HashSet源码详解(基于jdk1.8.0_261)
HashSet简介
- HashSet继承AbstractSet,实现了Set,Cloneable,java.io.Serializable接口,故可拷贝,可序列化;
- HashSet依赖于HashMap,在HashMap中放入元素实际上都是放入HashMap 的实例 map中作为key,每个value都使用new Object()填充,由于HashMap的key是唯一的,故HashSet中的元素是唯一的;
- HashSet在多线程环境下是线程不安全的,可以外部加锁或使用其他并发线程安全类代替或Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet(...));
- HashSet的迭代器也具有fail-fast机制;
- 可以存null;(因为HashMap的key是唯一的)
为什么HashMap的key是唯一的?
因为 当一个元素准备加入map中时,先通过HashMap的hash函数计算出其hash值,在通过 (n -1 ) & hash 得到他的索引,若该位置为空,立即将元素的key value放入,否则若key相等,则替换value值,若key不等,启动哈希冲突方法,或用链表存,或用红黑树存冲突的节点。相同的key一定得到一样的hash,故存放的位置一定相同,只替换value,不同的key,hash值可能相同,但存放的位置一定不同。故HashMap中key是唯一的,故HashSet中元素是唯一的;
HashSet UML简图
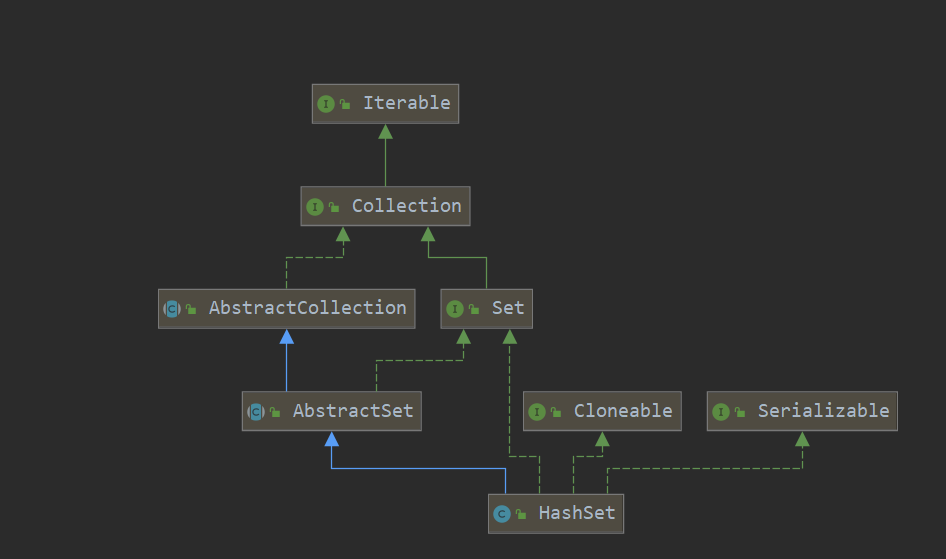
HashSet API概述
字段
static final long serialVersionUID = -5024744406713321676L;
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
map 字段主要用于存储数据,HashSet本质上的数据结构就是HashMap,HashMap的key存储实际元素,PRESENT字段填充所有k-v对的value值
构造函数
public HashSet()
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c)
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
public HashSet(int initialCapacity)
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) //为LinkedHashMap服务,多一个dummy参数是为了和两个参数的构造函数区别开
override或新增的方法
public Iterator<E> iterator() //返回元素的迭代器
public int size()
public boolean isEmpty()
public boolean contains(Object o)
public boolean add(E e)
public boolean remove(Object o)
public void clear()
public Object clone()
public Spliterator<E> spliterator()
private方法
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
直接继承或来自接口的default方法
--------------继承自AbstractSet的方法----------------
public boolean equals(Object o)
public int hashCode()
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
--------------继承自AbstrctCollection的方法----------
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)
public String toString()
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
public Object[] toArray()
------------来自接口的defalut的方法------------------
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) //来自Iterable接口
default Stream<E> stream() //来自Colletion接口
default Stream<E> parallelStream() //来自Colletion接口
HashSet源码详解
package java.util;
import java.io.InvalidObjectException;
import sun.misc.SharedSecrets;
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
static final long serialVersionUID = -5024744406713321676L;
//存储HashSet的元素的数据结构,可以看出HashSet 和 HashMap 存在 has-a 关系
//HashSet中元素都放入map中当key
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
//所有的value都用PRESENT代替
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
// 构造一个空的HashSet实例,初始化容量为16,load factor = 0.75
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
// 用一个集合c填充HashSet,load factor = 0.75,容量为 Math.max((int)(c.size()/.75f) +1 ,16)
// c = null时 会抛异常
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
addAll(c);
}
//构造一个空的HashSet.capacity,load factor自定义
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
//构造一个空的HashSet,load factor = 0.75f,容量自定义
public HashSet(int initialCapacity) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity);
}
//包权限的HashSet构造函数,被用于LinkedHashSet类,dummy参数是为了和上述两个参数的构造函数区别开
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
//返回HashMap的keySet的迭代器,即为HashSet元素的迭代器
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return map.keySet().iterator();
}
//返回集合中的元素个数
public int size() {
return map.size();
}
//判空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return map.isEmpty();
}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this set
* contains an element <tt>e</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this set is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contains the specified element
*/
