基于校园网络问题的最小生成树的两种算法
 题目背景:
题目背景:
学校有10个学院,3个研究所,1个大型图书馆,4所实验室,现在知道他们之间的距离,想在他们之间建设网线,求最小的花费
这题暑假根本没看,不过最近正好在研究图论和树,今晚就不打游戏了,继续写博客提升自己的认识水平吧。
拿到这题一看就知道要求最小的花费,肯定是最小生成树问题了啊,最小生成树问题不存在环路的,也就是当前节点不可能通过自身或者别的节点回到自己
如何保证不能回到自身节点呢?
我们采用一种放法,叫做避圈法:在生成树的过程中,我们把已经生成树中的节点看成一个集合,把剩下的节点看成另一个集合,从连接两个集合中选取最小边即可(这里的集合就是连通分量)
最小生成树有两种算法:Prim算法和kruskal算法
首先我们先说说Prim算法:
Prim算法步骤:
我直接附上一张到来的图吧

步骤
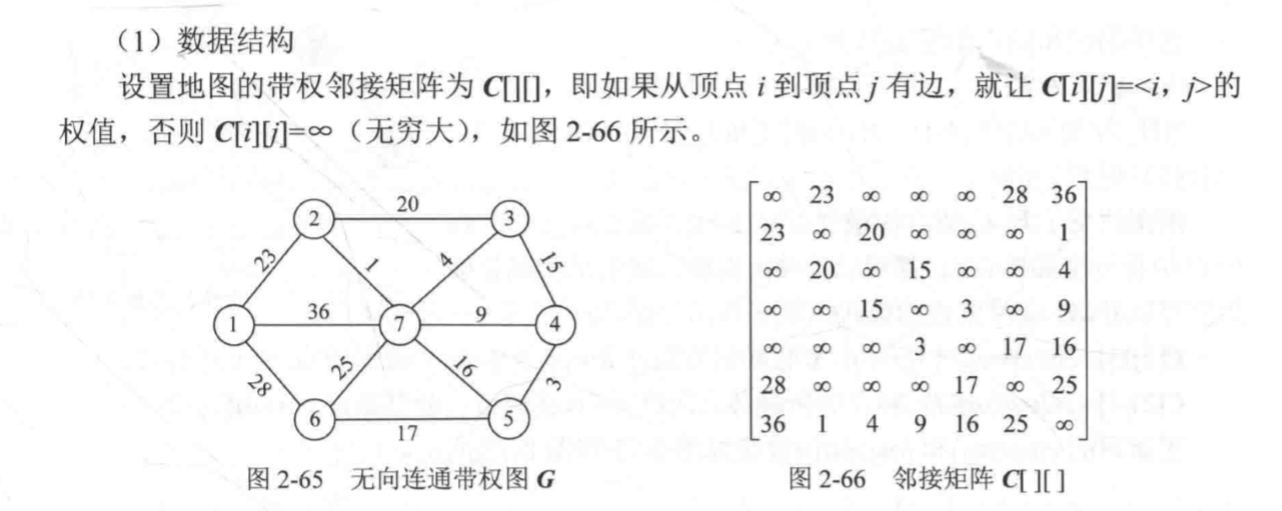
1: 确定合适的数据结构用邻接矩阵来存储图,就是矩阵的存储图的权值,要是存在边(u,x)那么G(u,x)=边上权值,bool 数组s[],如果s[i]=true;表示定点i加入了集合V
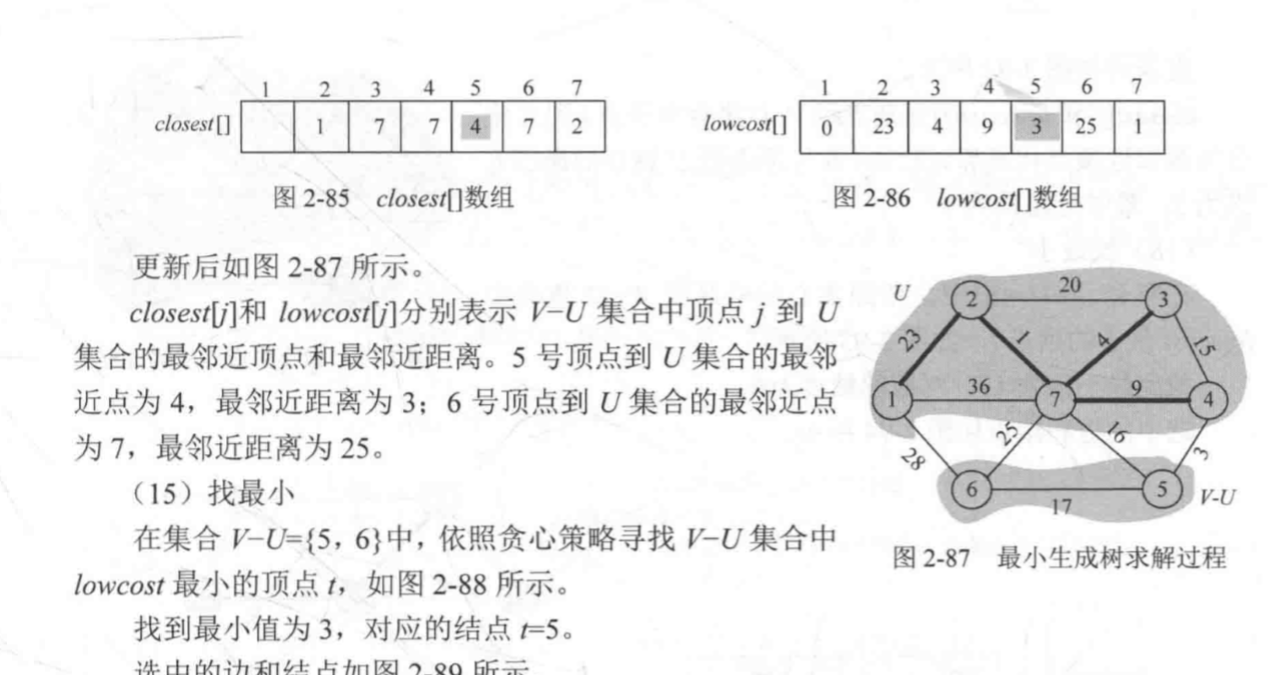
从图上可以直观地看出那些是最小的边,但是如何实现呢?这里可以设置两个数组,一个closeset[j],用来表示u-v中的定点j到达集合U最近的节点,另一个数组为lowcost[j]表示
