FisherLDA
一 问题描述
• 在 UCI 数据集商的 iris 和 sonar 数据上验证算法的有效性;
• 训练和测试样本有三种方式进行划分:
1)将数据随机分训练样本和测试,多次平均求结果
2)k 折交叉验证
3)留 1 法
二 解决问题的方法
※ 总体概览和声明:
用 fisher 判别分析法训练数据并进行测试。
所用编程语言:Python 所用样本划分方法:K 折交叉验证
所画结果分为两类:iris 数据集的测试样本分布图。
Sonar 数据集经过 3,10,20,30, 40,50,60 维训练后准确度折线图。
1. Fisher 判别分析原理和流程 原理:Fisher linear discriminant analysis(简称 Fisher LDA)是由 FSHER 在 1936 年提出来 的方法。主要思想是将高维样本通过数学变换投影到一维空间中再对其进行分类。如图:
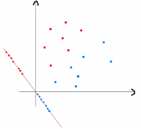
我们通过计算类内离散度矩阵和类间离散度矩阵来判别样本。
假设有N个样本为分别为X=[X1,X2 ……… Xn];用来区分二分类的直线(投影函数)为:
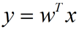
类均值向量为 :
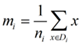
定义各类类内离散度矩阵以及总类内离散度矩阵为:
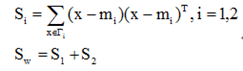
类间离散度矩阵为:
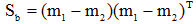
投影后,均值变为:
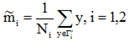
类内离散度矩阵变为一个值(对于两类问题):
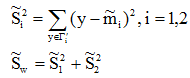
类间离散度矩阵变为两类均值差的平方:
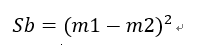
此处m上应该有波浪号
通过化简可以求得Fisher判别准则变为:式1.1
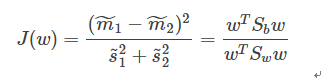
我们的目的就是求使得式1.1最大的投影方向W。因为W幅值的调节不会影响其方向,因此该问题变为一个优化问题:
Max WT*Sb*W(WT是W的转置)
s.t. WT*Sw*W=c(c不等于0)
此时,可引入拉格朗日乘子使该问题转化为一个无约束的优化问题:
L(w,d)= WT*Sb*W -d(WT*Sw*W-c)
通过化简可以得到:W*=Sw求逆*(m1-m2)
代码流程:
1, 取数据,并将其划分为训练集和测试集,此处使用K折交叉验证,通过调参,最终发现7折或8折交叉准确率最大。此处取7折交叉结果作为示例。划分数据的代码存于(util)文件中。对样本标签进行编码。
2, 计算d维的各类的类均值向量Mi
3, 计算类内离散度矩阵和类间离散度矩阵向量
4, 求解矩阵广义特征值问题
5, 为新特征子空间选择线性判别法
6, 将样本转化为新的子空间
7, 计算错误率和准确率
8, 画出训练集的分布关系(只针对iris数据集)
9, 改变样本维度,循环。最后计算所有准确率的平均数(只针对sonar数据集)
10, 画出准确率随着样本维度增加的折线图(只针对sonar数据集)
Iris数据集代码文件:fisherLDA主要程序, util1将数据划分为数据集和训练集的程序, load数据输入转换成矩阵的程序
iris数据集文件:fisherLDA1, util2, load1功能与上面一一对应
这些代码多数来源于github,如有需要请前去搜索,很容易搜到。笔者只进行了一些改动来满足不同的数据。代码环境,pycharm编辑器。win10,64位anaconda,记得将util和load类型的文件保存在Lib当中,python3.6
1 #!/usr/bin/python3 2 from load import loader as loader #作者自己写的程序 3 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder 4 import numpy as np 5 from log import log #作者自己写的程序 6 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 7 import util1 as util1 #作者自己写的程序 8 9 #第一个函数,计算均值向量 10 def computeMeanVec(X, y, uniqueClass): 11 """ 12 Step 1: Computing the d-dimensional mean vectors for different class 计算均值向量 13 """ 14 np.set_printoptions(precision=4)#保留四位小数 15 16 mean_vectors = [] 17 for cl in range(1,len(uniqueClass)+1): 18 mean_vectors.append(np.mean(X[y==cl], axis=0)) #axis = 0:压缩行,对各列求均值,返回 1* n 矩阵 19 log('Mean Vector class %s: %s\n' %(cl, mean_vectors[cl-1]))# 20 return mean_vectors 21 22 #第二个函数,计算类内离散度矩阵 23 def computeWithinScatterMatrices(X, y, feature_no, uniqueClass, mean_vectors): 24 # 2.1 Within-class scatter matrix 25 S_W = np.zeros((feature_no, feature_no))#初始化矩阵吧 26 for cl,mv in zip(range(1,len(uniqueClass)+1), mean_vectors): 27 class_sc_mat = np.zeros((feature_no, feature_no)) # scatter matrix for every class 28 for row in X[y == cl]: 29 row, mv = row.reshape(feature_no,1), mv.reshape(feature_no,1) # make column vectors 30 class_sc_mat += (row-mv).dot((row-mv).T) 31 S_W += class_sc_mat # sum class scatter matrices 32 log('within-class Scatter Matrix: {}\n'.format(S_W)) 33 34 return S_W 35 36 #计算类间离散度矩阵 37 def computeBetweenClassScatterMatrices(X, y, feature_no, mean_vectors): 38 # 2.2 Between-class scatter matrix 39 overall_mean = np.mean(X, axis=0) 40 41 S_B = np.zeros((feature_no, feature_no)) 42 for i,mean_vec in enumerate(mean_vectors): 43 n = X[y==i+1,:].shape[0] 44 mean_vec = mean_vec.reshape(feature_no, 1) # make column vector 45 overall_mean = overall_mean.reshape(feature_no, 1) # make column vector 46 S_B += n * (mean_vec - overall_mean).dot((mean_vec - overall_mean).T) 47 log('between-class Scatter Matrix: {}\n'.format(S_B)) 48 49 return S_B 50 51 def computeEigenDecom(S_W, S_B, feature_no): 52 """ 53 Step 3: Solving the generalized eigenvalue problem for the matrix S_W^-1 * S_B 54 求解矩阵 S_W^-1 * S_B 的广义特征值问题 55 """ 56 m = 10^-6 # add a very small value to the diagonal of your matrix before