有限元方法[Matlab]-笔记
1.【数学公式】mathtype和word2016集成2.【MathType】word2016数学公式编号3.【Matlab】基于KDtree的最近邻搜索和范围搜索4.【Matlab】判断点和多面体位置关系的两种方法实现5.《空间三角面片对相交判断算法》的matlab实现_ 0.2微秒6.Mpmath库-学习笔记
7.有限元方法[Matlab]-笔记
8.结构动力学教材-学习笔记9.复合材料力学基础及有限元分析10.【数值计算方法】数值积分&微分-python实现11.【数值计算方法】2&3维高斯积分的python实现12.【数值计算方法】线性方程组的迭代解法13.【数值计算方法】线性方程组迭代算法的Python实现14.【数值计算方法】线性方程组的迭代解法-数值实验15.【数值计算方法】非线性方程求根16.【数值计算方法】非线性方程求根-数值实验17.【数值计算方法】常微分方程初值问题的数值解
<< MATLAB Codes for Finite Element Analysis - Solids and Structures (Ferreira) >> 笔记
目录
第一章:matlab基础
略
第二章: 离散系统
笔记、例题


Matlab代码
problem1.m
% MATLAB codes for Finite Element Analysis % Problem 1: 3 springs problem % clear memory clear ; % ? define vars P=10; % N ki=[1;1;1;1]; % elementNodes: connections at elements elementNodes=[1 2; 2 3; 2 4]; % numberElements: number of Elements numberElements=size(elementNodes,1); % numberNodes: number of nodes numberNodes=4; % for structure: % displacements: displacement vector N x 1 % force : force vector N x 1 % stiffness: stiffness matrix N x N displacements=zeros(numberNodes,1); %#ok<PREALL> force=zeros(numberNodes,1); stiffness=zeros(numberNodes); % applied load at node 2 force(2)=P; % computation of the system stiffness matrix for e=1:numberElements % elementDof: element degrees of freedom (Dof) elementDof=elementNodes(e,:) ; stiffness(elementDof,elementDof)=... stiffness(elementDof,elementDof)+ki(e)*[1 -1;-1 1]; end % boundary conditions and solution % prescribed dofs prescribedDof=[1;3;4]; % free Dof : activeDof % setdiff() 函数-->求两个数组的差集 % C = setdiff(A,B) 返回 A 中存在但 B 中不存在的数据,不包含重复项.C 是有序的. activeDof=setdiff((1:numberNodes)',prescribedDof); % solution % !KU=F --> U=K\F displacements=stiffness(activeDof,activeDof)\force(activeDof); % positioning all displacements displacements1=zeros(numberNodes,1); displacements1(activeDof)=displacements; % output displacements/reactions outputDisplacementsReactions(displacements1,stiffness,numberNodes,prescribedDof)
outputDisplacementsReactions.m
function outputDisplacementsReactions(displacements,stiffness,GDof,prescribedDof) % output of displacements and reactions in % tabular form % GDof: total number of degrees of freedom of the problem % displacements disp('Displacements') %displacements=displacements1; jj=1:GDof; % format [jj' displacements] % reactions F=stiffness*displacements; reactions=F(prescribedDof); disp('reactions') [prescribedDof reactions] end
第三章:1D 杆单元
笔记

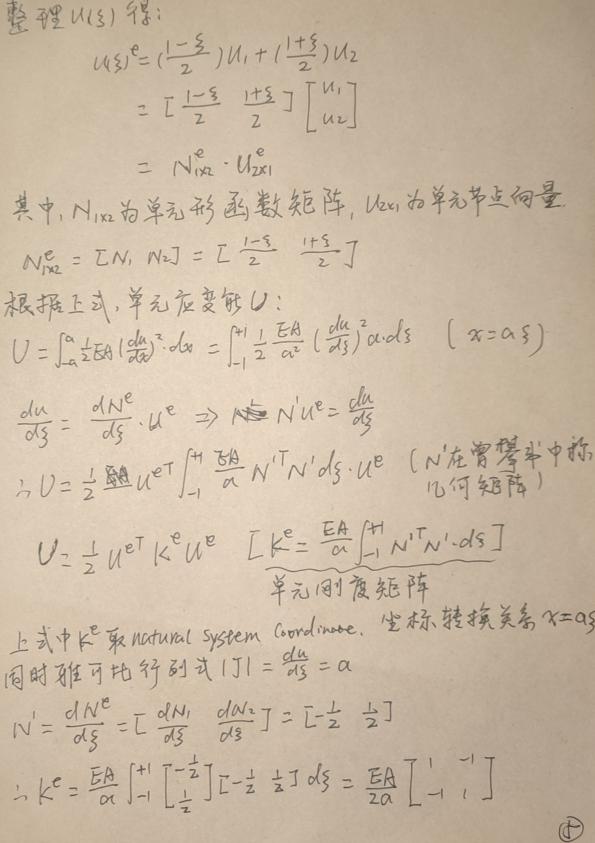

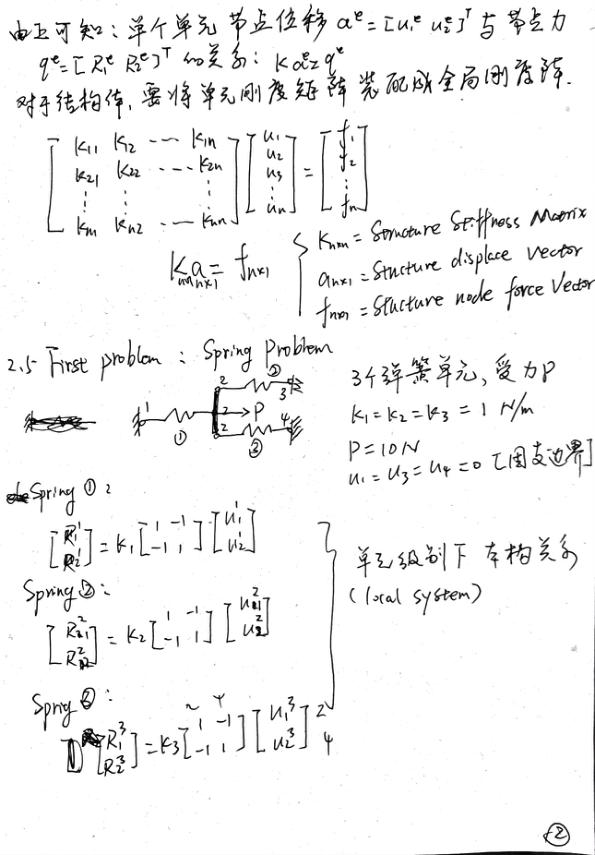
例题1

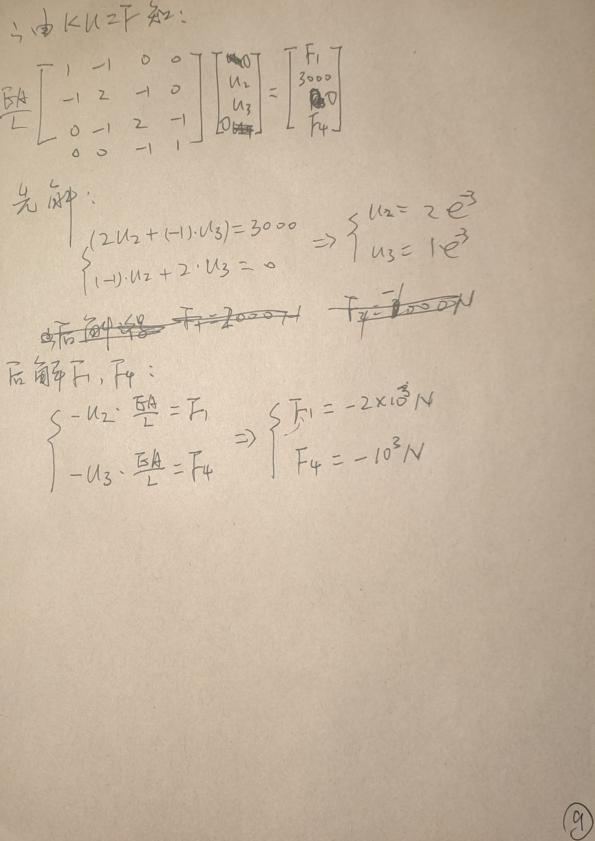
matlab 代码
problem2.m
% antonio ferreira 2008 % clear memory clear all % E; modulus of elasticity % A: area of cross section % L: length of bar E = 30e6;A=1;EA=E*A; L = 90; % generation of coordinates and connectivities % numberElements: number of elements numberElements=3; % generation equal spaced coordinates nodeCoordinates=linspace(0,L,numberElements+1); xx=nodeCoordinates; % numberNodes: number of nodes numberNodes=size(nodeCoordinates,2); % elementNodes: connections at elements ii=1:numberElements; elementNodes(:,1)=ii; elementNodes(:,2)=ii+1; % for structure: % displacements: displacement vector % force : force vector % stiffness: stiffness matrix displacements=zeros(numberNodes,1); %#ok<PREALL> force=zeros(numberNodes,1); stiffness=zeros(numberNodes,numberNodes); % applied load at node 2 force(2)=3000.0; % computation of the system stiffness matrix for e=1:numberElements; % elementDof: element degrees of freedom (Dof) elementDof=elementNodes(e,:) ; nn=length(elementDof); length_element=nodeCoordinates(elementDof(2))... -nodeCoordinates(elementDof(1)); detJacobian=length_element/2;invJacobian=1/detJacobian; % central Gauss point (xi=0, weight W=2) [shape,naturalDerivatives]=shapeFunctionL2(0.0); Xderivatives=naturalDerivatives*invJacobian; % B matrix B=zeros(1,nn); B(1:nn) = Xderivatives(:); stiffness(elementDof,elementDof)=stiffness(elementDof,elementDof)+B'*B*2*detJacobian*EA; end % boundary conditions and solution % prescribed dofs fixedDof=find(xx==min(nodeCoordinates(:)) | xx==max(nodeCoordinates(:)))'; prescribedDof=[fixedDof] % free Dof : activeDof activeDof=setdiff([1:numberNodes]',[prescribedDof]); % solution GDof=numberNodes; displacements=solution(GDof,prescribedDof,stiffness,force); % output displacements/reactions outputDisplacementsReactions(displacements,stiffness,numberNodes,prescribedDof) disp(stiffness) disp(force) disp(displacements)
