【题解】Uva[UVA11626] Convex Hull
凸包模板题。
之前写过拿 Graham 算法求凸包的,为了不重复/多学点知识,那这次拿 Andrew 算法求凸包吧qaq
*此文章所有图片均为作者手画。
Andrew 算法
假设我们有这些点:
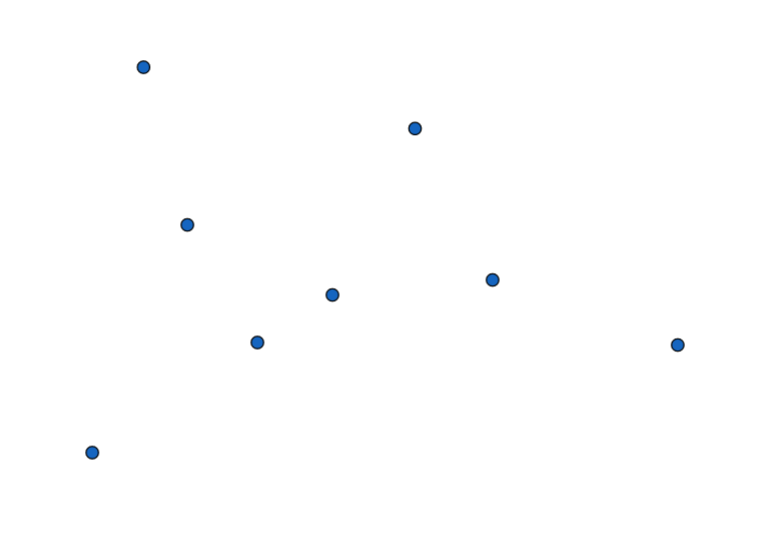

首先把所有点以横坐标为第一关键字,纵坐标为第二关键字排序。
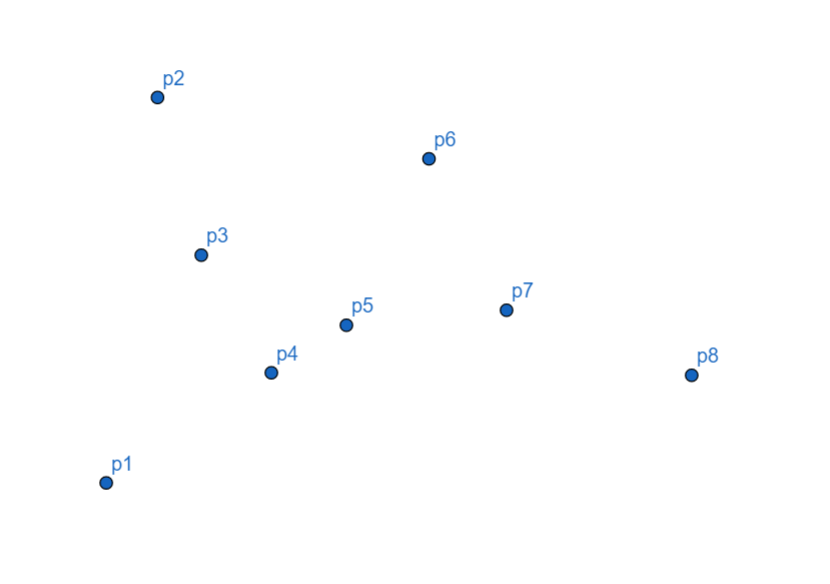
