捕获摄像头进行直方图均衡化
图像增强
- 图像增强目的是提高图像在特定应用领域的视觉质量
- 图象增强包括光滑、锐化、提取边缘、反转、去噪以及各种滤波等等处理。
- 目的是经过处理后的图像更适合特定的应用(主要是主观的观察分析)
- 没有通用的理论和方法,主观评价为主
图像增强分为两大类:
- 空间域图像增强:“空间域”指图像的平面本身。
- 频率域图像增强:在Fourier变换的基础上处理。
一幅图像被压缩为直方图后,空间信息丢失了
-
性质1:一个特定的图像有唯一的直方图,但反之不成立。
-
性质2:在图象中特定对象的直方图是平移不变的。
-
性质3:在图象中特定对象的直方图是旋转不变的。
-
性质4: 图像的面积 $ = \displaystyle\int_0^\infty H(D)$
-
性质5:对离散图像,\(\sum_{D=0}^{255} H(D) = NL * NS\)
其中NL和NS分别为图像的行和列。
-
性质6:如果一图像由两个不连接的区域组成,则整幅图像的直方图是两个区域的直方图之和。
直方图的用途
- 图像的基本处理工具:光照均衡化,特征表达。
- 检查图像使用灰度级范围的合理性。【0-255】
- 图象二值化边界阈值选择。
数字图像下的直方图均衡化步骤
- 概率:
\(p_r(r_k)\frac{n_k}{n},k=0,1,2,.....,L-1\)
- 累积分布函数︰
\(P(r_k) = \sum{_{j=0}^k}p_r(r_j) = \sum{_{j=0}^k} \frac{n_k}{n} ,k=0,1,2,.....,L-1\)
- 灰度级映射计数变换函数:
\(s_k = T(r_k) = (L-1)*\sum{_{j=0}^k}p_r(r_j) = \sum{_{j=0}^k} \frac{n_k}{n} ,k=0,1,2,.....,L-1\)
- 将\(s_k\),四舍五入,如果有相同的\([s_k]\),则合并。
from os import cpu_count
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import sys
import math as m
sys.path.append('./')
class HistogramEqualization:
def __init__(self):
pass
def rgb2hsi(self, img_src):
# 对于图像不足3通道的,直接返回原图像
if len(img_src.shape) < 3:
return img_src
img = img_src.astype(np.float32)/255 # 归一化处理
img_r = img[:, :, 0] # 获取红色通道图像
img_g = img[:, :, 1] # 获取绿色通道图像
img_b = img[:, :, 2] # 获取蓝色通道图像
# 执行转换方程
sum_rgb = img_r + img_g + img_b # 求各通道像素值之和
np.where(sum_rgb > 0, sum_rgb, sys.float_info.min)
# 计算S分量
S = 1 - (3 * np.minimum(np.minimum(img_r, img_g), img_b)) / sum_rgb
# 计算H分量
den = ((0.5 * (img_r + img_r - img_g - img_b)) / (np.sqrt((img_r - img_g) * (img_r - img_g) + (img_r - img_b) * (img_g - img_b)) + sys.float_info.min))
# 防止求arccos时参数超出区间[-1, 1]
den[den > 1] = 1
den[den < -1] = -1
H = np.arccos(den)
index = np.where(img_b > img_g) # 找出B>G的坐标值
H[index] = 2 * m.pi - H[index]
H /= 2 * m.pi
H[S == 0] = 0
# 计算I分量
I = sum_rgb / 3
# 拼接三个颜色通道并返回
hsi = np.zeros(img.shape, dtype=np.float32)
hsi[:, :, 0] = H
hsi[:, :, 1] = S
hsi[:, :, 2] = I
return hsi
# HSI色彩空间转换为RGB色彩空间
def hsi2rgb(self, hsi):
# 对于图像不足3通道的,直接返回原图像
if len(hsi.shape) < 3:
return hsi
H = hsi[:, :, 0] # 提取H分量
S = hsi[:, :, 1] # 提取S分量
I = hsi[:, :, 2] # 提取I分量
R = np.zeros(H.shape, dtype=np.float32) # 创建红色通道
G = np.zeros(H.shape, dtype=np.float32) # 创建绿色通道
B = np.zeros(H.shape, dtype=np.float32) # 创建蓝色通道
H *= 2 * m.pi # 扩充弧度范围[0, 2*pi]
# 色调[0, 2*pi/3)范围内对应红->绿
boolh = np.where((H >= 0) & (H < 2 * m.pi / 3)) # 找出符合条件的二维图像数组下标
