Linux内核_IO宏
Linux内核_IO系列宏主要用于创建实现驱动接口“ioctl()”传递的命令变量(cmd),使用该宏可以区别应用程序传入的cmd请求方式和内容,如数据传递方向、可读、可写等。
1.命令码
在使用_IO宏之前,有必要知道ioctl传递命令码(cmd)含义。Linux内核定义了cmd值是以一个32bit的整型数表示,把32bit划分为4块区域,每块区域表示不同的含义,如图表示。
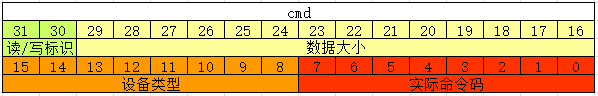
【1】bit7~bit0,实际命令序号,称为“基数域”。
【2】bit15~bit8,设备类型,用于区别不同驱动设备,称为“魔数域”。
【3】bit29~bit15, 命令码传输数据大小,即“ ioctl()”函数 中的 arg 变量的内存大小。
【4】bit31~bit30,用于区分该命令的数据传输方式,读或者写。
2._IO宏
2.1 置位_IO宏
在理解cmd码的含义及分布区域后,实质上,置位_IO宏就是Linux内核定义出来方便用户编写驱动程序时,对命令码的某一bit或者多bit置位。置位_IO系列宏定义有4个,应用于不同场合。
| 宏 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| _IO(type,nr) | 创建不带参数cmd,只传输命令 |
| _IOR(type,nr,size) | 创建从设备读取数据cmd |
| _IOW(type,nr,size) | 创建往设备写入数据cmd |
| _IOW(type,nr,size) | 创建双向传输数据cmd |
【1】4个函数分别用于不同场合,对应cmd“读写标识”。
【2】参数“type”表示cmd“魔数区域”。魔数范围为 0~255 。魔数一般使用英文字符 (包括大小写)来表示。设备驱动程序从应用程序传递进来的命令获取魔数,与自身待处理的魔数比较,相同则执行相关操作。不同的设备驱动程序最好设置不同的魔数,但并不是要求绝对,也是可以使用其他设备驱动程序已用过的魔数。
【3】参数“nr”表示cmd“基数区域”,即不同的命令序号。不同命令序号最好使用不同的序号,但也可以使用相同的,设备驱动使用时可以通过cmd其他区域判断。
【4】参数“size”表示cmd命令大小,使用时只需填参数类型即可,宏内已经调用“sizeof()”计算大小。
_IO宏原型位于Linux内核“/includ/asm-generic/ioctl.h”下。
#ifndef _ASM_GENERIC_IOCTL_H
#define _ASM_GENERIC_IOCTL_H
/* ioctl command encoding: 32 bits total, command in lower 16 bits,
* size of the parameter structure in the lower 14 bits of the
* upper 16 bits.
* Encoding the size of the parameter structure in the ioctl request
* is useful for catching programs compiled with old versions
* and to avoid overwriting user space outside the user buffer area.
* The highest 2 bits are reserved for indicating the ``access mode''.
* NOTE: This limits the max parameter size to 16kB -1 !
*/
/*
* The following is for compatibility across the various Linux
* platforms. The generic ioctl numbering scheme doesn't really enforce
* a type field. De facto, however, the top 8 bits of the lower 16
* bits are indeed used as a type field, so we might just as well make
* this explicit here. Please be sure to use the decoding macros
* below from now on.
*/
#define _IOC_NRBITS 8
#define _IOC_TYPEBITS 8
/*
* Let any architecture override either of the following before
* including this file.
*/
#ifndef _IOC_SIZEBITS
# define _IOC_SIZEBITS 14
#endif
#ifndef _IOC_DIRBITS
# define _IOC_DIRBITS 2
#endif
#define _IOC_NRMASK ((1 << _IOC_NRBITS)-1)
#define _IOC_TYPEMASK ((1 << _IOC_TYPEBITS)-1)
#define _IOC_SIZEMASK ((1 << _IOC_SIZEBITS)-1)
#define _IOC_DIRMASK ((1 << _IOC_DIRBITS)-1)
#define _IOC_NRSHIFT 0
#define _IOC_TYPESHIFT (_IOC_NRSHIFT+_IOC_NRBITS)
#define _IOC_SIZESHIFT (_IOC_TYPESHIFT+_IOC_TYPEBITS)
#define _IOC_DIRSHIFT (_IOC_SIZESHIFT+_IOC_SIZEBITS)
/*
* Direction bits, which any architecture can choose to override
* before including this file.