相对于 Graham 算法来说,Andrew 算法排序更简单,按 \(x, y\) 坐标排序,时间复杂度也更低(一般的坐标系中排序方法)。
首先将 \(p_1\) 入栈。
然后也将 \(p_2\) 入栈,\(p_2\) 可能在,也可能不在,等着之后判断。
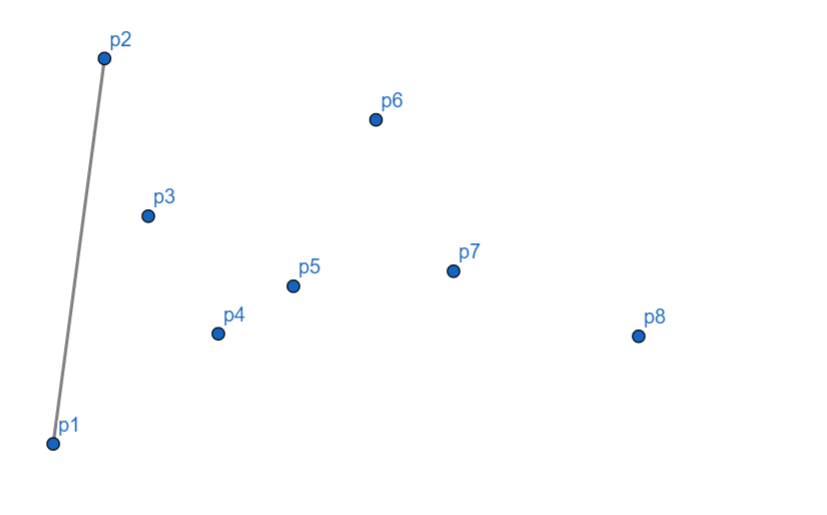
随后,发现 \(p_3\) 偏右,所以我们将 \(p_2\) 出栈。
