32.vueX
1.概念
Vuex就是一个状态管理模式,VueX包含了一套对state的操作规范,集中存储所有组件的状态。
管理各个组件共享的数据,类似session,存的过程就是管理,数据的每一次赋值就是当次状态。
session存储数据,
Vue简单模型

-
state,驱动应用的数据源;
-
view,以声明方式将 state 映射到视图;
-
actions,响应在 view 上的用户输入导致的状态变化。
2.搭建
使用的vue ui勾选了vux,实则不需要手动创建。
1.安装
npm install vuex --save
2.新建store文件夹,在文件夹下创建index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
3.在main.js中引用并挂载这个文件
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
3.通信功能
之前使用的是父传子通信方式,现在使用Vuex来进行组件之间的通信
例:
在store的index.js中定义公共数据counter
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
counter:1000
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
在components文件夹下的HelloVuex.vue文件中调用这个数据
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{$store.state.counter}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'HelloVuex',
// 父子传值
// props:{
// counter:Number
// },
data() {
return {
}
},
activated() {
},
watch: {
},
created(){
},
mounted(){
},
methods:{
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
4.修改index.js中的公共数据
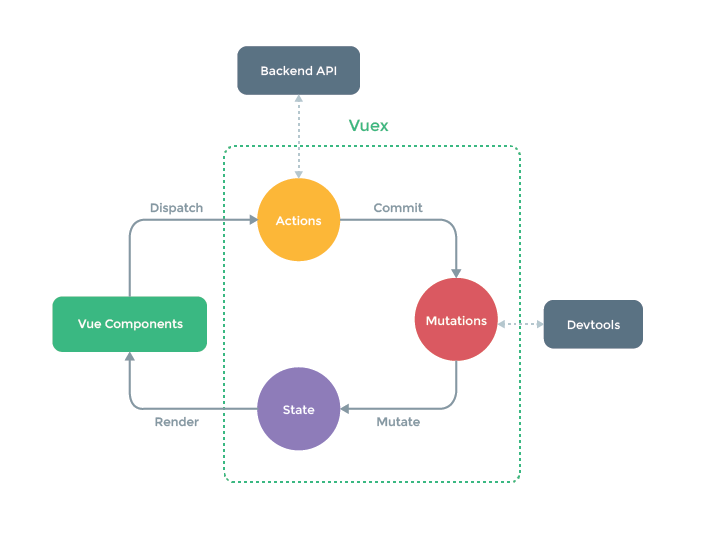
虽然$store.state.count++也可对公共值进行修改,但这样操作Devtools监听不到state每一次修改的状态,就是当多个组件修改同一个公共值时,追踪不到是哪个组件修改的。
当修改Mutations时有异步操作时,Devtools跟踪不到,所以异步操作(如发送网络请求)在Actions中进行操做的。
4.通过Mutations修改值
在vue 中,只有mutation 才能改变state. mutation 类似事件,每一个mutation都有一个类型和一个处理函数,因为只有mutation 才能改变state, 所以处理函数自动会获得一个默认参数 state. 所谓的类型其实就是名字,
-
案例一
点击click对值进行修改
store/index.js
state中定义counter值,mutations中对值进行修改
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
counter:1000
},
mutations: {
increment(state){
state.counter++
},
decrement(state){
state.counter--
}
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
2.App.vue中定义点击事件
这里点击事件里是用commit而不是直接调用
<template>
<div id="app">
<h2>--------App内容</h2>
<h2>{{message}}</h2>
<h2>{{$store.state.counter}}</h2>
<button @click="addition">+</button>
<button @click="subtraction">-</button>
<h2>------hello vue 内容</h2>
<hello-vuex ></hello-vuex>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloVuex from './components/HelloVuex.vue'
export default{
name:'App',
components:{
HelloVuex
},
data(){
return{
message:'你好',
// counter:0
}
},
methods:{
addition(){
this.$store.commit('increment')
},
subtraction(){
this.$store.commit('decrement')
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
-
案例二:对传入的值进行click进行增加
App.vue
<button @click="addCount(5)">+5</button>
methods中定义点击事件
addCount(count){
this.$store.commit('incrementCount',count)
},
store/index.js中
定义counter
state: {
counter: 1000,
},
nutations对传入的值进行修改
mutations: {
incrementCount(state, count) {
state.counter += count
},
}
-
案例三:添加学生信息
store/index.js中
state定义students
state: {
students: [
{ id: 110, name: 'xx', age: 18 },
{ id: 111, name: 'xj', age: 19 },
{ id: 112, name: 'jx', age: 20 },
{ id: 113, name: 'jj', age: 21 },
]
},
App.vue template
<button @click="addStudent">添加学生</button>
App.vue methods中
addStudent(){
const stu = {id:114,name:'aaa',age:18}
this.$store.commit('addStudent',stu)
}
state定义students,添加到state中
addStudent(state,stu){
state.students.push(stu)
}
-
mutations提交风格
当App.vue的methods中addcount改为如下提交格式
<template>
