Spring_配置Bean & 属性配置细节
1.Spring容器
在 Spring IOC 容器读取 Bean 配置创建 Bean 实例之前, 必须对它进行实例化. 只有在容器实例化后, 才可以从 IOC 容器里获取 Bean 实例并使用.
Spring 提供了两种类型的 IOC 容器实现.
BeanFactory: IOC 容器的基本实现.
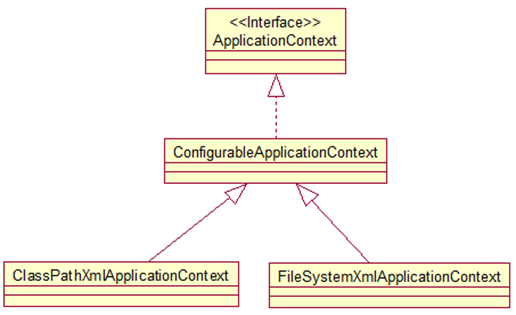
①ApplicationContext: 提供了更多的高级特性. 是 BeanFactory 的子接口.
②BeanFactory 是 Spring 框架的基础设施,面向 Spring 本身;
ApplicationContext 面向使用 Spring 框架的开发者,几乎所有的应用场合都直接使用 ApplicationContext 而非底层的 BeanFactory
无论使用何种方式, 配置文件时相同的.
2.ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext 的主要实现类:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从 类路径下加载配置文件
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext: 从文件系统中加载配置文件
ConfigurableApplicationContext 扩展于 ApplicationContext,新增加两个主要方法:
refresh() 和 close(), 让 ApplicationContext 具有启动、刷新和关闭上下文的能力
ApplicationContext 在初始化上下文时就实例化所有单例的 Bean。
WebApplicationContext 是专门为 WEB 应用而准备的,它允许从相对于 WEB 根目录的路径中完成初始化工作
3.从 IOC 容器中获取 Bean
调用 ApplicationContext 的 getBean() 方法
如:Helloword helloword = (Helloword) ctx.getBean("helloWorld2");
4.依赖注入的方式
Spring 支持 3 种依赖注入的方式
属性注入(setter方法注入)
<bean id="helloWorld2" class="com.aff.spring.beans.Helloword"> <property name="name2" value="Spring"></property> </bean>
构造器注入
<!-- 通过 构造方法 来配置 bean 属性 --> <bean id="car" class="com.aff.spring.beans.Car"> <constructor-arg value="Audi" index="0"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="SHANGHAI" index="1"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="3000000" type="double"></constructor-arg> </bean>
工厂方法注入(很少使用,不推荐)
5.属性配置细节
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd"> <!--配置bean class : bean 的全类名, 通过反射的方式再IOC 容器中创建bean 所以要求 Bean 中必须有无参数的构造器 id: 标识容器中 bean. id 唯一 --> <bean id="helloWorld2" class="com.aff.spring.beans.Helloword"> <property name="name2" value="Spring"></property> </bean> <!-- 通过 构造方法 来配置 bean 属性 --> <bean id="car" class="com.aff.spring.beans.Car"> <constructor-arg value="Audi" index="0"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="SHANGHAI" index="1"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="3000000" type="double"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- 使用构造器注入属性值可以指定参数的位置和参数的类型,以区分重载的构造器 --> <bean id="car2" class="com.aff.spring.beans.Car"> <constructor-arg value="Baoma" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg> <!-- 如果字面值包含特殊字符可以使用<![CDATA[]]> 包裹起来--> <!-- 属性值 也可以使用value 子节点 进行配置 --> <constructor-arg type="java.lang.String"> <value><![CDATA[<SHANGHAI**>]]></value> </constructor-arg> <constructor-arg type="int"> <value>234</value> </constructor-arg> </bean> <bean id="person" class="com.aff.spring.beans.Person"> <property name="name" value="Tom"></property> <property name="age" value="23"></property> <!-- 可以使用 property 的ref 属性 建立 bean之间的引用关系 --> <!-- <property name="car" ref="car2"></property> --> <!-- 也可以内部bean, 不能被外部引用的 , 只能在内部使用--> <property name="car"> <bean class="com.aff.spring.beans.Car"> <constructor-arg value="Ford"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="Changan"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="30000" type="double"></constructor-arg> </bean> </property> </bean> <bean id="person2" class="com.aff.spring.beans.Person"> <constructor-arg value="AAA"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="26"></constructor-arg> <!-- <constructor-arg ref="car2"></constructor-arg> --> <!-- 测试值 null --> <!-- <constructor-arg><null/></constructor-arg> --> <constructor-arg ref="car"></constructor-arg> <!--为级联属性赋值,注意:属性需要先初始化后才可以为级联属性赋值, 否则的话会有异常 --> <property name="car.maxSpeed" value="260"></property> </bean> <!--测试如何配置集合属性 --> <bean id="person3" class="com.aff.spring.beans.collection.Person"> <property name="name" value="Colin"></property> <property name="age" value="25"></property> <property name="cars" > <!--使用list 节点为List 类型的属性赋值 --> <list> <ref bean="car"/> <ref bean="car2"/> <bean class="com.aff.spring.beans.Car"> <constructor-arg value="Ford"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="Changan"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="30000" type="double"></constructor-arg> </bean> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置 Map 属性值 --> <bean id="newPerson" class="com.aff.spring.beans.collection.NewPerson"> <property name="name" value="Mike"></property> <property name="age" value="26"></property> <property name="cars" > <map> <entry key="AA" value-ref="car"></entry> <entry key="BB" value-ref="car2"></entry> </map> </property> </bean> <!