STL源码剖析之Adapter以及functor adapter初体验
2011-07-01 21:52 Aga.J 阅读(1037) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报1 adapter在设计模式上的定义如下:将一个class的接口转换为另一个class的接口,使得原本因为接口不兼容而不能合作的classes可以一起运作。
2 STL提供多种adapter,其中
改变functor(仿函数)的接口的叫做 function adapter。
改变 container(容器)接口的叫做container adapter
改变 iterator(迭代器)接口的叫做iterator adapter
3 container adapter
容器queue和stack就是一种container adapter,他们修饰deque的接口形成一种新的容器接口
4 iterator adapter
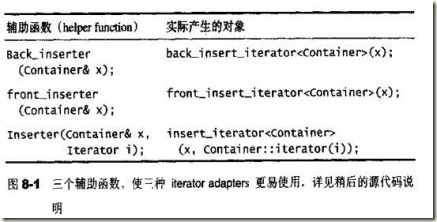
Insert iterator, reverse iterator, iostream iterator都属于 iterator adapter。
Insert iterator 将 一般的 iterator 的赋值操作(assign) 修饰为 插入(insert)操作,例如back_insert_iterator, front_insert_iterator, insert_iterator。
Reverse iterator 将 一般的iterator的前进方向逆转,使得原本应该前进的++操作变成了后退操作。Iostream iterator 将 iterator 绑定到某个iostream上,使其拥有输入功能。
//use case
#include<iterator>
#include<deque>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
Int main()
{
Ostream_iterator<int> outite( cout, “ ” );
//将outite绑定到cout,每次对outite指派一个元素,然后就接一个” ”
Int ia[]={0,1,2,3,4,5};
Deque<int> id( ia, ia+6);
Copy ( id.begin(), id.end(0, outite); //相当于cout<<0 1 2….
Cout<<endl;
Copy( ia+1, ia+2, front_inserter( id) );
Copy( id.begin(), id.end(), outite); // 相当于cout<<1 0 1 2 3 4 5
Cout<<endl;
Copy( ia+3, ia+4, back_inserter(id));
Copy( id.begin(), id.end(), outite); // 10123453
Cout<<endl;
}
5 functor adapter
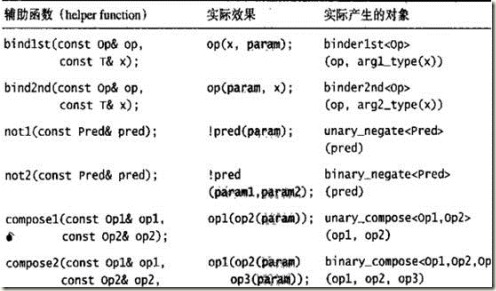
Functor adapter的价值在于,通过它们之间的绑定,组合,修饰,几乎可以无限制的创造出各种可能的表达式,搭配STL算法一起演出。例如,我们可能希望找出某个序列中所有不小于12的元素个数,虽然,“不小于“或者”大于或等于“,我们可以选择STL内建的仿函数greater_euqal,但是如果希望完全按照题目,可以这样做
Not1( bind2nd( less<int>(), 12 ))
这个式子将less的第二个参数绑定为12,再加上否定操作,就形成了不小于12的语义,凑成了一个表达式。 可以和任何”可接受表达式为参数”的算法匹配。
//use
#include< algorithm>
#include< functional>
#include< vector>
#include< iostream>
#include< iterator>
Using namespace std;
Int main()
{
Ostream_iterator<int> outite( cout,””);
Int ia[6]={2,21,12,7,19,23};
Vector<int> iv( ia, ia+6);
Foreach( iv.begin, iv.end, compose1( bind2nd( multiplies<int>(),3), bind2nd(plus<int>().2) ));
// 对每个元素v身上执行 (v+2)*3
Copy( iv.begin(), iv.end(), outite);
Cout<<endl;
Transform( iv.begin(), iv.end(), outite, compose1( bind2nd(multipies<int>(),3), bind2nd(plus<int> (),2 ) ));
Cout<<endl;
}
为什么会有functior adapter,因为仿函数就是将function call操作符重载的一种class,而任何算法接受一个仿函数时,在其演算过程中调用该仿函数的operator(), 这使得不具备仿函数之形,而又真函数之实的“一般函数“和”成员函数“感到为难,所以STL提供了众多的配接器,使得这些普通函数可以无缝的和其他配接器和算法结合起来。
//use case
#include< algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
Using namespace std;
Void print(int i) //这里有个既存函数,希望可以在STL体系中复用
{ cout<<i<<’ ‘;}
Class Int
{
Public:
Explicit int(int i): m_i(i) {}
Void print1() const{cout<<’[’<<m_i<<’]’;} //这个函数也希望可以在STL体系中复用
Private:
Int m_i;
};
Int main()
{
Ostream_iterator< int> outite( cout, “ ” );
Int ia[6]={2,21,12,7,19,23};
Vector<int> iv( ia, ia+6);
Cout<<count_if ( iv,begin(), iv.end(), not1(bind2nd( less<int>(), 12));
Cout<<endl;
Transform( iv,begin() , iv,end(), outite, compose1( bind2nd( multiplies<int>(),3), bind2nd(plus<int>(),2) ));
Cout<<endl;
Copy( iv.begin(), iv.end(), outite);
Cout<<endl;
For_each( iv.begin(), iv.end(), print); //用函数指针搭配STL算法
For_each( iv.begin(), iv.end(), ptr_fun(print)); //用ptrfun修饰一般函数,并匹配STL算法
}
上述是各种function adapter和辅助函数,实际效果。
附网上的仿函数好文:
