MySQL查询——select
SELECT
select的完整语法:
select col1, col2,... # 业务查询的字段 from table_name # 选取的哪张表 [where single_conditions] # single_conditions条件表达式,个体约束(条件) [[group by column_name1] # column_name1以哪个字段名分组 [having group_conditions]] # group_conditionds条件表达式,分组约束 [order by column_name2] # column_name2以哪个字段进行排序 [limit N,M] # 执行完之后,跳过N条记录,选取M条记录
上述如果都有:执行顺序from->where->group by->having->order by->limit->select
列的结果显示
1、去掉重复的数据:distinct(针对于记录而言,不是针对于列的数据而言)
# 查看员工的职位 select title from s_emp; select distinct title from s_emp; # 每个部门下有哪些职位 select dept_id,title from s_emp; select distinct dept_id,title from s_emp;# 联合唯一
2、运算符:+、-、*、/、%(只列举一个)
# 查看员工年薪 select salary*12 from s_emp; select id,last_name,salary*12 as year_salary from s_emp; # 查看员工当前年薪以及月薪提高100美元后的年薪 select id,last_name,salary*12 old_year_salary,(salary+100)*12 as new_year_salary from s_emp;
3、列与列的数据拼接:concat(column_name1, "拼接符", column_name2[, "拼接符"])
# 查看员工基本信息(编号,全名,工资) select id,concat(first_name,' ',last_name) as name,salary from s_emp;
4、将null值转换为特定值:ifnull(column_name, 特定值)
# 查看员工工资(没有工资的显示为0) select id,last_name,ifnull(salary,0.00) as salary from s_emp;
where conditions
MySQL的运算符概念及作用:
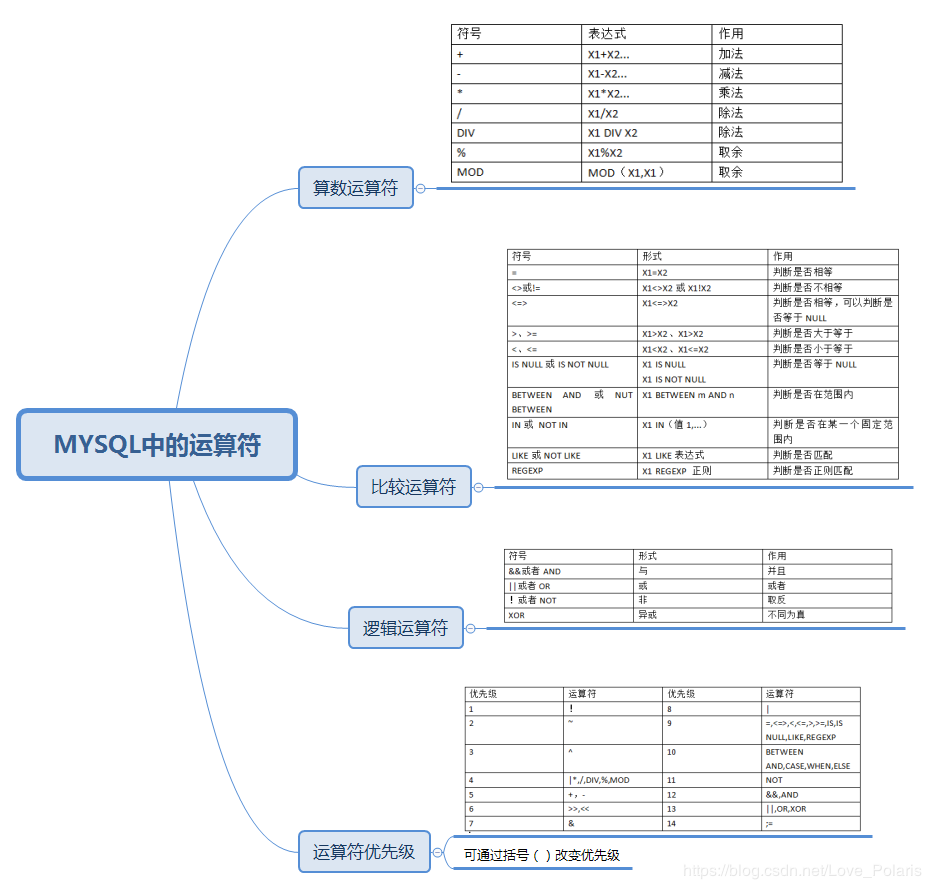
主要是根据conditions的条件查询结果集
1、比较运算符:=、<、>、>=、<=、!=、<=>(同is null)、<>(同!=)
# 查看拥有白领工资的员工有哪些(1200,2000) select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where salary>1200 and salary<2000; # 查看有工资的员工信息 select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where salary is not null; select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where salary <> null;# erro # 查看没有工资的员工的信息 select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where salary is null; select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where salary <=> null; select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where salary != 1200;# null数据未取到
2、逻辑运算符:and(&&)、or(||)、not
查看41号部门的员工信息并且工资大于1200或者43号部门工资小于2000的员工信息 select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where (dept_id=41 and salary>1200) or (dept_id=43 and salary<2000);
3、在XXX区间:between ... and ... 不在XXX区间:not between ... and ...
