Android开发 - ViewGroup解析与自定义xml属性
ViewGroup解析
-
ViewGroup是一个特殊的View,可以包含其他视图(称为子视图)。而ViewGroup是View的子类,所以ViewGroup可以当成普通的UI组件使用。ViewGroup是布局和视图容器的基类,该类还定义了
ViewGroup.LayoutParams用作布局参数基类的类![]()
-
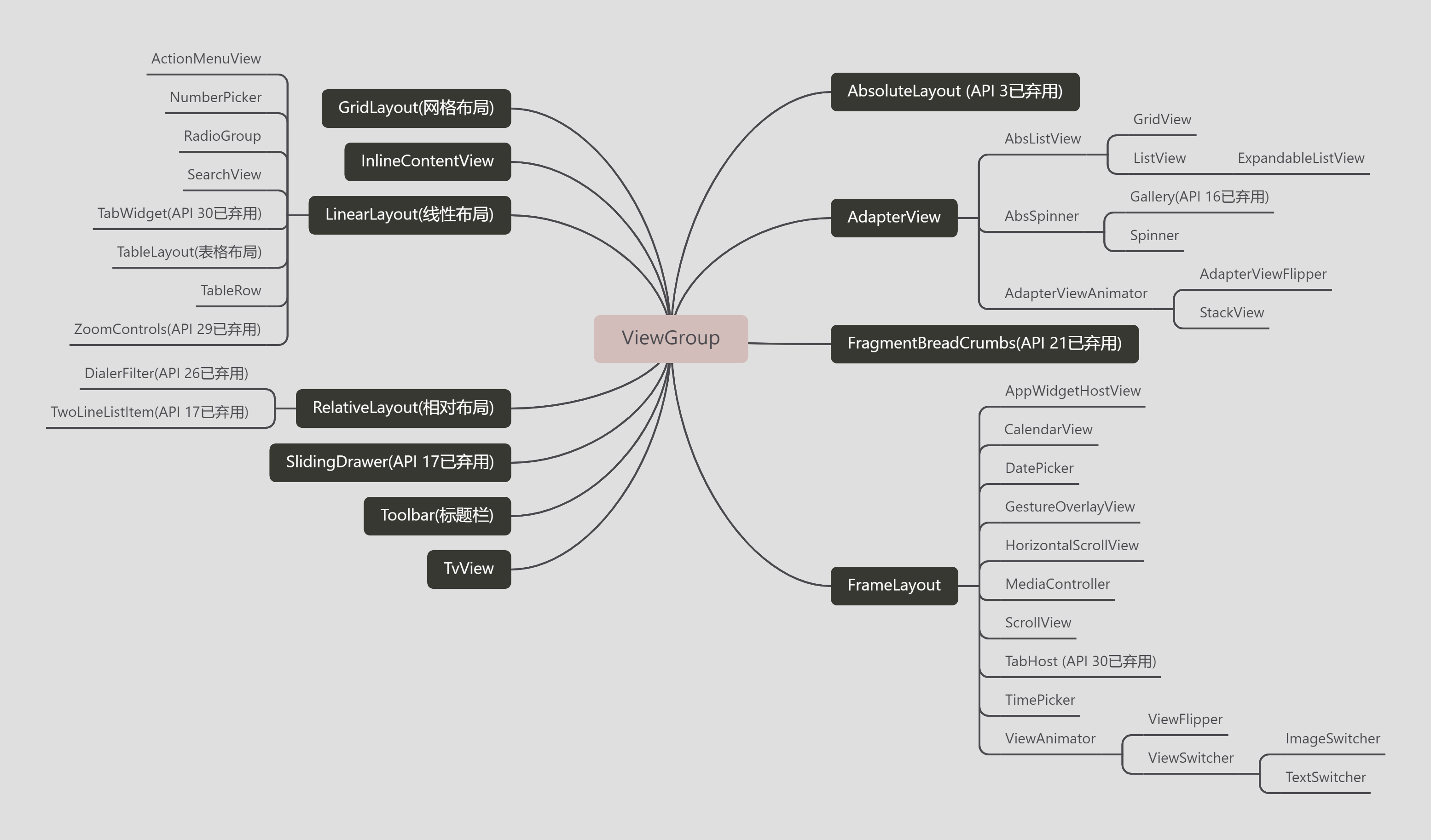
由于ViewGroup的直接子类和间接子类比较多,上图描述了展示了部分子类。下面把放在
android.widget包下的ViewGroup的全部子类展示出来
自定义ViewGroup
ViewGroup常用重写方法
onMeasure()
- 遍历自己的子View对自己的每一个子View进行measure(测量),绝大多数时候对子View的measure都可以直接用
measureChild()这个方法来替代。确定子View的宽高和自己的宽高以后再调用setMeasuredDimension将ViewGroup自身的宽和高传给它的父View,才可以继续写onLayout()方法
onSizeChanged()
- 在
onMeasure()后执行,只有大小发生了变化才会执行onSizeChange()
onLayout()
- 排列所有子View的位置,通过
getChildCount()获取所有子view,也就是getChildAt获取childview调用各自的layout(int l, int t, int r, int b)方法来排列自己
onDraw()
- 自定义ViewGroup默认不会触发onDraw方法,需要
设置背景色 setBackgroundColor()或者setWillNotDraw(false)来手动触发
注意事项
- ViewGroup的
onLayout()方法是必须重写的,而onDraw()方法默认是不会调用。如果想执行onDraw方法,可以通过下面两种方法:- 设置透明背景:
- 在构造函数中:
setBackgroundColor(Color.TRANSPARENT); - 在xml中:
android:background="@color/transparent"
- 在构造函数中:
- 在构造函数中添加
setWillNotDraw(false)不进行自行绘制View
- 设置透明背景:
代码实例
图例

创建CustomLayout继承ViewGroup
/**
* 编写自定义ViewGroup的示例。
*/
public class CustomLayout extends ViewGroup {
// private int childHorizontalSpace = 20;
// private int childVerticalSpace = 20;
private int childHorizontalSpace;
private int childVerticalSpace;
//从代码创建视图时使用的简单构造函数。
public CustomLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
//从XML使用视图时调用的构造函数。
public CustomLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray attrArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomLayout);
if (attrArray != null) {
childHorizontalSpace = attrArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomLayout_horizontalSpace, 12);
childVerticalSpace = attrArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomLayout_verticalSpace, 12);
MLog.e(getClass().getName(),"HorizontalSpace:"+childHorizontalSpace+"|VerticalSpace:"+childVerticalSpace);
attrArray.recycle();
}
//此视图是否自行绘制
setWillNotDraw(false);
}
/**
* 负责设置子控件的测量模式和大小 根据所有子控件设置自己的宽和高
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
MLog.e(getClass().getName(),"onMeasure");
// 获得它的父容器为它设置的测量模式和大小
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// 如果是warp_content情况下,记录宽和高
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
//记录每一行的宽度,width不断取最大宽度
int lineWidth = 0;
//每一行的高度,累加至height
int lineHeight = 0;
int count = getChildCount();
int left = getPaddingLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
// 遍历每个子元素
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE) //判断子元素可见性是不可见
continue; //继续
// 测量每一个child的宽和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 得到child的LayoutParams
ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
// 当前子空间实际占据的宽度 水平空间(childHorizontalSpace)
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + childHorizontalSpace;
// 当前子空间实际占据的高度 垂直空间(childVerticalSpace)
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + childVerticalSpace;
if (lp != null && lp instanceof MarginLayoutParams) {
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) lp;
childWidth += params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin; //childWidth = params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin + childWidth
