Android开发 - Bundle传值的理解与使用
什么是Bundle
-
Bundle经常出现在以下场合:
Activity状态数据的保存与恢复涉及到的两个回调: void onSaveInstanceState (Bundle outState) void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) Fragment的setArguments方法:void setArguments (Bundle args) 消息机制中的Message的setData方法:void setData (Bundle data) ... -
Bundle从字面上解释为“一捆、一批、一包”,结合上述几个应用场合,可以知道Bundle是用来传递数据的。我们经常使用Bundle在Activity之间传递数据,传递的数据可以是boolean、byte、int、long、float、double、string等基本类型或它们对应的数组,也可以是对象或对象数组。当Bundle传递的是对象或对象数组时,必须实现Serializable 或Parcelable接口。下面分别介绍Activity之间如何传递基本类型、传递对象:
- Bundle的两个常用方法:
putXxx(String key,Xxx value):Xxx表示一系列的数据类型,比如String、int、float、Parcelable、Serializable等类型,以“键值对”(key-value,可以理解为一个Map<K,V>)形式保存数据getXxx(String key):根据key值获取Bundle中的value数据
- Bundle的两个常用方法:
Bundle源码分析
Bundle的声明
-
public final class Bundle extends BaseBundle implements Cloneable, Parcelable:可以看出以下几点:-
它使用final修饰,所以不可以被继承
-
它实现了两个接口,cloneable(复制)和Parcelable(打包),这就意味着他必须实现以下方法:
public Object clone() //克隆数据 public int describeContents() //写入数据 public void writeToParcel(Parcel parcel, int flags) //将数据打包 public void readFromParcel(Parcel parcel) //读取数据 public static final Parcelable.Creator<Bundle> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<Bundle>() //将打包的数据实例化
-
Bundle的内存结构
ArrayMap<String, Object> mMap = null;:使用的是ArrayMap,这个集合类存储的也是键值对,但是与Hashmap不同的是,hashmap采用的是“数组+链表”的方式存储,而Arraymap中使用的是两个数组进行存储,一个数组存储key,一个数组存储value,内部的增删改查都将会使用二分查找来进行,这个和SparseArray差不多,只不过sparseArray的key值只能是int类型的,而Arraymap可以是map型,所以在数据量不大的情况下可以使用这两个集合代替hashmap去优化性能
Get/Put解析
-
Bundle其实就是一个容器,内部使用了Arraymap去存储数据,那么就必然会提供get与put方法,由于Bundle支持的数据类型太多,这里我们就举例布尔类型的,其他类型的方式都差不多:
getBoolean:
public boolean getBoolean(String key, boolean defaultValue) { unparcel(); Object o = mMap.get(key); if (o == null) { return defaultValue; } try { return (Boolean) o; } catch (ClassCastException e) { typeWarning(key, o, "Boolean", defaultValue, e); return defaultValue; } }- 数据读取的逻辑就是通过key从ArrayMap里读出保存的数据,并转换成对应的类型返回,当没找到数据或发生类型转换异常时返回缺省值(
default-value类似null的空值)
putBoolean:
public void putBoolean(@Nullable String key, boolean value) { unparcel(); mMap.put(key, value); }unparcel():
-
先来看下BaseBundle中mParcelledData的定义:
Parcel mParcelledData = null;- 在大部分情况下mParcelledData都是null,因此
unparcel()直接返回。当使用构造函数public Bundle(Bundle b)创建Bundle时,会给mParcelledData赋值;
oid copyInternal(BaseBundle from, boolean deep) { synchronized (from) { if (from.mParcelledData != null) { if (from.isEmptyParcel()) { mParcelledData = NoImagePreloadHolder.EMPTY_PARCEL; //第一种取值 } else { mParcelledData = Parcel.obtain(); //第二种取值 mParcelledData.appendFrom(from.mParcelledData, 0, from.mParcelledData.dataSize()); mParcelledData.setDataPosition(0); } } else { mParcelledData = null; //第三种取值 } if (from.mMap != null) { if (!deep) { mMap = new ArrayMap<>(from.mMap); } else { final ArrayMap<String, Object> fromMap = from.mMap; final int N = fromMap.size(); mMap = new ArrayMap<>(N); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { mMap.append(fromMap.keyAt(i), deepCopyValue(fromMap.valueAt(i))); } } } else { mMap = null; } mClassLoader = from.mClassLoader; } }- 从上述代码片段可以知道mParcelledData的取值有3种情况:
