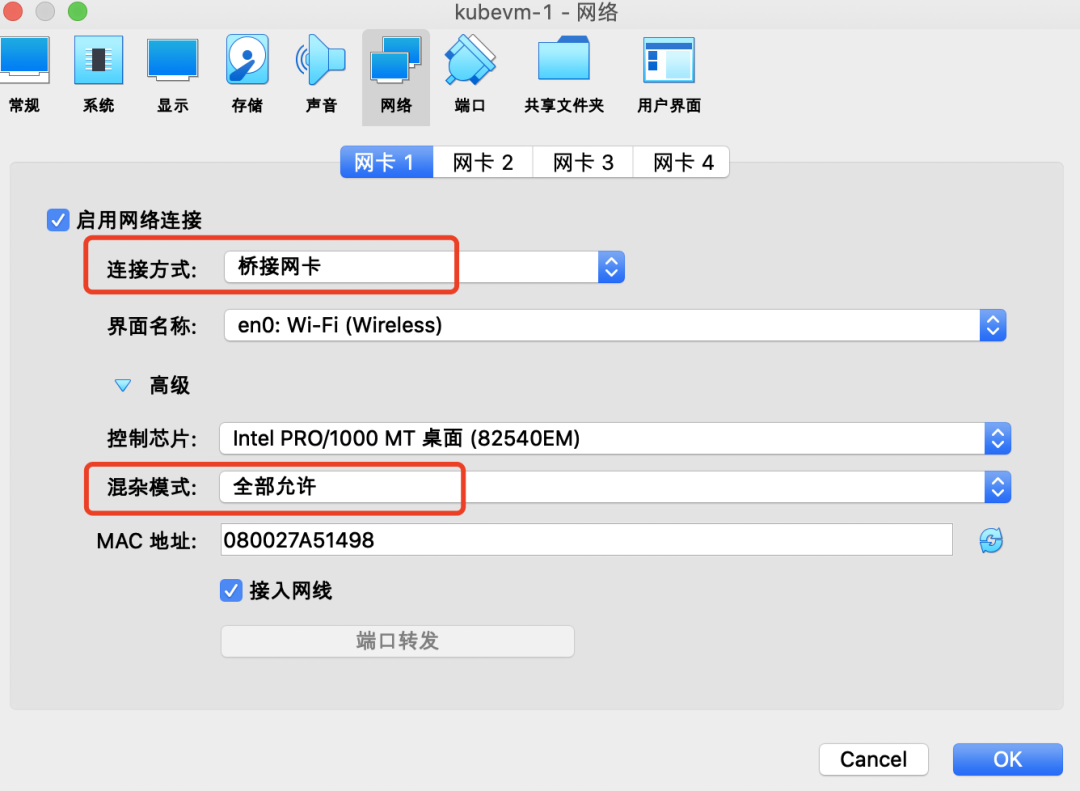
设置网络为【桥接网卡】
2、安装系统
启动虚拟机,进入安装界面,根据安装向导:
-
设置时区;
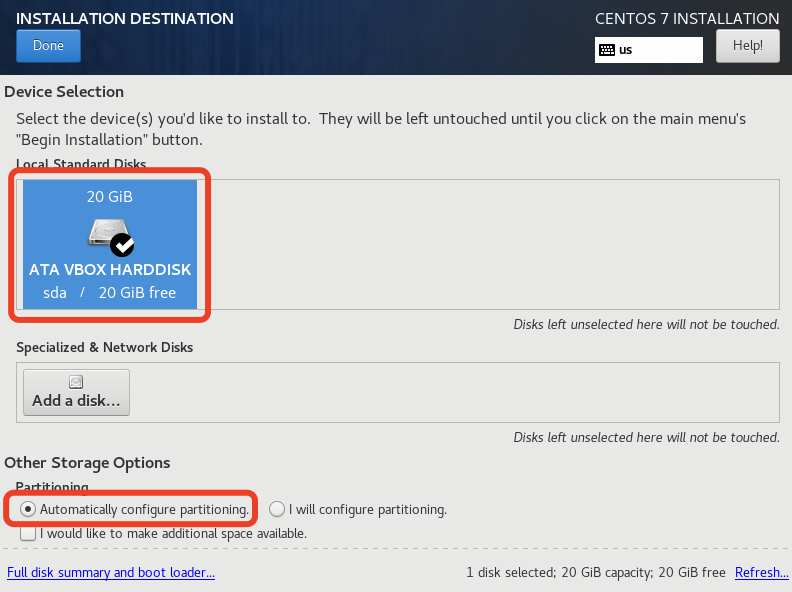
- 选择安装磁盘并分区(直接自动分区即可);
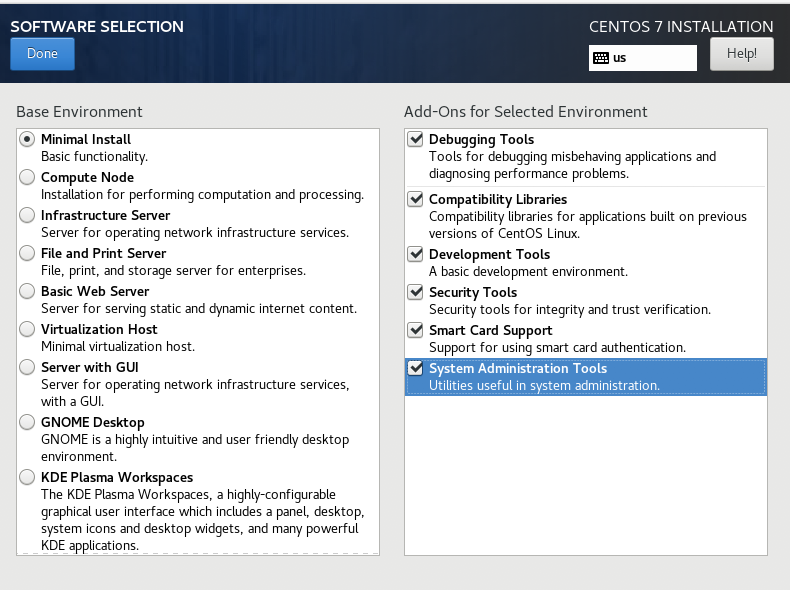
- 安装模式选【Minimal Install】,附加软件全选;
- "NETWORK & HOST NAME"中打开OnBoot,主机名如果不在这里设置,在安装完系统后可以通过“hostnamectl”命令设置;
- 安装过程中可以设置root用户密码或者添加新用户,我们这里图省事就直接用root账户了。
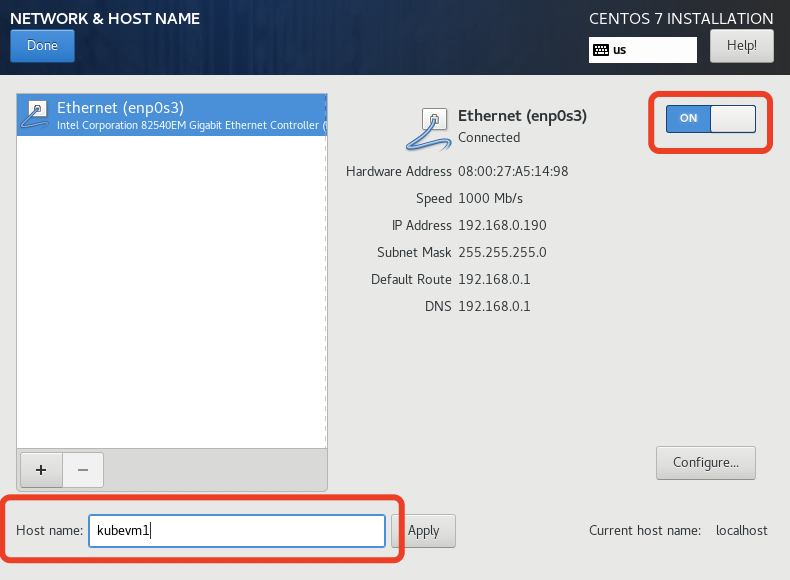
等待系统安装完毕后,重起虚拟机,为了操作方便,我们使用宿主机的终端ssh到虚拟机。
PS:由于是最小化安装,是没有ifconfig命令的,所以我们可以通过ip addr获取到虚拟机IP,然后再通过ssh登陆。
3、系统设置
1)禁用SELinux
-
临时关闭:命令行执行 setenforce 0
-
永久关闭:修改/etc/selinux/config文件,将SELINUX=enforcing改为SELINUX=disabled
2)关闭防火墙
systemctl disable firewalld && systemctl stop firewalld
3)关闭交换分区
swapoff -a && sed -i '/ swap / s/^/#/' /etc/fstab
4)更改iptables设置
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables
PS:如果提示找不到bridge-nf-call-iptables,可执行一下命令:
modprobe br_netfilter
二、安装Docker
yum install docker -y
三、安装Kubernetes
1、设置yum源
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo << EOF [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64 enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 repo_gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF
2、添加docker镜像
vim /etc/docker/daemon.json 添加如下内容: "registry-mirrors": ["https://registry.docker-cn.co"]
3、安装kubectl、kubeadm、kubelet
yum install -y kubelet-1.19.16 kubeadm-1.19.16 kubectl-1.19.16
4、启动docker和kubelet
systemctl enable docker && systemctl start docker
systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet
四、Kubernetes集群安装与配置
1、复制虚拟机并配置hosts
我们首先复制出两个虚拟机,并分别修改其hostname为kubevm2和kubevm3。
hostnamectl set-hostnam xxx
将三台虚拟机的地址写入到宿主机和每一台虚拟机的hosts文件中:
vim /etc/hosts 192.168.0.187 kubevm1 192.168.0.185 kubevm2 192.168.0.184 kubevm3
2、初始化master(kubevm1)
在kubevm1上执行kubeadm init
[root@kubevm1 ~]# kubeadm init --apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.56.120 --image-repository=registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers --kubernetes-version=v1.19.16 --service-cidr=10.1.0.0/16 --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 W0518 23:27:14.470037 2551 configset.go:348] WARNING: kubeadm cannot validate component configs for API groups [kubelet.config.k8s.io kubeproxy.config.k8s.io] [init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.19.16 [preflight] Running pre-flight