inversion 57 #在反演之前向矩阵的对角线增加一个非常小的值 58 # noinspection PyTypeChecker 59 eig_vals, eig_vecs = np.linalg.eig(np.linalg.inv(S_W+np.eye(S_W.shape[1])*m).dot(S_B)) 60 61 for i in range(len(eig_vals)): 62 eigvec_sc = eig_vecs[:,i].reshape(feature_no, 1) 63 log('\nEigenvector {}: \n{}'.format(i+1, eigvec_sc.real)) 64 log('Eigenvalue {:}: {:.2e}'.format(i+1, eig_vals[i].real)) 65 66 for i in range(len(eig_vals)): 67 eigv = eig_vecs[:,i].reshape(feature_no, 1) 68 # noinspection PyTypeChecker 69 np.testing.assert_array_almost_equal(np.linalg.inv(S_W+np.eye(S_W.shape[1])*m).dot(S_B).dot(eigv), 70 eig_vals[i] * eigv, 71 decimal=6, err_msg='', verbose=True) 72 log('Eigenvalue Decomposition OK') 73 74 return eig_vals, eig_vecs 75 76 def selectFeature(eig_vals, eig_vecs, feature_no): 77 """ 78 Step 4: Selecting linear discriminants for the new feature subspace 79 """ 80 # 4.1. Sorting the eigenvectors by decreasing eigenvalues 81 # Make a list of (eigenvalue, eigenvector) tuples 82 eig_pairs = [(np.abs(eig_vals[i]), eig_vecs[:,i]) for i in range(len(eig_vals))] 83 84 # Sort the (eigenvalue, eigenvector) tuples from high to low by the value of eigenvalue 85 eig_pairs = sorted(eig_pairs, key=lambda k: k[0], reverse=True) 86 87 log('Eigenvalues in decreasing order:\n') 88 for i in eig_pairs: 89 log(i[0]) 90 91 log('Variance explained:\n') 92 eigv_sum = sum(eig_vals) 93 for i,j in enumerate(eig_pairs): 94 log('eigenvalue {0:}: {1:.2%}'.format(i+1, (j[0]/eigv_sum).real)) 95 96 # 4.2. Choosing k eigenvectors with the largest eigenvalues - here I choose the first two eigenvalues 97 W = np.hstack((eig_pairs[0][1].reshape(feature_no, 1), eig_pairs[1][1].reshape(feature_no, 1))) 98 log('Matrix W: \n{}'.format(W.real)) 99 100 return W 101 102 def transformToNewSpace(X, W, sample_no, mean_vectors, uniqueClass): 103 """ 104 Step 5: Transforming the samples onto the new subspace 105 """ 106 X_trans = X.dot(W) 107 mean_vecs_trans = [] 108 for i in range(len(uniqueClass)): 109 mean_vecs_trans.append(mean_vectors[i].dot(W)) 110 111 #assert X_trans.shape == (sample_no,2), "The matrix is not size of (sample number, 2) dimensional." 112 113 return X_trans, mean_vecs_trans 114 115 def computeErrorRate(X_trans, mean_vecs_trans, y): 116 """ 117 Compute the error rate 118 """ 119 120 """ 121 Project to the second largest eigenvalue 122 """ 123 uniqueClass = np.unique(y) 124 threshold = 0 125 for i in range(len(uniqueClass)): 126 threshold += mean_vecs_trans[i][1] 127 threshold /= len(uniqueClass) 128 log("threshold: {}".format(threshold)) 129 130 errors = 0 131 for (i,cl) in enumerate(uniqueClass): 132 label = cl 133 tmp = X_trans[y==label, 1] 134 # compute the error numbers for class i 135 num = len(tmp[tmp<threshold]) if mean_vecs_trans[i][1] > threshold else len(tmp[tmp>=threshold]) 136 log("error rate in class {} = {}".format(i, num*1.0/len(tmp))) 137 errors += num 138 139 errorRate = errors*1.0/X_trans.shape[0] 140 log("Error rate for the second largest eigenvalue = {}".format(errorRate)) 141 log("Accuracy for the second largest eigenvalue = {}".format(1-errorRate)) 142 143 144 """ 145 Project to the largest eigenvalue - and return 146 """ 147 uniqueClass = np.unique(y) 148 threshold = 0 149 for i in range(len(uniqueClass)): 150 threshold += mean_vecs_trans[i][0] 151 threshold /= len(uniqueClass) 152 log("threshold: {}".format(threshold)) 153 154 errors = 0 155 for (i,cl) in enumerate(uniqueClass): 156 label = cl 157 tmp = X_trans[y==label, 0] 158 # compute the error numbers for class i 159 num = len(tmp[tmp<threshold]) if mean_vecs_trans[i][0] > threshold else len(tmp[tmp>=threshold]) 160 log("error rate in class {} = {}".format(i, num*1.0/len(tmp))) 161 errors += num 162 163 errorRate = errors*1.0/X_trans.shape[0] 164 log("Error rate = {}".format(errorRate)) 165 log("Accuracy = {}".format(1-errorRate)) 166 167 return 1-errorRate, threshold 168 169 170 171 172 def plot_step_lda(X_trans, y, label_dict, uniqueClass, dataset, threshold): 173 174 ax = plt.subplot(111) 175 for label,marker,color in zip(range(1, len(uniqueClass)+1),('^', 's','d'),('blue', 'red','green')): 176 plt.scatter(x=X_trans[:,0].real[y == label], 177 y=X_trans[:,1].real[y == label], 178 marker=marker, 179 color=color, 180 alpha=0.5, 181 label=label_dict[label] 182 ) 183 184 plt.xlabel('LDA1') 185 plt.ylabel('LDA2') 186 187 leg = plt.legend(loc='upper right', fancybox=True) 188 #loc 图例所有figure位置,右上。 