20192312吴欣欣 哈夫曼编码实践 实验报告
20192312 2020-2021-1 实验七 《查找与排序》实验报告
课程:《程序设计与数据结构》
班级: 1923
姓名: 吴欣欣
学号:20192312
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2020年12月10日
必修/选修: 必修
1.实验内容
设有字符集:S={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j,k,l,m,n.o.p.q,r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z}。
给定一个包含26个英文字母的文件,统计每个字符出现的概率,根据计算的概率构造一颗哈夫曼树。
并完成对英文文件的编码和解码。
要求:
(1)准备一个包含26个英文字母的英文文件(可以不包含标点符号等),统计各个字符的概率
(2)构造哈夫曼树
(3)对英文文件进行编码,输出一个编码后的文件
(4)对编码文件进行解码,输出一个解码后的文件
(5)撰写博客记录实验的设计和实现过程,并将源代码传到码云
(6)把实验结果截图上传到云班课
2.实验过程及结果
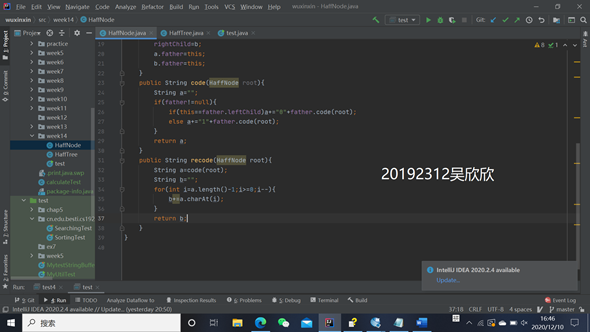
1.编写结点类,除叶子结点,既字母外,其他结点权重为子结点权重之和。同时实现对节点的编码。
package week14;
public class HaffNode<T>{
char data;
int weight;
HaffNode father,leftChild,rightChild;
public HaffNode(char s){
this.data=s;
weight=0;
father=null;
leftChild=null;
rightChild=null;
}
public HaffNode(HaffNode a,HaffNode b){
this.data=' ';
weight=a.weight+b.weight;
father=null;
leftChild=a;
rightChild=b;
a.father=this;
b.father=this;
}
public String code(HaffNode root){//逆向编码
String a="";
if(father!=null){
if(this==father.leftChild)a+="0"+father.code(root);
else a+="1"+father.code(root);
}
return a;
}
public String recode(HaffNode root){
String a=code(root);
String b="";
for(int i=a.length()-1;i>=0;i--){
b+=a.charAt(i);
}
return b;
}
}

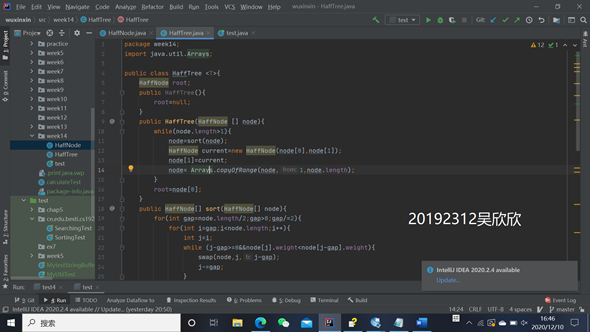
2.编写哈夫曼树,排序后连接权重最小的两结点并插入新结点再排序。
package week14;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HaffTree <T>{
HaffNode root;
public HaffTree(){
root=null;
}
public HaffTree(HaffNode [] node){
while(node.length>1){
node=sort(node);
HaffNode current=new HaffNode(node[0],node[1]);
node[1]=current;
node= Arrays.copyOfRange(node,1,node.length);
}
root=node[0];
}
public HaffNode[] sort(HaffNode[] node){
for(int gap=node.length/2;gap>0;gap/=2){
for(int i=gap;i<node.length;i++){
int j=i;
while (j-gap>=0&&node[j].weight<node[j-gap].weight){
swap(node,j,j-gap);
j-=gap;
}
}
}
return node;
}
