一.Overview
resource constraints:
space
time
Data Structure
array, stack, queue, priority queue, linked list, tree, heap, graph
For most algorithms, running time depends on “size” of the input.
Find max element of an array
int FindMaxElement(int a[]){
int max=a[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
if(max<a[i]){
max=a[i];
}
}
return max;
}
We say the time complexity of this algorithm is O(n).
for (int i=0; i<5;i++){
print ("i="+i);
}
Time Complexity: O(1)
Simplification Rules
3 = O(1)
3n = O(n)
O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
O(n) + O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
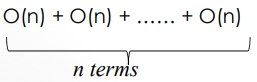
O(n2 )
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++){
k = k + i + j;
}
}
Time Complexity = O(1)*n*n = O(n2 )
Asymptotic running time of some algorithms
|
O(1)
|
Constant time
|
Compare two numbers
|
|
O(log n)
|
Logarithmic
|
Binary search (on a sorted array)
|
|
O(n)
|
Linear time
|
Search (on a unsorted array)
|
|
O(n log n)
|
|
Merge sort
|
|
O(n2 )
|
Quadratic
|
Selection sort
|
|
O(n3)
|
Cubic
|
Matrix multiplication
|
|
O(2n)
|
Exponential
|
Brute-force search on boolean satisfiability problem
|
|
O(n!)
|
Factorial
|
Brute-force search on traveling salesman problem
|
Arrays
静态数组是包含n个元素的定长容器,from the range [0, n-1]
插入O(n)

删除O(n)

线性搜索O(n)
int findElement(int a[],int target){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(a[i]==target){
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
worse:O(n)
best:O(1)
average:O(n)
Most of the time we are interested in the worse case
二分法搜索
int binarySearch(int num[],int target){
int left=0;
int right=num.length-1;
int mid;
while(left<right){
mid=(left+right)/2;
if(target==num(mid)){
return mid;
}
else if(target<num(mid)){
right=mid-1;
}
else{
left=mid+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
worse case: the target is not in the array:O(n)
时间复杂度可以表示O(logn)
时间复杂度为O(n2):
选择排序
插入排序
时间复杂度为O(nlogn):
并归排序
快速排序

Hash函数
x是一个数据对象
x.key表示位置
x.data表示数值
空间复杂度O(n)
时间复杂度O(1)

Which data structure can support fast searching, while using small space?
将hash键转换为hash值

h(293) = 293 mod 5 = 3
hash function h(k) = k mod m

How do we solve the collision problem
拉链法:链表存储冲突值

开地址法:将冲突值存到下一个位置
计算冲突因子
α=n/m
Measures how full the hash table is
To maintain reasonable performance, keep λ<1
链地址法
Worst case: a hash bucket may store all the keys

Average case: a hash bucket stores = n / m keys
n is the number of keys, m is the total number of buckets
Search
Compute the hash value: O(1)
Search the linked list of a bucket
Worst case cost
Search a bucket that contains all n keys: O(n) time
Total time: O(1)+O(n) = O(n)
Average case cost
Search a bucket: O(α) time
where α = n / m is the hash table’s load factor
Total time: O(1)+O(α) = O(1+α)
Cost of insert
Worst case cost:Compute the hash value: O(1)
Insert the key into a linked list: O(1)
Total time: O(1) + O(1) = O(1)
Cost of delete
Searching time + Deletion time in a linked list
Worst case cost: O(n) + O(1) = O(n)
Average case cost: O(1+α) + O(1) = O(1+α)
开地址法
Example: h0 (k) = k mod m
h(k, i) = ( h0 (k) + i ) mod m

For linear probing, performance degrade significantly when λ > 0.5
To maintain reasonable efficiency, the hash table should be less than half full.
keep λ < 0.5
What if the key is not a integer
Sum of ASCII code of all the characters in the string
Linked List
Head: The first node in a linked list
Tail: The last node in a linked list
Pointer: Reference to another node
Node: An object containing data and pointer(s)

class Node:
def __init__(self,initdata):
self.data = initdata
self.next = None
Node insertion

Create a traverser pointer and seek up to but not including the node we want to insert

Advance traverser pointer before the node be inserted




insert a node at the beginning of a linked list

remove9 from the following sll





Arrays vs Linked List
|
Operation
|
Array
|
Linked List
|
|
Find (by position)
|
• O(1) - Support random access
|
Does not support random access
Require sequential search, which takes O(n) time
|
|
Find (by target value)
|
O(n) - Sequential Search • O(log (n)) - Binary Search
|
O(n) - Sequential Search Does not support Binary Search
|
|
Insert/Remove
|
𝑂(1): Insert at tail
O(n): General Case
|
O(1) – Efficient insertion/removal at the front or end of the list.
If the item is in the middle of the list, it may take O(n ) to locate the item to be deleted!
|
Array
Size must be predetermined
Empty spaces when the list contains few elements
Support random access
Efficient searching with binary search
Insertion/deletion may need require the shifting of data
Linked List
No limit for the no. of elements
Requires more space per element in the list (store the reference for the next element)
High overhead when the elements’ size is small
Tree
在计算机科学中,树是层次结构的抽象模型
一组节点一组连接节点对的边
树的任何两个节点之间只有一条路径
路径是一个或多个节点的序列
连接图无循环
与算术表达式关联的二叉树
内部节点:运算符
外部节点:操作数

术语
除根节点外,每个节点都只有一个父节点
叶子节点:没有孩子的树节点
路径长度:路径中的边数
节点的祖先:父母,祖父母,外祖父母等
节点的后代:孩子,孙子,孙子等
长度
到任何叶节点(从该节点开始)的最大路径长度
每个叶节点的高度为0
树中节点的最大级别是树的高度

深度
The node's level (depth) of a node n is the length of the path from n to the root
根的深度为零
节点的级别是指从根到该节点的路径的长度
由节点及其后代组成的树
如果二叉树(除了最后一个树)的所有级别都包含尽可能多的节点,并且从左到右填充了最后一个级别的节点,则树是完整的
Number of nodes in perfect binary tree
完美二叉树中的节点数
n=2^(h+1)-1
h=lg(n+1)-1
Binary Search Tree
对于树的每个节点n,所有值(键)都存储在其左子树中
其左子树中(其根是左子节点的树)小于n中存储的值v,stored存储在右侧子树中的所有值都大于v
boolean search(int target){
p=tree;
while(!p){
if(p.data==target){
return p.data;
}
else if(target<p.data){
p=p.left;
}
else{
p=p.right;
}
}
return null;
}
Insertion in BST
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == NULL)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent=NULL;
Node* pcur = _root;
while (pcur)
{
if (pcur->_key == key) //有key节点,则不再插入
return false;
if (pcur->_key > key)
{
parent = pcur;
pcur = pcur->_left;
}
else if (pcur->_key < key)
{
parent = pcur;
pcur = pcur->_right;
}
}
if (parent->_key < key)
parent->_right = new Node(key);
else
parent->_left = new Node(key);
return true;
}
找最小值
int minimum(tree x){
while(x.value!=NULL){
x=x.left;
}
return x.value;
}
二叉搜索树