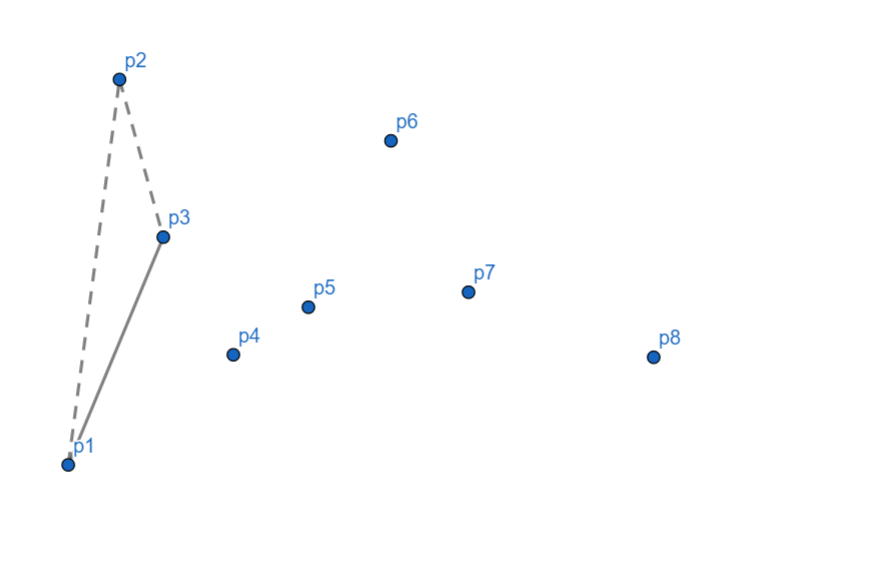
发现 \(p_4\) 依然偏右,\(p_3\) 出栈,\(p_4\) 入栈。
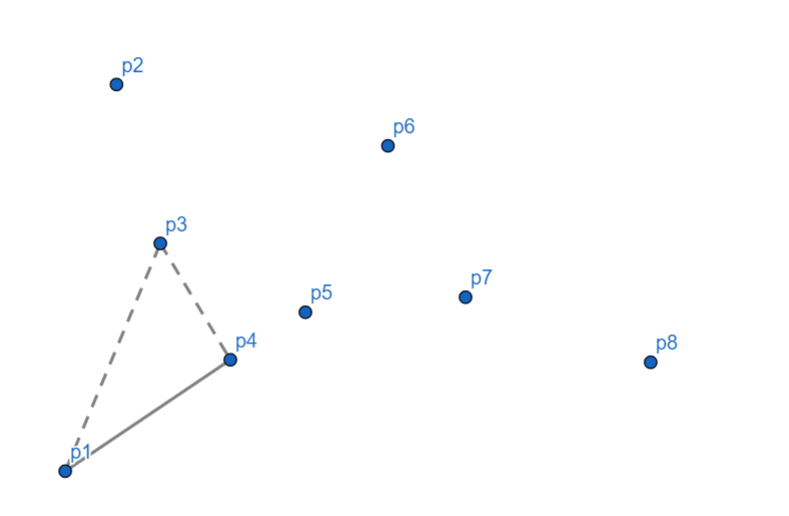
\(p_5\) 向右,\(p_4\) 出栈,\(p_5\) 入栈。
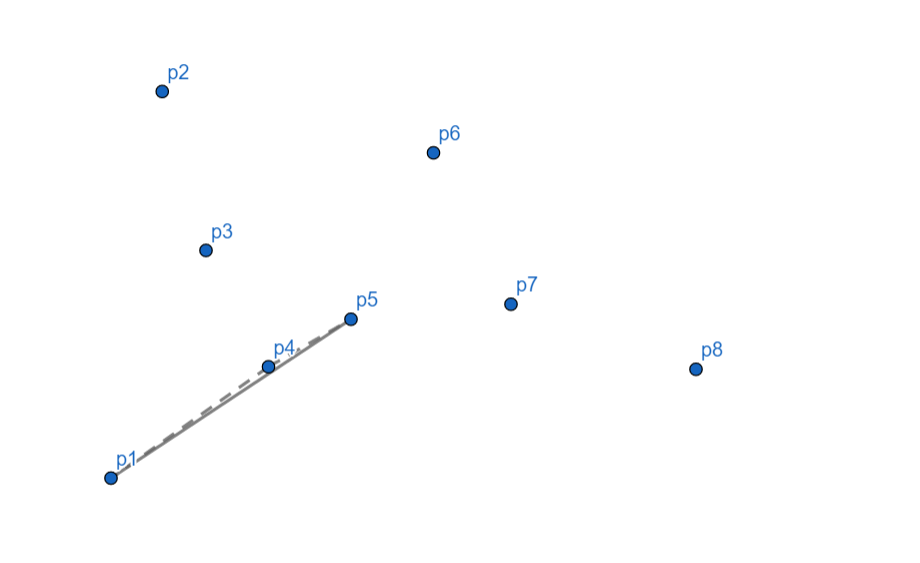
\(p_6\) 向左,入栈。
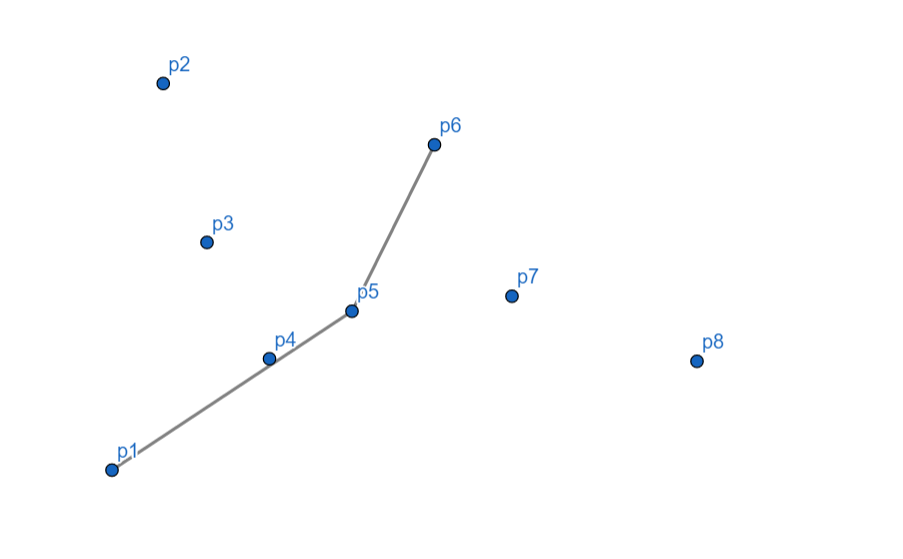