fancybox控制是否应在构成图例背景的FancyBboxPatch周围启用圆边 189 leg.get_frame().set_alpha(0.5) 190 plt.title('Fisher LDA: {} data projection onto the first 2 linear discriminants'.format(dataset)) 191 192 # plot the the threshold line 绘出分界线 193 [bottom, up] = ax.get_ylim() 194 #plt.axvline(x=threshold.real, ymin=bottom, ymax=0.3, linewidth=2, color='k', linestyle='--') 195 plt.axvline(threshold.real, linewidth=2, color='g') 196 197 # hide axis ticks 198 plt.tick_params(axis="both", which="both", bottom="off", top="off", 199 labelbottom="on", left="off", right="off", labelleft="on") 200 201 # remove axis spines 202 ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False) 203 ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False) 204 ax.spines["bottom"].set_visible(False) 205 ax.spines["left"].set_visible(False) 206 207 plt.grid() 208 #plt.tight_layout 209 plt.show() 210 211 def mainFisherLDAtest(dataset='iris', alpha=0.5): #def mainFisherLDAtest(dataset='sonar', alpha=0.5): 212 # load data 213 path = dataset + '/' + dataset + '.data' 214 load = loader(path)#取数据 215 [X, y] = load.load() 216 # noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences 217 [X, y, testX, testY] = util1.divide(X, y, alpha)#训练集和训练集标签,测试集和测试集标签 218 X = np.array(X) #数组 219 testX = np.array(testX)#测试集 220 221 feature_no = X.shape[1] # define the dimension读取矩阵的维度,返回列数也就是样本维度 222 print(feature_no) 223 sample_no = X.shape[0] # define the sample number返回行数也就是样本个数 224 225 # preprocessing 226 enc = LabelEncoder() 227 label_encoder = enc.fit(y)#对Y进行编码 228 229 230 y = label_encoder.transform(y) + 1#将Y变成正数 231 print(y) 232 testY = label_encoder.transform(testY) + 1#与上文一样 233 # noinspection PyTypeChecker 234 uniqueClass = np.unique(y) # define how many class in the outputs确定有几类输出 235 label_dict = {} # define the label name 236 for i in range(1, len(uniqueClass)+1): 237 label_dict[i] = "Class"+str(i) 238 log(label_dict) #打印类别 239 240 # Step 1: Computing the d-dimensional mean vectors for different class 241 mean_vectors = computeMeanVec(X, y, uniqueClass) 242 243 244 # Step 2: Computing the Scatter Matrices 245 S_W = computeWithinScatterMatrices(X, y, feature_no, uniqueClass, mean_vectors) 246 S_B = computeBetweenClassScatterMatrices(X, y, feature_no, mean_vectors) 247 248 # Step 3: Solving the generalized eigenvalue problem for the matrix S_W^-1 * S_B 249 eig_vals, eig_vecs = computeEigenDecom(S_W, S_B, feature_no) 250 251 # Step 4: Selecting linear discriminants for the new feature subspace为新特征子空间选择线性判别法 252 W = selectFeature(eig_vals, eig_vecs, feature_no) 253 254 # Step 5: Transforming the samples onto the new subspace将样本转化为新的子空间 255 X_trans, mean_vecs_trans = transformToNewSpace(testX, W, sample_no, mean_vectors, uniqueClass) 256 257 258 # Step 6: compute error rate 259 accuracy, threshold = computeErrorRate(X_trans, mean_vecs_trans, testY) 260 261 262 # plot 263 plot_step_lda(X_trans, testY, label_dict, uniqueClass, dataset, threshold) 264 #原文这句话被注释了plot_step_lda(X_trans, testY, label_dict, uniqueClass, dataset, threshold) 265 266 return accuracy 267 268 269 270 271 if __name__ == "__main__": 272 dataset = ['ionosphere', 'iris'] # choose the dataset 273 alpha = 0.5 # choose the train data percentage 274 accuracy = mainFisherLDAtest(dataset[1], alpha) 275 print(accuracy)