public void swap(HaffNode [] node,int a,int b){
HaffNode temp;
temp=node[a];
node[a]=node[b];
node[b]=temp;
}
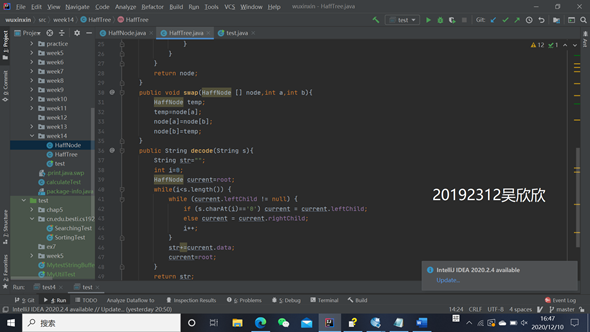
public String decode(String s){//解码
String str="";
int i=0;
HaffNode current=root;
while(i<s.length()) {
while (current.leftChild != null) {
if (s.charAt(i)=='0') current = current.leftChild;
else current = current.rightChild;
i++;
}
str+=current.data;
current=root;
}
return str;
}
}
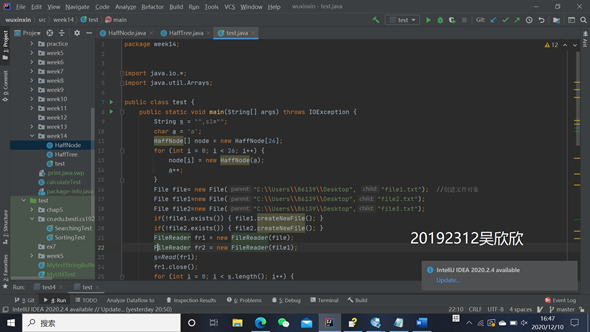
3.测试代码
package week14;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String s = "",s1="";
char a = 'a';
HaffNode[] node = new HaffNode[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
node[i] = new HaffNode(a);
a++;
}
File file= new File("C:\\Users\\86139\\Desktop", "file1.txt"); //创建文件对象
File file1=new File("C:\\Users\\86139\\Desktop","file2.txt");
File file2=new File("C:\\Users\\86139\\Desktop","file3.txt");
if(!file1.exists()) { file1.createNewFile(); }
if(!file2.exists()) { file2.createNewFile(); }
FileReader fr1 = new FileReader(file);
FileReader fr2 = new FileReader(file1);
s=Read(fr1);
fr1.close();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int num = s.charAt(i) - 'a';
node[num].weight++;
}
HaffNode[] node1 = Arrays.copyOf(node, node.length);
FileWriter fw1=new FileWriter(file1);
FileWriter fw2=new FileWriter(file2);
String code = "";
HaffTree tree = new HaffTree(node1);
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int num = s.charAt(i) - 'a';
code += node[num].recode(tree.root);
}
fw1.write(code);
fw1.close();
s=Read(fr2);
fr2.close();
fw2.write(tree.decode(s));
fw2.close();
}
public static String Read(FileReader fr) throws IOException {
String s="";
char[] data = new char[26];
int length =0;
while ((length = fr.read(data)) > 0) {
s+= new String(data, 0, length);
}
return s;
}
}

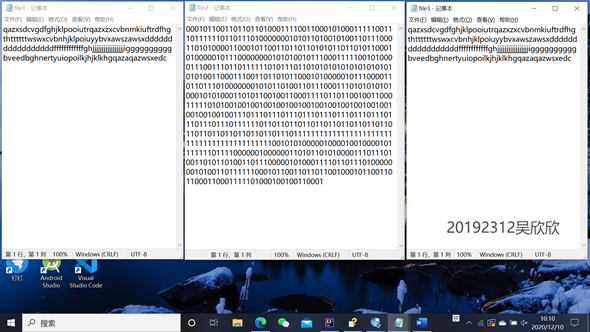
3.心得体会
巩固了File,以及FileReader等知识,同时又重新回顾了排序的相关内容。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号