\(p_7\) 向右,\(p_6\) 出栈,\(p_7\) 入栈。
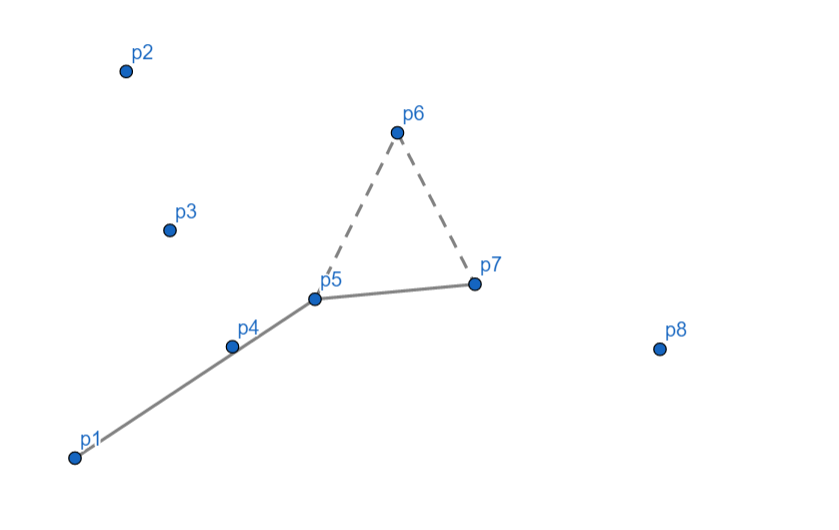
\(p_8\) 向右,\(p_7\) 出栈,继续检查发现相对于 \(p_5\) \(p_8\) 仍然向右,\(p_5\) 出栈,\(p_8\) 入栈。
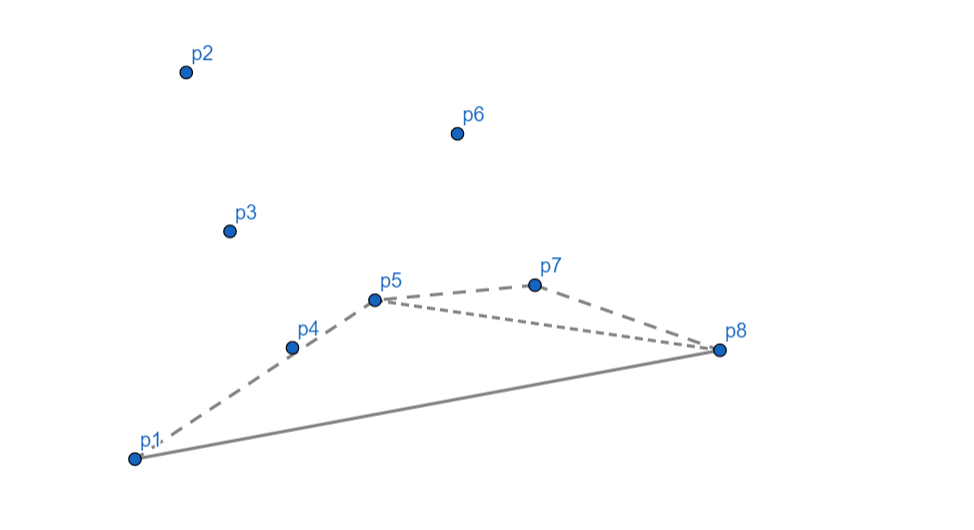
此时,我们发现,凸包明明还空一半就到头了???