v-u集合中定点j到达集合u的最小权值
2:初始化邻接矩阵G,数组closest[],lowcost[]和s[]
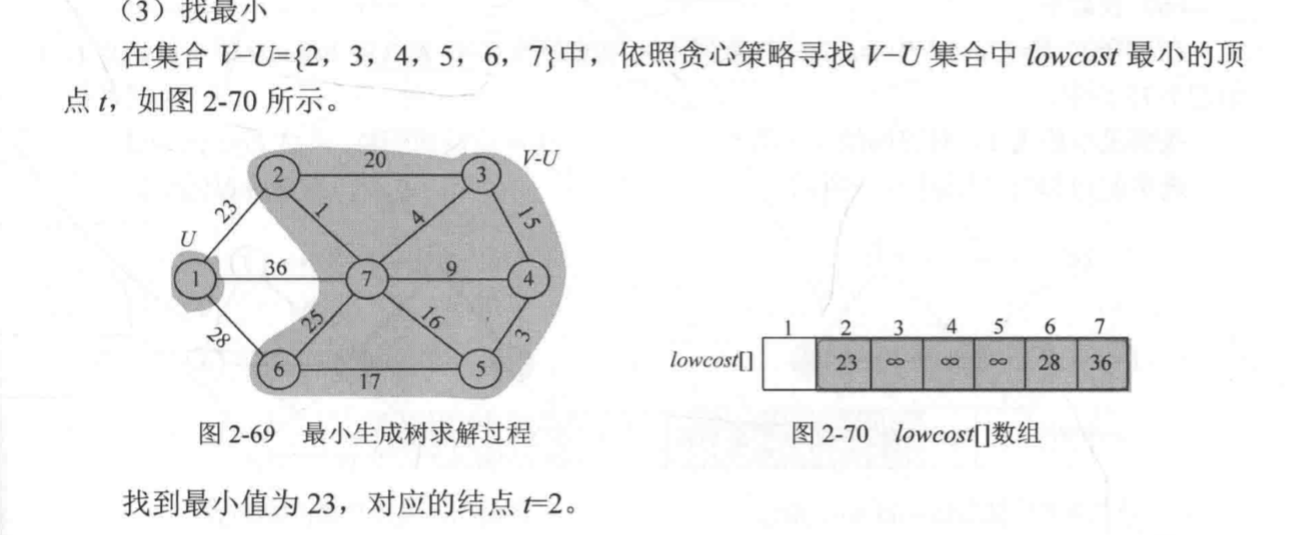
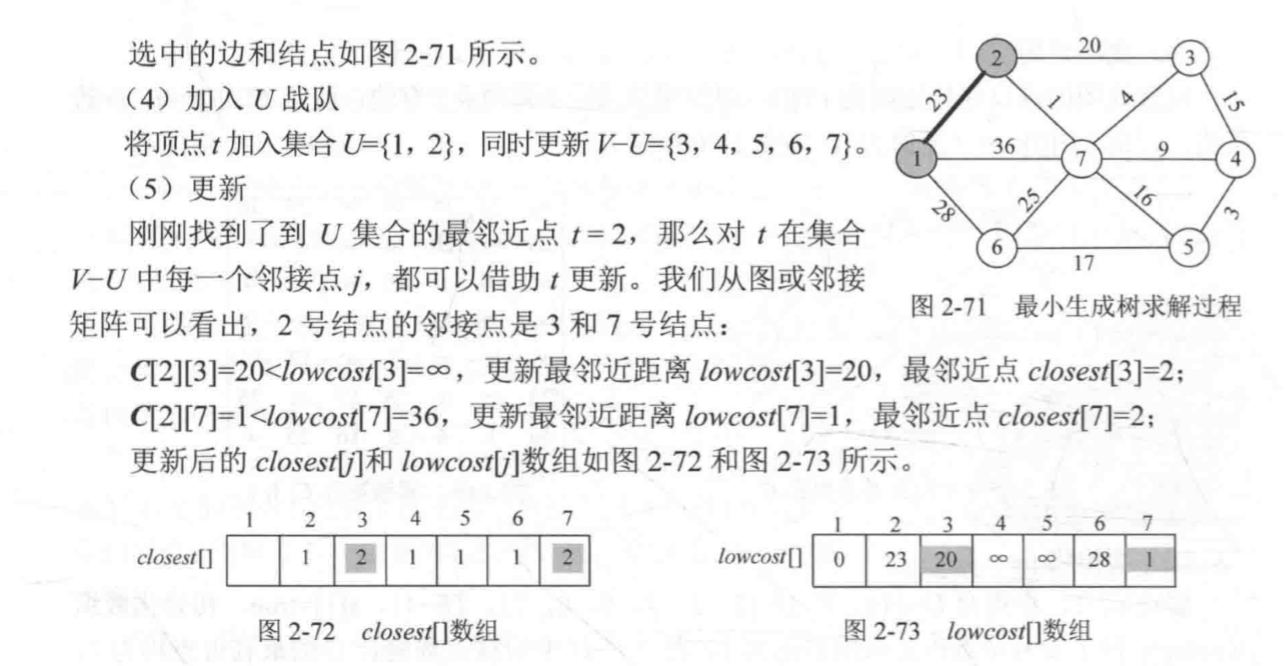
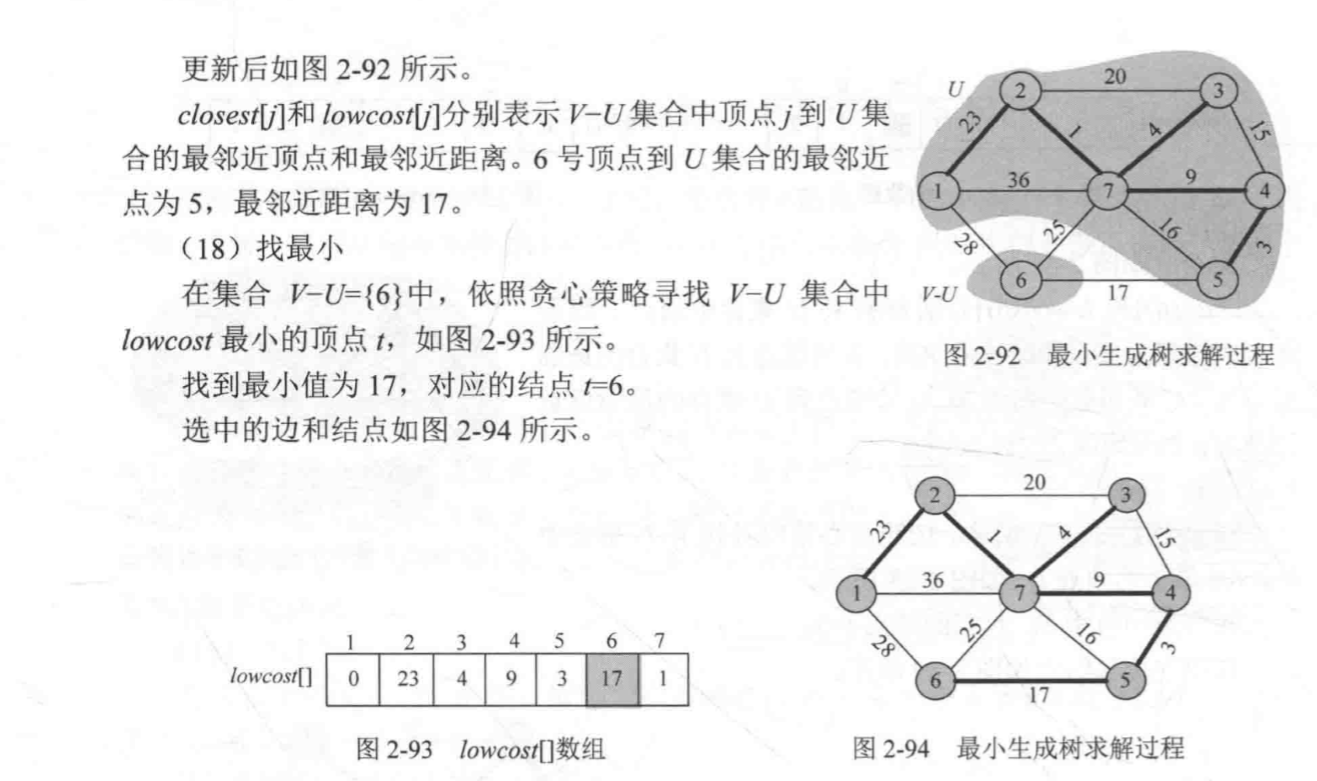
3:从定点u0开始,寻找距离u0最近的v-u集合中的顶点t,并更新两个数组和一个s数组
4:将顶点t加入集合u中
5:如果集合v-u,算法结束,否则,跳转步骤6
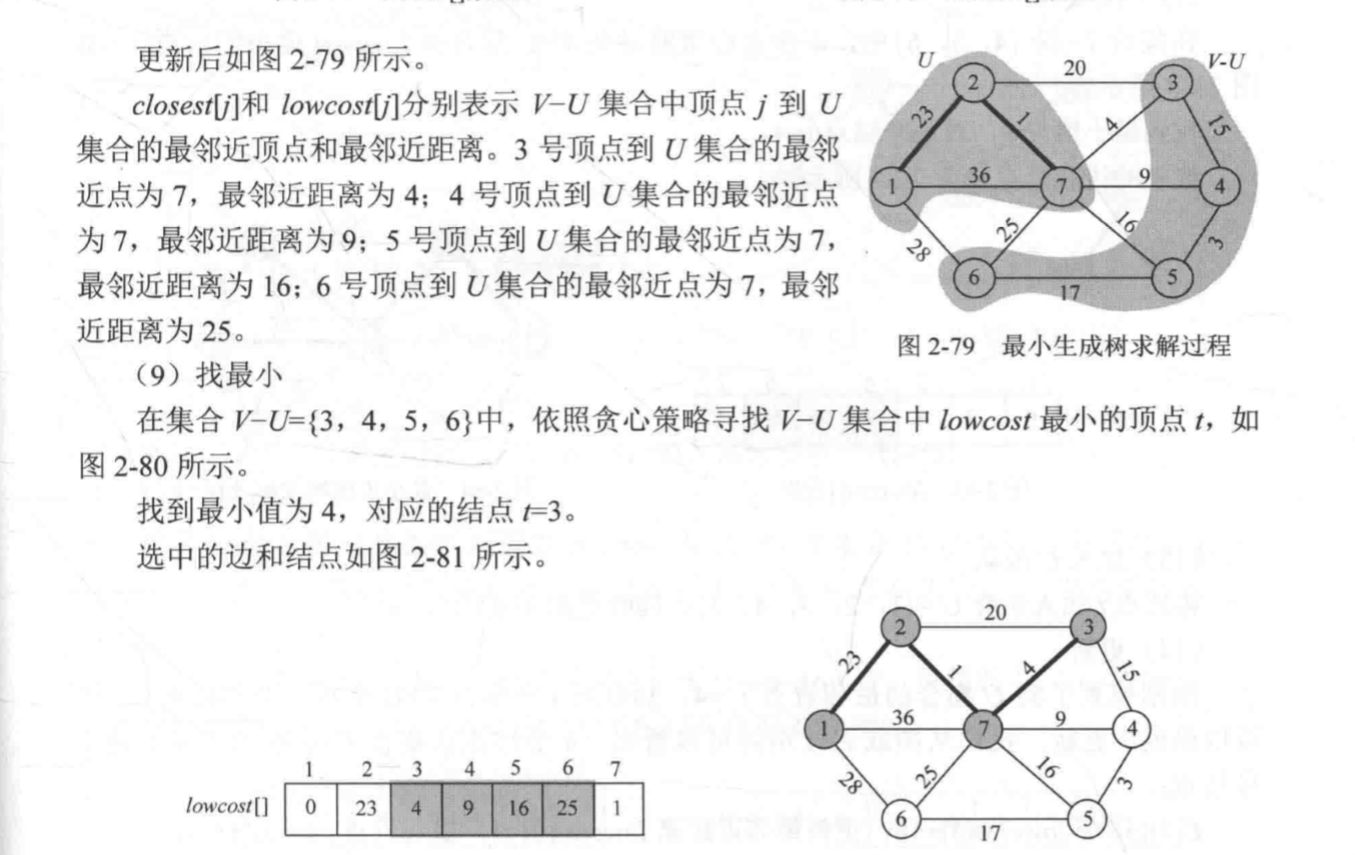
6:对于集合v-u中的所有顶点j,更新lowcost和closest,并转到步骤3
图解(太懒了,还是盗图来的快,哈哈哈):







实现代码:(有点问题,过几天再改)
#include<iostream> using namespace std; const int INF=100000; const int N=100; bool s[N]; int colsest[N]; int lowcost[N]; void Prim(int n,int u,int c[N][N]) { int i,j; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(i!