Spring_自动装配 & bean之间的关系 & bean的作用域
1.自动装配
beans-autowire.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd"> <bean id="address2" class="com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Address" p:city="hefei" p:street="wanda"></bean> <bean id="address" class="com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Address" p:city="wuhu" p:street="wanda"></bean> <bean id="car" class="com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Car" p:brand="audi" p:price="250000"></bean> <!-- 可以使用autowire 属性指定自动装配的方式 byName 根据bean 的名字和当前 bean 的setter 风格的属性名进行自动装配,若有匹配的, 则进行自动装配,
若没有匹配的, 则不装配 byType 根据 bean的类型 和当前bean 的属性的类型进行自动装配,
若IOC容器中有一个以上的类型匹配的bean, 则抛异常 --> <bean id="person" class="com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Person" p:name="Hxl" autowire="byName"></bean> </beans>
Main.java
package com.aff.spring.beans.autowire; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans-autowire.xml"); Person person = (Person) ctx.getBean("person"); System.out.println(person); //Person [name=Hxl, addres=Address [city=hefei, street=wanda], car=Car [brand=audi, price=250000.0]] } }
Person.java
package com.aff.spring.beans.autowire; public class Person { private String name; private Address address; private Car car; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + ", car=" + car + "]"; } }
Address.java
package com.aff.spring.beans.autowire; public class Address { private String city; private String street; public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getStreet() { return street; } public void setStreet(String street) { this.street = street; } @Override public String toString() { return "Address [city=" + city + ", street=" + street + "]"; } public Address() { super(); } public Address(String city, String street) { super(); this.city = city; this.street = street; } }
Car.java
package com.aff.spring.beans.autowire; public class Address { private String city; private String street; public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getStreet() { return street; } public void setStreet(String street) { this.street = street; } @Override public String toString() { return "Address [city=" + city + ", street=" + street + "]"; } public Address() { super(); } public Address(String city, String street) { super(); this.city = city; this.street = street; } }
2.bean之间的关系:继承;依赖
beans-relation.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 抽象bean: bean 的abstract 属性为true 的bean ,
这样的bean 不能被IOC 容器实例化,只用来被继承配置 --> <!--若一个bean的 class 属性都没有指定,则该bean 必须为一个抽象bean--> <bean id="address" p:city="hefei" p:street="wanda" abstract="true"></bean> <!-- bean 配置的继承 : 使用 bean 的parent 属性 指定继承 那个bean的配置 --> <bean id="address2" class="com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Address" p:street="buxinjie" parent="address"></bean> <bean id="car" class="com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Car" p:brand="audi" p:price="260000"></bean> <!-- 要求再配置 Person 时 , 必须有一个关联的Car 换句话说, Person 这个bean 依赖于Car这个bean--> <bean id="person" class="com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Person" p:name="Tom" p:address-ref="address2" depends-on="car"></bean> </beans>
Main
package com.aff.spring.beans.relation; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Address; import com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Person; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans-relation.xml"); // Address address = (Address) ctx.getBean("address"); // System.out.println(address); // Address [city=hefei, street=wanda] Address address2 = (Address) ctx.getBean("address2"); System.out.println(address2); // Address [city=hefei, street=buxinjie] Person person = (Person) ctx.getBean("person"); System.out.println(person); //Person [name=Tom, address=Address [city=hefei, street=buxinjie], car=null] } }
3.bean 的作用域:singleton;prototype;
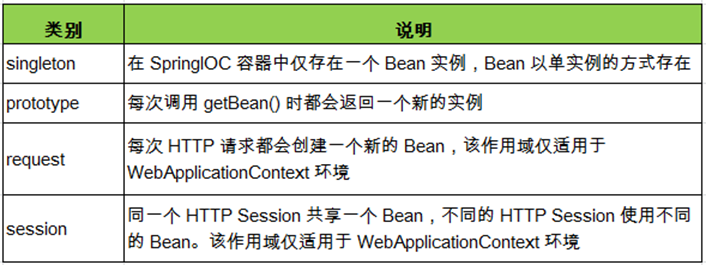
beans-scope.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 使用bean 的scope 属性来配置 bean 的作用域 singleton 默认的,容器初始化时创建bean实例, 在整个生命周期内只创建一个bean, 单例的 prototype : 原型的,容器初始化 不创建bean的实例,而在每次请求时都创建一个新的bean 实例,并返回 --> <bean id="car" class="com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Car" scope="singleton"> <property name="brand" value="audi"></property> <property name="price" value="250000"></property> </bean> </beans>
Main
package com.aff.spring.beans.scope; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.aff.spring.beans.autowire.Car; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans-scope.xml"); Car car = (Car) ctx.getBean("car"); Car car2 = (Car) ctx.getBean("car"); System.out.println(car==car2); //true } }
目录
All that work will definitely pay off


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号