然而这是意料之中,我们这种算法必然会只算出一半的凸包。
所以我们需要再从排序末尾的点(也就是 \(p_8\))出发,按照一模一样的方式再算一遍就行了。
当然如果我们走过的点就不许要再走了(除了 \(p_1\))
从 \(p_8\) 到 \(p_7\),向左,\(p_7\) 入栈。
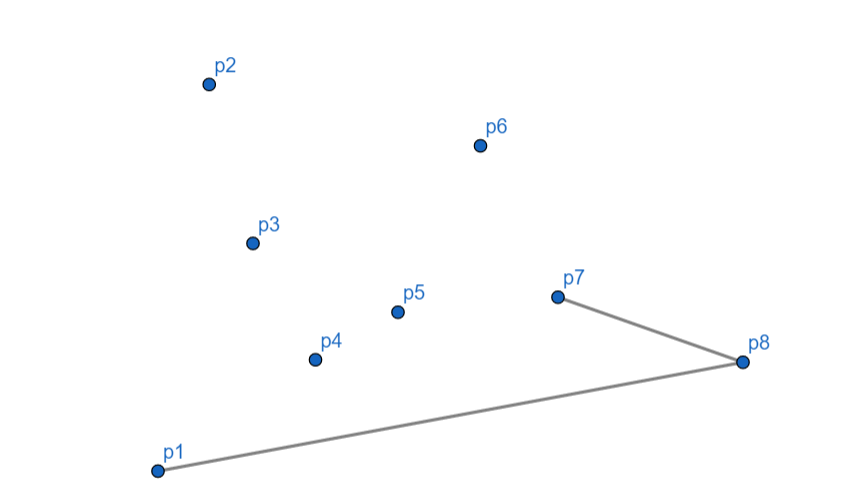
\(p_6\) 向右,\(p_7\) 出栈,\(p_6\) 入栈。
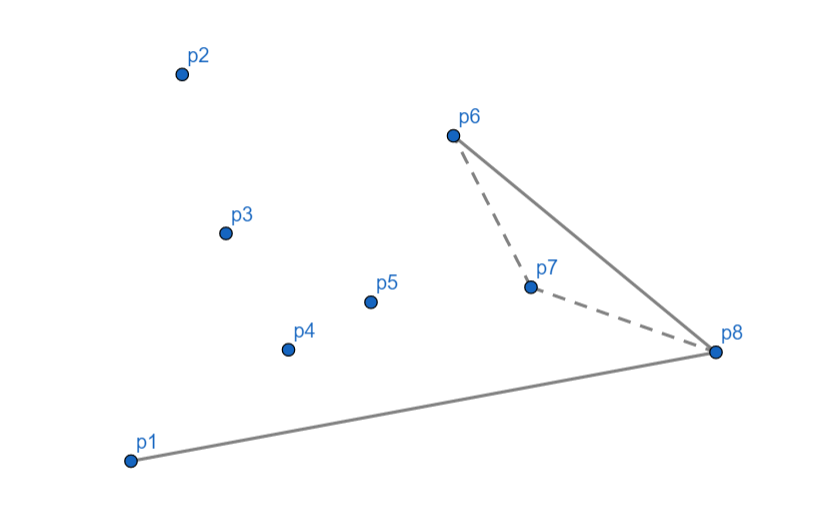
\(p_5\) 向左,入栈。
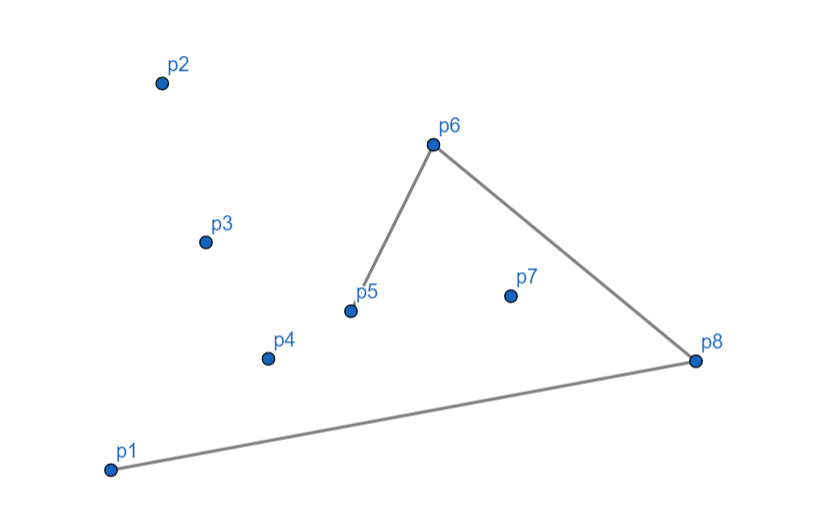
\(p_4\) 向左,入栈。
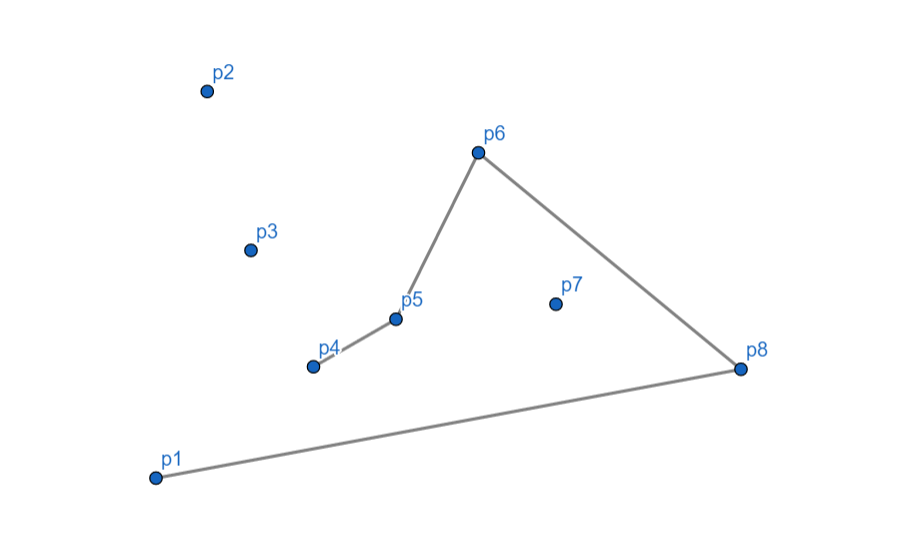
\(p_3\) 向右,\(p_4\) 出栈,对于 \(p_5\) \(p_3\) 依然向右,\(p_5\) 出栈,\(p_3\) 入栈。
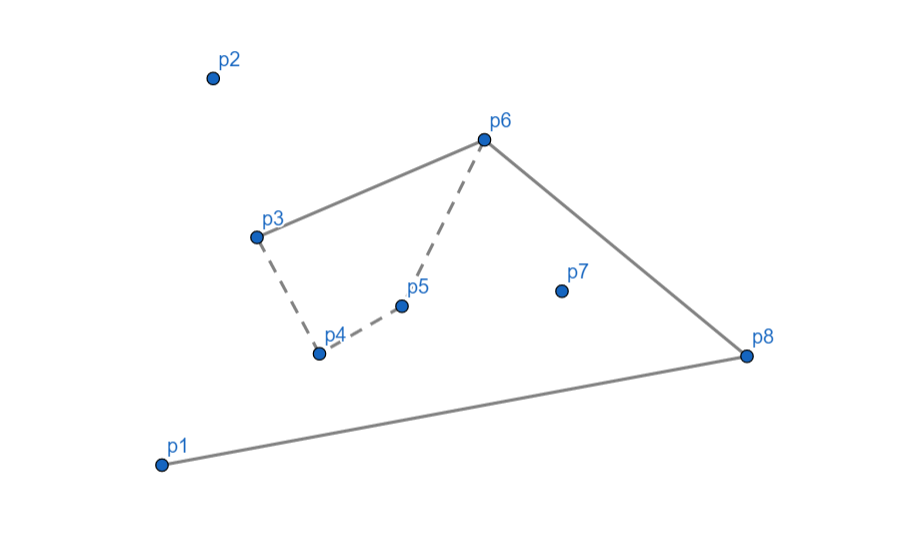
\(p_2\) 向右,\(p_3\) 出栈,\(p_2\) 入栈。
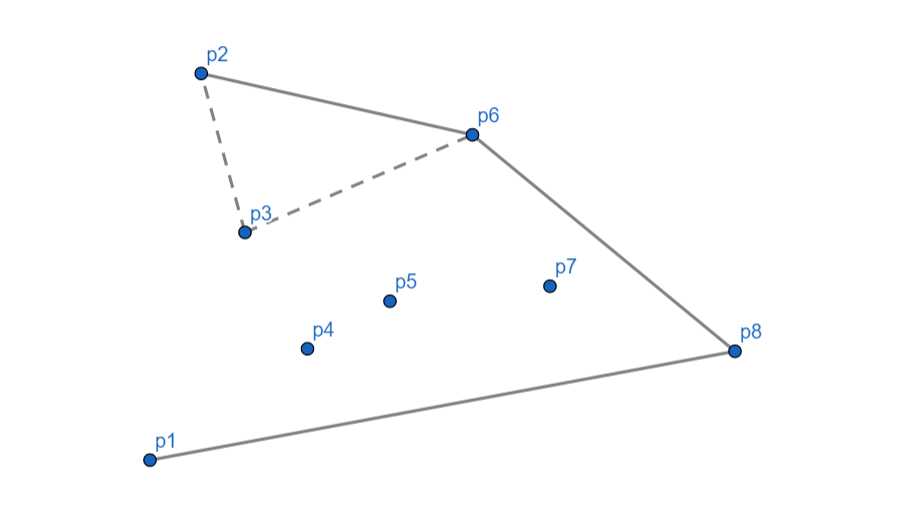
最后将 \(p_2\) 和 \(p_1\) 连起来。
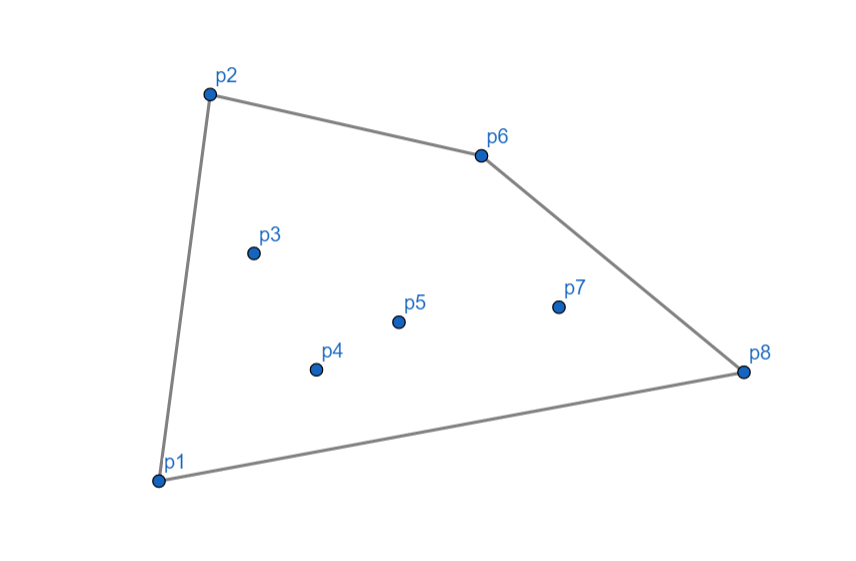
至此,我们的 Andrew 算法就完成了!
扫描的时间复杂度:\(O(n)\)(已过滤常数)
排序时间复杂度:\(O(n \log n)\)
总时间复杂度:\(O(n \log n)\)
