Spring17_声明式事务控制13
一、编程式事务控制相关对象
1、PlatformTransactionManager
PlatformTransactionManager 接口是 spring 的事务管理器,它里面提供了我们常用的操作事务的方法。
Dao 层技术是hibernate时:org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager
2、TransactionDefinition
TransactionDefinition 是事务的定义信息对象,里面有如下方法:
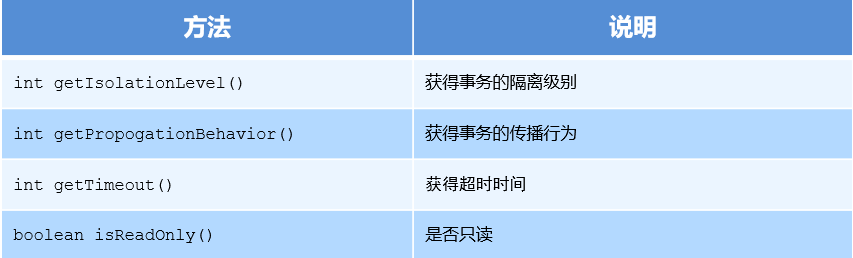
1. 事务隔离级别
设置隔离级别,可以解决事务并发产生的问题,如脏读、不可重复读和虚读。
-
- ISOLATION_DEFAULT
- ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED
- ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED
- ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ
- ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE
2. 事务传播行为
-
- REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的 选择(默认值)
- SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务)
- MANDATORY:使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常
- REQUERS_NEW:新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起。
- NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
- NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常
- NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行 REQUIRED 类似的操作
- 超时时间:默认值是-1,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置
- 是否只读:建议查询时设置为只读
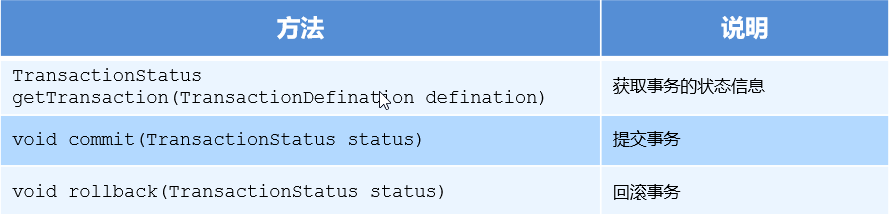
3、TransactionStatus
TransactionStatus 接口提供的是事务具体的运行状态,方法介绍如下。

编程式事务控制三大对象
- PlatformTransactionManager
- TransactionDefinition
- TransactionStatus
1、什么是声明式事务控制
Spring 的声明式事务顾名思义就是采用声明的方式来处理事务。这里所说的声明,就是指在配置文件中声明,用在 Spring 配置文件中声明式的处理事务来代替代码式的处理事务。
声明式事务处理的作用
-
- 事务管理不侵入开发的组件。具体来说,业务逻辑对象就不会意识到正在事务管理之中,事实上也应该如此,因为事务管理是属于系统层面的服务,
而不是业务逻辑的一部分,如果想要改变事务管理策划的话,也只需要在定义文件中重新
-
- 在不需要事务管理的时候,只要在设定文件上修改一下,即可移去事务管理服务,无需改变代码重新编译,这样维护起来极其方便
注意:Spring 声明式事务控制底层就是AOP。
2、声明式事务控制的实现
声明式事务控制明确事项:
- 谁是切点?
- 谁是通知?
- 配置切面?
新建一个module:itheima_spring_transaction
a. 引入tx命名空间
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
b. 配置事务增强
<!--平台事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--事务增强配置-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
c. 配置事务 AOP 织入
<!--事务的aop增强-->
<aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="myPointcut" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"></aop:advisor> </aop:config>
d. applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd "> <!--加载jdbc.properties--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/> <!--数据源对象DataSource--> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <!--Jdbc模版对象--> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/> </bean> <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/> </bean> <!--配置事务增强--> <!--平台事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!--切点方法的事务参数的配置--> <!--事务增强配置--> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <!-- <tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" timeout="-1" read-only="false"/>--> <!-- <tx:method name="*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>--> <tx:method name="*"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!--配置事务 AOP 织入--> <!--事务的aop增强--> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="myPointcut" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.*.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/> </aop:config> </beans>
e. com.itheima.dao.AccountDao.java
public interface AccountDao { public void out(String outMan, double money); public void in(String inMan, double money); }
f. com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl.java
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } public void out(String outMan, double money) { jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money = money-? where name=?", money,outMan); } public void in(String inMan, double money) { jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money = money-? where name=?", money,inMan); } }
g. com.itheima.service.AccountService.java
public interface AccountService { public void transfer(String outMan,String inMan,double money); }
h. com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl.java
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private AccountDao accountDao; public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) { this.accountDao = accountDao; } //测试事务控制转账业务代码 public void transfer(String outMan, String inMan, double money) { accountDao.out(outMan, money); int i = 1/0; accountDao.in(inMan, money); } }
i. com.itheima.controller.AccountController.java
public class AccountController{ public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); AccountService bean = app.getBean(AccountService.class); bean.transfer("tom","lucy",500); } }
执行main方法,数据库account表中name为tom及lucy中money都会-500。
3、切点方法的事务参数的配置
<!--事务增强配置-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
其中,tx:method 代表切点方法的事务参数的配置,例如:
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" timeout="-1" read-only="false"/>
- name:切点方法名称
- isolation:事务的隔离级别
- propogation:事务的传播行为
- timeout:超时时间
- read-only:是否只读
4、知识要点
声明式事务控制的配置要点
- 平台事务管理器配置
- 事务通知的配置
- 事务aop织入的配置
三、基于注解的声明式事务控制
1、使用注解配置声明式事务控制
1. 编写 AccoutDao
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void out(String outMan, double money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=money-? where name=?",money,outMan);
}
public void in(String inMan, double money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=money+? where name=?",money,inMan);
}
}
2. 编写 AccoutService
@Service("accountService")
@Transactional
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void transfer(String outMan, String inMan, double money) {
accountDao.out(outMan,money);
int i = 1/0;
accountDao.in(inMan,money);
}
}
3. 编写 applicationContext.xml 配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd "> <!--组件扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"/>
<!--事务的注解驱动--> <tx:annotation-driven/> <!--加载jdbc.properties--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/> <!--数据源对象DataSource--> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <!--Jdbc模版对象--> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!--平台事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> </beans>
2、注解配置声明式事务控制解析
1. 使用 @Transactional 在需要进行事务控制的类或是方法上修饰,注解可用的属性同 xml 配置方式,例如隔离级别、传播行为等。
2. 注解使用在类上,那么该类下的所有方法都使用同一套注解参数配置。
3. 使用在方法上,不同的方法可以采用不同的事务参数配置。 4Xml配置文件中要开启事务的注解驱动<tx:annotation-driven />
3、知识要点
注解声明式事务控制的配置要点
- 平台事务管理器配置(xml方式)
- 事务通知的配置(@Transactional注解配置)
- 事务注解驱动的配置 tx:annotation-driven/






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构