iris数据导入代码和分割为训练集和测试集代码
1 import pandas as pd 2 3 4 5 class loader(object): 6 7 8 9 def __init__(self,file_name, split_token = ','):#def __init__(self,file_name , split_token = ','): 10 11 self.file_name = 'iris/iris.data' 12 13 self.split_token = split_token 14 15 16 17 def load(self): 18 19 df = pd.io.parsers.read_csv( 20 21 filepath_or_buffer='请在此处写上自己数据的本地路径', # 原文 filepath_or_buffer = self.file_name,笔者用的windows,在路径中用了反斜杠 22 23 header = None, 24 25 sep = self.split_token) #原文 sep = self.split_token) 26 27 28 print(df) 29 print(df.shape[1]) 30 self.dimension = df.shape[1]-1 31 print(self.dimension) 32 33 df.columns = list(range(self.dimension)) + ['label'] #原文df.columns = range(self.dimension) + ['label'] 34 print(df.columns) 35 df.dropna(how = 'all', inplace = True) # to drop the empty line at file-end 滤除缺失数据 36 37 df.tail() #查看低端数据 38 39 40 41 self.X = df[list(range(self.dimension))].values # 原文self.X = df[range(self.dimension)].values 42 43 self.Y = df['label'].values 44 45 distinct_label = list(set(self.Y)) #创建分类标签列表 46 47 48 49 if len(distinct_label) != 3: #原文 if len(distinct_label) != 2: 50 51 raise Exception('Three Labels Required\n','Label Sets:\n',distinct_label) 52 #原文 raise Exception('Two Labels Required\n','Label Sets:\n',distinct_label) 53 #raise Exception是一个函数,用于线程出现异常时抛出错误 54 55 56 self.Y = list(map(lambda x: {distinct_label[0]:1, distinct_label[1]:2,distinct_label[2]:3}[x], self.Y)) 57 #原文 self.Y = map(lambda x: {distinct_label[0]: 1, distinct_label[1]: -1}[x], self.Y) 58 print(self.Y) 59 60 return [self.X, self.Y] 61 62 63 64 if __name__ == "__main__": 65 66 loader = loader('iris/iris.data') #原文 loader = loader('ionosphere/ionosphere.data') 67 68 [X, y] = loader.load() 69 70 print (X.shape)#X是整个数据的大小,Y是标签,共有三个标签
1 import random 2 3 import math 4 5 import numpy as np 6 7 #将数据分为训练集和数据集 8 9 def divide(dataX, dataY, alpha):#x是数据,y是标签 10 11 [positiveX, negativeX,X2] = split(dataX, dataY)#分出三类 12 13 posNum1 = int(len(positiveX) * alpha) # alpha=0.5 14 15 negNum1 = int(len(negativeX) * alpha) 16 17 X2Num1 = int(len(X2) * alpha) 18 19 posNum2 = len(positiveX) - posNum1 # 将第一类,第二类,第三类都平均分为两份,一份测试集,一份训练集,这里采用九折交叉 20 21 negNum2 = len(negativeX) - negNum1 22 23 X2Num2 = len(X2) - X2Num1 24 25 26 27 posOrder = np.random.permutation(len(positiveX))#分别给两类标上序号 28 29 negOrder = np.random.permutation(len(negativeX)) 30 31 X2Order = np.random.permutation(len(X2)) 32 33 dataX1 = []#训练集数据 34 35 dataY1 = []#训练集标签 36 37 dataX2 = []#测试集数据 38 39 dataY2 = []#测试集标签 40 41 42 43 44 for i in range(posNum1): #原文是for i in xrange(posNum1):但是xrange只能用于python2.x,以下全部替换了 45 46 dataX1.append(positiveX[posOrder[i]]) 47 48 dataY1.append(1) 49 50 for i in range(posNum2): 51 52 dataX2.append(positiveX[posOrder[i + posNum1]]) 53 54 dataY2.append(1) 55 56 for i in range(negNum1): 57 58 dataX1.append(negativeX[negOrder[i]]) 59 60 dataY1.append(-1) 61 62 for i in range(negNum2): 63 64 dataX2.append(negativeX[negOrder[i + negNum1]]) 65 66 dataY2.append(-1) 67 for i in range(X2Num1): 68 69 dataX1.append(X2[X2Order[i]]) 70 71 dataY1.append(2) 72 73 for i in range(X2Num2): 74 75 dataX2.append(X2[X2Order[i + negNum1]]) 76 77 dataY2.append(2) 78 79 80 81 return [dataX1, dataY1, dataX2, dataY2]#返回的是平分的两类数据,x 为数据,y是标签 82 83 84 85 def resample(dataX, dataY): 86 87 ''' 88 89 sample an equivalent size dataset uniformly from the original one从原始样本中均匀地采样等效大小的数据集 90 91 ''' 92 93 instances = len(dataX) 94 95 96 97 sampleX = [] 98 99 sampleY = [] 100 101 102 103 for i in range(instances): 104 105 chosen = random.randint(0, instances-1) 106 107 sampleX.append(dataX[chosen]) 108 109 sampleY.append(dataY[chosen]) 110 111 112 113 return [sampleX, sampleY] 114 115 116 117 def split(dataX, dataY): 118 119 ''' 120 121 divide the whole dataset into positive and negative ones 把整个数据集分为正数和负数 122 123 ''' 124 125 instances = len(dataX) 126 127 