solution.m
function displacements=solution(GDof,prescribedDof,stiffness,force) % function to find solution in terms of global displacements activeDof=setdiff([1:GDof]', ... [prescribedDof]); U=stiffness(activeDof,activeDof)\force(activeDof); displacements=zeros(GDof,1); displacements(activeDof)=U; end
shapeFunctionL2.m
function [shape,naturalDerivatives]=shapeFunctionL2(xi) % shape function and derivatives for L2 elements % shape : Shape functions % naturalDerivatives: derivatives w.r.t. xi % xi: natural coordinates (-1 ... +1) shape=([1-xi,1+xi]/2)'; naturalDerivatives=[-1;1]/2; end
例题2
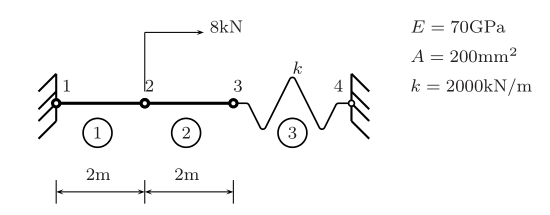

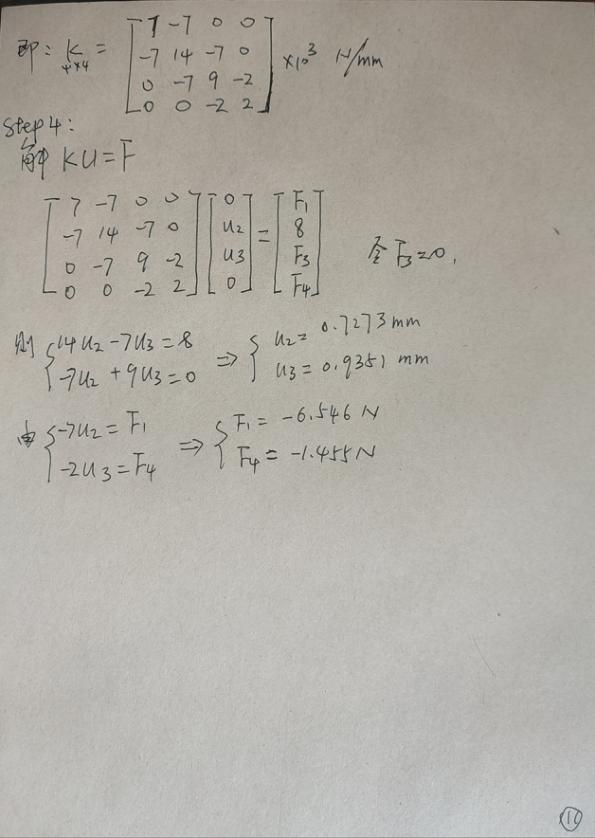
matlab 代码
problem3Structure.m
% MATLAB codes for Finite Element Analysis % antonio ferreira 2008 % clear memory clear all % p1 : structure p1=struct(); % E; modulus of elasticity % A: area of cross section % L: length of bar % k: spring stiffness E=70000; A=200; k=2000; % generation of coordinates and connectivities % numberElements: number of elements p1.numberElements=3; p1.numberNodes=4; p1.elementNodes=[1 2; 2 3; 3 4]; p1.nodeCoordinates=[0 2000 4000 4000]; p1.xx=p1.nodeCoordinates; % GDof: total degrees of freedom p1.GDof=p1.numberNodes; % for structure: % displacements: displacement vector % force : force vector % stiffness: stiffness matrix p1.displacements=zeros(p1.GDof,1); p1.force=zeros(p1.GDof,1); p1.stiffness=zeros(p1.GDof); % applied load at node 2 p1.force(2)=8000.0; % computation of the system stiffness matrix for e=1:p1.numberElements; % elementDof: element degrees of freedom (Dof) elementDof=p1.elementNodes(e,:) ; L=p1.nodeCoordinates(elementDof(2))-p1.nodeCoordinates(elementDof(1)); if e<3 ea(e)=E*A/L; else ea(e)=k; end p1.stiffness(elementDof,elementDof)=p1.stiffness(elementDof,elementDof)+ea(e)*[1 -1;-1 1]; end % prescribed dofs p1.prescribedDof=[1;4]; % solution p1.displacements=solutionStructure(p1); % output displacements/reactions outputDisplacementsReactionsStructure(p1) % Displacements % ans = % 1.0000 0 % 2.0000 3.3333 % 3.0000 0 % 4.0000 0 % reactions % ans = % 1.0000 -3.3333 % 3.0000 -3.3333 % 4.0000 -3.3333
outputDisplacementsReactionsStructure.m
function outputDisplacementsReactionsStructure(p) % output of displacements and reactions in % tabular form % GDof: total number of degrees of freedom of % the problem % displacements disp('Displacements') jj=1:p.GDof; [jj' p.displacements] % reactions F=p.stiffness*p.displacements; reactions=F(p.prescribedDof); disp('reactions') [p.prescribedDof reactions]
shapeFunctionL2Structure.m
function shapeL2=shapeFunctionL2Structure(xi) % shape function and derivatives for L2 elements % shape : Shape functions % naturalDerivatives: derivatives w.r.t. xi % xi: natural coordinates (-1 ... +1) shapeL2=struct() shapeL2.shape=([1-xi,1+xi]/2)'; shapeL2.naturalDerivatives=[-1;1]/2; end % end function shapeFunctionL2
solutionStructure.m
function displacements = solutionStructure(p) % function to find solution in terms of global displacements activeDof=setdiff([1:p.GDof]', [p.prescribedDof]); U=p.stiffness(activeDof,activeDof)\p.force(activeDof); displacements=zeros(p.GDof,1); displacements(activeDof)=U; end
第四章 2D桁架分析
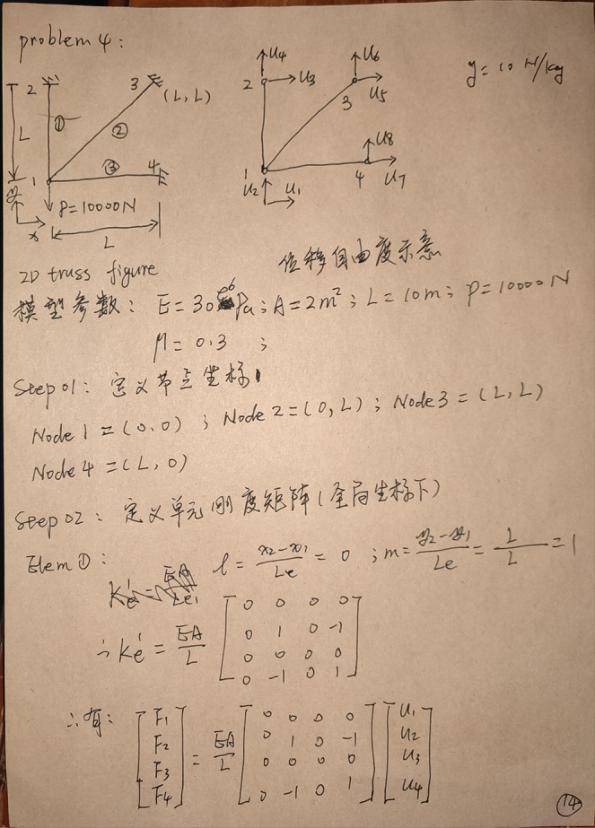
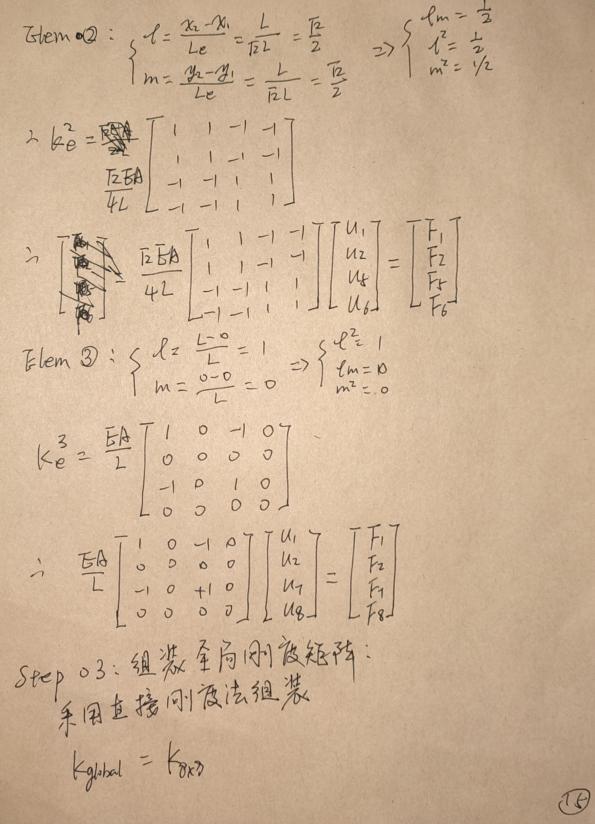
笔记:单元刚度矩阵推导


例题1
模型参数:
- 杨氏模量E=30e6 Pa ,泊松比 \(\mu\) =0.3
- A=2 m^2
- L=10 m
- P=10000 N
手算过程

Abaqus 模拟结果
inp文件在码云repo中
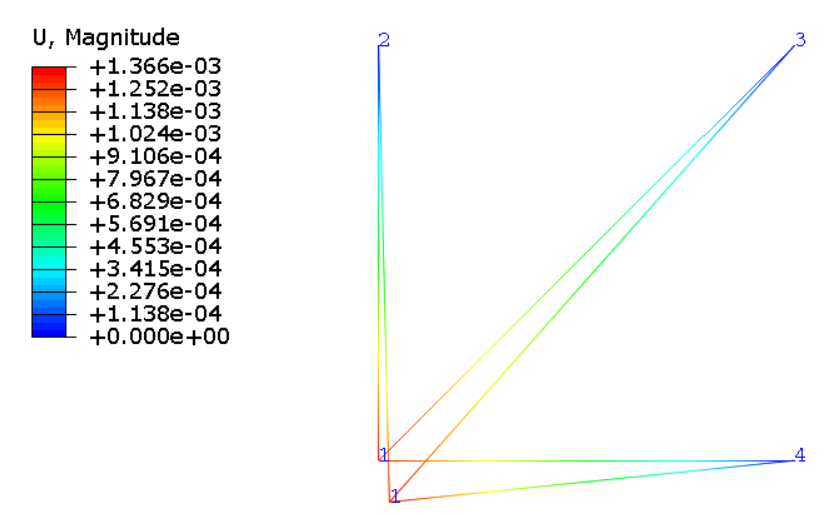
U and RF result :
******************************************************************************** Probe Values Report, written on Tue Apr 16 21:43:02 2024 Source ------- ODB: C:/Users/Administrator/Documents/learnFEM/Matlb Fea Codes repo/fea-codes-of-matlab/chapter04/problem4/abaqus/Job-2.odb Step: Step-1 Frame: Increment 1: Step Time = 1.000 Variable: U, U1 Probe values reported at nodes Part Instance Node ID Orig. Coords Def. Coords X Y Z X Y Z ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- PART-1-1 1 0. 0. 0. 345.178E-06 -1.32149E-03 0. PART-1-1 2 0. 10. 0. 0. 10. 0. PART-1-1 3 10. 10. 0. 10. 10. 0. PART-1-1 4 10. 0. 0. 10. 0. 0. Part Instance Node ID Attached elem U, U1 U, U2 RF, RF1 RF, RF2 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- PART-1-1 1 3 345.178E-06 -1.32149E-03 0. 0. PART-1-1 2 1 0. -7.92893E-33 0. 7.92893E+03 PART-1-1 3 2 -2.07107E-33 -2.07107E-33 2.07107E+03 2.07107E+03 PART-1-1 4 3 2.07107E-33 0. -2.07107E+03 -0.
