Exploring TCP state machine by graphs
States
TCP includes 11 states, they are:
LISTEN
SYN_SENT
SYN_RECV
ESTABLISHED
FIN_WAIT1
CLOSE_WAIT
FIN_WAIT2
LAST_ACK
TIME_WAIT
CLOSED
CLOSING
@include/net/tcp_states.h:
/* Definitions for the TCP protocol sk_state field. */
#ifndef _LINUX_TCP_STATES_H
#define _LINUX_TCP_STATES_H
enum {
TCP_ESTABLISHED = 1,
TCP_SYN_SENT,
TCP_SYN_RECV,
TCP_FIN_WAIT1,
TCP_FIN_WAIT2,
TCP_TIME_WAIT,
TCP_CLOSE,
TCP_CLOSE_WAIT,
TCP_LAST_ACK,
TCP_LISTEN,
TCP_CLOSING, /* Now a valid state */
TCP_MAX_STATES /* leave at the end! */
};
#define TCP_STATE_MASK 0xF
#define TCP_ACTION_FIN (1 << 7)
enum {
TCPF_ESTABLISHED = (1 << 1),
TCPF_SYN_SENT = (1 << 2),
TCPF_SYN_RECV = (1 << 3),
TCPF_FIN_WAIT1 = (1 << 4),
TCPF_FIN_WAIT2 = (1 << 5),
TCPF_TIME_WAIT = (1 << 6),
TCPF_CLOSE = (1 << 7),
TCPF_CLOSE_WAIT = (1 << 8),
TCPF_LAST_ACK = (1 << 9),
TCPF_LISTEN = (1 << 10),
TCPF_CLOSING = (1 << 11)
};
#endif /* _LINUX_TCP_STATES_H */
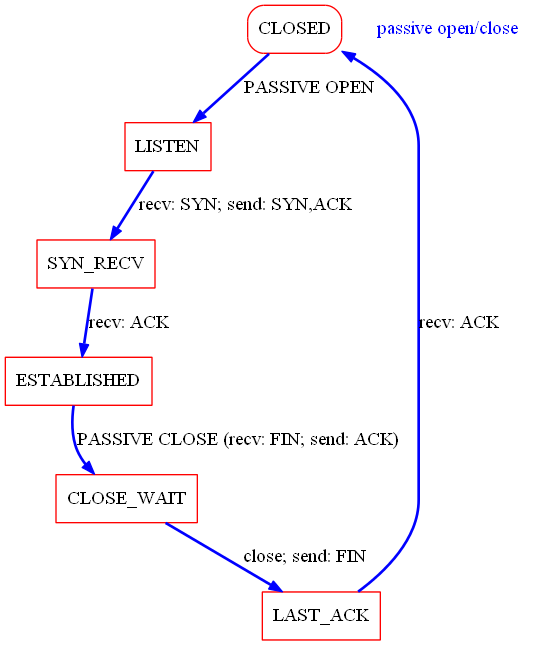
View of Server
Passive open and passive close often performed by Server, the normal routine is illustrated as follow.
I denote the passive open/close transitions with a blue line (normal transitions are in bold).
View of Client
Ative open and Active close often performed by Client, the normal routine is illustrated as follow.
I denote the active open/close transitions with a green line (normal transitions are in bold).

As a whole
We know while most TCP state transitions are normal, it also has some unnormal transitions, including:
simultaneous open
simultaneous close
RST and etc.
I use dashed line to denote this kind of transitions.

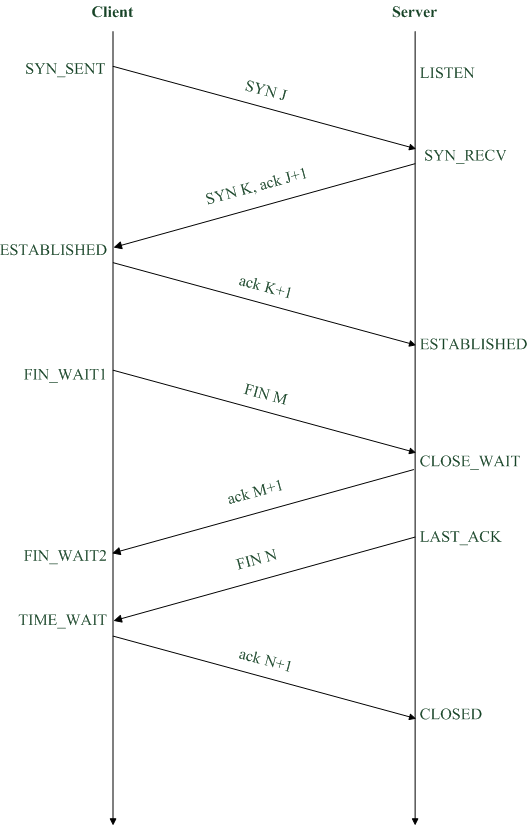
Sequence chart
(1)Normal sequence chart (including active open/close, passive open/close)
(2)simultaneous open

(3)simultaneous close

Author
zhangskd @ csdn blog




