EL
EL 全名为 Expression Language,为方便存取数据所自定义的语言,可以在 JSP 网页中直接使用 EL .
EL 主要的语法结构:
${sessionScope.user.sex}
所有 EL 都是以 ${ 为起始、以} 为结尾的。
EL 提供 . 和 [ ] 两种运算符来存取数据。
${sessionScope.user.sex}
等于
${sessionScope.user["sex"]
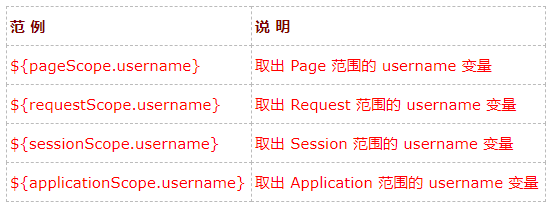
${username}。它的意思是取出某一范围中名称为 username的变量。
因为我们并没有指定哪一个范围的 username,所以它的默认值会先从 Page 范围找,假如找不到,
再依序到 Request、Session、Application 范围。假如途中找到 username,就直接回传,
不再继续找下去,但是假如全部的范围都没有找到时,就回传 null.
自动转换
${param.count + 20}
假若窗体传来 count 的值为 10 时,那么上面的结果为 30。
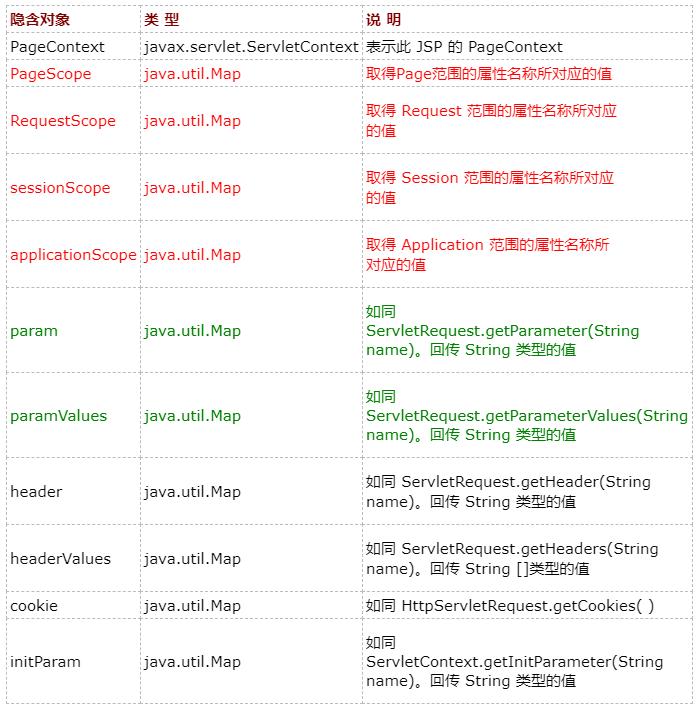
EL 隐含对象总共有 11 个
注意:
Param.jsp 主要使用 EL 的隐含对象 param来接收数据。
但是必须注意:假若要取得多重选择的复选框的值时,必须使用 paramValues,
例如:使用 paramValues 来取得“兴趣”的值
兴趣: ${paramValues.habit[0]}
${paramValues.habit[1]}
假若我们在 cookie 中
设定一个名称为 userCountry 的值,那么可以使用${cookie.userCountry}来取得它。
initParam就像其他属性一样,我们可以自行设定 web 站台的环境参数(Context),
当我们想取得这些参数时,可以使用 initParam 隐含对象去取得它,
例如:
<context-param> <param-name>userid</param-name> <param-value>mike</param-value> </context-param>
直接使用 ${initParam.userid}来取得名称为 userid,其值为 mike 的参数。
${pageContext}来取得其他有关用户要求或页面的详细信息
${pageContext.request.contextPath} 服务的 web application 的名称
Empty 运算符
Empty 运算符主要用来判断值是否为 null 或空的,
例如:
${ empty param.name }
empty 可以作用于一个集合,若该集合不存在或集合中没有元素, 其结果都为 true
条 件 运算符:${ A ? B : C}
代码说明
<%@page import="java.util.ArrayList"%> <%@page import="java.util.List"%> <%@page import="com.aff.javaweb.Customer"%> <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- 7. EL 的运算符 --> ${param.score > 60 ? "及格" : "不及格" } <br> <% List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>(); names.add("abc"); request.setAttribute("names", names); %> <!-- empty 可以作用于一个集合, 若该集合不存在或集合中没有元素, 其结果都为 true --> names is empty: ${empty requestScope.names } <br> <!-- 6. 其他隐含对象: pageContext 等(cookie, header, initParam 只需了解.) --> pageContext: pageContext 即为 PageContext 类型, 但只能读取属性就可以一直的 . 下去。 <br> contextPath: ${pageContext.request.contextPath } <br> sessionId: ${pageContext.session.id } <br> sessionAttributeNames: ${pageContext.session.attributeNames } <br> initParam: ${initParam.initName } <br> Accept-Language: ${header["Accept-Language"] } <br> JSESSIONID: ${cookie.JSESSIONID.name } -- ${cookie.JSESSIONID.value } <br> <!-- 5. 与输入有关的隐含对象: param, paramValues --> score: ${param.score } <%-- <%= request.getParameter("score") %> --%> <br> names: ${paramValues.name[0].class.name } <%-- <%= request.getParameterValues("name")[0].getClass().getName() %> --%> <br> <!-- 4. 隐含对象之与范围相关的: pageScope, requestScope, sessionScope, applicationScope --> time: ${applicationScope.time.time } <%-- <%= application.getAttribute("time") %> --%> <br> <!-- 3. EL 可以进行自动的类型转换 --> score: ${param.score + 11} <br> score: <%= request.getParameter("score") + 11 %> <br> <!-- 2. EL 中的隐含对象 --> <% Customer cust2 = new Customer(); cust2.setAge(28); request.setAttribute("customer", cust2); %> age: ${customer.age } <br> <!-- 1. EL 的 . 或 [] 运算符 --> age: ${sessionScope.customer["age"] } <%-- Customer customer = (Customer)session.getAttribute("customer"); out.print(customer.getAge()); --%> <% Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setName("HXL"); session.setAttribute("com.aff.customer", customer); %> <br> <!-- 如果域对象中的属性名带有特殊字符, 则使用 [] 运算符会很方便. --> name: ${sessionScope["com.aff.customer"].name } </body> </html>