可以看出,手算和abaqus的U结果完全一致.
matlab 代码
problem4.m
% ! problem4.m --> based on <<MATLAB codes for Finite Element Analysis>> clear ; clc format default p=struct(); % define model parameters p.E = 30e6; p.A = 2; p.L = 10; p.P = -10000; % define elems and nodes p.nodes=[0 0 ; % node's coordinates (x,y) 0 p.L ; p.L p.L ; p.L 0 ]; p.elems=[1 2 ; 1 3 ; 1 4]; p.node_num=size(p.nodes,1); p.elem_num=size(p.elems,1); p.node_Coord_x=p.nodes(:,1); p.node_Coord_y=p.nodes(:,2); % define problem's dimension : 1D/2D/3D; % = each node's dof p.problem_dimension=size(p.nodes,2); % global degree of freedom number p.global_dof_num=2*p.node_num; % define global Nodal displacement colum vector p.displacements=zeros(p.global_dof_num,1); p.node_forces=zeros(p.global_dof_num,1); % define boundary conditions % fixed dof p.fix_dof=[3 4 5 6 7 8]'; % load dof and amplitude p.load_dof=2; % initial global stiffness matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix=zeros(p.global_dof_num); % compute all ElemStiffnessMatrix and assembly stiff matrix elem_global_dof_num=2*size(p.elems,2); p.elemStiffs=zeros(elem_global_dof_num,elem_global_dof_num,p.elem_num); for i=1:p.elem_num connectivity=p.elems(i,:); % elem's all dof : a 2d truss node has 2 node,each node have 2 dof, % i-th node --> U_(2*i-1) and U_(2*i) dof(displacement of node) elem_dof=[connectivity(1)*2-1 connectivity(1)*2 ... connectivity(2)*2-1 connectivity(2)*2]; node1_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(1)); node1_y=p.node_Coord_y(connectivity(1)); node2_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(2)); node2_y=p.node_Coord_y(connectivity(2)); elem_length=sqrt((node1_x-node2_x).^2+(node1_y-node2_y).^2); l=(node2_x-node1_x)/elem_length; m=(node2_y-node1_y)/elem_length; k_e=(p.E*p.A/elem_length)*... [l*l l*m -l*l -l*m; l*m m*m -l*m -m*m; -l*l -l*m l*l l*m; -l*m -m*m l*m m*m]; p.elemStiffs(:,:,i)=k_e; % assemble stiffness matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix(elem_dof,elem_dof)=... p.global_stiffness_matrix(elem_dof,elem_dof)+k_e; end % apply boundary condition p.displacements(p.fix_dof)=0; p.node_forces(p.load_dof)=p.P; % solution KU=F p = solutionStruct(p); % show compute result disp('displacements of dofs :') disp([(1:p.global_dof_num)', p.displacements]) disp('forces of dofs :') disp([(1:p.global_dof_num)',p.node_forces]) figure axis equal % plot undeformed mesh draw_2Dtruss_mesh(p.nodes,p) % plot deformed mesh deformed_node_coordinate=cal_deformed_nodes(p,500.0); draw_2Dtruss_mesh(deformed_node_coordinate,p) title('位移变形') grid on function new_p=solutionStruct(p) % free dof in structure free_dof=setdiff((1:p.global_dof_num)',p.fix_dof); % solute the equation :KU=F --> U=K\F U=p.global_stiffness_matrix(free_dof,free_dof)\p.node_forces(free_dof); p.displacements(free_dof)=U; % displacements=zeros(p.global_dof_num,1); p.node_forces=p.global_stiffness_matrix*p.displacements; new_p=p; end function deformed_node_coordinate=cal_deformed_nodes(p,scale) % initial deformed_node_coordinate=p.nodes; if p.problem_dimension==2 index1=1:2:p.global_dof_num; index2=2:2:p.global_dof_num; deformed_node_coordinate(:,1)=deformed_node_coordinate(:,1)+p.displacements(index1)*scale; deformed_node_coordinate(:,2)=deformed_node_coordinate(:,2)+p.displacements(index2)*scale; elseif p.problem_dimension==3 index1=1:3:p.global_dof_num; index2=2:3:p.global_dof_num; index3=3:3:p.global_dof_num; deformed_node_coordinate(:,1)=deformed_node_coordinate(:,1)+p.displacements(index1); deformed_node_coordinate(:,2)=deformed_node_coordinate(:,2)+p.displacements(index2); deformed_node_coordinate(:,3)=deformed_node_coordinate(:,3)+p.displacements(index3); end end function draw_2Dtruss_mesh(nodes,p) xy=zeros(size(p.elems,2)*p.elem_num,p.problem_dimension); cur1=1; cur2=0; for i =1:p.elem_num connectivity=p.elems(i,:); attach_node_num=size(connectivity,2); cur1=cur2+1; cur2=cur2+attach_node_num; coord=zeros(attach_node_num,p.problem_dimension); for j=1:size(connectivity,2) coord(j,:)=nodes(connectivity(j),:); end xy(cur1:cur2,:)=coord; end line(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),"Marker","o","LineWidth",1,"Color",rand(1,3)) end
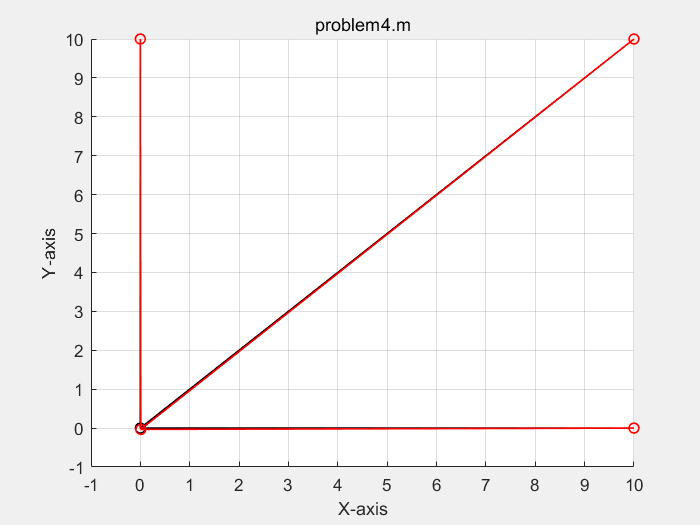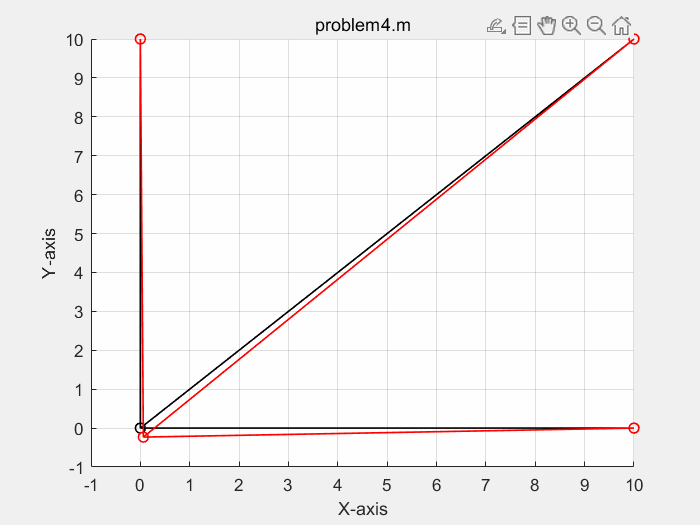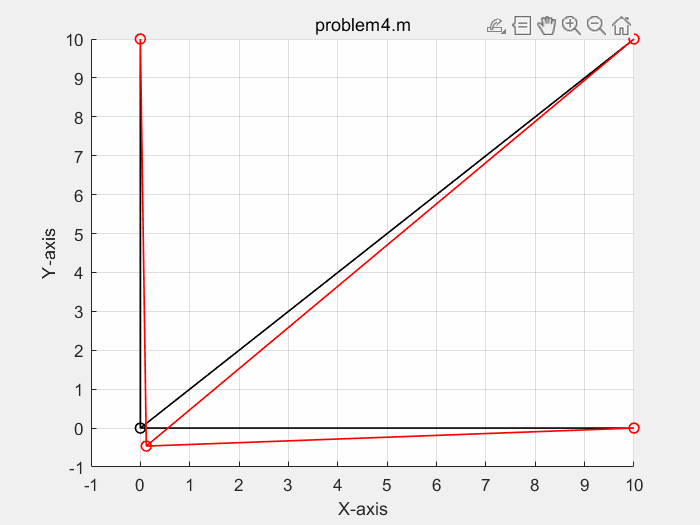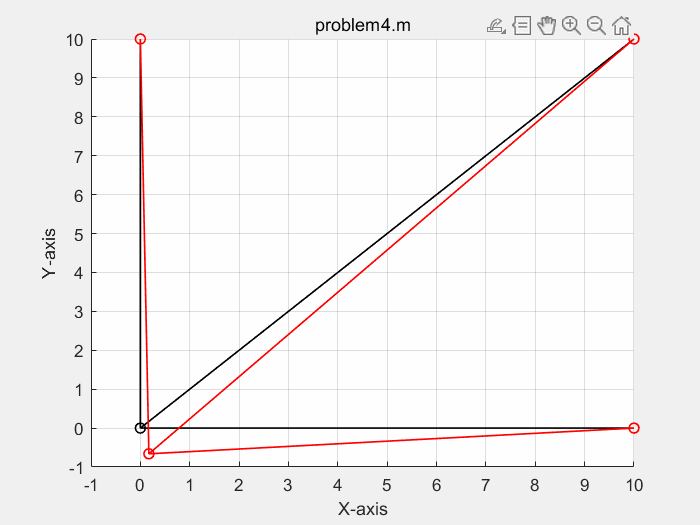
三种方式,计算结果一致
例题2
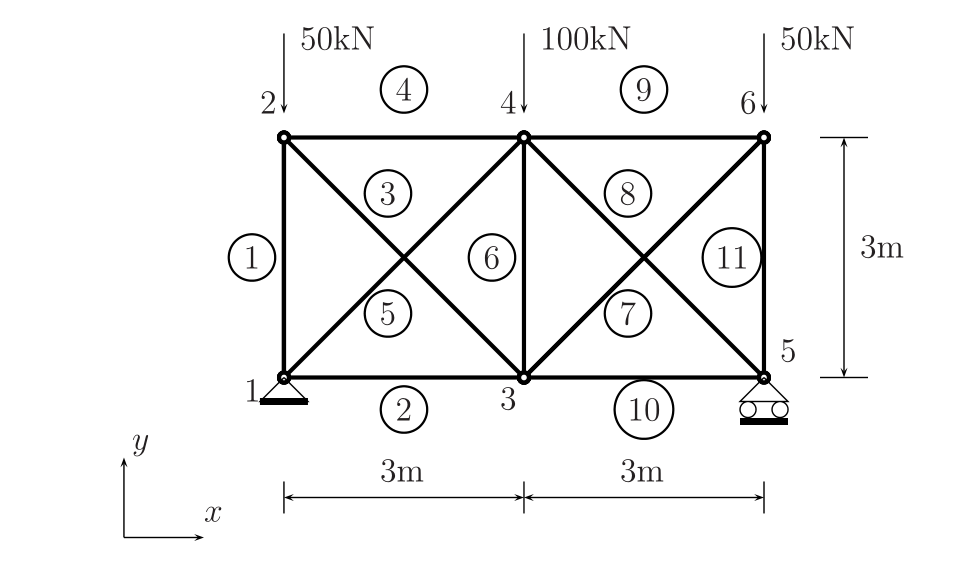
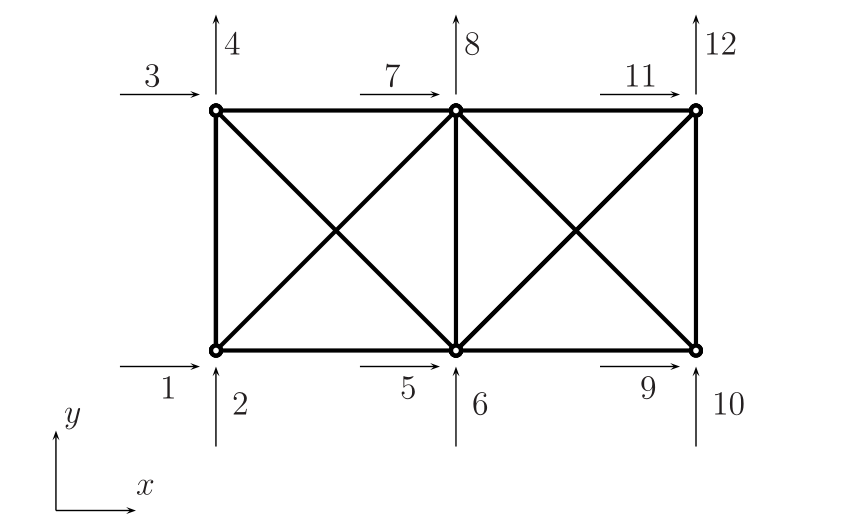
模型参数:
- 杨氏模量E = 70 GPa,泊松比 \(\mu\) = 0.3
- 桁架横截面积 A = \(3e^{-4} m^2\)
- L = 3 m
Abaqus 结果
待补充...
matlab 计算
基于problem4.m 代码,作如下修改即可:
% define model parameters % unit:SI(m) p.E = 70e9; p.A = 3e-4; p.L = 3; p.P = 1000*[-50;-100;-50]; disp('单位制:SI(m)') % define elems and nodes p.nodes=[0 0 ; % node's coordinates (x,y) 0 p.L ; p.L 0 ; p.L p.L ; 2*p.L 0 ; 2*p.L p.L]; p.elems=[1 2 ; 1 3; 2 3; 2 4; 1 4; 3 4; 3 6; 4 5; 4 6; 3 5; 5 6]; ...... % define boundary conditions % fixed dof p.fix_dof=[1 2 10]'; % load dof and amplitude p.load_dof=[4 8 12]'; ......