childHeight += params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin; //childHeight = params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin + childHeight += params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin
}
//如果加入当前child,则超出最大宽度,则的到目前最大宽度给width,叠加height 然后开启新行
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) {
width = Math.max(lineWidth, childWidth);// 取最大的
lineWidth = childWidth; // 重新开启新行,开始记录
// 叠加当前高度,
height += lineHeight; // height = lineHeight + height
// 开启记录下一行的高度
lineHeight = childHeight;
child.setTag(new Location(left, top + height, childWidth + left - childHorizontalSpace, height + child.getMeasuredHeight() + top));
} else {
// 否则累加值lineWidth,lineHeight取最大高度
child.setTag(new Location(lineWidth + left, top + height, lineWidth + childWidth - childHorizontalSpace + left, height + child.getMeasuredHeight() + top));
lineWidth += childWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
}
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth) + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
height += lineHeight;
sizeHeight += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
height += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
setMeasuredDimension((modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeWidth : width, (modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeHeight : height);
}
/**
* 记录子控件的坐标
*/
public class Location {
public Location(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
this.left = left;
this.top = top;
this.right = right;
this.bottom = bottom;
}
public int left;
public int top;
public int right;
public int bottom;
}
//计算当前View以及子View的位置
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
MLog.e(getClass().getName(),"onLayout");
//获取子View个数
int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//获取子View
View child = getChildAt(i);
//判断是否显示
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE)
continue;
//获取子View的坐标
Location location = (Location) child.getTag();
//设置子View位置
child.layout(location.left, location.top, location.right, location.bottom);
}
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
MLog.e(getClass().getName(),"onSizeChanged");
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
MLog.e(getClass().getName(),"onDraw");
}
}
使用自定义CustomLayout
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.scc.demo.view.CustomLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="@dimen/dimen_20"
custom:horizontalSpace="10dp"
custom:verticalSpace="20dp">
<!--一定记得添加前缀-->
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="破阵子·为陈同甫赋壮词以寄" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="宋·辛弃疾" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="醉里挑灯看剑" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="梦回吹角连营" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="八百里分麾下炙" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="五十弦翻塞外声" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="沙场秋点兵" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="马作的卢飞快" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="弓如霹雳弦惊(增加点长度)" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="了却君王天下事" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="赢得生前身后名" />