positiveX = [] 128 129 negativeX = [] 130 131 X2=[] 132 133 for i in range(instances): 134 135 if dataY[i] == 1: 136 137 positiveX.append(dataX[i]) 138 139 elif dataY[i] == 2 : 140 141 negativeX.append(dataX[i]) 142 143 else : 144 145 X2.append(dataX[i]) 146 147 148 149 return [positiveX, negativeX,X2] 150 151 152 153 def F_norm(matrix): 154 155 ''' 156 157 calculate the Frobenius norm of a matrix i.e |vec(A)|_2 计算矩阵的Frobenius范数,即VEC(A)2 158 159 ''' 160 161 squared = map(lambda x: x**2, matrix) 162 163 squared_sum = np.sum(squared) 164 165 return math.sqrt(squared_sum) 166 167 168 169 def M_norm(matrix, vector): 170 171 ''' 172 173 calculate the M-norm of a matrix i.e \sqrt{v.T * M * v} 计算矩阵的m范数,即\sqrt{v.t*m *v}。 174 175 ''' 176 177 squared = np.dot(vector.T, np.dot(matrix, vector)) 178 179 return math.sqrt(squared[0][0])
sonar代码。功能同上顺序
1 #!/usr/bin/python3 2 from load1 import loader as loader #作者自己写的程序 3 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder 4 import numpy as np 5 from log import log #作者自己写的程序 6 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 7 import util2 as util2 #作者自己写的程序 8 9 #第一个函数,计算均值向量 10 def computeMeanVec(X, y, uniqueClass): 11 """ 12 Step 1: Computing the d-dimensional mean vectors for different class 计算均值向量 13 """ 14 np.set_printoptions(precision=4)#保留四位小数 15 16 mean_vectors = [] 17 for cl in range(1,len(uniqueClass)+1): 18 mean_vectors.append(np.mean(X[y==cl], axis=0)) #axis = 0:压缩行,对各列求均值,返回 1* n 矩阵 19 log('Mean Vector class %s: %s\n' %(cl, mean_vectors[cl-1]))# 20 return mean_vectors 21 22 #第二个函数,计算类内离散度矩阵 23 def computeWithinScatterMatrices(X, y, feature_no, uniqueClass, mean_vectors): 24 # 2.1 Within-class scatter matrix 25 S_W = np.zeros((feature_no, feature_no))#初始化矩阵吧 26 for cl,mv in zip(range(1,len(uniqueClass)+1), mean_vectors): 27 class_sc_mat = np.zeros((feature_no, feature_no)) # scatter matrix for every class 28 for row in X[y == cl]: 29 row, mv = row.reshape(feature_no,1), mv.reshape(feature_no,1) # make column vectors 30 class_sc_mat += (row-mv).dot((row-mv).T) 31 S_W += class_sc_mat # sum class scatter matrices 32 log('within-class Scatter Matrix: {}\n'.format(S_W)) 33 34 return S_W 35 36 #计算类间离散度矩阵 37 def computeBetweenClassScatterMatrices(X, y, feature_no, mean_vectors): 38 # 2.2 Between-class scatter matrix 39 overall_mean = np.mean(X, axis=0) 40 41 S_B = np.zeros((feature_no, feature_no)) 42 for i,mean_vec in enumerate(mean_vectors): 43 n = X[y==i+1,:].shape[0] 44 mean_vec = mean_vec.reshape(feature_no, 1) # make column vector 45 overall_mean = overall_mean.reshape(feature_no, 1) # make column vector 46 S_B += n * (mean_vec - overall_mean).dot((mean_vec - overall_mean).T) 47 log('between-class Scatter Matrix: {}\n'.format(S_B)) 48 49 return S_B 50 51 def computeEigenDecom(S_W, S_B, feature_no): 52 """ 53 Step 3: Solving the generalized eigenvalue problem for the matrix S_W^-1 * S_B 54 求解矩阵 S_W^-1 * S_B 的广义特征值问题 55 """ 56 m = 10^-6 # add a very small value to the diagonal of your matrix before inversion 57 #在反演之前向矩阵的对角线增加一个非常小的值 58 # noinspection PyTypeChecker 59 eig_vals, eig_vecs = np.linalg.eig(np.linalg.inv(S_W+np.eye(S_W.shape[1])*m).dot(S_B)) 60 61 for i in range(len(eig_vals)): 62 eigvec_sc = eig_vecs[:,i].reshape(feature_no, 1) 63 log('\nEigenvector {}: \n{}'.format(i+1, eigvec_sc.real)) 64 log('Eigenvalue {:}: {:.2e}'.format(i+1, eig_vals[i].real)) 65 66 for i in range(len(eig_vals)): 67 eigv = eig_vecs[:,i].reshape(feature_no, 1) 68 # noinspection PyTypeChecker 69 np.testing.assert_array_almost_equal(np.linalg.inv(S_W+np.eye(S_W.shape[1])*m).dot(S_B).dot(eigv), 70 eig_vals[i] * eigv, 71 decimal=6, err_msg='', verbose=True) 72 log('Eigenvalue Decomposition OK') 73 74 return eig_vals, eig_vecs 75 76 def selectFeature(eig_vals, eig_vecs, feature_no): 77 """ 78 Step 4: Selecting linear discriminants for the new feature subspace 