mParcelledData = EMPTY_PARCELmParcelledData = Parcel.obtain()mParcelledData = null
- 在大部分情况下mParcelledData都是null,因此
总结
-
在
unparcel()方法中就对上述几种情况做了不同的处理,当mParcelledData = null时,直接返回 -
当
mParcelledData = EMPTY_PARCEL时,会创建一个容量为1的ArrayMap对象 -
当
mParcelledData = Parcel.obtain()时,则会将里面的数据读出,并创建一个ArrayMap,并将数据存储到ArrayMap对象里面,同时将mParcelledData回收并置为null
- 数据读取的逻辑就是通过key从ArrayMap里读出保存的数据,并转换成对应的类型返回,当没找到数据或发生类型转换异常时返回缺省值(
Bundle的使用
各种常用类型的Put/Get方法
- Bundle提供了,用于读写基本类型的数据。Bundle操作基本数据类型的API表格如下所示:
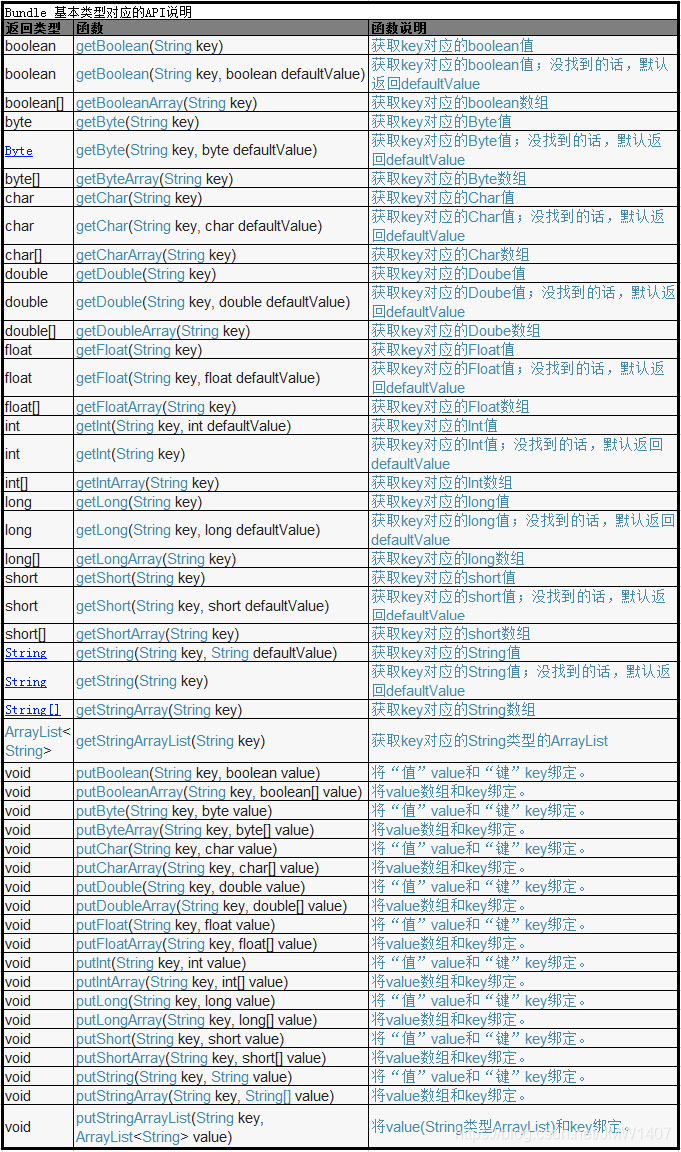
传递基本类型的对象
-
数据打包
Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,Main2Activity.class); //设置数据 String name = "zhangSan"; String num = "88888"; //把数据保存到Bundle里 bundle.putString("name", name); bundle.putString("num", num); //把bundle放入intent里 intent.putExtra("Message", bundle); startActivity(intent);//开始打包 -
读取数据
Intent intent = getIntent(); //实例化一个Bundle Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras(); String name = bundle.getString("name"); String num = bundle.getString("num");
Activity通过Arguments给fragment类传值
-
当Activity类动态加载fragment时可以通过fragment的
setArguments()传入值,并在fragment类中通过fragment的getArguments()方法获得传入的值。 -
数据打包
Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); fragment01 fragment01 = new fragment01();//自定义的fragment类 //设置数据 String name = "zhangSan"; String num = "88888"; //把数据保存到Bundle里 bundle.putString("name", name); bundle.putString("num", num); //把bundle通过Arguments放入要传值的fragment类里 fragment01.setArguments(bundle); -
读取数据
String name = getArguments().getString("name"); String num = getArguments().getString("num");
传递Serializable类型的对象
-
Serializable:是一个对象序列化的接口。一个类只有实现了Serializable接口,它的对象才是可序列化的。因此如果要序列化某些类的对象,这些类就必须实现Serializable接口。而实际上,Serializable是一个空接口,没有什么具体内容,它的目的只是简单的标识一个类的对象可以被序列化
-
打包数据
People people = new people(); //People类 //设置数据 String Name = "zhangSan"; String Num = "88888"; people.setName(Name); people.setNum(Num); //实例化一个Bundle Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); //把people数据放入到bundle中 bundle.putSerializable("people", people); Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,Main2Activity.class); //把bundle放入intent里 intent.putExtras(bundle); startActivity(intent);//开始打包 -
读取数据
Intent intent = getIntent(); // 实例化一个Bundle Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras(); //获取里面的people里面的数据 People people = (people) bundle.getSerializable("people"); String name = people.getName(); String num = people.getNum();



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号