=u) { colsest[i]=u; lowcost[i]=c[u][i]; s[i]=false; } else lowcost[i]=0; } s[u]=true; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { int temp=INF; int t=u; for(j=1;j<=n;j++) { if(!s[j]&&lowcost[j]<temp) { temp=lowcost[j]; t=j; } } if(t==u) break; s[t]=true; for(j=1;j<=n;j++) { if(!s[j]&&lowcost[j]<c[t][j]) { lowcost[j]=c[t][j]; colsest[j]=t; } } } } int main() { int c[N][N]; int n,m,u,v,w; int u0; cout<<"Please enter the number of node and edge"<<endl; cin>>n>>m; int sumcost=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) c[i][j]=INF; cout<<"Please enter the num of u v w"<<endl; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { cin>>u>>v>>w; c[u][v]=c[v][u]=w; } cout<<"Please enter u0 at random"<<endl; cin>>u0; Prim(n,u0,c); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { sumcost+=lowcost[i]; } cout<<"The mininum of the cost"<<endl; cout<<sumcost<<endl; return 0; }
另一种方法是利用kruskal算法,这种算法的时间复杂度当然比Prim算法低啦
首先kruskal算法用的也是一种贪心策略,不过它的实现是通过并查集啦,kruskal与prim区别
kruskal是通过找最小边,通过边联通两个分量以至于不会有环产生,而Prim是找顶点相邻的最近点
直白的说就是一个是通过边找点,另一个就是通过点找边
既然要利用并查集,那我好像还要在写一写并查集的文章了,哈哈哈,督促与激励一下自己吧
这种方法我就直接附上代码吧(步骤在注释中)
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N=100; int n,m; int father[N]; struct Edge{ int u,v,w; }e[N*N]; bool cmp(Edge a,Edge b) { return a.w<b.w; } void Init(int n) { for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) father[i]=i; } int Find(int x) { if(x==father[x]) return x; else return father[x]=Find(father[x]); } void Merge(int a,int b) { int ta=Find(a); int tb=Find(b); if(ta==tb) return ; if(ta>tb) father[ta]=tb; else father[tb]=ta; } int kruskal(int n) { sort(e,e+m,cmp); int ans=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(Merge(e[i].u,e[i].v)) { ans+=e[i].w; n--; if(n==1) return ans; } } return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号