对g2o图优化的理解与c++实践
g2o
g2o是General(Hyper)Graph Optimization [1] 的缩写,是一个C ++框架(g2o在github的代码,注意有Python库和.Net库的g2o)。它把优化问题变成一个图。节点是要优化的变量,边是误差。它将许多典型的顶点和边缘实现为可以直接调用和使用的类,例如VertexSE3Expmap在SE3空间中表示机器人姿势,VertexSBAPointXYZ以表示3-D点,EdgeProjectXYZ2UV以表示相机图像平面中的3D点的观察。此外,实现了典型的优化求解器算法。使用g2o库,SLAM研究人员需要做的是定义问题中的节点和边缘,将它们添加到g2o提供的求解器中,它将执行所有优化的东西。g2o现在是SLAM研究人员中广泛使用的库,被许多着名的SLAM或VO作品采用,如: ORB_SLAM [2]和SVO [3]。
介绍
SLAM问题需要后端来优化地图和在其前端构建的姿势。后端通常是过滤框架(如EKF)或图形优化(即束调整)。如今,图形优化更受欢迎,并已成为最先进的方法。图优化的一般思想是将SLAM问题表示为图结构。如下图所示,图形包含两种类型的元素,节点(顶点)和约束(边缘)。
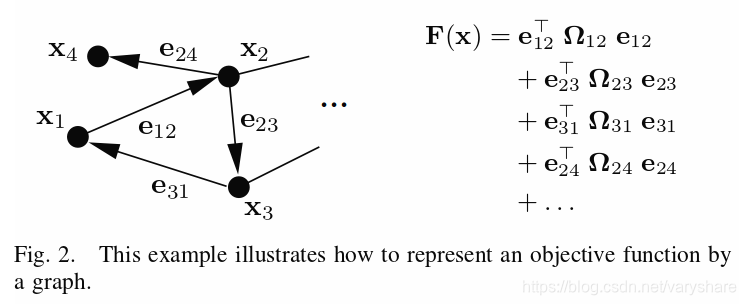
对于SLAM问题,机器人的关键帧姿势或地图中的地标位置表示为节点,而关键帧和关键帧,关键帧和地标,或地标和地标之间的观测和几何模型表示为连接某些的约束。节点。给定图形,图形优化旨在找到节点值的最佳估计,其最小化由约束确定的误差。因此,SLAM后端被转换为最小二乘最小化问题,可以通过以下等式来描述:
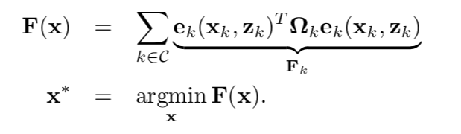
cmakelists.txt文件如下:
cmake_minimum_required( VERSION 2.8 )
project( g2o_curve_fitting )
set( CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release" )
set( CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O3" )
# 添加cmake模块以使用ceres库
list( APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake_modules )
# 寻找G2O
find_package( G2O REQUIRED )
include_directories(
${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS}
"/usr/include/eigen3"
)
# OpenCV
find_package( OpenCV REQUIRED )
include_directories( ${OpenCV_DIRS} )
add_executable( curve_fitting main.cpp )
# 与G2O和OpenCV链接
target_link_libraries( curve_fitting
${OpenCV_LIBS}
g2o_core g2o_stuff
)
c++代码为:
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
optimizer.setVerbose(false);
g2o::BlockSolver_6_3::LinearSolverType * linearSolver;
if (DENSE) {
linearSolver= new g2o::LinearSolverDense<g2o
::BlockSolver_6_3::PoseMatrixType>();
} else {
linearSolver
= new g2o::LinearSolverCholmod<g2o
::BlockSolver_6_3::PoseMatrixType>();
}
g2o::BlockSolver_6_3 * solver_ptr
= new g2o::BlockSolver_6_3(linearSolver);
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(solver_ptr);
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);
double focal_length= 1000.;
Vector2d principal_point(320., 240.);
vector<g2o::SE3Quat,
aligned_allocator<g2o::SE3Quat> > true_poses;
g2o::CameraParameters * cam_params
= new g2o::CameraParameters (focal_length, principal_point, 0.);
cam_params->setId(0);
if (!optimizer.addParameter(cam_params)) {
assert(false);
}
int vertex_id = 0;
for (size_t i=0; i<15; ++i) {
Vector3d trans(i*0.04-1.,0,0);
Eigen:: Quaterniond q;
q.setIdentity();
g2o::SE3Quat pose(q,trans);
g2o::VertexSE3Expmap * v_se3
= new g2o::VertexSE3Expmap();
v_se3->setId(vertex_id);
if (i<2){
v_se3->setFixed(true);
}
v_se3->setEstimate(pose);
optimizer.addVertex(v_se3);
true_poses.push_back(pose);
vertex_id++;
}
// Note: code has been simplified for demo convenience
for (size_t i=0; i<true_points.size(); ++i){
g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ * v_p
= new g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ();
v_p->setId(point_id);
v_p->setMarginalized(true);
v_p->setEstimate(true_points.at(i)
+ Vector3d(Sample::gaussian(1),
Sample::gaussian(1),
Sample::gaussian(1)));
optimizer.addVertex(v_p);
for (size_t j=0; j<true_poses.size(); ++j){
// Add edges. See the following passage.
}
++point_id;
}
for (size_t j=0; j<true_poses.size(); ++j){
Vector2d z
= cam_params->cam_map(true_poses.at(j).map(true_points.at(i)));
double sam = Sample::uniform();
z += Vector2d(Sample::gaussian(PIXEL_NOISE),
Sample::gaussian(PIXEL_NOISE));
g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV * e
= new g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV();
e->setVertex(0, dynamic_cast<g2o::OptimizableGraph::Vertex*>(v_p));
e->setVertex(1, dynamic_cast<g2o::OptimizableGraph::Vertex*>
(optimizer.vertices().find(j)->second));
e->setMeasurement(z);
e->information() = Matrix2d::Identity();
e->setParameterId(0, 0);
optimizer.addEdge(e);
}
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
cout << "Performing full BA:" << endl;
optimizer.optimize(10);
参考文献:
[1] Rainer Kuemmerle, Giorgio Grisetti, Hauke Strasdat, Kurt Konolige, and Wolfram Burgard g2o: A General Framework for Graph Optimization IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2011
[2] ORB_SLAM
[3] SVO
[4] SLAM Implementation: Bundle Adjustment with g2o





