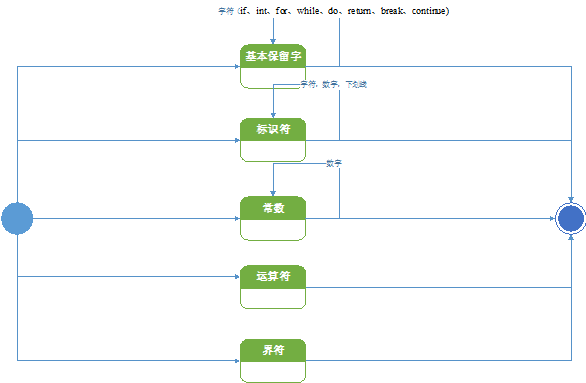
根据状态转换图手工构造词法分析程序
编制一个读单词过程,源程序为一个文件,读取该文件,识别出各个具有独立意义的单词,即基本保留字、标识符、常数、运算符、界符五大类。并依次输出各个单词的内部编码及单词符号自身值。
单词的内部编码如下:
1、保留字:if、int、for、while、do、return、break、continue;单词种别码为1;
2、标识符:除保留字外的以字母开头,后跟字母、数字的字符序列;单词种别码为2;
3、常数为无符号整形数;单词种别码为3;
4、运算符包括:+、-、*、/、=;单词种别码为4;
5、分隔符包括:,、;、{、}、(、); 单词种别码为5。
1、词法分析器的功能和输出格式
词法分析器的功能是输入源程序,输出单词符号。词法分析器的单词符号常常表示成以下的二元式(单词种别码,单词符号的属性值)。本实验中,采用的是一类符号一种种别码的方式。
2、各类单词的文法
<标识符>→<字母><字母数字串>
<字母数字串>→<字母><字母数字串>|<数字><字母数字串>|ε
<无符号整数>→<数字>|<数字><无符号整数>
<运算符>→ + | - | * | / | =
<界符>→ , | ; | ( | ) | { | }
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/* 各种变量的定义 */
string keywords[36] = { "char", "short", "int", "unsigned", "long", "float", "double",
"struct", "union", "void", "enum", "const", "typedef", "auto",
"static", "break", "case", "continue", "default", "do", "else",
"for", "if", "return", "switch", "while", "sizeof", "printf",
"FILE", "fopen", "NULL", "fclose", "exit", "read", "close",
"fprintf" };
char delimiters[] = { '[', ']', '(', ')', '{', '}', '\'', '\"', ',', ';', ':' };
char operators[5] = { '+', '-', '*', '/', '=' };
ifstream infile; /* 输入文件 */
ofstream outfile; /* 输出文件 */
char buffer1[64]; /* 缓冲数组 1*/
char buffer2[64]; /* 缓冲数组 2*/
char *pointer; /* 扫描指针 */
/* 各种函数的声明 */
bool isChar(char c);/* 是否是字母 */
bool isDigit(char c);/* 是否是 0-9*/
bool isUnderline(char c);/* 是否是下划线 */
bool isEnter(char c);/* 是否是换行 */
bool isDelimiter(char c);/* 是否是界符 */
bool isOperator(char c);/* 是否是运算符 */
int getLength(char *s);/* 求一个字符串的长度 */
bool isIdentifier(char *s);/* 是否是标识符 */
bool isNumber(char *s);/* 是否为数字 */
bool isKeyword(string s);/* 是否是关键字 */
char getChar();/* 实现双缓冲扫描文件 */
void write(string str1, string str2);/* 写入文件,并且在屏幕上打印 */
/* 程序入口: main 函数 */
int main()
{
char cc = '\0';
string str = "";
pointer = buffer1;
buffer1[63] = buffer2[63] = -1; // 数组尾数值为 -1
infile.open("in.txt", ios::binary);// 二进制文件 outfile.open ("out.txt",ios::trunc);// 再次写入覆盖文件已有内容
for (int i = 0; i <= 62; i++)
buffer1[i] = infile.get();// 将文件中字符放入第一缓冲区
for (;;)
{
str = "";
cc = getChar();
str += cc;
AAA: if (isDelimiter(cc))/* 是否是界符 */
{
write(" 分隔符 ", str);
}
else if (isOperator(cc))/* 是否是操作符 */
{
write(" 运算符 ", str);
}
else if (isEnter(cc))/* 是否是换行符 */
{
write(" 换行 ", "\\n");
}
else if (isUnderline(cc) || isChar(cc))/* 是否是标识符 */
{
for (;;)
{
cc = getChar();
if (!(isChar(cc) || isDigit(cc) || isUnderline(cc)))
{
if (isKeyword(str))
{
write(" 保留字 ", str);
}
else{
write(" 标识符 ", str);
}
str = cc;
goto AAA;
}
str += cc;
}
}
else if (isDigit(cc))/* 是否是数字 */
{
for (;;)
{
cc = getChar();
if (!(isDigit(cc)) && cc != '.')