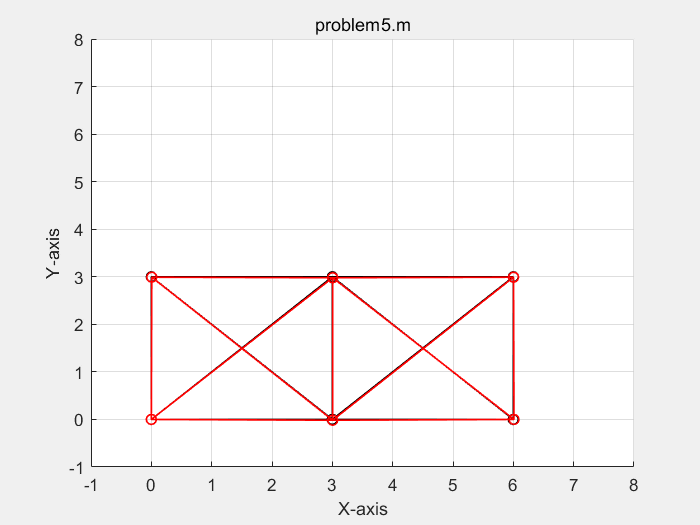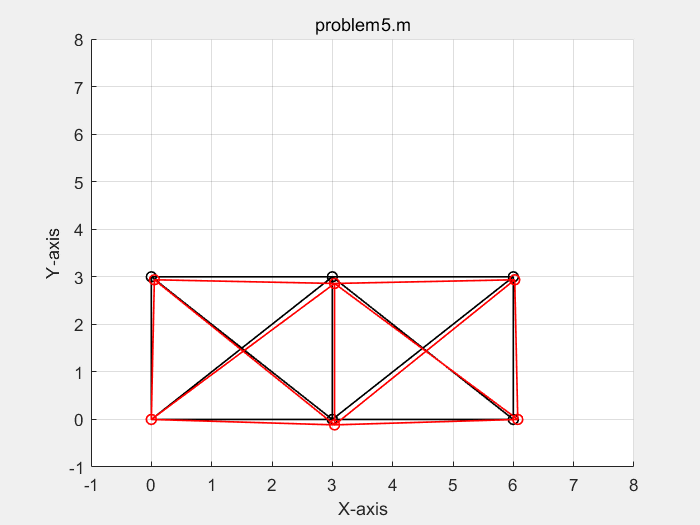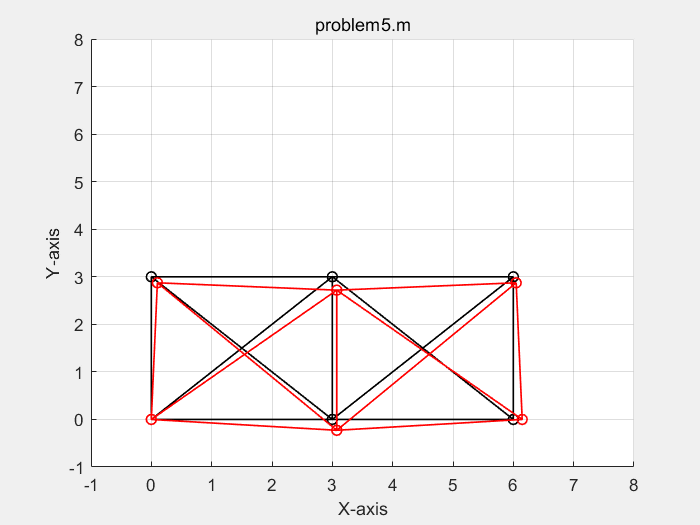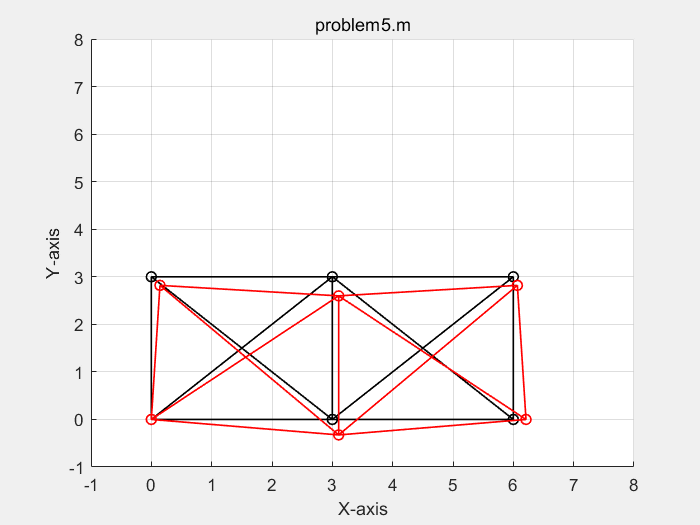
单位制:SI(m) displacements of dofs : 1.0000 0 2.0000 0 3.0000 0.0071 4.0000 -0.0090 5.0000 0.0052 6.0000 -0.0163 7.0000 0.0052 8.0000 -0.0201 9.0000 0.0105 10.0000 0 11.0000 0.0034 12.0000 -0.0090 forces of dofs : 1.0e+05 * 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 -0.5000 0.0001 -0.0000 0.0001 -0.0000 0.0001 -0.0000 0.0001 -1.0000 0.0001 0.0000 0.0001 1.0000 0.0001 0 0.0001 -0.5000
第五章 3D 桁架分析
笔记 - 3d truss 单元刚度矩阵

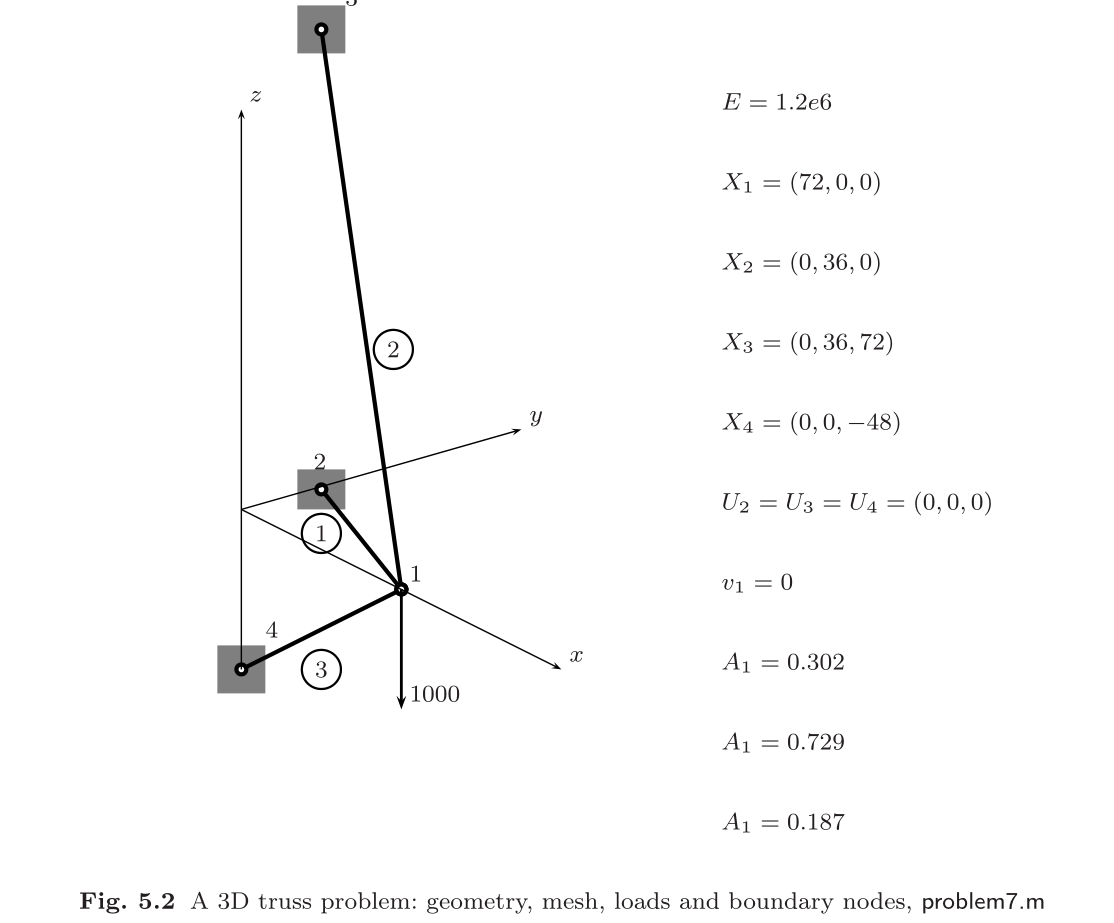
例题 1
matlab 计算
- problem7.m 代码
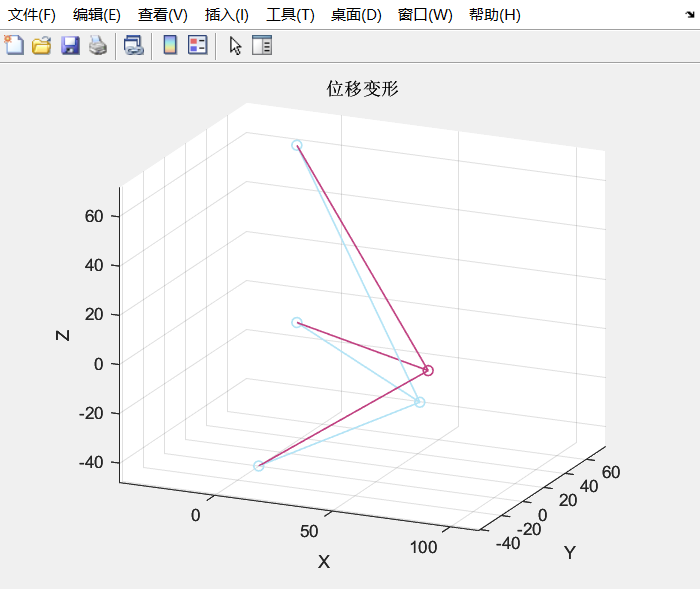
% ! problem7.m --> based on <<MATLAB codes for Finite Element Analysis>> clear ; clc format default p=struct(); % define model parameters % unit:SI(m) p.E = 1.2e6; p.A = [0.302 0.729 0.187]'; p.P = -1000; disp('单位制:SI(m)') % define elems and nodes p.nodes=[72 0 0 ; % node's coordinates (x,y,z) 0 36 0; 0 36 72; 0 0 -48]; p.elems=[1 2 ; 1 3; 1 4]; p.node_num=size(p.nodes,1); p.elem_num=size(p.elems,1); p.node_Coord_x=p.nodes(:,1); p.node_Coord_y=p.nodes(:,2); p.node_Coord_z=p.nodes(:,3); % define problem's dimension : 1D/2D/3D; % = each node's dof p.problem_dimension=size(p.nodes,2); % global degree of freedom number p.global_dof_num=p.problem_dimension*p.node_num; % define global Nodal displacement colum vector p.displacements=zeros(p.global_dof_num,1); p.node_forces=zeros(p.global_dof_num,1); % define boundary conditions % fixed dof p.fix_dof=[2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12]'; % load dof and amplitude p.load_dof=3; % initial global stiffness matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix=zeros(p.global_dof_num); % compute all ElemStiffnessMatrix and assembly stiff matrix elem_global_dof_num=p.problem_dimension*size(p.elems,2); p.elemStiffs=zeros(elem_global_dof_num,elem_global_dof_num,p.elem_num); for i=1:p.elem_num connectivity=p.elems(i,:); % elem's all dof : a 3d truss node has 2 node,each node have 3 dof, % i-th node --> U_(3*i-2) / U_(3*i-1) / U_(3*i) dof(displacement of node) elem_dof=[connectivity(1)*3-2 connectivity(1)*3-1 connectivity(1)*3 ... connectivity(2)*3-2 connectivity(2)*3-1 connectivity(2)*3]; node1_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(1)); node1_y=p.node_Coord_y(connectivity(1)); node1_z=p.node_Coord_z(connectivity(1)); node2_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(2)); node2_y=p.node_Coord_y(connectivity(2)); node2_z=p.node_Coord_z(connectivity(2)); elem_length=sqrt((node1_x-node2_x).^2+(node1_y-node2_y).^2+(node1_z-node2_z).^2); Cx=(node2_x-node1_x)/elem_length; Cy=(node2_y-node1_y)/elem_length; Cz=(node2_z-node1_z)/elem_length; T=[Cx*Cx Cx*Cy Cx*Cz; Cx*Cy Cy*Cy Cy*Cz; Cx*Cz Cy*Cz Cz*Cz]; k_e=(p.E*p.A(i)/elem_length)*[T -T;-T T]; p.elemStiffs(:,:,i)=k_e; % assemble stiffness matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix(elem_dof,elem_dof)=... p.global_stiffness_matrix(elem_dof,elem_dof)+k_e; end % apply boundary condition p.displacements(p.fix_dof)=0; p.node_forces(p.load_dof)=p.P; % solution KU=F p = solutionStruct(p); % calculate stress p.stress=zeros(p.elem_num,1); for i=1:p.elem_num connectivity=p.elems(i,:); % elem's all dof : a 3d truss node has 2 node,each node have 3 dof, % i-th node --> U_(3*i-2) / U_(3*i-1) / U_(3*i) dof(displacement of node) elem_dof=[connectivity(1)*3-2 connectivity(1)*3-1 connectivity(1)*3 ... connectivity(2)*3-2 connectivity(2)*3-1 connectivity(2)*3]; node1_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(1)); node1_y=p.node_Coord_y(connectivity(1)); node1_z=p.node_Coord_z(connectivity(1)); node2_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(2)); node2_y=p.node_Coord_y(connectivity(2)); node2_z=p.node_Coord_z(connectivity(2)); elem_length=sqrt((node1_x-node2_x).