查看拥有白领工资的员工有哪些(1200,2000) select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where salary>1200 and salary<2000; # 下面是闭区间 select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where salary between 1199 and 2001; #[1199,2001] # 不在区间内 select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where salary not between 1200 and 2000; #(-&,1200)or(2000,+&)
4、在集合中: in () 不在集合中:not in ()
# 查看41,42,43号部门的员工有哪些 select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where dept_id=41 and dept_id=42 and dept_id=43; # 和上面的等价 select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where dept_id in(41,42,43); # 查看不是41,42,43号部门的员工有哪些 select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where dept_id!=41 and dept_id!=42 and dept_id!=43; # 和上面的等价 select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where dept_id not in(41,42,43)
6、模糊匹配:like :%:0到多个字符匹配;_:1个字符匹配;[ ]:范围内的匹配的单个字符;[^ ]:范围外的匹配的单个字符; 不模糊匹配: not
# 查看职位以VP开头的员工有哪些 select id,last_name,salary from s_emp where title like 'VP%'; select id,last_name,title from s_emp where title not like 'VP%'; # 查看员工信息,名字以C开头,并且字符数不小于5个字符 select id,last_name from s_emp where last_name like 'C____%'; #查看客户信息,客户名称中包含单引号的客户 select id,name from s_cutomer where name like "%'%";
group by column_name
涉及的组函数:计数count()、最小值min()、最大值max()、平均值avg()、总和sum()
# 查看员工总数 select count(*) as count_num from s_emp; # 默认分组(以表格为单元) select count(id) as count_num from s_emp; # 统计有工资的员工个数 select count(salary) as count_num from s_emp; # 查看每个部门的员工个数 select dept_id,count(*) as nums from s_emp group by dept_id; # 进行分组后,select的结果只能是组的概念,不允许出现个体概念(last_name) select dept_id,count(*) as nums,last_name from s_emp group by dept_id; # errro # 默认以逗号拼接 group_concat(),这个函数很重要 select dept_id,count(*) as nums,group_concat(last_name) from s_emp group by dept_id; # 查看每个部门薪资大于1200的员工总数(信息) select dept_id,count(*) nums,group_concat(last_name),group_concat(salary) from s_emp where salary > 1200 group by dept_id; # 查看部门平均薪资 select avg(salary) from s_emp group by dept_id; # 查看部门平均薪资>2000员工总数 select dept_id,count(*) nums,avg(salary) from s_emp group by dept_id having avg(salary)>2000; # 查看每个部门员工总数,部门平均薪资大于1000,并且每个员工的薪资>900 select dept_id,count(*),avg(salary) from s_emp where salary >900 group by dept_id having avg(salary)>1000
排序order by:升序ASC;逆序DESC
# 查看员工的员工ID,名字,月薪,部门ID,部门ID进行升序排序,相同部门的员工在一起按照薪资从高到低排序 select id,last_name,dept_id,salary from s_emp order by dept_id asc,salary desc; # 如果进行排序的时候,需要对字段先进行转码,后排序 select id,last_name,dept_id,salary from s_emp order by conver(dept_id asc,salary using gbk2312) desc;
限制记录数目:limit N,M 跳过N条记录,查询M条记录
# 跳过3条记录,查询5条记录,这一般用于分页比较合理 # 擦昏地当前页数和记录数 select id,last_name,dept_id,salary from s_emp order by dept_id asc,salary desc limit 3, 5 # 当数据表的记录上万条,比如超过1万条记录 # 建议使用子查询进行分页,这样效率高点,因为子查询是在索引文件(所以你文件比较小,数据文件比较大,处理上就比较慢)上执行的 select id, last_name, dept_id, salary from s_emp where id >=( select id from s_emp order by id limit 10000, 1 ) limit 10;


