图->有向无环图->拓扑排序
文字描述
关于有向无环图的基础定义:
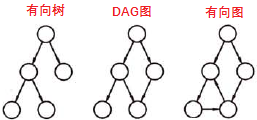
一个无环的有向图称为有向无环图,简称DAG图(directed acycline graph)。DAG图是一类较有向树更一般的特殊有向图。
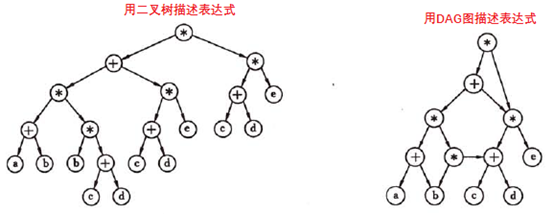
举个例子说明有向无环图的应用。假如有一个表达式: ((a+b)*(b*(c+d))+(c+d)*e)*((c+d)*e), 可以用之前讨论的二叉树来表示,也可以用有向无环图来表示,如下图。显然有向无环图实现了对相同子式的共享,从而比二叉树更节省空间。
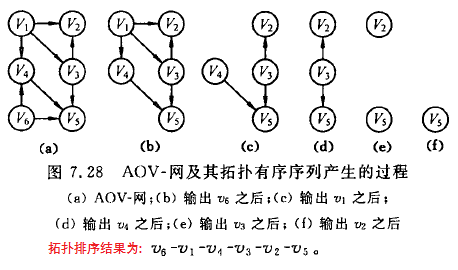
关于拓扑排序的基础定义:
由某个集合上的一个偏序得到该集合上的一个全须,这个操作称之为拓扑排序。理解起来可能有点费解,但是通俗的讲,就是如下几个操作步骤:
1 在有向图中选一个没有前驱的顶点且输出之
2 从图中删除该顶点和所有以它为尾的弧。
重复上述两步,直至全部顶点均已输出,或者当前图中不存在无前驱的顶点为止。后一种情况说明有向图中存在环。
备注:AOV-网(Activity On Vertex Network)的意思是用顶点表示活动,用弧表示活动间的优先关系的有向图称为顶点表示活动的网。
示意图:

算法分析
对n个顶点和e条弧的有向图而言,建立求各顶点的入度的时间复杂度为O(e);建零入度顶点栈的时间复杂度为O(n);在拓扑排序过程中,若有向图无环,则每个顶点进一次栈,出一次栈,入度减1的操作在while语句中总共进行e次,所以总的时间复杂度为O(n+e)。
代码实现

1 // 2 // Created by lady on 18-12-28. 3 // 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 #include <stdlib.h> 6 #define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20 //最大顶点数 7 typedef enum {DG,DN, UDG, UDN} GraphKind; //{有向图,有向网,无向图,无向网} 8 typedef struct ArcNode{ 9 int adjvex; //该弧所指向的顶点的位置 10 struct ArcNode *nextarc; //指向下一条弧的指针 11 char info; //该弧相关信息的指针 12 }ArcNode; 13 typedef struct VNode{ 14 char data[10];//顶点信息 15 ArcNode *firstarcIN;//第一条以该顶点为弧头的弧结点,其他顶点->该结点 16 ArcNode *firstarcOUT;//第一条以该顶点为弧尾的弧结点,该结点->其他顶点 17 }VNode, AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; 18 typedef struct{ 19 AdjList vertices; 20 int vexnum;//图的顶点数 21 int arcnum;//图的弧数 22 int kind; //图的种类标志 23 }ALGraph; 24 25 //根据顶点信息,返回该顶点在图中的位置坐标。 26 int LocateVex(ALGraph *G, char data[]) 27 { 28 int i = 0; 29 for(i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++){ 30 if(!strncmp(G->vertices[i].data, data, strlen(G->vertices[i].data))){ 31 return i; 32 } 33 } 34 return -1; 35 } 36 37 //利用头插法,在弧结点链表头部,插入位置v的弧结点 38 int InsFirst(ArcNode *L, int v) 39 { 40 if((L==NULL) || (v<0)){ 41 return -1; 42 } 43 ArcNode *n = (ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ArcNode)); 44 n->adjvex = v; 45 n->nextarc = L->nextarc; 46 L->nextarc = n; 47 return 0; 48 } 49 50 //采用邻接表存储方法,创建有向图 51 int CreateDG(ALGraph *G) 52 { 53 printf("开始创建一个有向图,请输入顶点数,弧数:"); 54 int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; 55 char v1[10] = {0}, v2[10]={0}; 56 char tmp[20] = {0}; 57 G->kind = DG; 58 scanf("%d,%d", &G->vexnum, &G->arcnum); 59 for(i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++){ 60 printf("输入第%d个顶点: ", i+1); 61 memset(G->vertices[i].data, 0, sizeof(G->vertices[i].data)); 62 scanf("%s", G->vertices[i].data); 63 G->vertices[i].firstarcOUT = (struct ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ArcNode)); 64 G->vertices[i].firstarcOUT->adjvex = -1; 65 G->vertices[i].firstarcOUT->nextarc = NULL; 66 G->vertices[i].firstarcIN = (struct ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ArcNode)); 67 G->vertices[i].firstarcIN->adjvex = -1; 68 G->vertices[i].firstarcIN->nextarc = NULL; 69 } 70 for(k=0; k<G->arcnum; k++) 71 { 72 printf("输入第%d条弧(顶点1, 顶点2): ", k+1); 73 memset(tmp, 0, sizeof(tmp)); 74 scanf("%s", tmp); 75 sscanf(tmp, "%[^','],%s[^\\n]", v1, v2); 76 i = LocateVex(G, v1); 77 j = LocateVex(G, v2); 78 if(i<0 || j<0){ 79 printf("<%s,%s> is a invalid arch!\n", v1, v2); 80 return -1; 81 } 82 InsFirst(G->vertices[i].firstarcOUT, j); 83 InsFirst(G->vertices[j].firstarcIN, i); 84 } 85 return 0; 86 } 87 88 void printG(ALGraph *G) 89 { 90 printf("\n"); 91 if(G->kind == DG){ 92 printf("类型:有向图;顶点数 %d, 弧数 %d\n", G->vexnum, G->arcnum); 93 }else if(G->kind == DN){ 94 printf("类型:有向网;顶点数 %d, 弧数 %d\n", G->vexnum, G->arcnum); 95 }else if(G->kind == UDG){ 96 printf("类型:无向图;顶点数 %d, 弧数 %d\n", G->vexnum, G->arcnum); 97 }else if(G->kind == UDN){ 98 printf("类型:无向网;顶点数 %d, 弧数 %d\n", G->vexnum, G->arcnum); 99 } 100 int i = 0; 101 ArcNode *p = NULL; 102 printf("邻接表:\n"); 103 for(i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++){ 104 printf("(%d,%s)\t", i,G->vertices[i].data); 105 p = G->vertices[i].firstarcOUT; 106 while(p){ 107 if(p->adjvex >= 0) 108 printf("(%d,%s)\t", p->adjvex, G->vertices[p->adjvex].data); 109 p = p->nextarc; 110 } 111 printf("\n"); 112 } 113 printf("逆邻接表:\n"); 114 for(i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++){ 115 printf("(%d,%s)\t", i,G->vertices[i].data); 116 p = G->vertices[i].firstarcIN; 117 while(p){ 118 if(p->adjvex >= 0) 119 printf("(%d,%s)\t", p->adjvex, G->vertices[p->adjvex].data); 120 p = p->nextarc; 121 } 122 printf("\n"); 123 } 124 return; 125 } 126 127 #define STACK_INIT_SIZE 20 //栈的初始分配量大小 128 #define STACK_INCREMENT 5 //栈容量不足时需新增的容量大小 129 typedef struct { 130 int *base; //指向栈底指针 131 int *top; //指向栈顶指针 132 int stacksize; //栈的当前容量大小 133 }SqStack; 134 135 int InitStack(SqStack *s); //初始化一个栈 136 int StackEmpty(SqStack *s); //判断栈是否为空 137 int Push(SqStack *S, int *e); //入栈函数 138 int Pop(SqStack *S, int *e); //出栈函数 139 140 //算法各个顶点的入度,并将结果存放在indegree数组中 141 int FindInDegree(ALGraph *G, int indegree[]) 142 { 143 printf("\n对各个顶点求入度...\n"); 144 int i = 0; 145 ArcNode *p = NULL; 146 for(i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++) { 147 p = G->vertices[i].firstarcIN; 148 while (p) { 149 if (p->adjvex >= 0) { 150 indegree[i] += 1; 151 } 152 p = p->nextarc; 153 } 154 } 155 for(i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++){ 156 printf("(%d,%s)的入度为%d\n", i, G->vertices[i].data, indegree[i]); 157 } 158 return 0; 159 } 160 161 //进行拓扑排序 162 int ToplogicalSort(ALGraph *G) 163 { 164 int i = 0; 165 int k = 0; 166 int count = 0; 167 int indegree[MAX_VERTEX_NUM] = {0}; 168 ArcNode *p = NULL; 169 SqStack S; 170 //求各个顶点的入度 171 FindInDegree(G, indegree); 172 if(InitStack(&S) <0){ 173 return -1; 174 } 175 //将入度为0的顶点入栈. 