<TextView
style="@style/TvStyle"
android:text="可怜白发生!" />
</com.scc.demo.view.CustomLayout>
自定义属性
-
在
app/src/main/res/values/attrs.xml中添加属性<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="CustomLayout"> <attr name="verticalSpace" format="dimension" /> <attr name="horizontalSpace" format="dimension" /> </declare-styleable> </resources>
使用自定义属性
-
在xml中使用
-
一定要添加
xmlns:test=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto”添加之后才能在xml中使用自定义属性,如下代码:<com.scc.demo.view.CustomLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_margin="@dimen/dimen_20" custom:horizontalSpace="10dp" custom:verticalSpace="20dp"> </com.scc.demo.view.CustomLayout>
-
-
在Java中使用
TypedArray attrArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomLayout); if (attrArray != null) { //参数1:获取xml中设置的参数;参数2:获取失败使用参数2作为默认值 childHorizontalSpace = attrArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomLayout_horizontalSpace, 12); childVerticalSpace = attrArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomLayout_verticalSpace, 12); MLog.e(getClass().getName(),"HorizontalSpace:"+childHorizontalSpace+"|VerticalSpace:"+childVerticalSpace); //TypedArray对象池的大小默认为5,使用时记得调用recyle()方法将不用的对象返回至对象池来达到重用的目的。 attrArray.recycle(); }
ViewGroup属性
ViewGroup的XML属性以及相关方法
-
android:addStatesFromChildren:设置此 ViewGroup 的可绘制状态是否还包括其子级的可绘制状态 -
android:alwaysDrawnWithCache:定义 ViewGroup 是否始终使用其绘图缓存绘制其子项 -
android:animateLayoutChanges:与setLayoutTransition(LayoutTransition)方法相关,定义布局更改(由添加和删除项目引起)是否导入致 LayoutTransition 运行 -
android:animationCache:定义布局动画是否为其子项创建绘图缓存 -
android:clipChildren:与setClipChildren(boolean)方法相关,定义孩子是否被限制在其边界内绘制 -
android:clipToPadding:与setClipToPadding(boolean)方法相关,如果填充不为零,则定义 ViewGroup 是否将裁剪其子项并将任何 EdgeEffect 调整大小(但不裁剪)到其填充 -
android:descendantFocusability:定义 ViewGroup 和它的后代在寻找一个 View 来获得焦点时的关系 -
android:layoutAnimation:定义第一次布局 ViewGroup 时使用的布局动画 -
android:layoutMode:与setLayoutMode(int)方法相关,定义此 ViewGroup 的布局模式 -
android:persistentDrawingCache:定义绘图缓存的持久性 -
android:splitMotionEvents:与setMotionEventSplittingEnabled(boolean)方法相关,设置此 ViewGroup 是否应在触摸事件调度期间拆分 MotionEvents 以分隔子视图
ViewGroup.LayoutParams
- LayoutParams 被视图用来告诉他们的父母他们想要如何布局。基本的 LayoutParams 类只是描述了视图的宽度和高度的大小。对于每个维度,它可以指定以下之一:
- MATCH_PARENT:这意味着视图希望与其父视图一样大(减去填充)
- WRAP_CONTENT:这意味着视图希望足够大以包含其内容(加上填充)
- 确切的数字
ViewGroup.LayoutParams(子组件)的XML属性:android:layout_height:指定视图的基本高度android:layout_width:指定视图的基本宽度
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams
- 支持边距的布局的每个子布局信息
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(子组件)的XML属性及相关方法:android:layout_margin:指定此视图左侧、顶部、右侧和底部的额外空间android:layout_marginBottom:与setMargins(int,int,int,int)方法相关,指定此视图底部的额外空间android:layout_marginEnd:与setMarginEnd(int)方法相关,指定此视图末端的额外空间android:layout_marginHorizontal:指定此视图左侧和右侧的额外空间android:layout_marginLeft:与setMargins(int,int,int,int)方法相关,指定此视图左侧的额外空间android:layout_marginRight:与setMargins(int,int,int,int)方法相关,指定此视图右侧的额外空间android:layout_marginStart:与setMarginStart(int)方法相关,指定此视图开始侧的额外空间android:layout_marginTop:与setMargins(int,int,int,int)方法相关,指定此视图顶部的额外空间android:layout_marginVertical:指定此视图顶部和底部的额外空间



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号