EL&JSTL26_EL表达式2
一、概念
Expression Language 表达式语言
二、作用
替换和简化jsp页面中java代码的编写
三、语法
${表达式}
浏览器访问http://localhost/day17/el/el1.jsp
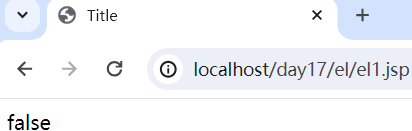
四、注意
jsp默认支持el表达式的。如果要忽略el表达式
1. 设置jsp中page指令中:isELIgnored="true" 忽略当前jsp页面中所有的el表达式
2. \${表达式} :忽略当前这个el表达式
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> ${3 > 4} \${3 > 4} </body> </html>
浏览器访问:
五、使用
1、运算:
运算符:
1. 算数运算符: + - * /(div) %(mod)
2. 比较运算符: > < >= <= == !=
3. 逻辑运算符: &&(and) ||(or) !(not)
4. 空运算符: empty
功能:用于判断字符串、集合、数组对象是否为null或者长度是否为0
${empty list}:判断字符串、集合、数组对象是否为null或者长度为0
${not empty str}:表示判断字符串、集合、数组对象是否不为null并且长度>0
<%@ page import="java.util.ArrayList" %> <%@ page import="java.util.List" %> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h3>算数运算符</h3> ${3 + 4}<br> ${3 / 4}<br> ${3 div 4}<br> ${3 % 4}<br> ${3 mod 4}<br> <h3>比较运算符</h3> ${3 == 4}<br> ${3 > 4}<br> ${3 != 4}<br> <h3>逻辑运算符</h3> ${3 > 4 && 3 < 4}<br> ${3 > 4 and 3 < 4}<br> ${3 > 4 || 3 < 4}<br> <h3>empty运算符</h3> <% String str = "abc"; String str1 = ""; String str2 = null; request.setAttribute("str",str); request.setAttribute("str1",str1); request.setAttribute("str2",str2); List list = new ArrayList(); request.setAttribute("list",list); %> ${empty str}<br> ${not empty str}<br> ${empty str1}<br> ${empty str2}<br> ${not empty list}<br> </body> </html>

2、获取值
1. el表达式只能从域对象中获取值
2. 语法:
1. ${域名称.键名}:从指定域中获取指定键的值,没有值则返回空字符串
域名称 对应的对象
1. pageScope --> pageContext
2. requestScope --> request
3. sessionScope --> session
4. applicationScope --> application(ServletContext)
举例:在request域中存储了name=张三
获取:${requestScope.name}
2. ${键名}:表示依次从最小的域中(pageContext->request->session->application)查找是否有该键对应的值,直到找到为止。
3. 获取对象、List集合、Map集合的值
1. 对象:${域名称.键名.属性名}
本质上会去调用对象的getter方法
2. List集合:${域名称.键名[索引]}
3. Map集合:
${域名称.键名.key名称}
${域名称.键名["key名称"]}
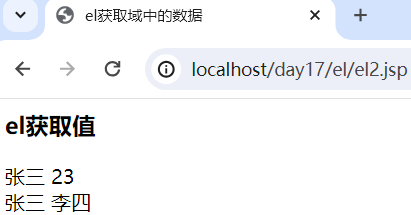
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>el获取域中的数据</title> </head> <body> <% //在域中存储数据 session.setAttribute("name","李四"); request.setAttribute("name","张三"); session.setAttribute("age","23"); %> <h3>el获取值</h3> ${requestScope.name} ${requestScope.hah} ${sessionScope.age} <br> ${name} ${sessionScope.name} </body> </html>
package cn.itcast.domain; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; public class User { private String name; private int age; private Date birthday; /** * 逻辑视图 * @return */ public String getBirStr(){ if(birthday != null){ //1.格式化日期对象 SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); //2.返回字符串即可 return sdf.format(birthday); }else{ return ""; } } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } }
<%@ page import="cn.itcast.domain.User" %> <%@ page import="java.util.*" %> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>el获取数据</title> </head> <body> <% User user = new User(); user.setName("张三"); user.setAge(23); user.setBirthday(new Date()); request.setAttribute("u",user); List list = new ArrayList(); list.add("aaa"); list.add("bbb"); list.add(user); request.setAttribute("list",list); Map map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("sname","李四"); map.put("gendar","男"); map.put("user",user); request.setAttribute("map",map); %> <h3>el获取对象中的值</h3> ${requestScope.u}<br> <%-- 通过的是对象的属性来获取 setter或getter方法,去掉set/get,再将剩余部分的首字母变为小写 setName-->Name-->name --%> ${requestScope.u.name}<br> ${u.age}<br> ${u.birthday}<br> ${u.birthday.year}<br> ${u.birStr}<br> <h3>el获取List值</h3> ${list}<br> ${list[0]}<br> ${list[1]}<br> ${list[20]}<br> ${list[2].name}<br> <h3>el获取Map值</h3> ${map.gendar}<br> ${map.sname}<br> ${map["gendar"]}<br> ${map.user.name}<br> </body> </html>

3、隐式对象:
el表达式中有11个隐式对象
pageContext对象功能:获取jsp其他八个内置对象
其中${pageContext.request.contextPath}:动态获取虚拟目录
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>el隐式对象</title>
</head>
<body>
${pageContext.request}<br>
<h4>在jsp页面动态获取虚拟目录</h4>
${pageContext.request.contextPath}
</body>
</html>
浏览器访问这个页面:http://localhost/day17/el/el4.jsp