--配置Properties 属性值 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.aff.spring.beans.collection.DataSource"> <property name="properties"> <!-- 使用props 和prop 子节点为 Properties 属性赋值 --> <props> <prop key="user">root</prop> <prop key="password">123456</prop> <prop key="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql:///test</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置 单例的 集合 bean 以供 多个bean 进行引用 ,需要导入util 命名空间--> <util:list id="cars"> <ref bean="car" /> <ref bean="car2" /> </util:list> <bean id="person4" class="com.aff.spring.beans.collection.Person"> <property name="name" value="Jack"></property> <property name="age" value="15"></property> <property name="cars" ref="cars"></property> </bean> <!--通过 p,命名空间为bean 的属性赋值, 需要先导入 p 命名空间 , 相对于传统方式更加简洁 --> <bean id="person5" class="com.aff.spring.beans.collection.Person" p:age="30" p:name="Lin" p:cars-ref="cars"> </bean> </beans>
Main.java
package com.aff.spring.beans.collection; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Person person = (Person) ctx.getBean("person3"); System.out.println(person); //Person [name=Colin, age=25, cars=[Car [brand=Audi, corp=SHANGHAI, price=3000000.0, maxSpeed=260], Car [brand=Baoma, corp=<SHANGHAI**>, price=0.0, maxSpeed=234]]] NewPerson newPerson = (NewPerson) ctx.getBean("newPerson"); System.out.println(newPerson); //NewPerson [name=Mike, age=26, cars={AA=Car [brand=Audi, corp=SHANGHAI, price=3000000.0, maxSpeed=260], BB=Car [brand=Baoma, corp=<SHANGHAI**>, price=0.0, maxSpeed=234]}] DataSource dataSource= (DataSource) ctx.getBean("dataSource"); System.out.println(dataSource); //DataSource [properties={driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, user=root, password=123456, jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///test}] System.out.println(dataSource.getProperties()); //{driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, user=root, password=123456, jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///test} Person person4 = (Person) ctx.getBean("person4"); System.out.println(person4); //Person [name=Jack, age=15, cars=[Car [brand=Audi, corp=SHANGHAI, price=3000000.0, maxSpeed=260], Car [brand=Baoma, corp=<SHANGHAI**>, price=0.0, maxSpeed=234]]] Person person5 = (Person) ctx.getBean("person5"); System.out.println(person5); //Person [name=Lin, age=30, cars=[Car [brand=Audi, corp=SHANGHAI, price=3000000.0, maxSpeed=260], Car [brand=Baoma, corp=<SHANGHAI**>, price=0.0, maxSpeed=234]]] } }
DataSource.java
package com.aff.spring.beans.collection; import java.util.Properties; public class DataSource { private Properties properties; public Properties getProperties() { return properties; } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } @Override public String toString() { return "DataSource [properties=" + properties + "]"; } public DataSource() { super(); } public DataSource(Properties properties) { super(); this.properties = properties; } }
NewPerson
package com.aff.spring.beans.collection; import java.util.Map; import com.aff.spring.beans.Car; public class NewPerson { private String name; private int age; private Map<String, Car> cars; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Map<String, Car> getCars() { return cars; } public void setCars(Map<String, Car> cars) { this.cars = cars; } public NewPerson() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public NewPerson(String name, int age, Map<String, Car> cars) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.cars = cars; } @Override public String toString() { return "NewPerson [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", cars=" + cars + "]"; } }
Person.java
package com.aff.spring.beans.collection; import java.util.List; import com.aff.spring.beans.Car; public class Person { private String name ; private int age; private List<Car> cars; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public List<Car> getCars() { return cars; } public void setCars(List<Car> cars) { this.cars = cars; } public Person() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Person(String name, int age, List<Car> cars) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.cars = cars; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", cars=" + cars + "]"; } }
需要的架包
commons-logging.jar
spring-aop-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-core-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-expression-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
目录


