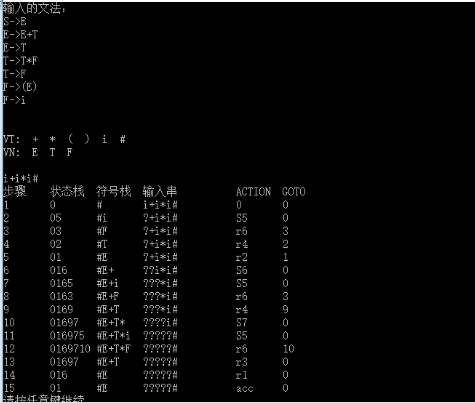
SLR(1)分析法分析过程
对下列文法,用SLR(1)分析法对任意输入的符号串进行分析:
(1)S->E
(2)E->E+T
(3)E->T
(4)T->T*F
(5)T->F
(6)F->(E)
(7)F->i
【设计思想】
(1)总控程序,也可以称为驱动程序。对所有的LR分析器总控程序都是相同的。
(2)分析表或分析函数,不同的文法分析表将不同,同一个文法采用的LR分析器不同时,分析表将不同,分析表又可以分为动作表(ACTION)和状态转换(GOTO)表两个部分,它们都可用二维数组表示。
(3)分析栈,包括文法符号栈和相应的状态栈,它们均是先进后出栈。
分析器的动作就是由栈顶状态和当前输入符号所决定。
- LR分析器由三个部分组成:
- 其中:SP为栈指针,S[i]为状态栈,X[i]为文法符号栈。状态转换表用GOTO[i,X]=j表示,规定当栈顶状态为i,遇到当前文法符号为X时应转向状态j,X为终结符或非终结符。
- ACTION[i,a]规定了栈顶状态为i时遇到输入符号a应执行。动作有四种可能:
(1)移进:
action[i,a]= Sj:状态j移入到状态栈,把a移入到文法符号栈,其中i,j表示状态号。
(2)归约:
action[i,a]=rk:当在栈顶形成句柄时,则归约为相应的非终结符A,即文法中有A- B的产生式,若B的长度为R(即|B|=R),则从状态栈和文法符号栈中自顶向下去掉R个符号,即栈指针SP减去R,并把A移入文法符号栈内,j=GOTO[i,A]移进状态栈,其中i为修改指针后的栈顶状态。
(3)接受acc:
当归约到文法符号栈中只剩文法的开始符号S时,并且输入符号串已结束即当前输入符是'#',则为分析成功。
(4)报错:
当遇到状态栈顶为某一状态下出现不该遇到的文法符号时,则报错,说明输入端不是该文法能接受的符号串。
源程序
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
#define numStates 6
#define numInputs 3
int t(char);
int go(char);
char terminals[numInputs] = { '(', ')', '$' };
string table[numStates][numInputs] =
{ // ( ) $
{ "s:2", "r:S~!", "r:S~!" },
{ "", "", "a:" },
{ "s:2", "r:S~!", "r:S~!" },
{ "", "s:4", "" },
{ "s:2", "r:S~!", "r:S~!" },
{ "", "r:S~(S)S", "r:S~(S)S" }
};
char nonterminals[1] = { 'S' };
int gotos[numStates][1] =
{
{ 1 },
{ -1 },
{ 3 },
{ -1 },
{ 5 },
{ -1 }
};
int main()
{
char k;
const int spacing = 10;
int state;
char in;
string action;
vector < pair < char, int > > stack;
stack.push_back(make_pair('$', 0));
cout << "hello, Press Return to step through parse" << endl << endl;
string input = "()()$";
cout << "Enter your input string to recognize: ";
getline(cin, input);
input += '$';
cout << setfill('=') << left << setw(2 * spacing) << "Stack"
<< setw(2 * spacing) << "Input"
<< setw(2 * spacing) << "Action" << endl << setfill(' ');
while (1)
{
// Display stack
cout << endl;
int u = 0;
for (u = 0; u<stack.size(); u++)
cout << stack[u].first << " " << stack[u].second << " ";
for (; u<7; u++)
cout << " ";
for (int u = input.size(); u<spacing; u++)
cout << " ";
// Display input
cout << setw(spacing) << input;
// Display the action code to take
cout << setw(spacing) << left << action;
state = stack.back().second;
in = input[0];
action = table[state][t(in)];
// Stepping pause
cin.get();
cout << "=> ";
// blank/error cell
if (action == "")
{
cout << "ERROR input not accepted" << endl;
return 0;
}
// Accepted cell
else if (action[0] == 'a')
{
cout << "INPUT STRING ACCEPTED" << endl;
return 0;
}
// Reduction
else if (action[0] == 'r')
{
cout << "Reducing '" << action.substr(4, action.length() - 1)
<< "' on the stack to " << action[2];
for (int i = action.length() - 1; i>3; i--)
{
if (stack.back().first == action[i])
stack.pop_back();
// Epsilons do not consume anything
else if (action[i] == '!')
continue;
else
{
cout << "Error in reduce, expected "
<< stack.back().first << endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout << " Then goto state " << gotos[stack.back().second][go(action[2])] << endl;
stack.push_back(
make_pair(
action[2],
gotos[stack.back().second][go(action[2])]));
}
// Shift
else if (action[0] == 's')
{
cout << "Shifting top of input to stack and moving to state " << action[2] << endl;
stack.push_back(
make_pair(
input[0],
action[2] - 48));
input.erase(0, 1);
}
}
return 0;
}
int t(char terminal)
{ // Linear search bad
for (int i = 0; i<numInputs; i++)
if (terminals[i] == terminal)
return i;
cout << "t(): There was an error in look finding '" << terminal << "' in the table." << endl;
return -1;
}
int go(char nterminal)
{ // Linear search bad
for (int i = 0; i<numInputs; i++)
if (nonterminals[i] == nterminal)
return i;
cout << "go(): There was an error in look finding '" << nterminal << "' in the table." << endl;
return -1;
}
结果