MapReduce编程之Join多种应用场景与使用
Join操作概述
在关系型数据库中 Join 是非常常见的操作,各种优化手段已经到了极致。在海量数据的环境下,不可避免的也会碰到这种类型的需求, 例如在数据分析时需要连接从不同的数据源中获取到数据。不同于传统的单机模式,在分布式存储下采用 MapReduce 编程模型,也有相应的处理措施和优化方法。
我们先简要地描述待解决的问题。假设有两个数据集:气象站数据库和天气记录数据库,并考虑如何合二为一。一个典型的查询是:输出气象站的历史信息,同时各行记录也包含气象站的元数据信息。
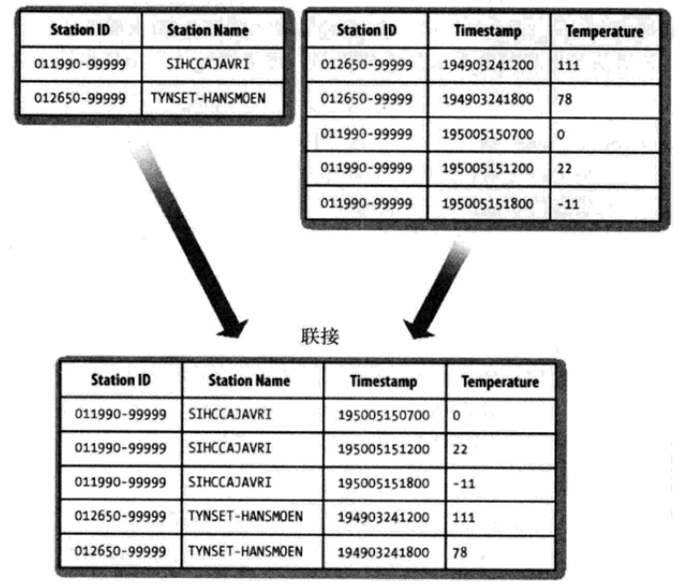
Reduce join
在Reudce端进行连接是MapReduce框架实现join操作最常见的方式,其具体的实现原理如下:
Map端的主要工作:为来自不同表(文件)的key/value对打标签以区别不同来源的记录。然后用连接字段作为key,其余部分和新加的标志作为value,最后进行输出。
reduce端的主要工作:在reduce端以连接字段作为key的分组已经完成,我们只需要在每一个分组当中将那些来源于不同文件的记录(在map阶段已经打标志)分开,最后进行合并就ok了
Reduce Join 实现方式一
● 适用场景:两个表连接
● 实现方式:二次排序

● 代码实现:
JoinStationMapper 处理来自气象站数据,代码如下所示。
package com.dajiangtai.hadoop.join;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
public class JoinStationMapper extends Mapper< LongWritable,Text,TextPair,Text>{
protected void map(LongWritable key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
String[] arr = StringUtils.split(value.toString(),"\\s+");//解析气象站数据
if(arr.length==2){//满足这种数据格式
//key=气象站id value=气象站名称
context.write(new TextPair(arr[0],"0"),new Text(arr[1]));
}
}
}
JoinRecordMapper 处理来自天气记录数据,代码如下所示。
package com.dajiangtai.hadoop.join;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
public class JoinRecordMapper extends Mapper< LongWritable,Text,TextPair,Text>{
protected void map(LongWritable key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
String[] arr = StringUtils.split(value.toString(),"\\s+");//解析天气记录数据
if(arr.length==3){
//key=气象站id value=天气记录数据
context.write(new TextPair(arr[0],"1"),new Text(arr[1]+"\t"+arr[2]));
}
}
}
自定义TextPair作为JoinStationMapper和JoinRecordMapper的输出key。
package com.dajiangtai.hadoop.join;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import java.io.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.*;
public class TextPair implements WritableComparable {
private Text first;//Text 类型的实例变量 first
private Text second;//Text 类型的实例变量 second
public TextPair() {
set(new Text(),new Text());
}
public TextPair(String first, String second) {
set(new Text(first),new Text(second));
}
public TextPair(Text first, Text second) {
set(first, second);
}
public void set(Text first, Text second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
public Text getFirst() {
return first;
}
public Text getSecond() {
return second;
}
//将对象转换为字节流并写入到输出流out中
public void write(DataOutput out)throws IOException {
first.write(out);
second.write(out);
}
//从输入流in中读取字节流反序列化为对象
public void readFields(DataInput in)throws IOException {
first.readFields(in);
second.readFields(in);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return first.hashCode() *163+second.hashCode();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(o instanceof TextPair) {
TextPair tp = (TextPair) o;
return first.equals(tp.first) && second.equals(tp.second);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return first +"\t"+ second;
}
//排序
public int compareTo(TextPair o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(!first.equals(o.first)){