79 """ 80 # 4.1. Sorting the eigenvectors by decreasing eigenvalues 81 # Make a list of (eigenvalue, eigenvector) tuples 82 eig_pairs = [(np.abs(eig_vals[i]), eig_vecs[:,i]) for i in range(len(eig_vals))] 83 84 # Sort the (eigenvalue, eigenvector) tuples from high to low by the value of eigenvalue 85 eig_pairs = sorted(eig_pairs, key=lambda k: k[0], reverse=True) 86 87 log('Eigenvalues in decreasing order:\n') 88 for i in eig_pairs: 89 log(i[0]) 90 91 log('Variance explained:\n') 92 eigv_sum = sum(eig_vals) 93 for i,j in enumerate(eig_pairs): 94 log('eigenvalue {0:}: {1:.2%}'.format(i+1, (j[0]/eigv_sum).real)) 95 96 # 4.2. Choosing k eigenvectors with the largest eigenvalues - here I choose the first two eigenvalues 97 W = np.hstack((eig_pairs[0][1].reshape(feature_no, 1), eig_pairs[1][1].reshape(feature_no, 1))) 98 log('Matrix W: \n{}'.format(W.real)) 99 100 return W 101 102 def transformToNewSpace(X, W, sample_no, mean_vectors, uniqueClass): 103 """ 104 Step 5: Transforming the samples onto the new subspace 105 """ 106 X_trans = X.dot(W) 107 mean_vecs_trans = [] 108 for i in range(len(uniqueClass)): 109 mean_vecs_trans.append(mean_vectors[i].dot(W)) 110 111 #assert X_trans.shape == (sample_no,2), "The matrix is not size of (sample number, 2) dimensional." 112 113 return X_trans, mean_vecs_trans 114 115 def computeErrorRate(X_trans, mean_vecs_trans, y): 116 """ 117 Compute the error rate 118 """ 119 120 """ 121 Project to the second largest eigenvalue 122 """ 123 uniqueClass = np.unique(y) 124 threshold = 0 125 for i in range(len(uniqueClass)): 126 threshold += mean_vecs_trans[i][1] 127 threshold /= len(uniqueClass) 128 log("threshold: {}".format(threshold)) 129 130 errors = 0 131 for (i,cl) in enumerate(uniqueClass): 132 label = cl 133 tmp = X_trans[y==label, 1] 134 # compute the error numbers for class i 135 num = len(tmp[tmp<threshold]) if mean_vecs_trans[i][1] > threshold else len(tmp[tmp>=threshold]) 136 log("error rate in class {} = {}".format(i, num*1.0/len(tmp))) 137 errors += num 138 139 errorRate = errors*1.0/X_trans.shape[0] 140 log("Error rate for the second largest eigenvalue = {}".format(errorRate)) 141 log("Accuracy for the second largest eigenvalue = {}".format(1-errorRate)) 142 143 144 """ 145 Project to the largest eigenvalue - and return 146 """ 147 uniqueClass = np.unique(y) 148 threshold = 0 149 for i in range(len(uniqueClass)): 150 threshold += mean_vecs_trans[i][0] 151 threshold /= len(uniqueClass) 152 log("threshold: {}".format(threshold)) 153 154 errors = 0 155 for (i,cl) in enumerate(uniqueClass): 156 label = cl 157 tmp = X_trans[y==label, 0] 158 # compute the error numbers for class i 159 num = len(tmp[tmp<threshold]) if mean_vecs_trans[i][0] > threshold else len(tmp[tmp>=threshold]) 160 log("error rate in class {} = {}".format(i, num*1.0/len(tmp))) 161 errors += num 162 163 errorRate = errors*1.0/X_trans.shape[0] 164 log("Error rate = {}".format(errorRate)) 165 log("Accuracy = {}".format(1-errorRate)) 166 167 return 1-errorRate, threshold 168 169 170 171 172 def plot_step_lda(X_trans, y, label_dict, uniqueClass, dataset, threshold): 173 174 ax = plt.subplot(111) 175 for label,marker,color in zip(range(1, len(uniqueClass)+1),('^', 's','d'),('blue', 'red','green')): 176 plt.scatter(x=X_trans[:,0].real[y == label], #X[:,0]就是取所有行的第0个数据, X[:,1] 就是取所有行的第1个数据 177 y=X_trans[:,1].real[y == label], 178 marker=marker, 179 color=color, 180 alpha=0.5, 181 label=label_dict[label] 182 ) 183 184 plt.xlabel('LDA1') 185 plt.ylabel('LDA2') 186 187 leg = plt.legend(loc='upper right', fancybox=True) 188 #loc 图例所有figure位置,右上。 