//判断HashSet中是否包含对象o
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return map.containsKey(o);
}
//添加一个元素,若添加成功,返回true
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
//移除对象o
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
//移除所有的元素
public void clear() {
map.clear();
}
//返回HashSet的浅拷贝
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object clone() {
try {
HashSet<E> newSet = (HashSet<E>) super.clone();
newSet.map = (HashMap<E, Object>) map.clone();
return newSet;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
//序列化
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out HashMap capacity and load factor
s.writeInt(map.capacity());
s.writeFloat(map.loadFactor());
// Write out size
s.writeInt(map.size());
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (E e : map.keySet())
s.writeObject(e);
}
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read capacity and verify non-negative.
int capacity = s.readInt();
if (capacity < 0) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal capacity: " +
capacity);
}
// Read load factor and verify positive and non NaN.
float loadFactor = s.readFloat();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
}
// Read size and verify non-negative.
int size = s.readInt();
if (size < 0) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal size: " +
size);
}
// Set the capacity according to the size and load factor ensuring that
// the HashMap is at least 25% full but clamping to maximum capacity.
capacity = (int) Math.min(size * Math.min(1 / loadFactor, 4.0f),
HashMap.MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
// Constructing the backing map will lazily create an array when the first element is
// added, so check it before construction. Call HashMap.tableSizeFor to compute the
// actual allocation size. Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to
// what is actually created.
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess()
.checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, HashMap.tableSizeFor(capacity));
// Create backing HashMap
map = (((HashSet<?>)this) instanceof LinkedHashSet ?
new LinkedHashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor) :
new HashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor));
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E e = (E) s.readObject();
map.put(e, PRESENT);
}
}
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new HashMap.KeySpliterator<E,Object>(map, 0, -1, 0, 0);
}
}
HashSet示例
package collectionlearn;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
hashSet.addAll(Arrays.asList(1,4,7,9,5,6,8));
System.out.println(hashSet);
hashSet.add(100);
hashSet.add(200);
hashSet.add(300);
if(! hashSet.add(300)) {
System.out.println("元素已存在");
hashSet.remove(300);
System.out.println("元素已移除");
}
System.out.println(hashSet);
if(hashSet.contains(4)){
System.out.println("4已存在");
}
HashSet<Integer> copyhashSet = null;
if(! hashSet.isEmpty()){
copyhashSet = (HashSet<Integer>) hashSet.clone();
hashSet.clear();
System.out.println("hashSet已清空");
System.out.println(hashSet);
}
System.out.println("copyHashSet :" + copyhashSet);
Set<Integer> set = copyhashSet.stream().filter(x -> x > 10).collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(set);
}
}
- 结果
[1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
元素已存在
元素已移除
[1, 4, 100, 5, 6, 7, 8, 200, 9]
4已存在
hashSet已清空
[]
copyHashSet :[1, 4, 100, 5, 6, 7, 8, 200, 9]
[100, 200]
面试session
- 谈谈你对HashSet的认识?
HashSet本质上的数据结构就是HashMap,Hashset中加入的每个元素都为map的key,所有value值都利用PRESENT字段填充,PSESENT字段是个static final 的Object实例。由于HashMap key的唯一性保证了HashSet中元素的唯一性。
初稿完


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号