<button @click="addCount(5)">+5</button>
</template>
<script>
addCount(count){
this.$store.commit({
type:'incrementCount',
count
})
},
</script>store/index.js的mutations
incrementCount(state, count) {
console.log(count);
// state.counter += count
},这里的count传入的实则是payload对象,count只是一个变量名字,打印一下得到的是
{type: "incrementCount", count: 5}所以修改为
incrementCount(state,payload ) {
state.counter += payload.count
},
5.getters
获取state值,对state值进行加工计算,相当于computed钩子。
其实,这个操作也能在APP.vue的computed钩子中实现,但这只是计算单个页面,而getters是可以被所有页面去获得值的
-
案例一:展示counter值的平方。
store/index.js
state定义counter值
state: {
counter: 1000,
},
getters
getters: {
powerCounter(state) {
return state.counter * state.counter
},
}
App.vue响应展示
<h2>{{ $store.getters.powerCounter }}</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.getters.more20stuLength }}</h2>
-
案例二:筛选大于二十岁的信息与length
store/index.js定义students
state: {
students: [
{ id: 110, name: 'xx', age: 18 },
{ id: 111, name: 'xj', age: 19 },
{ id: 112, name: 'jx', age: 20 },
{ id: 113, name: 'jj', age: 21 },
]
},getters筛选大于20岁
getters: {
more20stu(state) {
return state.students.filter(s => s.age > 19)
},
//获取长度第一种写法
more20stuLength(state, getters) {
return getters.more20stu.length
},
//获取长度第二种写法
// more20stuLength(state){
// return state.students.filter(s=>s.age>20).length
// },
}
App.vue响应展示
<h2>{{ $store.getters.more20stu }}</h2>
-
案例三:筛选大于用户输入的岁数信息
App.vue
<h2>{{ $store.getters.moreAgestu(20) }}</h2>
strore/index.js中定义students值
state: {
students: [
{ id: 110, name: 'xx', age: 18 },
{ id: 111, name: 'xj', age: 19 },
{ id: 112, name: 'jx', age: 20 },
{ id: 113, name: 'jj', age: 21 },
]
},
getters
moreAgestu(state) {
// return function(age){
// return state.students.filter(s=>s.age>age)
// }
return age => {
return state.students.filter(s => s.age > age)
}
}
6.VueX响应式
修改值和删除值
App.vue
<h2>------App内容:info对象的内容是否为响应式的------</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.state.info }}</h2>
<button @click="updateInfo">修改信息</button>
methods
updateInfo(){
this.$store.commit('updataInfo')
}
store/index.js中
定义值
state: {
info: [
{ name: 'xxjj', age: 20 }
]
},
mutations
updataInfo(state) {
// 1修改属性
// console.log(state.info[0].age);
// state.info[0].age = 22
// 2添加属性
// (错误做法)这种方法不行,做不到响应式
// state.info[0].address = '洛杉矶'
//(正确做法)
// Vue.set(state.info[0],'address' , "洛杉矶")
// 3删除属性
//错误做法
//delete state.info.age
// 正确做法
Vue.delete(state.info[0],'age')
}
7.Action
使用mutation操作更新state的时候,使用异步修改数据。
当存在异步数据时,devtools工具没有跟踪到数据,所以不能在mutation中进行异步操作。
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
-
Action 提交的是 mutation中,而不是直接变更状态。
-
Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
案例:1
App.vue设一个点击事件
<button @click="updateInfo">修改信息</button>
methods定义点击事件

提交给Action中的函数时的方法是dipatch而不是commit,再通过Actions离commit提交给Mutations函数。
methods:{
updateInfo(){
this.$store.dispatch('aUpdataInfo',()=>{
console.log('里面已经完成了');
})
this.$store.dispatch("aUpdataInfo", {
message: "我是携带的信息",
success: () => {
console.log("里面已经完成了");
},
});
}
}
store/index.js中
括号内使用的是context而不是state,
actions: {
aUpdataInfo(context,payload){
console.log(context);