fancybox控制是否应在构成图例背景的FancyBboxPatch周围启用圆边 189 leg.get_frame().set_alpha(0.5) 190 plt.title('Fisher LDA: {} data projection onto the first 2 linear discriminants'.format(dataset)) 191 192 # plot the the threshold line 绘出分界线 193 [bottom, up] = ax.get_ylim() 194 #plt.axvline(x=threshold.real, ymin=bottom, ymax=0.3, linewidth=2, color='k', linestyle='--') 195 plt.axvline(threshold.real, linewidth=2, color='g') 196 197 # hide axis ticks 198 plt.tick_params(axis="both", which="both", bottom="off", top="off", 199 labelbottom="on", left="off", right="off", labelleft="on") 200 201 # remove axis spines 202 ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False) 203 ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False) 204 ax.spines["bottom"].set_visible(False) 205 ax.spines["left"].set_visible(False) 206 207 plt.grid() 208 #plt.tight_layout 209 plt.show() 210 #第二个图 211 def plot_step_lda2(accuracys): 212 ax = plt.subplot(111) 213 plt.xlabel('Demention') 214 plt.ylabel('Accuracy') 215 216 leg = plt.legend(loc='upper right', fancybox=True) 217 # loc 图例所有figure位置,右上。 fancybox控制是否应在构成图例背景的FancyBboxPatch周围启用圆边 218 leg.get_frame().set_alpha(0.5) 219 plt.title('Fisher LDA: {} data projection onto the first 2 linear discriminants'.format(dataset)) 220 plt.axis([0, 60, 0, 1]) 221 x=[3, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60] 222 y=accuracys 223 plt.plot(x,y,linewidth=1,color='b') 224 plt.show() 225 226 def mainFisherLDAtest(dataset='sonar', alpha=0.5): #def mainFisherLDAtest(dataset='sonar', alpha=0.5): 227 # load data 228 path = dataset + '/' + dataset + '.data' 229 load = loader(path)#取数据 230 [X, y] = load.load() 231 [x1,y1]=[X,y] 232 # noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences 233 #改动,进行交叉验证 234 dimension=[3,10,20,30,40,50,60] 235 accuracys=[0,0,0,0,0,0,0] 236 accnumber=0 237 for i in range(7): 238 [X, y]=[x1,y1] 239 j=dimension[i] 240 [X, y, testX, testY] = util2.divide(X, y, alpha,j)#训练集和训练集标签,测试集和测试集标签 241 X = np.array(X) #数组 242 testX = np.array(testX)#测试集 243 244 feature_no = X.shape[1] # define the dimension读取矩阵的维度,返回列数也就是样本维度 245 print(feature_no) 246 sample_no = X.shape[0] # define the sample number返回行数也就是样本个数 247 248 # preprocessing 249 enc = LabelEncoder() 250 label_encoder = enc.fit(y)#对Y进行编码 251 252 253 y = label_encoder.transform(y) + 1#将Y变成正数 254 print(y) 255 testY = label_encoder.transform(testY) + 1#与上文一样 256 # noinspection PyTypeChecker 257 uniqueClass = np.unique(y) # define how many class in the outputs确定有几类输出 258 label_dict = {} # define the label name 259 for i in range(1, len(uniqueClass)+1): 260 label_dict[i] = "Class"+str(i) 261 log(label_dict) #打印类别 262 263 # Step 1: Computing the d-dimensional mean vectors for different class 264 mean_vectors = computeMeanVec(X, y, uniqueClass) 265 266 267 # Step 2: Computing the Scatter Matrices 268 S_W = computeWithinScatterMatrices(X, y, feature_no, uniqueClass, mean_vectors) 269 S_B = computeBetweenClassScatterMatrices(X, y, feature_no, mean_vectors) 270 271 # Step 3: Solving the generalized eigenvalue problem for the matrix S_W^-1 * S_B 272 eig_vals, eig_vecs = computeEigenDecom(S_W, S_B, feature_no) 273 274 # Step 4: Selecting linear discriminants for the new feature subspace为新特征子空间选择线性判别法 275 W = selectFeature(eig_vals, eig_vecs, feature_no) 276 277 # Step 5: Transforming the samples onto the new subspace将样本转化为新的子空间 278 X_trans, mean_vecs_trans = transformToNewSpace(testX, W, sample_no, mean_vectors, uniqueClass) 279 280 281 # Step 6: compute error rate 282 accuracy, threshold = computeErrorRate(X_trans, mean_vecs_trans, testY) 283 284 285 # plot 286 plot_step_lda(X_trans, testY, label_dict, uniqueClass, dataset, threshold) 287 #plot_step_lda(X_trans, testY, label_dict, uniqueClass, dataset, threshold) 288 accuracys[accnumber] = accuracy 289 accnumber = accnumber + 1 290 plot_step_lda2(accuracys) 291 accuracy = ( accuracys[0] + accuracys[1] +accuracys[2] + accuracys[3] + accuracys[4] + accuracys[5]+ accuracys[6])/6 292 return accuracy 293 294 295 296 297 if __name__ == "__main__": 298 dataset = ['ionosphere', 'sonar'] # choose the dataset 299 alpha = 0.7 # choose the train data percentage 300 accuracy = mainFisherLDAtest(dataset[1], alpha) 301 print(accuracy)