return first.compareTo(o.first);
}
else if(!second.equals(o.second)){
return second.compareTo(o.second);
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}
自定义分区KeyPartitioner
package com.dajiangtai.hadoop.join;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
//joinkey + "0"
public class KeyPartitioner extends Partitioner< TextPair,Text>{
public int getPartition(TextPair key,Text value,int numPartitions){
return (key.getFirst().hashCode()&Integer.MAX_VALUE)% numPartitions;
}
}
自定义分组GroupingComparator
package com.dajiangtai.hadoop.join;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
public class GroupingComparator extends WritableComparator{
protected GroupingComparator(){
super(TextPair.class, true);
}
@Override
//Compare two WritableComparables.
public int compare(WritableComparable w1, WritableComparable w2){
TextPair ip1 = (TextPair) w1;
TextPair ip2 = (TextPair) w2;
Text l = ip1.getFirst();
Text r = ip2.getFirst();
return l.compareTo(r);
}
}
由于 TextPair 经过了二次排序,所以 reducer 会先接收到气象站数据。因此从中抽取气象站名称,并将其作为后续每条输出记录的一部分写到输出文件。JoinReducer 的代码如下所示。
package com.dajiangtai.hadoop.join;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
public class JoinReducer extends Reducer< TextPair,Text,Text,Text>{
protected void reduce(TextPair key, Iterable< Text> values,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
Iterator< Text> iter = values.iterator();
Text stationName = new Text(iter.next());//气象站名称
while(iter.hasNext()){
Text record = iter.next();//天气记录的每条数据
Text outValue = new Text(stationName.toString()+"\t"+record.toString());
context.write(key.getFirst(),outValue);
}
}
}
下面我们定义作业的驱动类 ReduceJoinBySecondarySort,在该类中,关键在于根据组合键的第一个字段(即气象站 ID)进行分区和分组,即使用一个自定义的 Partitioner 和 一个自定义的分组 comparator 作为TextPair 的嵌套类。ReduceJoinBySecondarySort 类的代码如下所示。
package com.dajiangtai.hadoop.join;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.MultipleInputs;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
/*
* 通过二次排序实现reduce join
* 适用场景:其中一个表的连接字段key唯一
*/
public class ReduceJoinBySecondarySort extends Configured implements Tool{
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();// 读取配置文件
Path mypath = new Path(args[2]);
FileSystem hdfs = mypath.getFileSystem(conf);// 创建输出路径
if (hdfs.isDirectory(mypath)) {
hdfs.delete(mypath, true);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "join");// 新建一个任务
job.setJarByClass(ReduceJoinBySecondarySort.class);// 主类
Path recordInputPath = new Path(args[0]);//天气记录数据源
Path stationInputPath = new Path(args[1]);//气象站数据源
Path outputPath = new Path(args[2]);//输出路径
MultipleInputs.addInputPath(job,recordInputPath,TextInputFormat.class,JoinRecordMapper.class);//读取天气记录Mapper
MultipleInputs.addInputPath(job,stationInputPath,TextInputFormat.class,JoinStationMapper.class);//读取气象站Mapper
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outputPath);
job.setReducerClass(JoinReducer.class);// Reducer