# 计算红色通道
R[boolh] = I[boolh] * (1 + (S[boolh] * np.cos(H[boolh])) / (np.cos(m.pi / 3 - H[boolh]) + sys.float_info.min))
# 计算蓝色通道
B[boolh] = I[boolh] * (1 - S[boolh])
# 计算绿色通道
G[boolh] = I[boolh] * 3 - (B[boolh] + R[boolh])
# 色调[2*pi/3, 4*pi/3)范围内对应绿->蓝
boolh = np.where((H >= 2 * m.pi / 3) & (H < 4 * m.pi / 3)) # 找出符合条件的二维图像数组下标
H[boolh] -= 2 * m.pi / 3
# 计算红色通道
R[boolh] = I[boolh] * (1 - S[boolh])
# 计算绿色通道
G[boolh] = I[boolh] * (1 + (S[boolh] * np.cos(H[boolh])) / (np.cos(m.pi / 3 - H[boolh])))
# 计算蓝色通道
B[boolh] = I[boolh] * 3 - (R[boolh] + G[boolh])
# 色调[4*pi/3, 2*pi]范围内对应蓝->红
boolh = np.where((H >= 4 * m.pi / 3) & (H < 2 * m.pi)) # 找出符合条件的二维图像数组下标
H[boolh] -= 4 * m.pi / 3
# 计算绿色通道
G[boolh] = I[boolh] * (1 - S[boolh])
# 计算蓝色通道
B[boolh] = I[boolh] * (1 + (S[boolh] * np.cos(H[boolh])) / (np.cos(m.pi / 3 - H[boolh])))
# 计算绿色通道
R[boolh] = I[boolh] * 3 - (B[boolh] + G[boolh])
# 拼接图像
rgb = np.zeros(hsi.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
rgb[:, :, 0] = (R * 255).astype(np.uint8)
rgb[:, :, 1] = (G * 255).astype(np.uint8)
rgb[:, :, 2] = (B * 255).astype(np.uint8)
return rgb
# 遍历每个像素点,把img里面的像素值转换成initImg的下标索引(0-256),并统计img相同像素点的个数
def toHisgram(self,img,initImg):
for i in range(img.shape[0]):
for j in range(img.shape[1]):
initImg[img[i,j]] +=1
return initImg
# 进行直方图均衡化,并返回最终图像
def toHist(self,img):
init_img =np.zeros(256,np.int32)
#直方图统计,获得概率
# hist = self.toHisgram(img,init_img)
hist,den= np.histogram(img,256,[0,255])
hist = hist/np.sum(hist) #统计的像素点(0-256)个数除以总数
cdf = np.zeros(256, dtype=np.float32)
#累计分布函数
np.cumsum(hist[0 : 256], dtype=np.float32, out=cdf[0 : 256])
#变换函数
t =np.zeros(256,np.uint8)
t[0 : 256] = 255 * cdf[0 : 256]
#合并
dstImg = np.zeros(img.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
dstImg[:,:] = t[img[:,:]]
return dstImg
#将RGB转换成HSI色彩空间域,返回HSI图像
def rgbToHsi(self,img):
r = img[:,:,0]
g = img[:,:,1]
b = img[:,:,2]
r = r.astype(np.float32)
g = g.astype(np.float32)
b = b.astype(np.float32)
I = (r+g+b)/3
I = I/255
img_min = np.min(img,axis=-1)
S = 1 - (3/(r+g+b)*img_min)
a = 0.5*((r-g)+(r-b))
botton = ((r-g)**2+((r-b)*(g-b))+ sys.float_info.min)**0.5
den =a /botton
den[den>1]=1
den[den<-1]=-1
H = np.arccos(den)
index = np.where(g<b)
H[index]= 2*m.pi-H[index]
H /= 2 * m.pi
H[S == 0] = 0
hsi = np.zeros([img.shape[0],img.shape[1],img.shape[2]],dtype=np.float32)
hsi[:,:,0] = H
hsi[:,:,1] = S
hsi[:,:,2] = I
return hsi
# 将HSI转换成RGB色彩空间域 ,返回RGB图像
def hsiToRgb(self,hsi):