1 import pandas as pd 2 3 4 5 class loader(object): 6 7 8 9 def __init__(self,file_name, split_token = ','):#def __init__(self,file_name , split_token = ','): 10 11 self.file_name = 'sonar/sonar.data' 12 13 self.split_token = split_token 14 15 16 17 def load(self): 18 19 df = pd.io.parsers.read_csv( 20 21 filepath_or_buffer='请在此处写上自己数据的本地路径', # 原文 filepath_or_buffer = self.file_name, 22 23 header = None, 24 25 sep = self.split_token) #原文 sep = self.split_token) 26 27 28 29 30 self.dimension = df.shape[1]-1 31 32 33 df.columns = list(range(self.dimension)) + ['label'] #原文df.columns = range(self.dimension) + ['label'] 34 35 df.dropna(how = 'all', inplace = True) # to drop the empty line at file-end 滤除缺失数据 36 37 df.tail() #查看低端数据 38 39 40 41 self.X = df[list(range(self.dimension))].values # 原文self.X = df[range(self.dimension)].values 42 43 self.Y = df['label'].values 44 45 distinct_label = list(set(self.Y)) #创建分类标签列表 46 47 48 49 if len(distinct_label) != 2: #原文 if len(distinct_label) != 2: 50 51 raise Exception('Two Labels Required\n','Label Sets:\n',distinct_label) 52 #原文 raise Exception('Two Labels Required\n','Label Sets:\n',distinct_label) 53 #raise Exception是一个函数,用于线程出现异常时抛出错误 54 55 56 self.Y = list(map(lambda x: {distinct_label[0]:1, distinct_label[1]:-1}[x], self.Y)) 57 #原文 self.Y = map(lambda x: {distinct_label[0]: 1, distinct_label[1]: -1}[x], self.Y) 58 59 return [self.X, self.Y] 60 61 62 63 if __name__ == "__main__": 64 65 loader = loader('ionosphere/ionosphere.data') #原文 loader = loader('ionosphere/ionosphere.data') 66 67 [X, y] = loader.load() 68 69 print (X.shape)#X是整个数据的大小,Y是标签,共有三个标签
import random import math import numpy as np #将数据分为训练集和数据集 #x是数据,y是标签 #divide a dataset into two parts, usually training and testing set def divide(dataX, dataY, alpha,i): print(i) d=[] for k in range(i): d.append(k) print(d) dataX=dataX[:,d] print(dataX) [positiveX, negativeX] = split(dataX, dataY)#分出两类 # alpha=0.5 posNum1 = int (len(positiveX) * alpha) negNum1 = int (len(negativeX) * alpha) posNum2 = len(positiveX) - posNum1 negNum2 = len(negativeX) - negNum1 # 将第一类,第二类 posOrder = np.random.permutation(len(positiveX))#分别给两类标上序号 negOrder = np.random.permutation(len(negativeX)) dataX1 = [] dataY1 = [] dataX2 = [] dataY2 = [] for i in range(posNum1): dataX1.append(positiveX[posOrder[i]]) dataY1.append(1) for i in range(posNum2): dataX2.append(positiveX[posOrder[i + posNum1]]) dataY2.append(1) for i in range(negNum1): dataX1.append(negativeX[negOrder[i]]) dataY1.append(-1) for i in range(negNum2): dataX2.append(negativeX[negOrder[i + negNum1]]) dataY2.append(-1) return [dataX1, dataY1, dataX2, dataY2]#返回的是平分的两类数据 def resample(dataX, dataY): ''' sample an equivalent size dataset uniformly from the original one从原始样本中均匀地采样等效大小的数据集 ''' instances = len(dataX) sampleX = [] sampleY = [] for i in range(instances): chosen = random.randint(0, instances-1) sampleX.append(dataX[chosen]) sampleY.append(dataY[chosen]) return [sampleX, sampleY] def split(dataX, dataY): ''' divide the whole dataset into positive and negative ones 把整个数据集分为正数和负数 ''' instances = len(dataX) positiveX = [] negativeX = [] for i in range(instances): if dataY[i] == 1: positiveX.append(dataX[i]) else: negativeX.append(dataX[i]) return [positiveX, negativeX] def F_norm(matrix): ''' calculate the Frobenius norm of a matrix i.e |vec(A)|_2 计算矩阵的Frobenius范数,即VEC(A)2 ''' squared = map(lambda x: x**2, matrix) squared_sum = np.sum(squared) return math.sqrt(squared_sum) def M_norm(matrix, vector): ''' calculate the M-norm of a matrix i.e \sqrt{v.T * M * v} 计算矩阵的m范数,即\sqrt{v.t*m *v}。 ''' squared = np.dot(vector.T, np.dot(matrix, vector)) return math.sqrt(squared[0][0])
就这些了。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号