^2+(node1_y-node2_y).^2+(node1_z-node2_z).^2); Cx=(node2_x-node1_x)/elem_length; Cy=(node2_y-node1_y)/elem_length; Cz=(node2_z-node1_z)/elem_length; p.stress(i)=(p.E/elem_length)*[-Cx -Cy -Cz Cx Cy Cz]*p.displacements(elem_dof); end % show compute result disp('displacements of dofs :') disp([(1:p.global_dof_num)', p.displacements]) disp('forces of dofs :') disp([(1:p.global_dof_num)',p.node_forces]) disp('3d truss elem stress :') disp([(1:p.elem_num)',p.stress]) figure axis equal % plot undeformed mesh draw_3Dtruss_mesh(p.nodes,p) % plot deformed mesh deformed_node_coordinate=cal_deformed_nodes(p,50.0); draw_3Dtruss_mesh(deformed_node_coordinate,p) title('位移变形') grid on function draw_3Dtruss_mesh(nodes,p) xy=zeros(size(p.elems,2)*p.elem_num,p.problem_dimension); cur1=1; cur2=0; for i =1:p.elem_num connectivity=p.elems(i,:); attach_node_num=size(connectivity,2); cur1=cur2+1; cur2=cur2+attach_node_num; coord=zeros(attach_node_num,p.problem_dimension); for j=1:size(connectivity,2) coord(j,:)=nodes(connectivity(j),:); end xy(cur1:cur2,:)=coord; end line(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),xy(:,3),"Marker","o","LineWidth",1,"Color",rand(1,3)) end
- 计算结果
单位制:SI(m) displacements of dofs : 1.0000 -0.0711 2.0000 0 3.0000 -0.2662 4.0000 0 5.0000 0 6.0000 0 7.0000 0 8.0000 0 9.0000 0 10.0000 0 11.0000 0 12.0000 0 forces of dofs : 1.0e+03 * 0.0010 0 0.0020 -0.2232 0.0030 -1.0000 0.0040 0.2561 0.0050 -0.1281 0.0060 0 0.0070 -0.7024 0.0080 0.3512 0.0090 0.7024 0.0100 0.4463 0.0110 0 0.0120 0.2976 3d truss elem stress : 1.0e+03 * 0.0010 -0.9482 0.0020 1.4454 0.0030 -2.8685
例题2
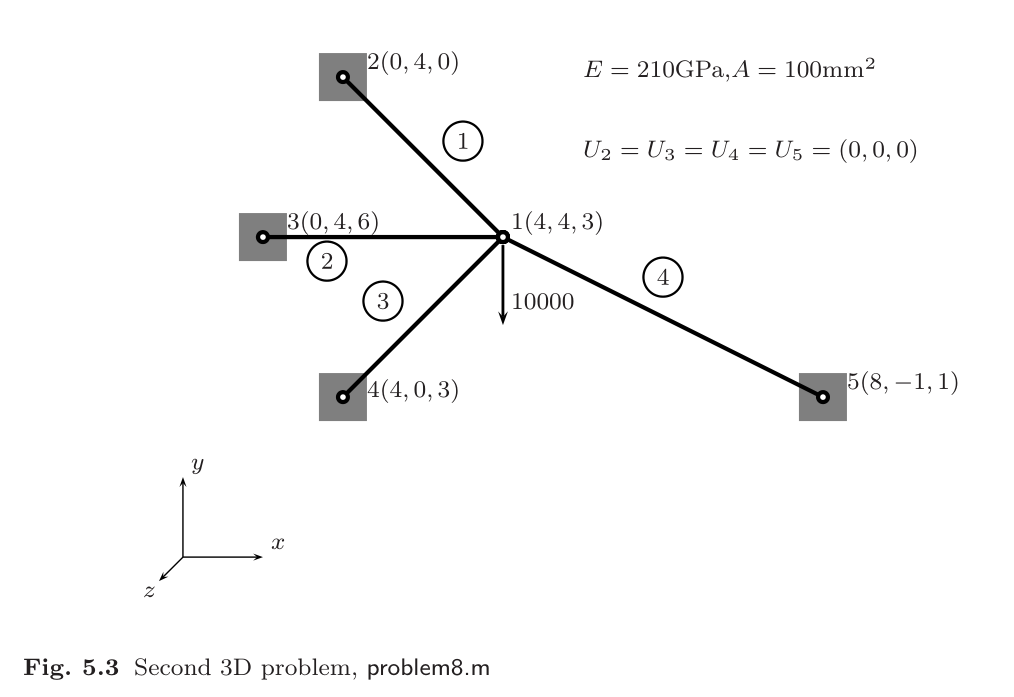
模型参数:
- E = 210000 Mpa,\(\mu\)=0.3
- A = 100 mm^2
- P =-10000 N
Abaqus 结果
waiting...
Matlab 计算
- problem8.m
基于problem7.m,修改参数,即可.
% define model parameters % unit:SI(mm) p.E = 210000; p.A = 100; p.P = -10000; disp('单位制:SI(mm)') % define elems and nodes p.nodes=[4 4 3 ; % node's coordinates (x,y,z) 0 4 0; 0 4 6; 4 0 3; 8 -1 1]; p.elems=[1 2 ; 1 3; 1 4; 1 5]; ...... % define boundary conditions % fixed dof p.fix_dof=[4:15]'; % load dof and amplitude p.load_dof=2; ......
- 计算结果
单位制:SI(mm) displacements of dofs : 1.0000 -0.0003 2.0000 -0.0015 3.0000 0.0003 forces of dofs : 1.0e+04 * 0.0004 0.0271 0.0005 0 0.0006 0.0203 0.0007 0.1355 0.0008 0 0.0009 -0.1016 0.0010 0 0.0011 0.7968 0.0012 0 0.0013 -0.1626 0.0014 0.2032 0.0015 0.0813 3d truss elem stress : 1.0000 -3.3865 2.0000 -16.9326 3.0000 -79.6809 4.0000 -27.2610 deformed nodes: 3.8791 3.3929 3.1075 0 4.0000 0 0 4.0000 6.0000 4.0000 0 3.0000 8.0000 -1.0000 1.0000
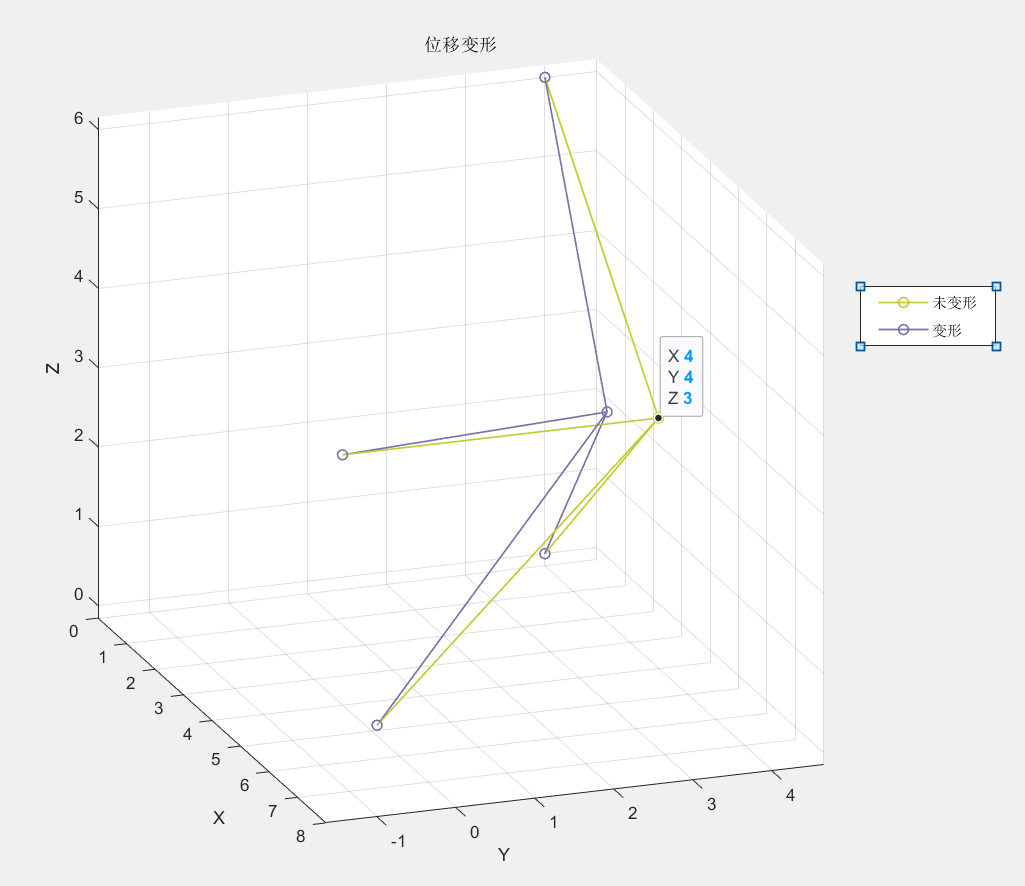
第六章 2D 欧拉-伯努利梁分析
单元刚度矩阵推导


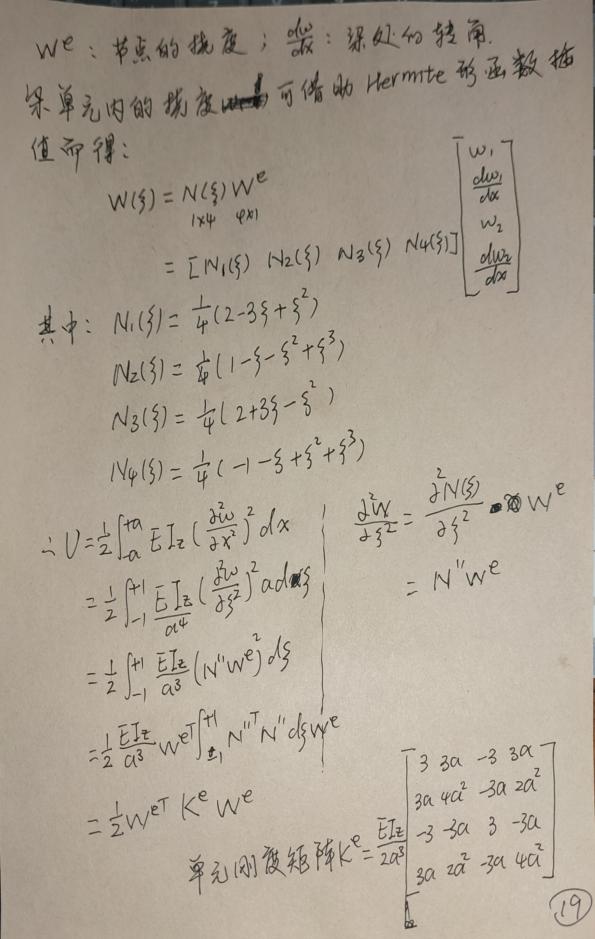
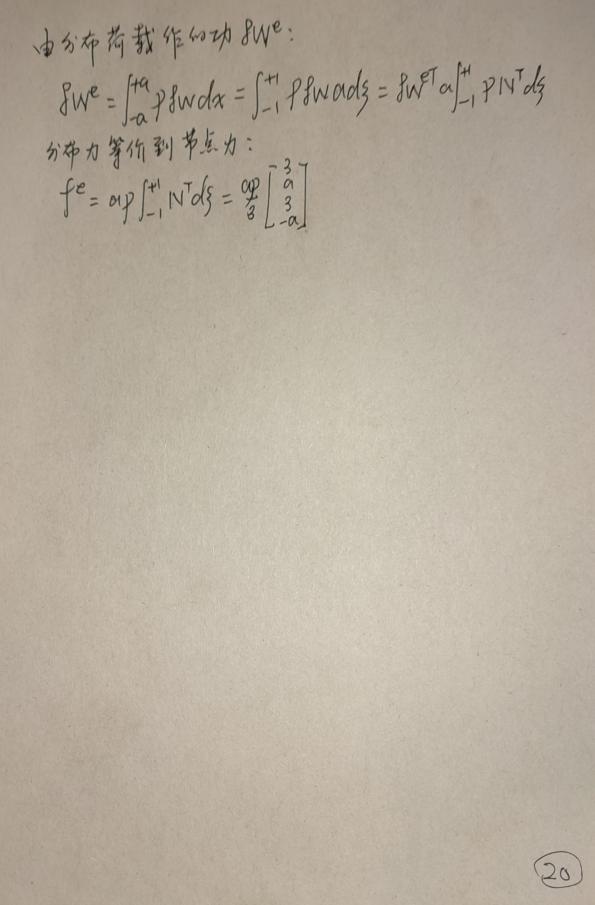
例题 1
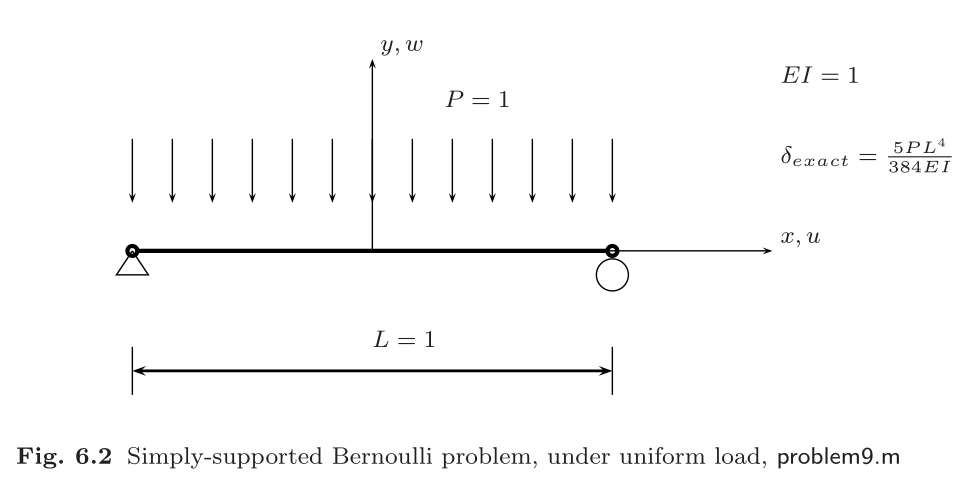
consider a simply-supported and clamped Bernoulli beam in bending, under uniform load
Abaqus 计算
Matlab 计算
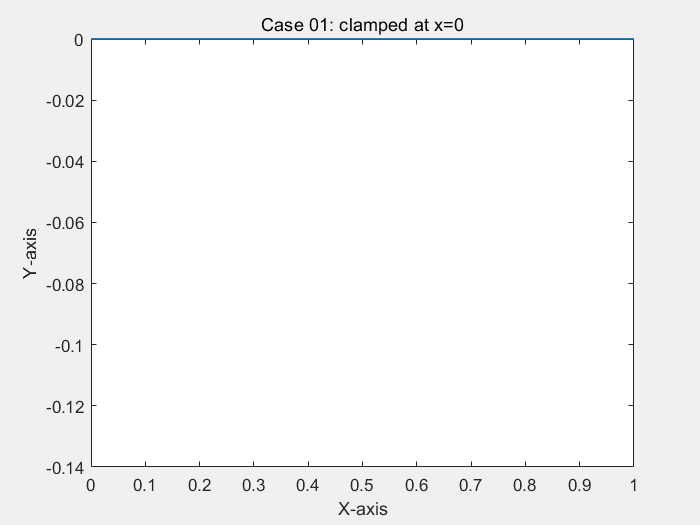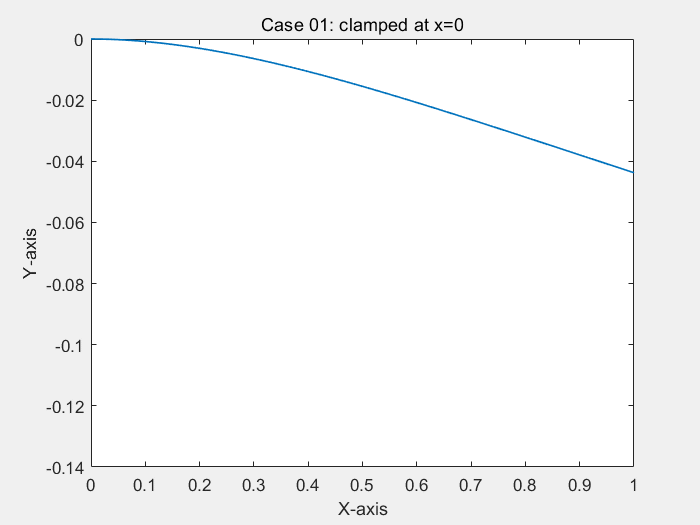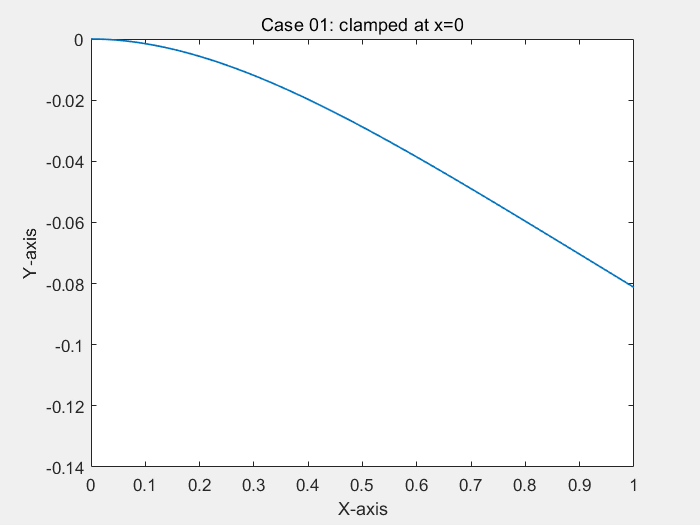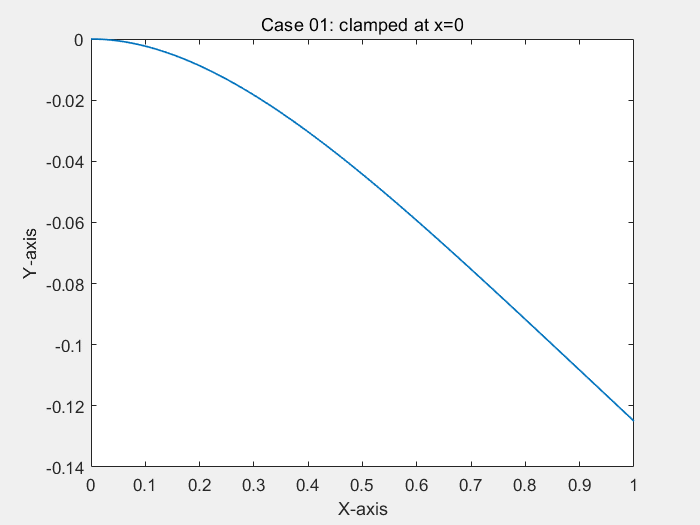
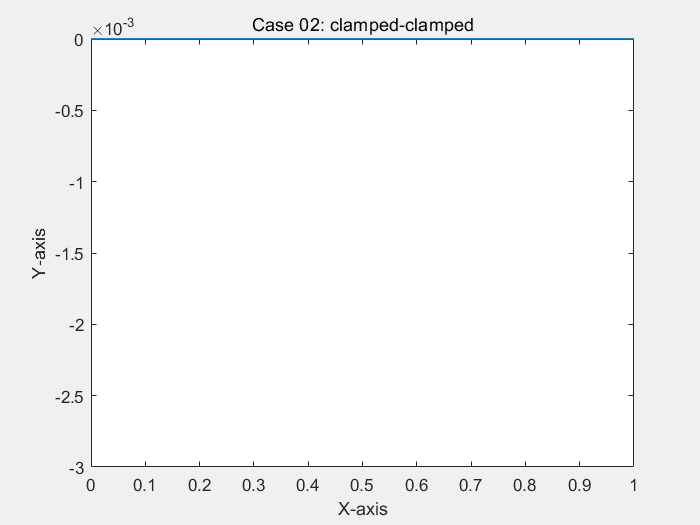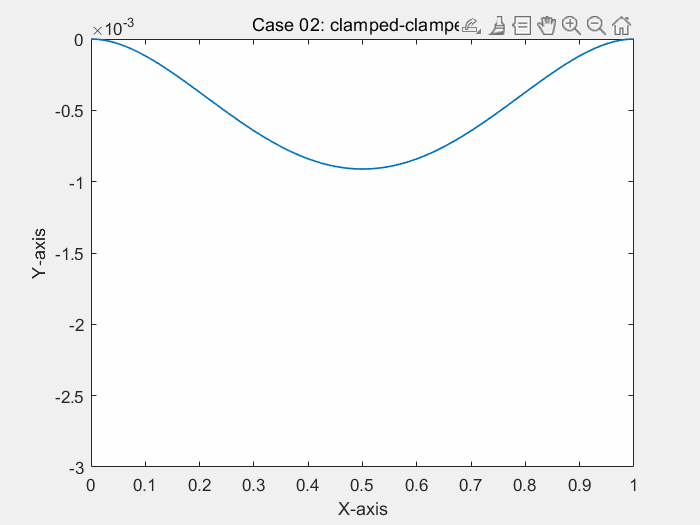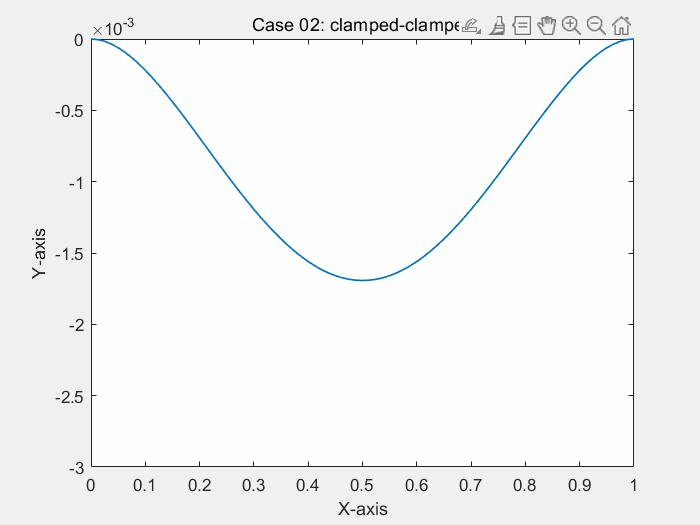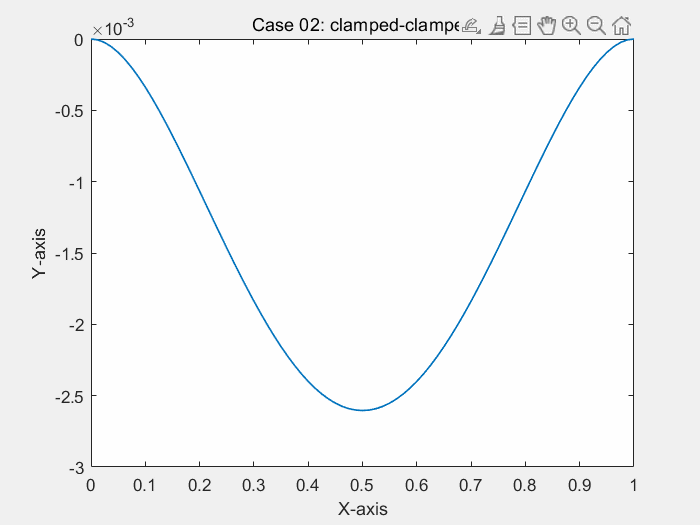
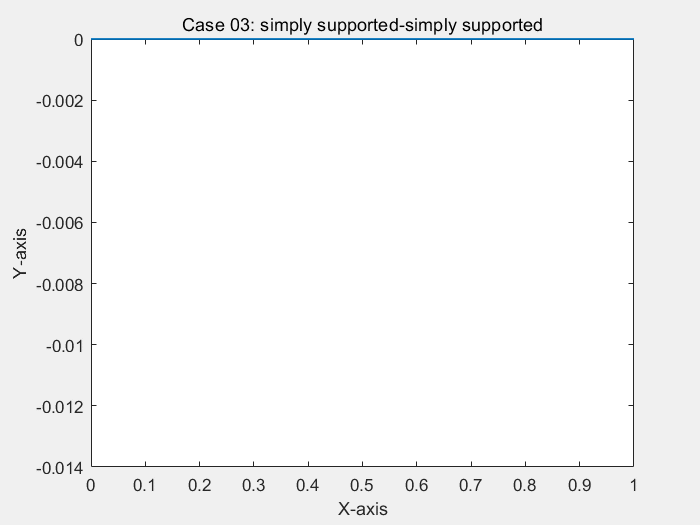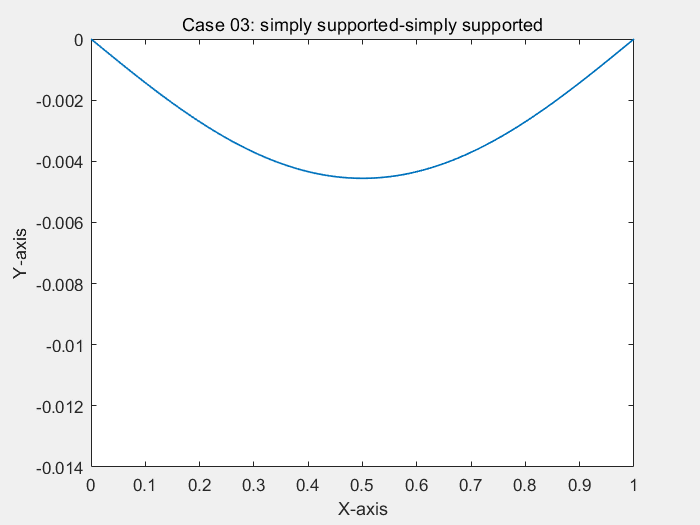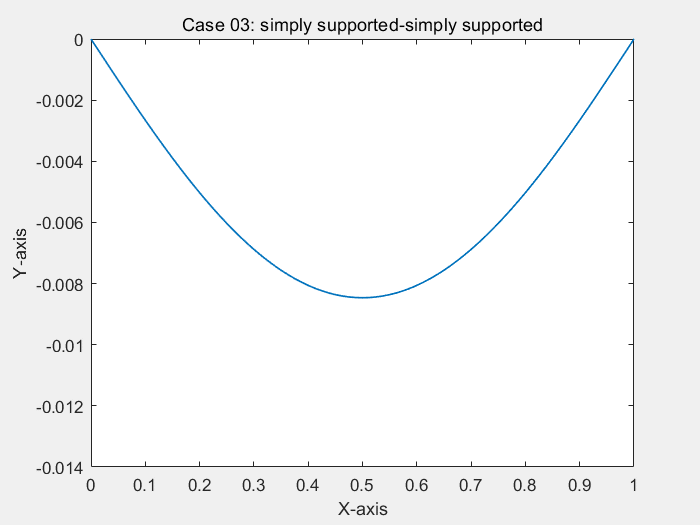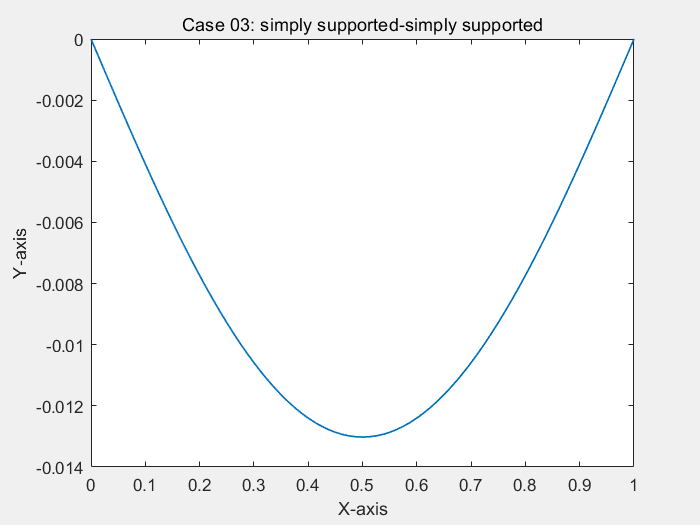