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#define line cout << endl
using namespace std;
const int NR = 1e5 + 5;
const double eps = 1e-7;
int n;
struct point {
double x, y;
point () {}
point (double a, double b) : x (a), y (b) {}
bool operator < (const point &b) const {
if (x < b.x) return 1;
if (x > b.x) return 0;
return y < b.y;
}
point operator - (const point &b) {
return point (x - b.x, y - b.y);
}
};
point p[NR], sp[NR];
int cmp (double x) {
if (fabs (x) < eps) return 0;
return x > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}
double dis (point a, point b) {
return sqrt ((a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y));
}
double cp (point a, point b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
int Andrew () {
sort (p + 1, p + 1 + n);
int len = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (len > 1 && cmp (cp (sp[len] - sp[len - 1], p[i] - sp[len - 1])) < 0)
len--;
sp[++len] = p[i];
}
int k = len;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
while (len > k && cmp (cp (sp[len] - sp[len - 1], p[i] - sp[len - 1])) < 0)
len--;
sp[++len] = p[i];
}
return len;
}
int main () {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> n;
char c;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y >> c;
int t = Andrew();
cout << t - 1 << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < t; i++)
printf ("%.0lf %.0lf\n", sp[i].x, sp[i].y);
}
return 0;
}
谢谢qaq


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号