二叉查询树(BST)
-
二叉树,每个节点只有一个父节点(根节点除外),每个节点都只有左右两个链接,分别指向自己的左子节点和右子节点
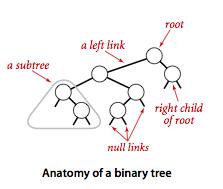
-
二叉查找树 (BST)是一颗二叉树,并且每个节点的值都大于等于其左子树中的所有节点的值而小于等于右子树的所有节点的值。
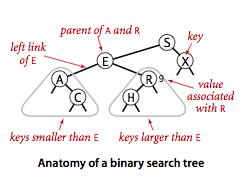
二叉树遍历
- 前序遍历:中左右
- 中序编列:左中右 (BST中序编列是递增顺序排序)
- 后续编列:左右中
具体实现<-点我
基本实现
public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
protected Node root;
protected class Node {
Key key;
Value val;
Node left;
Node right;
// 以该节点为根的子树节点总数
int N;
Node(Key key, Value val, int N) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.N = N;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size(root);
}
private int size(Node x) {
if (x == null)
return 0;
return x.N;
}
protected void recalculateSize(Node x) {
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
}
}
查找(get)
- 如果树是空的,则查找未命中;
- 如果被查找的键和根节点的键相等,查找命中;
- 否则递归地在子树中查找:如果被查找的键较小就在左子树中查找,较大就在右子树中查找。
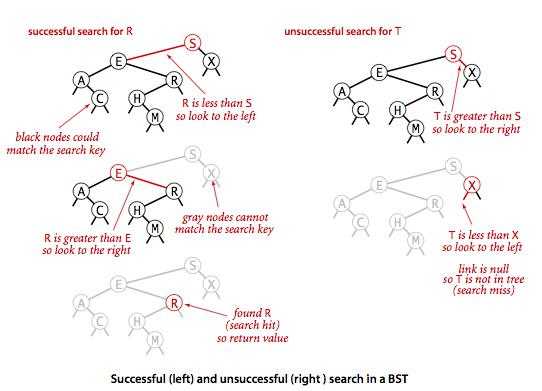
递归
public Value get(Key key) {
return get(root, key);
}
private Value get(Node root, Key key) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(root.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
return get(root.right, key);
} else if (cmp < 0) {
return get(root.left, key);
} else {
return root.value;
}
}
非递归
public Value get(Key key) {
return get(root, key);
}
private Value get(Node root, Key key) {
while (root != null) {
int cmp = key.compareTo(root.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
root = root.right;
} else if (cmp < 0) {
root = root.left;
} else {
return root.value;
}
}
return null;
}
插入(put)
当插入的键不存在于树中,需要创建一个新节点,并且更新上层节点的链接指向该节点,使得该节点正确地链接到树中。
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
root = put(root, key, value);
}
private Node put(Node root, Key key, Value value) {
//如果能找到对应key的节点就更新,
//否则创建一新的节点插入到树中
if (root == null) {
return new Node(key, value, 1);
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(root.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
root.left = put(root.left, key, value);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
root.right = put(root.right, key, value);
} else {
//找到更新
root.value = value;
}
//更新计数器
root.N = size(root.right)
+ size(root.left) + 1;
return root;
}
3.2.2 分析
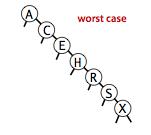
二叉查找树的算法运行时间取决于树的形状,而树的形状又取决于键被插入的先后顺序。
最好的情况下树是完全平衡的,每条空链接和根节点的距离都为 logN。
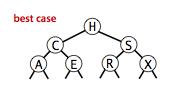
在最坏的情况下,树的高度为 N。
最大键和最小键(max,min)
- 如果根节点的左链接为空,那么一颗二叉查找树中的最小键就是根节点
- 如果左链接非空,那么树中的最小键就是左子树中的最小键
疯狂怼左儿子
public Key min() {
return min(root).key;
}
private Node min(Node root) {
if (root.left == null) {
return root;
}
return min(root.left);
}
疯狂怼右儿子
public Key max() {
return max(root).key;
}
private Node max(Node x) {
if (x.right == null) {
return x;
}
return max(x.right);
}
向上取整和向下取整(ceiling,floor)
向上取整(ceiling)就是指大于等于x的最小整数,向下取整(floor)是指小于等于x的最大整数
向下取整(floor)
取出的值肯定小于等于X,如果一个节点大于X,就肯定在左儿子下面,直到 节点(y)小于X,
就去y节点的右儿子中有没有(x>节点>y)