% ! problem9.m --> based on <<MATLAB codes for Finite Element Analysis>> clear ; clc format default p=struct(); Case=1; % define model parameters % unit:SI(mm) p.EI = 1; p.L = 1; % * distribute force p.P = -1; % define elems num of bornoulli beam p.elem_num=80; % define problem's dimension : 1D/2D/3D; % = each node's dof p.problem_dimension=2; % ? ------------------------------- % node's coordinates (x) p.nodes=linspace(0,p.L,p.elem_num+1)'; p.elems=zeros(p.elem_num,2); for i=1:p.elem_num p.elems(i,1)=i; p.elems(i,2)=i+1; end p.node_num=size(p.nodes,1); p.node_Coord_x=p.nodes(:,1); % global degree of freedom number p.global_dof_num=2*p.node_num; % define global Nodal displacement colum vector p.displacements=zeros(p.global_dof_num,1); p.node_forces=zeros(p.global_dof_num,1); % define boundary conditions if Case==1 % Case 01: clamped at x=0 % fixed dof p.fix_dof=[1 2]'; end if Case==2 % Case 02: clamped-clamped % fixed dof p.fix_dof=[1 p.elem_num*2+1 2 p.elem_num*2+2]'; end if Case==3 % Case 03: simply supported-simply supported p.fix_dof=[1 2*p.elem_num+1]'; end % initial global stiffness matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix=zeros(p.global_dof_num); % compute all ElemStiffnessMatrix and assembly stiff matrix elem_global_dof_num=p.problem_dimension*size(p.elems,2); p.elemStiffs=zeros(elem_global_dof_num,elem_global_dof_num,p.elem_num); for i=1:p.elem_num connectivity=p.elems(i,:); % elem's all dof : a 3d truss node has 2 node,each node have 2 dof, % i-th node --> w_(2*i-1) / dw_(2*i-2) / dof(displacement of node) elem_dof=[connectivity(1)*2-1 connectivity(1)*2 ... connectivity(2)*2-1 connectivity(2)*2 ]; node1_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(1)); node2_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(2)); elem_length=node2_x-node1_x; a=0.5*elem_length; k_e=(p.EI/(a^3))*0.5*[3 3*a -3 3*a; 3*a 4*a*a -3*a 2*a*a; -3 -3*a 3 -3*a; 3*a 2*a*a -3*a 4*a*a]; p.elemStiffs(:,:,i)=k_e; p.node_forces(elem_dof)=p.node_forces(elem_dof)+((p.P*a/3)*[3 a 3 -a])'; % assemble stiffness matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix(elem_dof,elem_dof)=... p.global_stiffness_matrix(elem_dof,elem_dof)+k_e; end % apply boundary condition p.displacements(p.fix_dof)=0; % solution KU=F p = solutionStruct_bornoulli_beam(p); plot(p.node_Coord_x,p.displacements(1:2:2*p.node_num),'.') minDispalce=min(p.displacements(1:2:2*p.node_num)); text(0.35,0.5*minDispalce,"挠度最小值:"+minDispalce) if Case==1 title("Case 01: clamped at x=0") end if Case==2 title("Case 02: clamped-clamped") end if Case==3 title("Case 03: simply supported-simply supported") end function new_p=solutionStruct_bornoulli_beam(p) % free dof in structure free_dof=setdiff((1:p.global_dof_num)',p.fix_dof); % solute the equation :KU=F --> U=K\F U=p.global_stiffness_matrix(free_dof,free_dof)\p.node_forces(free_dof); p.displacements(free_dof)=U; % displacements=zeros(p.global_dof_num,1); p.node_forces_fu=p.global_stiffness_matrix*p.displacements; new_p=p; end
例题2
matlab 计算
- problem10.m
% ! problem10.m --> based on <<MATLAB codes for Finite Element Analysis>> clear; clc; format compact; p=struct(); % define model paraeters p.E=1000000; p.L=10; t=p.L/1000; p.Iz=(1*t^3)/12; p.P=-1000; % define elems of bornoulli beam p.elem_num=20; % dof of each nornoulli beam nodes p.bornoulli_node_dof_num=2; p.spring_k=100; % ------------------------------- % node's coordinate p.nodes=linspace(0,p.L,p.elem_num+1)'; p.elems=zeros(p.elem_num,2); for i=1:p.elem_num p.elems(i,1)=i; p.elems(i,2)=i+1; end p.node_num=size(p.nodes,1); p.node_Coord_x=p.nodes(:,1); % global degree of freedom number: % ! bornoulli_beam node's dof + 1 spring node's dof p.global_dof_num=2*p.node_num; % define global Nodal displacement colum vector p.displacements=zeros(p.global_dof_num+1,1); p.node_forces=zeros(p.global_dof_num+1,1); % define