job.setPartitionerClass(KeyPartitioner.class);//自定义分区
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(GroupingComparator.class);//自定义分组
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(TextPair.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
return job.waitForCompletion(true)?0:1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String[] args0 = {"hdfs://djt002:9000/dajiangtai/records.txt"
,"hdfs://djt002:9000/dajiangtai/station.txt"
,"hdfs://djt002:9000/dajiangtai/ssReduceJoin-out"
};
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new ReduceJoinBySecondarySort(),args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
下载该样本数据上运行程序,获得以下输出结果。
011990-99999 SIHCCAJAVRI 195005150700 0 011990-99999 SIHCCAJAVRI 195005151200 22 011990-99999 SIHCCAJAVRI 195005151800 -11 012650-99999 TYNSET-HANSMOEN 194903241200 111 012650-99999 TYNSET-HANSMOEN 194903241800 78
Reduce Join 实现方式二
● 适用场景:两个表连接
● 实现方式:笛卡尔积
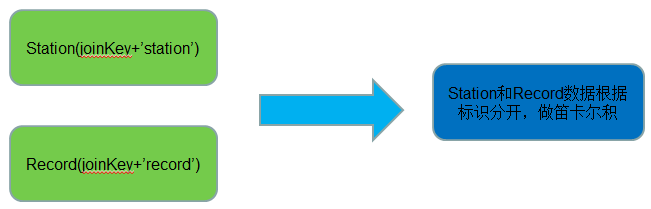
● 代码实现:
package com.dajiangtai.hadoop.join;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
/*
* 两个大表
* 通过笛卡尔积实现 reduce join
* 适用场景:两个表的连接字段key都不唯一(包含一对多,多对多的关系)
*/
public class ReduceJoinByCartesianProduct {
/**
为来自不同表(文件)的key/value对打标签以区别不同来源的记录。
然后用连接字段作为key,其余部分和新加的标志作为value,最后进行输出。
*/
public static class ReduceJoinByCartesianProductMapper extends Mapper<Object,Text,Text,Text>{
private Text joinKey=new Text();
private Text combineValue=new Text();
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String pathName=((FileSplit)context.getInputSplit()).getPath().toString();
//如果数据来自于records,加一个records的标记
if(pathName.endsWith("records.txt")){
String[] valueItems=StringUtils.split(value.toString(),"\\s+");
//过滤掉脏数据
if(valueItems.length!=3){
return;
}
joinKey.set(valueItems[0]);
combineValue.set("records.txt" + valueItems[1] + "\t" + valueItems[2]);
}else if(pathName.endsWith("station.txt")){
//如果数据来自于station,加一个station的标记
String[] valueItems=StringUtils.split(value.toString(),"\\s+");
//过滤掉脏数据
if(valueItems.length!=2){
return;
}
joinKey.set(valueItems[0]);
combineValue.set("station.txt" + valueItems[1]);
}
context.write(joinKey,combineValue);
}
}
/*
* reduce 端做笛卡尔积
*/
public static class ReduceJoinByCartesianProductReducer extends Reducer<Text,Text,Text,Text>{
private List<String> leftTable=new ArrayList<String>();
private List<String> rightTable=new ArrayList<String>();
private Text result=new Text();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//一定要清空数据
leftTable.clear();
rightTable.clear();
//相同key的记录会分组到一起,我们需要把相同key下来自于不同表的数据分开,然后做笛卡尔积
for(Text value : values){
String val=value.toString();
if(val.startsWith("station.txt")){
leftTable.add(val.replaceFirst("station.txt",""));
}else if(val.startsWith("records.txt")){
rightTable.add(val.replaceFirst("records.txt",""));
}
}
//笛卡尔积
for(String leftPart:leftTable){
for(String rightPart:rightTable){
result.set(leftPart+"\t"+rightPart);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: reducejoin <in> [