public Key floor(Key key) {
Node x = floor(root, key);
if(x == null)
return null;
return x.key;
}
private Node floor(Node x, Key key) {
if(x == null)
return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if(cmp == 0)
return x;
if(cmp < 0)
return floor(x.left, key);
Node t = floor(x.right, key);//如果 比他大 还要去判断一下右子树中有没有
if(t != null)
return t;
else
return x;
}
向上取整(ceiling)
取出的值肯定大于等于X,如果一个节点小于X,就肯定在右儿子下面,直到 节点(y)大于X,
就去y节点的左儿子中有没有(y>节点>x)
public Key ceiling(Key key) {
Node x = ceiling(root, key);
if (x == null) return null;
return x.key;
}
private Node ceiling(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0) return x;
if (cmp > 0) return ceiling(x.right, key);
Node t = ceiling(x.left, key);
if (t != null) return t;
else return x;
}
排名(rank)
rank(key) 返回 key 的排名。
- 如果键和根节点的键相等,返回左子树的节点数;
- 如果小于,递归计算在左子树中的排名;
- 如果大于,递归计算在右子树中的排名,加上左子树的节点数,再加上 1(根节点)。
public int rank(Key key) {
return rank(key, root);
}
private int rank(Key key, Node x) {
if (x == null)
return 0;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0)
return size(x.left);
else if (cmp < 0)
return rank(key, x.left);//如果一直比节点小一直走左边直到null返回0
else
return 1 + size(x.left) + rank(key, x.right);//
}
删除最大键和删除最小键
删除最小键
疯狂怼左儿子,当左儿子为NULL 时用右儿子挤掉自己
public void deleteMin() {
root = deleteMin(root);
}
private Node deleteMin(Node x) {
if (x.left == null) {
return x.right;
}
x.left = deleteMin(x.left);
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
删除最大键
疯狂怼右儿子,当右儿子为NULL 时用左儿子挤掉自己
public void deleteMax() {
root = deleteMax(root);
}
private Node deleteMax(Node x) {
if(x.right == null) return x.left;
x.right = deleteMax(x.right);
x.N = getSize(x.left) + getSize(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
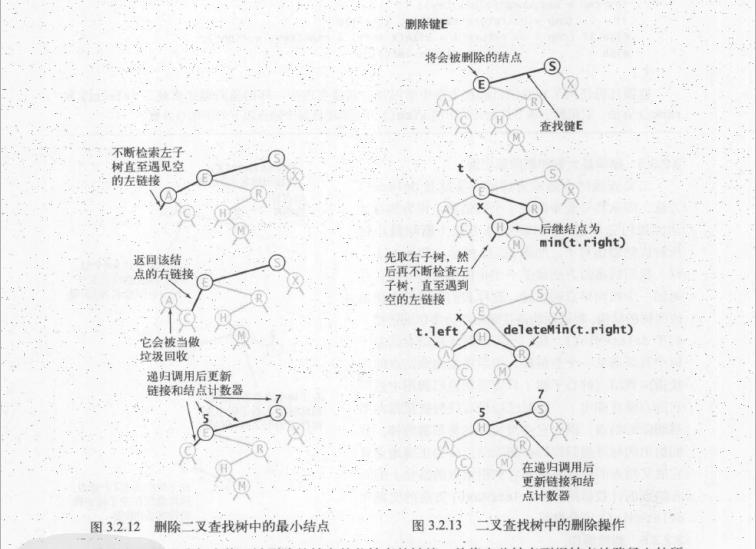
删除(delete)
注意看下面的配图,最难的一个实现
public void delete(Key key) {
root = delete(root, key);
}
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) {
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
x.left = delete(x.left, key);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
x.right = delete(x.right, key);
} else {
if (x.left == null) {
return x.right;
}
if (x.right == null) {
return x.left;
}
Node t = x;
x = min(t.right);
x.right = deleteMin(t.right);//更新X的右节点
x.left = t.left;
}
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
范围查询
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
return keys(min(), max());
}
private Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) {
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<>();
keys(root, queue, lo, hi);
return queue;
}
private void keys(Node x, Queue<Key> queue, Key lo, Key hi) {
if (x == null) {
return;
}
int cmplo = lo.compareTo(x.key);
int cmphi = hi.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmplo < 0) {
keys(x.left, queue, lo, hi);//左
}
if (cmplo <= 0 && cmphi >= 0) {
queue.add(x.key);//中
}
if (cmphi > 0) {
keys(x.right, queue, lo, hi);//右
}
}