|
C++ STL 学习 :for_each与仿函数(functor)(一)
|
|||||||
|
//源码实现与分析
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
struct State
{
public:
State(int state):m_state(state){}
~State(){std::cout<<"~state(),m_state="<<m_state;}
void setState(int state){m_state=state;}
int getState(){return m_state;}
void print() const {std::cout<<"State:print:"<<m_state<<std::endl;}
private:
int m_state;
};
void print(State* pstate)
{
(pstate)->print();
}
struct Printer
{
template<typename T> void operator()(T* t){t->print();}
};
int main()
{
std::vector<State*> vect;
vect.push_back(new State(0));
vect.push_back( new State(1) );
vect.push_back( new State(2) );
vect.push_back( new State(3) );
std::vector<State*>::iterator it(vect.begin());
std::vector<State*>::iterator ite(vect.end());
//传统的遍历需要我们取得迭代子进行对象的访问
for(;it!=ite;++it)
{
(*it)->print();
}
//可以尝试使用std自带的for_each,但是需要使用一个函数指针来实现。
std::for_each(vect.begin(),vect.end(),&print);
//其实for_each还是使用了for和迭代器,并把迭代器作为指针函数的参数传入来调用。
/*
template<class InputIterator, class Function>
Function for_each(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, Function f)
{
for ( ; first!=last; ++first ) f(*first);
return f;
}
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/algorithm/for_each/
*/
//下面试一试使用仿函数,需要先定义一个functor
Printer p;
std::for_each(vect.begin(),vect.end(),p);
//同样利用for_each函数,但是这次我们在模板参数中传入一个类对象,在foreach中使用对象的()操作符时调用所重载的函数,实现我们的目的
// 还是需要自己定义一个仿函数,这次试试function adapter
std::for_each(vect.begin(),vect.end(), std::mem_fun(&State::print));
/*
mem_fun的实现是怎样?
// TEMPLATE FUNCTION mem_fun
template<class _Result,class _Ty> inline
mem_fun_t<_Result, _Ty> mem_fun(_Result (_Ty::*_Pm)())
{ // return a mem_fun_t functor adapter
return (std::mem_fun_t<_Result, _Ty>(_Pm));
}
注意mem_fun的参数_Result(_Ty::*_Pm)()
注意函数实现中调用了mem_fun_t这个functor adapter
// TEMPLATE CLASS mem_fun_t
template< typename _Result, typename _Ty >
class mem_fun_t : public unary_function<_Ty *, _Result> //继承已有的unary_funcion
{
typedef _Result (_Ty::*_Pmemfun)();
public:
explicit mem_fun_t( _Pmemfun& pfunc )
: m_pfun( pfunc )
{ // construct from pointer
}
_Result operator()(_Ty *_Pleft) const
{ // call function
return ( (_Pleft->*m_pfun)() );
}
private:
_Pmemfun m_pfun; // the member function pointer
};
这样就比较清晰了,定义了仿函数mem_fun_t内部定义了一个【类成员函数指针】,
仿函数构造的时候将函数指针保存起来,当仿函数operator()被调用的时候,
就通过与一个类的实例关联起来从而实现了类成员函数的调用。
其调用流程是这样的,for_each把vector中的元素传送给mem_fun,
mem_fun【自己产生一个仿函数mem_fun_t】,然后仿函数调用其重载的()。
所以这里的functor adapter其实就是帮助我们实现一个仿函数来实现和算法的组合等便捷功能。
而且注意到mem_fun_t是如何帮助我们自动实现一个仿函数的
他需要我们传入&State:print,这时候其实也就记录了State类和print函数指针,还有print函数返回值【分别对应Ty Pm Result】然后再根据这些信息来实现一个仿函数,
*/
int i;
std::cin>>i;
}
//见C++ Reference解释:ptr_fun
Convert function pointer to function objectReturns a function object that encapsulates function f.也就是书里面介绍的方法(将一个普通函数转化为仿函数)mem_funConvert member function to function object (pointer version)Returns a function object that encapsulates member function f of type T. The member function returns a value of type S and, optionally, can take one parameter of type A.也就是网上文章中介绍的方法(将一个类成员函数转化为仿函数)
作者:Aga.J
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/aga-j
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
个人学习笔记仅供本人记录知识所用,不属发表性文章。