*/
#ifndef _IOC_NONE
# define _IOC_NONE 0U
#endif
#ifndef _IOC_WRITE
# define _IOC_WRITE 1U
#endif
#ifndef _IOC_READ
# define _IOC_READ 2U
#endif
#define _IOC(dir,type,nr,size) \
(((dir) << _IOC_DIRSHIFT) | \
((type) << _IOC_TYPESHIFT) | \
((nr) << _IOC_NRSHIFT) | \
((size) << _IOC_SIZESHIFT))
#ifdef __KERNEL__
/* provoke compile error for invalid uses of size argument */
extern unsigned int __invalid_size_argument_for_IOC;
#define _IOC_TYPECHECK(t) \
((sizeof(t) == sizeof(t[1]) && \
sizeof(t) < (1 << _IOC_SIZEBITS)) ? \
sizeof(t) : __invalid_size_argument_for_IOC)
#else
#define _IOC_TYPECHECK(t) (sizeof(t))
#endif
/* used to create numbers */
#define _IO(type,nr) _IOC(_IOC_NONE,(type),(nr),0)
#define _IOR(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))
#define _IOW(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))
#define _IOWR(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ|_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))
#define _IOR_BAD(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ,(type),(nr),sizeof(size))
#define _IOW_BAD(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),sizeof(size))
#define _IOWR_BAD(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ|_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),sizeof(size))
/* used to decode ioctl numbers.. */
#define _IOC_DIR(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_DIRSHIFT) & _IOC_DIRMASK)
#define _IOC_TYPE(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_TYPESHIFT) & _IOC_TYPEMASK)
#define _IOC_NR(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_NRSHIFT) & _IOC_NRMASK)
#define _IOC_SIZE(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_SIZESHIFT) & _IOC_SIZEMASK)
/* ...and for the drivers/sound files... */
#define IOC_IN (_IOC_WRITE << _IOC_DIRSHIFT)
#define IOC_OUT (_IOC_READ << _IOC_DIRSHIFT)
#define IOC_INOUT ((_IOC_WRITE|_IOC_READ) << _IOC_DIRSHIFT)
#define IOCSIZE_MASK (_IOC_SIZEMASK << _IOC_SIZESHIFT)
#define IOCSIZE_SHIFT (_IOC_SIZESHIFT)
#endif /* _ASM_GENERIC_IOCTL_H */
2.2 取位_IO宏
同理,取位_IO宏就是用于检查应用程序传入命令码的属性,判断与预期的命令码属性对比,一致则执行对应操作,从上述源码也可看出。
| 宏 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| _IOC_DIR | 检查cmd读写属性 |
| _IOC_TYPE | 检查cmd设备类型(魔数) |
| _IOC_NR | 检查cmd序号(基数) |
| _IOC_SIZE | 检查cmd传输数据大小 |
3.应用
例如,我们实现一个LED驱动程序的“ioctl”接口,通过传入不同命令码控制LED状态。
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <mach/gpio.h>
#include <mach/regs-gpio.h>
#include <plat/gpio-cfg.h>
#define LED_RD _IOR('L', 0x0, int)
#define LED_WR _IOW('L', 0x01, int)
#define DEVICE_NAME "DEV_LED"
#define LED_NO S5PV210_GPJ2(0)
static long led_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int temp = 0;
if(_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != 'L')
{
printk("cmd of type error\n");
return 0;
}
switch(cmd)
{
case LED_RD:
break;
case LED_WR:
if(IOC_OUT(cmd))
{
if(copy_from_user(&temp, (int __user*)arg, 4))
{
return -ENOTTY;
}
gpio_set_value(LED_NO, temp);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations led_dev_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.unlocked_ioctl = led_ioctl,
};
static struct miscdevice led_dev = {
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,
.name = DEVICE_NAME,
.fops = &led_dev_fops,
};
static int __init led_dev_init(void)
{
int ret;
ret = gpio_request(LED_NO, "LED");
if (ret)
{
printk("%s: request GPIO %d for LED failed, ret = %d\n", DEVICE_NAME, LED_NO, ret);
return ret;
}
s3c_gpio_cfgpin(LED_NO, S3C_GPIO_OUTPUT);
gpio_set_value(LED_NO, 1);
ret = misc_register(&led_dev);
return ret;
}
static void __exit led_dev_exit(void)
{
gpio_free(LED_NO);
misc_deregister(&led_dev);
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
module_init(led_dev_init);
module_exit(led_dev_exit);



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号