遍历树,找出所有叶子路径
一、示例:
树的结构:
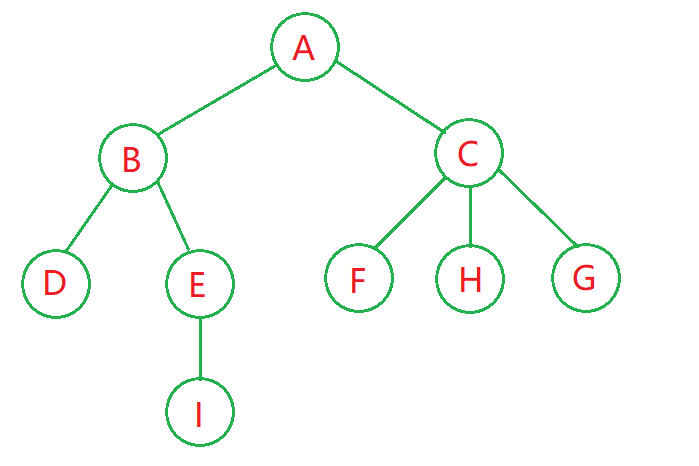
示例中自己构建了图片中的这棵树:
树节点模型:
public class TreeNode { String value; List<TreeNode> children; public TreeNode() { children = new ArrayList<>(); } public TreeNode(String value) { this.value = value; children = new ArrayList<>(); } @Override public String toString() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return value; } }
构建树:
// 创建一棵树 TreeNode root = new TreeNode("A"); // 第二层 root.children.add(new TreeNode("B")); root.children.add(new TreeNode("C")); // 第三层 root.children.get(0).children.add(new TreeNode("D")); root.children.get(0).children.add(new TreeNode("E")); root.children.get(1).children.add(new TreeNode("F")); root.children.get(1).children.add(new TreeNode("H")); root.children.get(1).children.add(new TreeNode("G")); // 第四层 root.children.get(0).children.get(1).children.add(new TreeNode("I"));
二、遍历方式
提供三种方式进行遍历:
① 递归形式的深度优先遍历:
/** * 深度优先遍历(递归方式) --- 树(Tree) */ public void recurTree(TreeNode root) { List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> path = new ArrayList<>(); path.add(root.value); findPath(result, root, path); System.out.println(result); } private void findPath(List<List<String>> result, TreeNode node, List<String> path) { if (node.children == null || node.children.size() <= 0) { result.add(path); return; } for (int i = 0; i < node.children.size(); i++) { TreeNode child = node.children.get(i); List<String> cPath = new ArrayList<>(); cPath.addAll(path); cPath.add(child.value); findPath(result, child, cPath, target); } }
② 非递归的深度优先遍历
/** * 深度优先遍历(非递归方式) ----- 查找树的所有叶子路径 * * @param root * 根节点 * @return 叶子路径的集合 */ public List<List<TreeNode>> dfsTree(TreeNode root) { Stack<TreeNode> nodeStack = new Stack<>(); Stack<List<TreeNode>> pathStack = new Stack<>(); List<List<TreeNode>> result = new ArrayList<>(); nodeStack.push(root); ArrayList<TreeNode> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); arrayList.add(root); pathStack.push(arrayList); while (!nodeStack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode curNode = nodeStack.pop(); List<TreeNode> curPath = pathStack.pop(); if (curNode.children == null || curNode.children.size() <= 0) { result.add(curPath); } else { int childSize = curNode.children.size(); for (int i = childSize - 1; i >= 0; i--) { TreeNode node = curNode.children.get(i); nodeStack.push(node); List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<>(curPath); list.add(node); pathStack.push(list); } } } return result; }
3. 广度优先遍历,遍历所有叶子路径
/** * 广度优先遍历 ---- 查找树的所有叶子路径 * * @param root * 根节点 * @return 叶子路径的集合 */ public List<List<TreeNode>> bfsTree(TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<>(); Queue<List<TreeNode>> qstr = new LinkedList<>(); List<List<TreeNode>> result = new ArrayList<>(); nodeQueue.add(root); ArrayList<TreeNode> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); qstr.add(arrayList); while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode curNode = nodeQueue.remove(); List<TreeNode> curList = qstr.remove(); if (curNode.children == null || curNode.children.size() <= 0) { curList.add(curNode); result.add(curList); } else { for (int i = 0; i < curNode.children.size(); i++) { TreeNode treeNode = curNode.children.get(i); nodeQueue.add(treeNode); List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<>(curList); list.add(curNode); qstr.add(list); } } } return result; }
三种方式的输出:
深度优先遍历(递归):[[A, B, D], [A, B, E, I], [A, C, F], [A, C, H], [A, C, G]]
广度优先遍历:[[A, B, D], [A, C, F], [A, C, H], [A, C, G], [A, B, E, I]]
深度优先遍历(非递归):[[A, B, D], [A, B, E, I], [A, C, F], [A, C, H], [A, C, G]]
三、总结
示例是查找树的所有叶子节点,举一反三,如果我们是查找树中满足某个条件的路径,也是非常容易了。比如下面中查找 “ E ” 的分支:
public void recurTree(TreeNode root) { List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> path = new ArrayList<>(); path.add(root.value); findPath(result, root, path, "E"); System.out.println(result); } private void findPath(List<List<String>> result, TreeNode node, List<String> path, String target) { if (target.equals(node.value)) { result.add(path); return; } if (node.children == null || node.children.size() <= 0) { return; } for (int i = 0; i < node.children.size(); i++) { TreeNode child = node.children.get(i); List<String> cPath = new ArrayList<>(); cPath.addAll(path); cPath.add(child.value); if (result.size() > 0) break; findPath(result, child, cPath, target); } }
输出:
[[A, B, E]]