176 for(i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++){ 177 if(!indegree[i]) { 178 Push(&S, &i); 179 } 180 } 181 printf("\n进行拓扑排序:"); 182 while(StackEmpty(&S)){ 183 //如果栈不为空 184 Pop(&S, &i); 185 //输入i号顶点并计数 186 printf("(%d,%s)\t", i, G->vertices[i].data); 187 ++count; 188 for(p=G->vertices[i].firstarcOUT; p; p=p->nextarc){ 189 //对i号顶点的每个邻接点的入度减1 190 k = p->adjvex; 191 if(!(--indegree[k])) { 192 //若入度减为0,则入栈 193 Push(&S, &k); 194 } 195 } 196 } 197 printf("\n"); 198 if(count < G->vexnum){ 199 printf("警告:该图有环路!!\n"); 200 return -1; 201 }else{ 202 return 0; 203 } 204 } 205 206 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 207 { 208 ALGraph G; 209 //创建有向图 210 if(CreateDG(&G)<0){ 211 printf("创建有向图时出错!\n"); 212 return -1; 213 } 214 //打印图 215 printG(&G); 216 //进行拓扑排序 217 ToplogicalSort(&G); 218 return 0; 219 } 220 221 222 int InitStack(SqStack *S){ 223 S->base = (int *) malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE * sizeof(int)); 224 if(!S->base){ 225 return -1; 226 } 227 S->top = S->base; 228 S->stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE; 229 return 0; 230 } 231 232 int StackEmpty(SqStack *s){ 233 if(s->base == s->top){ 234 return 0; 235 }else{ 236 return -1; 237 } 238 } 239 240 int Push(SqStack *s, int *e){ 241 if((s->top-s->base) >= s->stacksize){ 242 s->base = (int*)realloc(s->base, (s->stacksize+STACK_INCREMENT)*(sizeof(int))); 243 if(!s->base){ 244 return -1; 245 } 246 s->top = s->base + s->stacksize; 247 s->stacksize += STACK_INCREMENT; 248 } 249 if(e == NULL){ 250 return -1; 251 }else{ 252 *s->top = *e; 253 } 254 s->top += 1; 255 return 0; 256 } 257 258 int Pop(SqStack *s, int *e) 259 { 260 if(s->top == s->base) { 261 return -1; 262 }else{ 263 s->top -=1; 264 *e = *s->top; 265 return 0; 266 } 267 }
代码运行
/home/lady/CLionProjects/untitled/cmake-build-debug/untitled 开始创建一个有向图,请输入顶点数,弧数:6,8 输入第1个顶点: V1 输入第2个顶点: V2 输入第3个顶点: V3 输入第4个顶点: V4 输入第5个顶点: V5 输入第6个顶点: V6 输入第1条弧(顶点1, 顶点2): V1,V2 输入第2条弧(顶点1, 顶点2): V1,V3 输入第3条弧(顶点1, 顶点2): V1,V4 输入第4条弧(顶点1, 顶点2): V3,V2 输入第5条弧(顶点1, 顶点2): V3,V5 输入第6条弧(顶点1, 顶点2): V4,V5 输入第7条弧(顶点1, 顶点2): V6,V4 输入第8条弧(顶点1, 顶点2): V6,V5 类型:有向图;顶点数 6, 弧数 8 邻接表: (0,V1) (3,V4) (2,V3) (1,V2) (1,V2) (2,V3) (4,V5) (1,V2) (3,V4) (4,V5) (4,V5) (5,V6) (4,V5) (3,V4) 逆邻接表: (0,V1) (1,V2) (2,V3) (0,V1) (2,V3) (0,V1) (3,V4) (5,V6) (0,V1) (4,V5) (5,V6) (3,V4) (2,V3) (5,V6) 对各个顶点求入度... (0,V1)的入度为0 (1,V2)的入度为2 (2,V3)的入度为1 (3,V4)的入度为2 (4,V5)的入度为3 (5,V6)的入度为0 进行拓扑排序:(5,V6) (0,V1) (2,V3) (1,V2) (3,V4) (4,V5) Process finished with exit code 0
posted on 2018-12-29 12:09 LiveWithACat 阅读(1167) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号