疯狂Java学习笔记(023)
字节流:
抽象基类:
InputStream:
实现子类:
FileInputStream:
构造方法:
FileInputStream(File file):
FileInputStream(String name):
方法:
int read():
int read(byte[] bys):
缓冲字节输入流:
BufferedInputStream:
构造方法:
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in):
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in,int size):
方法:
int read():
int read(byte[] bys):
OutputStream:
实现子类:
FileOutputStream:
构造方法:
FileOutputStream(File file):
FileOutputStream(String name):
FileOutputStream(File file,boolean append):
FileOutputStream(String name,boolean append):
方法:
void write(int value):
void write(byte[] bys):
void write(byte[] bys,int off,int len):
缓冲字节输出流:
BufferedOutputStream:
构造方法:
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out):
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out,int size):
方法:
void write(int value):
void write(byte[] bys):
void write(byte[] bys,int off,int len):
字符流:
抽象基类:
Reader:
实现子类:
转换流:
InputSteramReader:
构造方法:
InputStreamReader(InputStream in):
InputStreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName):
方法:
int read():
int read(char[] chs):
简化子类:
FileReader:
构造方法:
FileReader(File file):
FileReader(String name):
方法和父类一样!!!
缓冲字符输入流:
BufferedReader:
构造方法:
BufferedReader(Reader in):
BufferedReader(Reader in,int size):
方法:
int read():
int read(char[] chs):
特殊方法:
String readLine():
Writer:
实现子类:
转换流:
OutputStreamWriter:
构造方法:
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out):
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out,String charsetName):
方法:
void write(int value):
void write(char[] chs):
void write(char[] chs,int off,int len):
void write(String s):
void write(String s,int off,int len):
简化子类:
FileWriter:
构造方法:
FileWriter(File file):
FileWriter(String name):
方法和父类一样!!!
缓冲字符输出流:
BufferedWriter:
构造方法:
BufferedWriter(Writer out):
BufferedWriter(Writer out,int size):
方法:
void write(int value):
void write(char[] chs):
void write(char[] chs,int off,int len):
void write(String s):
void write(String s,int off,int len):
特殊方法:
void newLine():
一、数据操作流
针对不同数据类型操作的流,属于字节流.底层包装的是基本的字节流,在读写数据的次数上进行了增强!
DataOutputStream:
DataOutputStream(OutputStream out):
方法:
void writeInt(int i):
void writeLong(long l):
void writeDouble(double d):
void writeFloat(float f):
void writeUTF(String s):
1.写出方法的源码
通过查看writeInt方法的源码:

发现实际上就是调用了底层字节流的四次write方法,依次将一个int型数据的四个字节写出到底层流中!!!写出的顺序是高位在前!!!其它方法原理相同!
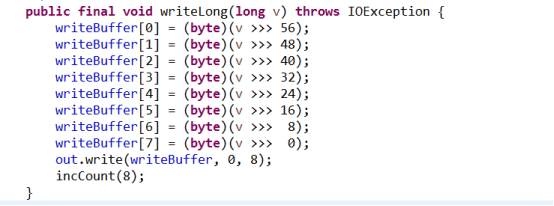
long型数据是先写到一个字节数组中,然后一次性将整个数组写出到底层的流中。
2.writeUTF(String s):
- 使用的是修改版的UTF-8编码:
- 先写出两个字节的控制字节:表示真实字符串编码后的字节数!!
- 然后写出的是字符串真实的字节数组!
- 即:写出数据的长度:最短:2+字符串长度
- 最长:2+字符串长度*3!
3.DateInputStream:
属于字节流,在读取不同数据类型的时候,进行了次数上的控制。
构造方法:
DataInputStream(InputStream in):
方法:
int read();
int readInt();
long readLong();
........
二、读取方法的源码
举例:以readInt方法为例,查看如何还原数据:

实际上,就是一次从底层流中读取四个字节,并按照高位在前的顺序,将int值还原。
1. readLong( ):方法

依次从底层的流中读取八个字节,并做相应的移位运算,将long型数据还原!!
三、自定义工具类
例如:实现int型数据和long型数据的原生数组的转换操作:
/*
* 数据操作的工具类:
*
* 方便int型long型数据和字节数组之间的转换!
*/
public class DataTools {
//私有构造方法
private DataTools(){}
//获取int型数据的数组:高位在前
public static byte[] int2Bytes(int i){
//创建一个数组,存放int型数据的四个字节
byte[] bys = new byte[4];
//将int型数据转换成四个字节
bys[0] = (byte)(i >> 24);
bys[1] = (byte)(i >> 16);
bys[2] = (byte)(i >> 8);
bys[3] = (byte)(i >> 0);
return bys;
}
//从数组还原int数据:高位在前
public static int bytes2Int(byte[] bys){
int i0 = (bys[0] & 0xFF) << 24;
int i1 = (bys[1] & 0xFF) << 16;
int i2 = (bys[2] & 0xFF) << 8;
int i3 = (bys[3] & 0xFF) << 0;
return i0 + i1 + i2 + i3;
}
//long -> byte[] : 高位在前
public static byte[] long2Bytes(long l){
byte[] bys = new byte[8];
bys[0] = (byte)(l >> 56);
bys[1] = (byte)(l >> 48);
bys[2] = (byte)(l >> 40);
bys[3] = (byte)(l >> 32);
bys[4] = (byte)(l >> 24);
bys[5] = (byte)(l >> 16);
bys[6] = (byte)(l >> 8);
bys[7] = (byte)(l >> 0);
return bys;
}
//byte[] -> long : 高位在前
public static long bytes2Long(byte[] bys){
long l0 = ((long)bys[0] & 0xFF) << 56;
long l1 = ((long)bys[1] & 0xFF) << 48;
long l2 = ((long)bys[2] & 0xFF) << 40;
long l3 = ((long)bys[3] & 0xFF) << 32;
long l4 = ((long)bys[4] & 0xFF) << 24;
long l5 = ((long)bys[5] & 0xFF) << 16;
long l6 = ((long)bys[6] & 0xFF) << 8;
long l7 = ((long)bys[7] & 0xFF) << 0;
return l0 | l1 | l2 | l3 | l4 | l5 | l6 | l7;
}
//通过封装jdk提供的数据流写出指定类型的数据
public static void writeInt(OutputStream out,int value) throws Exception{
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out);
dos.writeInt(value);
dos.close();
}
}
- 使用场景:凡是需要写出超过一个字节的场景,都可以使用!
- 使用系统提供的数据操作流或者使用字节定义的工具类!
- 自定义工具类的优点:不用开流和关流!直接使用即可!
四、打印流
按字节操作的字节流打印流和按字符操作的字符打印流,都是只有输出,没有输入。
1.字节打印流
PrintStream: 构造方法: PrintStream(File file): PrintStream(String name): PrintStream(OutputStream out): PrintStream(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush): 方法: print():不换行输出 println():换行输出 都是把参数转换成字符串再输出!!!
如:以printin(int value)为例:

2.System.out的本质
/* * System.out 实际上就是一个字节打印流!!! * */ public class PrintStreamDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //相当于获取了控制台的引用! PrintStream ps = System.out; ps.println("abc"); ps.println(300); ps.close(); } }
五、字符打印流
PrintWriter: 构造方法: PrintWriter(File file): PrintWriter(String name): PrintWriter(OutputStream out): PrintWriter(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush): PrintWriter(Writer out): PrintWriter(Writer out,boolean autoFlush):


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号