boundary conditions % ! BC: clamped at x=0 p.fix_dof=[1,2,p.global_dof_num+1]'; % initial global stiffness matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix=zeros(p.global_dof_num+1); % compute all ElemStiffnessMatrix and assembly stiff matrix beam_dof_num=p.bornoulli_node_dof_num*size(p.elems,2); p.elemStiffs=zeros(beam_dof_num,beam_dof_num,p.elem_num); for i=1:p.elem_num connectivity=p.elems(i,:); % elem's all dof : a 3d truss node has 2 node,each node have 2 dof, % i-th node --> w_(2*i-1) / dw_(2*i-2) / dof(displacement of node) elem_dof=[connectivity(1)*2-1 connectivity(1)*2 ... connectivity(2)*2-1 connectivity(2)*2 ]; node1_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(1)); node2_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(2)); elem_length=node2_x-node1_x; a=0.5*elem_length; k_e=(p.E*p.Iz/(a^3))*0.5*[3 3*a -3 3*a; 3*a 4*a*a -3*a 2*a*a; -3 -3*a 3 -3*a; 3*a 2*a*a -3*a 4*a*a]; p.elemStiffs(:,:,i)=k_e; p.node_forces(elem_dof)=p.node_forces(elem_dof)+((p.P*a/3)*[3 a 3 -a])'; % assemble stiffness matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix(elem_dof,elem_dof)=... p.global_stiffness_matrix(elem_dof,elem_dof)+k_e; end % add spring nodes into global_stiffness_matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix([p.global_dof_num-1,p.global_dof_num+1],[p.global_dof_num-1,p.global_dof_num+1])=... p.global_stiffness_matrix([p.global_dof_num-1,p.global_dof_num+1],[p.global_dof_num-1,p.global_dof_num+1])+p.spring_k*[1,-1;-1,1]; % apply boundary condition p.node_forces(p.fix_dof)=0; % solution KU=F p=solutionStruct(p); % ! display result disp('Bornoulli beam result !') disp('beam挠度:') omega_index=(1:2:p.global_dof_num)'; disp([omega_index,p.displacements(omega_index)]) disp('beam转角:') theta_index=(2:2:p.global_dof_num)'; disp([theta_index,p.displacements(theta_index)]) disp('beam支反力:') disp([p.fix_dof,p.node_forces(p.fix_dof)]) plot(p.node_Coord_x,p.displacements(omega_index),'-') title('Problem10.m')
- 计算结果
Bornoulli beam result ! beam挠度: 1.0e+05 * 0.0000 0 0.0000 -0.1722 0.0001 -0.6300 0.0001 -1.2909 0.0001 -2.0800 0.0001 -2.9297 0.0001 -3.7800 0.0001 -4.5785 0.0002 -5.2801 0.0002 -5.8473 0.0002 -6.2501 0.0002 -6.4661 0.0003 -6.4802 0.0003 -6.2849 0.0003 -5.8802 0.0003 -5.2737 0.0003 -4.4803 0.0003 -3.5225 0.0004 -2.4303 0.0004 -1.2413 0.0004 -0.0004 beam转角: 1.0e+05 * 0.0000 0 0.0000 -0.6588 0.0001 -1.1450 0.0001 -1.4738 0.0001 -1.6600 0.0001 -1.7188 0.0001 -1.6650 0.0002 -1.5138 0.0002 -1.2800 0.0002 -0.9788 0.0002 -0.6250 0.0002 -0.2338 0.0003 0.1800 0.0003 0.6012 0.0003 1.0149 0.0003 1.4062 0.0003 1.7599 0.0004 2.0612 0.0004 2.2949 0.0004 2.4462 0.0004 2.4999 beam支反力: 1.0e+04 * 0.0001 0.6000 0.0002 1.2479 0.0043 0.3750

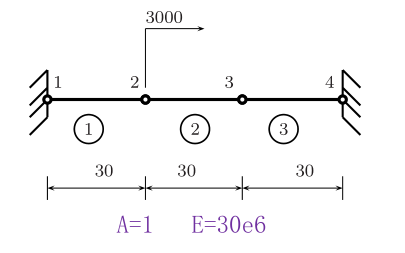
第7章 2d Frame单元静态分析
单元刚度矩阵推导
参见博文:【刚度矩阵推导】2d frame 单元
例题
Matlab 代码
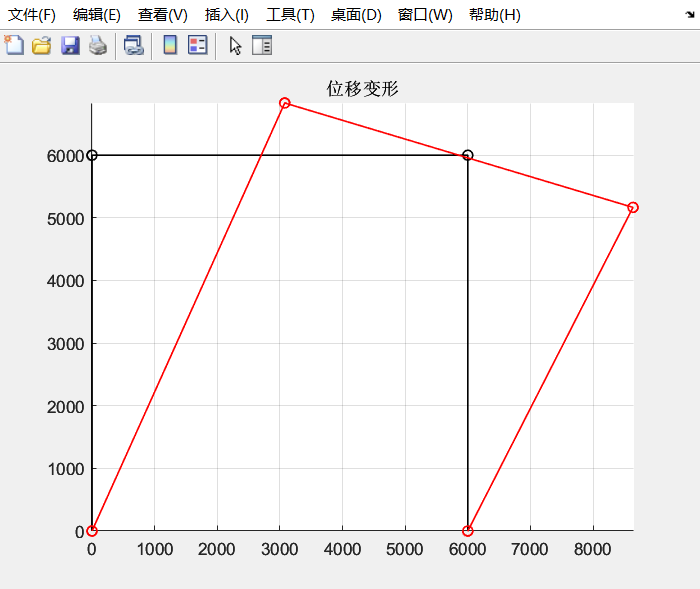
% ! problem10.m --> based on <<MATLAB codes for Finite Element Analysis>> % ! chpater 7 using 2d-frame element clear ; clc format default p=struct(); % define model parameters p.E = 210000; % SI(mm) p.A = 200; p.P = [15000 10e6]'; p.Iz=2e8; % define elems and nodes p.nodes=[0 0 ; % node's coordinates (x,y) 0 6000 ; 6000 6000 ; 6000 0;]; p.elems=[1 2; 2 3; 3 4;]; p.node_num=size(p.nodes,1); p.elem_num=size(p.elems,1); p.node_Coord_x=p.nodes(:,1); p.node_Coord_y=p.nodes(:,2); % define problem's dimension = each node's dof p.problem_dimension=3; % global degree of freedom number p.global_dof_num=3*p.node_num; % define global Nodal displacement colum vector p.displacements=zeros(p.global_dof_num,1); p.node_forces=zeros(p.global_dof_num,1); % define boundary conditions % fixed dof p.fix_dof=[1 2 3 10 11 12]'; % load dof and amplitude p.load_dof=[4 6]'; % initial global stiffness matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix=zeros(p.global_dof_num); % compute all ElemStiffnessMatrix and assembly stiff matrix elem_global_dof_num=p.problem_dimension*size(p.elems,2); p.elemStiffs=zeros(elem_global_dof_num,elem_global_dof_num,p.elem_num); for i=1:p.elem_num connectivity=p.elems(i,:); % elem's all dof : a 2d frame elem has 2 node,each node have 3 dof, % i-th node --> U_(3*i-2) and U_(3*i-1) and U_(3*i) dof(displacement of node) elem_dof=[connectivity(1)*3-2 connectivity(1)*3-1 connectivity(1)*3 connectivity(2)*3-2 connectivity(2)*3-1 connectivity(2)*3]; node1_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(1)); node1_y=p.node_Coord_y(connectivity(1)); node2_x=p.node_Coord_x(connectivity(2)); node2_y=p.node_Coord_y(connectivity(2)); elem_length=sqrt((node1_x-node2_x).^2+(node1_y-node2_y).^2); l=(node2_x-node1_x)/elem_length; m=(node2_y-node1_y)/elem_length; % coordinate transform matrix: U_l=L*U_g L=[l m 0 0 0 0; -m l 0 0 0 0; 0 0 1 0 0 0; 0 0 0 l m 0; 0 0 0 -m l 0; 0 0 0 0 0 1;]; % in local coordinates, the stiffness matrix of the frame element is obtained by com- % bination of the stiffness of the bar element and the Bernoulli beam element E=p.E; A=p.A; Iz=p.Iz; k_e_local=zeros(elem_global_dof_num,elem_global_dof_num); k_e_local(1,1)=(E*A)/elem_length; k_e_local(4,4)=(E*A)/elem_length; k_e_local(1,4)=-(E*A)/elem_length; k_e_local(4,1)=-(E*A)/elem_length; k_e_local(2,2)=12*E*Iz/(elem_length^3); k_e_local(2,3)=6*E*Iz/(elem_length^2); k_e_local(2,5)=12*E*Iz/(elem_length^3); k_e_local(2,6)=6*E*Iz/(elem_length^2); k_e_local(3,2)=6*E*Iz/(elem_length^2); k_e_local(5,2)=12*E*Iz/(elem_length^3); k_e_local(6,2)=6*E*Iz/(elem_length^2); k_e_local(3,3)=4*E*Iz/(elem_length); k_e_local(3,5)=-6*E*Iz/(elem_length*elem_length); k_e_local(3,6)=2*E*Iz/elem_length; k_e_local(6,3)=2*E*Iz/elem_length; k_e_local(5,3)=-6*E*Iz/(elem_length*elem_length); k_e_local(5,5)=12*E*Iz/(elem_length*elem_length*elem_length); k_e_local(5,6)=-6*E*Iz/(elem_length*elem_length); k_e_local(6,5)=-6*E*Iz/(elem_length*elem_length); k_e_local(6,6)=4*E*Iz/elem_length; k_e_global=L' *k_e_local *L; p.elemStiffs(:,:,i)=k_e_global; % assemble stiffness matrix p.global_stiffness_matrix(elem_dof,elem_dof)=... p.global_stiffness_matrix(elem_dof,elem_dof)+k_e_global; end % apply boundary condition p.displacements(p.fix_dof)=0; p.node_forces(p.load_dof)=p.P; % solution KU=F p = solutionStruct(p); % show compute result disp('displacements of dofs :') disp([(1:p.global_dof_num)', p.displacements]) disp('forces of dofs :') disp([(1:p.global_dof_num)',p.node_forces]) figure axis equal % plot undeformed mesh draw_2Dtruss_mesh(p.nodes,p,'black') deform_scale=500; deformed_node_coordinate=[p.node_Coord_x+deform_scale*p.displacements(3*(1:p.node_num)-2), ... p.node_Coord_y+deform_scale*p.displacements(3*(1:p.node_num)-1)]; % plot deformed mesh draw_2Dtruss_mesh(deformed_node_coordinate,p,'red') title('位移变形') grid on
第八章 3d Frame单元静态分析
略
第九章 analysis of grids
略
第十章 Timoshenko beams 静态分析
与欧拉-伯努利梁公式不同,Timoshenko梁公式考虑了横向剪切变形.因此,它能够模拟较薄或较厚的梁.本章对Timoshenko梁的静力弯曲、自由振动和屈曲进行了分析.
10.Timoshenko梁的静力分析-Formulation
本文来自博客园,作者:FE-有限元鹰,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/aksoam/p/18133331

![有限元方法[Matlab]-笔记](https://img2024.cnblogs.com/blog/2026433/202408/2026433-20240805095548845-1104772374.png) 《 MATLAB Codes for Finite Element Analysis - Solids and Structures (Ferreira) 》 的学习笔记
《 MATLAB Codes for Finite Element Analysis - Solids and Structures (Ferreira) 》 的学习笔记



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具