checks [preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster [preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection [preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull' [certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki" [certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key [certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local kubevm1] and IPs [10.1.0.1 192.168.56.120] [certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key [certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [kubevm1 localhost] and IPs [192.168.56.120 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key [certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [kubevm1 localhost] and IPs [192.168.56.120 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "sa" key and public key [kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes" [kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env" [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml" [kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet [control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler" [etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests" [wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s [kubelet-check] Initial timeout of 40s passed. [apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 43.002951 seconds [upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace [kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.19" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster [upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs [mark-control-plane] Marking the node kubevm1 as control-plane by adding the label "node-role.kubernetes.io/master=''" [mark-control-plane] Marking the node kubevm1 as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule] [bootstrap-token] Using token: wribbh.31c6e1tnddpnpwn9 [bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster [bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace [kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key [addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS [addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully! To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster. Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/ Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root: kubeadm join 192.168.56.120:6443 --token wribbh.31c6e1tnddpnpwn9 \ --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:1804e7ee43d7469839b3f5fdbf2c57f5d53eee1da6bc40c59a1b04fce6edddd5
接下来我们执行以下命令,这样我们就可以使用kubectl管理集群了:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
我们先查看下当前集群各个组件状态:
[root@kubevm1 ~]# kubectl get pods,svc -n kube-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/coredns-6d56c8448f-jf9gg 0/1 Pending 0 2m4s pod/coredns-6d56c8448f-m2cdp 0/1 Pending 0 2m3s pod/etcd-kubevm1 1/1 Running 0 2m17s pod/kube-apiserver-kubevm1 1/1 Running 0 2m17s pod/kube-controller-manager-kubevm1 1/1 Running 0 2m17s pod/kube-proxy-rv7g4 1/1 Running 0 2m4s pod/kube-scheduler-kubevm1 1/1 Running 0 2m17s NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/kube-dns ClusterIP 10.1.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 2m19s
我们发现coredns都处于NotReady状态,这是因为我们还没有安装网络组件。
3、安装网络插件
下载fannel的yaml配置文件:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
这里确认下yaml中Network是否与前面执行kubeadm init时--pod-network-cidr参数的值一致。
kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
等待一会儿,我们可以看到集群中网络服务对应的Pod都ok了:
[root@kubevm1 ~]# kubectl get pods,svc -n kube-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/coredns-6d56c8448f-jf9gg 1/1 Running 0 28m pod/coredns-6d56c8448f-m2cdp 1/1 Running 0 28m pod/etcd-kubevm1 1/1 Running 0 28m pod/kube-apiserver-kubevm1 1/1 Running 0 28m pod/kube-controller-manager-kubevm1 1/1 Running 0 28m pod/kube-flannel-ds-td89l 1/1 Running 0 13m pod/kube-proxy-rv7g4 1/1 Running 0 28m pod/kube-scheduler-kubevm1 1/1 Running 0 28m NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/kube-dns ClusterIP 10.1.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 28m
4、注册Node
在kubevm2、kubevm3中执行以下命令,注册到master:
kubeadm join 192.168.56.120:6443 --token wribbh.31c6e1tnddpnpwn9 \ --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:1804e7ee43d7469839b3f5fdbf2c57f5d53eee1da6bc40c59a1b04fce6edddd5
注册后我们使用kubectl get node查看一下:
[root@kubevm1 ~]# kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION kubevm1 Ready master 46m v1.19.16 kubevm2 Ready <none> 15m v1.19.16 kubevm3 Ready <none> 14m v1.19.16
ok,至此整个集群搭建完成。







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)