H = hsi[:,:,0]
S = hsi[:,:,1]
I = hsi[:,:,2]
H *=2*m.pi
rgb = np.zeros(hsi.shape,np.uint8)
R = np.zeros(H.shape, dtype=np.float32)
G = np.zeros(H.shape, dtype=np.float32)
B = np.zeros(H.shape, dtype=np.float32)
index = np.where((H>=0)&(H<2*m.pi/3))
R[index] = I[index] * (1+(S[index]*np.cos(H[index]))/(np.cos(m.pi/3-H[index])))
B[index] = I[index]*(1-S[index])
G[index] = 3*I[index]-(B[index]+R[index])
index = np.where((H>=2*m.pi/3)&(H<4*m.pi/3))
R[index] = I[index]*(1-S[index])
G[index] = I[index] * (1+(S[index]*np.cos(H[index]-2*m.pi/3))/(np.cos(m.pi-H[index])))
B[index] = 3*I[index]-(R[index]+G[index])
index = np.where((H>=4*m.pi/3)&(H<2*m.pi))
B[index] = I[index] * (1+(S[index]*np.cos(H[index]-4*m.pi/3))/(np.cos(5*m.pi/3-H[index])))
G[index] = I[index]*(1-S[index])
R[index] = 3*I[index]-(G[index]+B[index])
rgb[:,:,0] = (255*R).astype(np.uint8)
rgb[:,:,1] = (255*G).astype(np.uint8)
rgb[:,:,2] = (255*B).astype(np.uint8)
return rgb
# 计算熵,首先统计img像素点的个数,计算每个像素点在img的分布概率,遍历计算p[i]*m.log2(p[i]),乘以-1返回熵
def solveEntropy(self,img):
n = img.shape[0] * img.shape[1]
hist,den= np.histogram(img,256,[0,255])
p = hist / n
entropy = 0
for i in range(0,256):
if (p[i]==0):
continue
entropy += p[i]*m.log2(p[i])
return -1 * entropy
#计算图像亮度、对比度、熵值
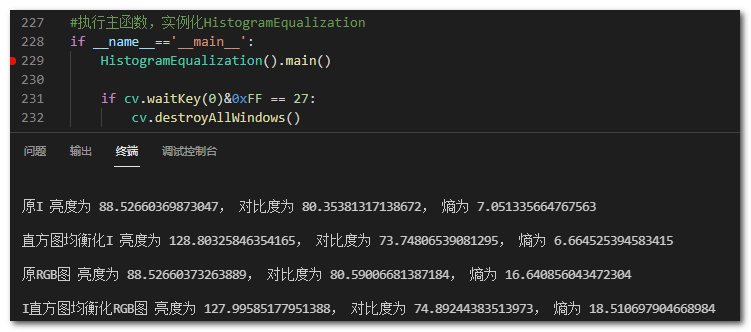
def compareResult(self,img,typeName):
light = np.mean(img)
contrast = np.std(img)
entropy = self.solveEntropy(img)
print(f"{typeName} 亮度为 {np.mean(img)}, 对比度为 {np.std(img)}, 熵为 {self.solveEntropy(img)}\n")
# 主函数 启动摄像头 处理每一帧的图像
def main(self):
cap = cv.VideoCapture(0)
while cap.isOpened():
ret,frame = cap.read()
hsi = self.rgb2hsi(frame)
# 直方图处理HSI亮度I
I = hsi[:,:,2]
I *= 255
self.compareResult(I,"原I")
I = I.astype(np.uint8)
I = self.toHist(I)
self.compareResult(I,"直方图均衡化I")
hsi[:,:,2] = I/255
rgb = self.hsiToRgb(hsi)
self.compareResult(frame,"原RGB图")
self.compareResult(rgb,"I直方图均衡化RGB图")
cv.imshow("Orgin RGB",frame)
cv.imshow("ToHist RGB",rgb)
if cv.waitKey(1)&0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
#执行主函数,实例化HistogramEqualization
if __name__=='__main__':
HistogramEqualization().main()
if cv.waitKey(0)&0xFF == 27:
cv.destroyAllWindows()


 在熟悉直方图均衡化的数学原理以及数字图像下直方图均衡化步骤基础上,利用Python语言编写图像直方图均衡化算法。先驱动USB摄像头,获取RGB彩色图像,然后用色彩空间转换函数,提取亮度通道进行直方图均衡化处理后,再转换为RGB色彩空间
在熟悉直方图均衡化的数学原理以及数字图像下直方图均衡化步骤基础上,利用Python语言编写图像直方图均衡化算法。先驱动USB摄像头,获取RGB彩色图像,然后用色彩空间转换函数,提取亮度通道进行直方图均衡化处理后,再转换为RGB色彩空间