{
write(" 常数 ", str);
str = cc;
goto AAA;
}
str += cc;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* 双缓冲扫描文件 */
char getChar()
{
if (*pointer == -1) /* 当前指针在缓冲区(不知是那个缓冲区)末尾 */
{
if (pointer == buffer1 + 63)/* 在第一 buffer 尾,向第二 buffer 读入数据 */
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 62; i++)
{
buffer2[i] = infile.get();
}
pointer = buffer2;
return getChar();
}
else if (pointer == buffer2 + 63)/* 在第二 buffer 尾,向第一 buffer 读入数据 */
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 62; i++)
{
buffer1[i] = infile.get();
}
pointer = buffer1;
return getChar();
}
else/* 在不是 buffer 尾的位置读到了 EOF, 说明完成了分析 */
{
infile.close();
outfile.close();
ofstream out;
cout << "\n\n\t 词法分析完毕! " << endl;
system("pause");
exit(-1);
}
}
return *pointer++;
}
/* 是否是字母 */
bool isChar(char c)
{
if ((c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') || (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z'))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/* 是否是 0-9*/
bool isDigit(char c)
{
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/* 是否是下划线 */
bool isUnderline(char c)
{
if (c == '_')
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/* 是否是换行 */
bool isEnter(char c)
{
if (c == '\n')
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/* 是否是界符 */
bool isDelimiter(char c)
{
for (int i = 0; i<10; i++)
{
if (c == delimiters[i])
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/* 是否是运算符 */
bool isOperator(char c)
{
for (int i = 0; i<5; i++)
{
if (c == operators[i])
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/* 求一个字符串的长度 */
int getLength(char *s)
{
int len = 0;
for (int i = 0;; i++)
{
if (s[i] != '\0')
{
len++;
}
else
{
return len;
}
}
}
/* 是否是标识符 */
bool isIdentifier(char *s)
{
int len = getLength(s);
if (isChar(s[0]) || isUnderline(s[0]))
{
for (int i = 1; i<len; i++)
{
if (!(isDigit(s[i]) || isDigit(s[i]) || isUnderline(s[i])))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/* 是否为数字 */
bool isNumber(char *s)
{
int len = getLength(s);
if (s[0] >= 1 && s[0] <= 9)
{
for (int i = 0; i<len; i++)
{
if (!isDigit(s[i]) && s[i] != '.')
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/* 是否是关键字 */
bool isKeyword(string s)
{
for (int i = 0; i<keywords->length(); i++)
{
if (s == keywords[i])
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/* 写入文件,并且在屏幕上打印 */
void write(string str1, string str2)
{
cout << str1 << " :" << str2 << endl;
outfile << "[ <" << str1 << "> : \"" << str2 << "\" ]" << endl;
}
- 实验结果

-
个人体会
这个实验让我认识到了词法扫描器的构建过程,以及如何用C++实现。

