React基础篇 (3)-- 生命周期
生命周期是react中的重要部分,理解它有助于我们更合理的书写逻辑。
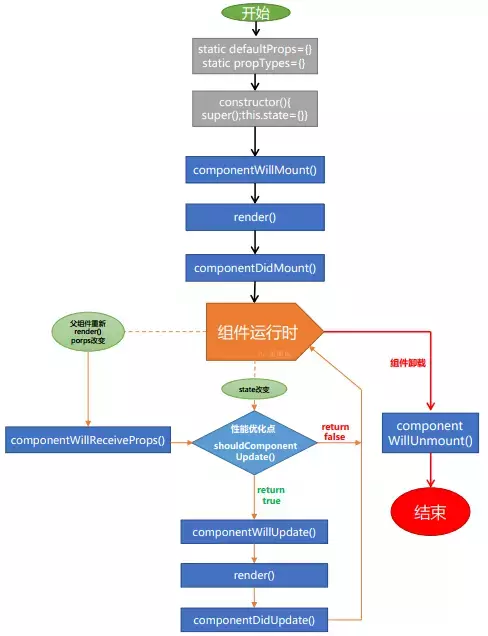
组件的生命周期可分成三个状态:
- Mounting:已插入真实 DOM
- Updating:正在被重新渲染
- Unmounting:已移出真实 DOM
生命周期的方法有:
componentWillMount :在渲染前调用,在客户端也在服务端。
componentDidMount : 在第一次渲染后调用,只在客户端。之后组件已经生成了对应的DOM结构。
可以在这个方法中调用setTimeout, setInterval或者发送AJAX请求等操作(防止异步操作阻塞UI)。
componentWillReceiveProps : 在组件接收到一个新的 prop (更新后)时被调用。这个方法在初始化render时不会被调用。
shouldComponentUpdate : 返回一个布尔值。在组件接收到新的props或者state时被调用。
componentWillUpdate : 在组件接收到新的props或者state但还没有render时被调用。在初始化时不会被调用。
componentDidUpdate : 在组件完成更新后立即调用。在初始化时不会被调用。
componentWillUnmount : 在组件从 DOM 中移除之前立刻被调用。
举例如下:
class Ani extends React.Component {
state={
data:0
}
setNewNumber=()=> {
this.setState({data: this.state.data + 1})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick = {this.setNewNumber}>INCREMENT</button>
<Content myNumber = {this.state.data}></Content>
</div>
);
}
}
class Content extends React.Component {
componentWillMount() {
console.log('Component WILL MOUNT!')
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('Component DID MOUNT!')
}
componentWillReceiveProps(newProps) {
console.log('Component WILL RECEIVE PROPS! newProps:',newProps)
}
shouldComponentUpdate(newProps, newState) {
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log('Component WILL UPDATE!');
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log('Component DID UPDATE!')
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('Component WILL UNMOUNT!')
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>{this.props.myNumber}</h3>
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Ani/>,document.getElementById("app"))
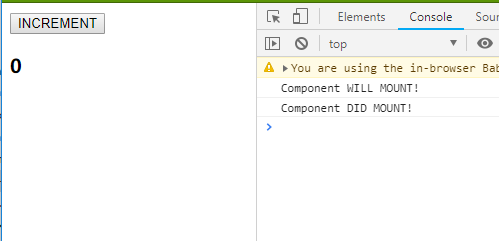
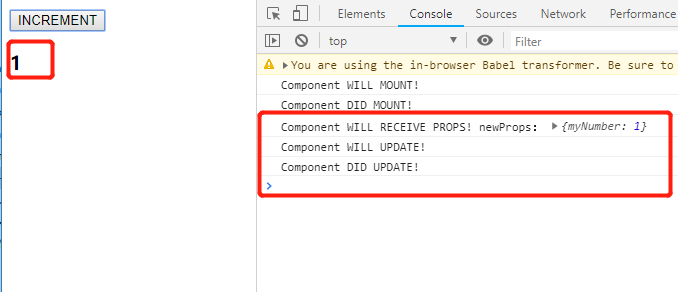
结果:
初始化:
更新状态:
参考文档:https://react.docschina.org/docs/state-and-lifecycle.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号