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('updataInfo')
console.log(payload.message);
payload.success()
}, 1000);
}
}
commit提交给mutation里的updataInfo
mutations: {
updataInfo(state) {
state.info[0].age = 22
}
}
案例2:
使用promise方式
dipatch提交aUpdataInfo与'我是携带信息'到action中的aUpdataInfo函数,在promise中使用 context.commit提交到mutation中的updataInfo,成功resolve('11111')而App.vue中使用.then获取resolve信息。
App.vue
<template>
<button @click="updateInfo">修改信息</button>
</template>
methods:{
updateInfo() {
this.$store
.dispatch('aUpdataInfo','我是携带信息')
.then(res=>{
console.log('里面完成的信息');
console.log(res);
})
}
}
store/index.js
updataInfo(state) {
state.info[0].age = 22
}
actions: {
aUpdataInfo(context,payload){
console.log(context);
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('updataInfo');
console.log(payload);
resolve('11111')
})
})
}
},
8.Modules
由于使用的单一状态数,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象,当应用变得非常复杂时,store对象就有可能变得相当雍正。
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割。
-
案例1:modules中定义两个模块
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
值得注意的是如下模块需要写在export default new Vuex.Store({})上面
要不然会报错。
使用moduleA中的name值
const moduleA = {
state: {
name: 'cfy'
},
mutations: {
},
getters: {
},
actions: {
},
}
App.vue中
因为moduleA分支中的数据会自动添加到总的state中,所以调用时使用
$store.state.a.name
<div id="app">
<h2>------App内容:modules中的内容------</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.state }}</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.state.a.name }}</h2>
</div>
-
案例2:mutation修改名字
store/index.js
const moduleA = {
state: {
name: 'cfy'
},
mutations: {
updataName(state, payload) {
console.log(payload);
state.name = payload
}
},
}
App.vue
<template>
<button @click="updataName">修改名字</button>
</template>
methods: {
updataName() {
this.$store.commit("updataName", "lisi");
},
}
}
store/index.js
const moduleA = {
state: {
name: 'cfy'
},
mutations: {
updataName(state, payload) {
console.log(payload);
state.name = payload
}
},
}
-
案例3:getter
App.vue
<h2>{{ $store.getters.fullName }}</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.getters.fullName2 }}</h2>
<h2>{{ $store.getters.fullName3 }}</h2>store/index.js
这里的fullName中调用的state是ModuleA中的state, fullName2中调用的getters也是ModuleA中的不是根中的,而想要获取根中的数据
fullName3中添加值rootState来获取根中的state数据,同理rootGetters获取根中getters,rootMutations,rootActions
const moduleA = {
state: {
name: 'cfy'
},
getters: {
fullName(state) {
return state.name + '1111'
},
fullName2(state, getters) {
return getters.fullName + '2222'
},
fullName3(state,getters,rootState){
return getters.fullName2+rootState.counter
}
},
}-
案例4:Action
-
App.vue
提交到Action中使用dispatch
<template>
<button @click="asyncUpdataName">异步修改名字</button>
</template>
methods:{
asyncUpdataName(){
this.$store.dispatch('aUpdataName')
}
}
store/index.js
再从Action发送异步请求到mutations中
const moduleA = {
mutations: {
updataName(state, payload) {
console.log(payload);
state.name = payload
}
},
actions: {
aUpdataName(context){
console.log(context);
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('updataName','xj')
},20)
}
},
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号