【人工智能】遗传算法求解振荡不收敛函数在区间内的最值
写在前面:本博客为本人原创,严禁任何形式的转载!本博客只允许放在博客园(.cnblogs.com),如果您在其他网站看到这篇博文,请通过下面这个唯一的合法链接转到原文!
本博客全网唯一合法URL:http://www.cnblogs.com/acm-icpcer/p/8932874.html
(本篇博客的数学推导参考了:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27755195/article/details/56597467,源码为我自己所写)
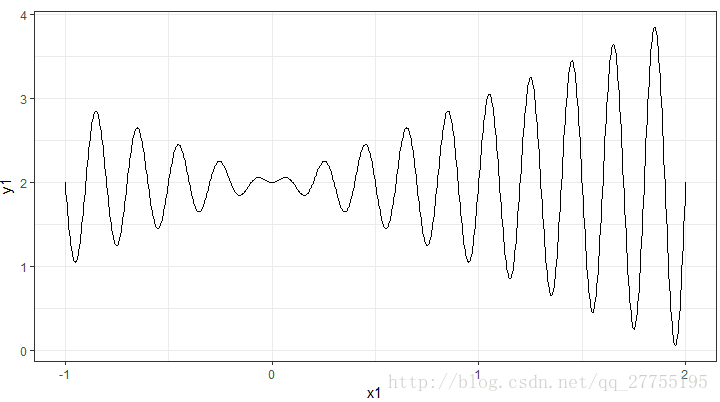
对于发散函数:f(x)=x∗sin(10∗π∗x)+2,x属于[1,2],求其在定义域上的最大值及坐标点。
先看函数图像:
f
很明显的震荡函数,对计算机来说,当给定区间很大的时候,即使求一阶导数找到驻点,并求函数在驻点处的值,由于驻点会很多,所以本质上来说这还是暴力求解法。
当然了,对于计算机来说,使用泰勒展开式求解也是可以的,但是如果对精度有要求的话,选择佩亚诺型余项的等价无穷小的阶数也是个很头疼的问题。
那么如果使用遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm,GA)来求解,先在给定区间均匀铺开一堆点,观察点集的收敛状况,我们可以看出:
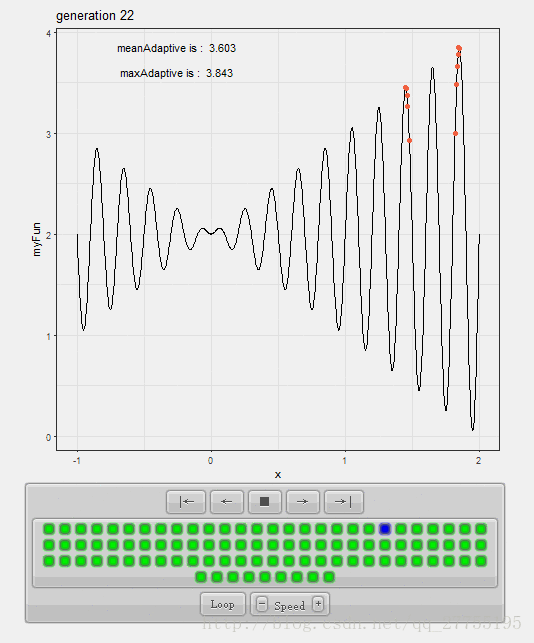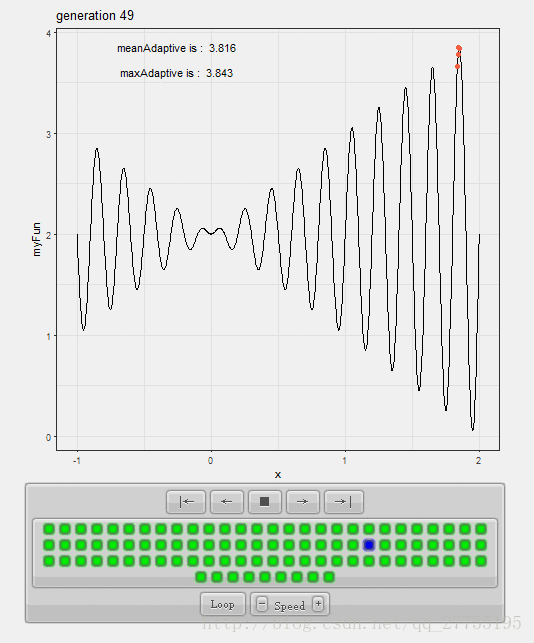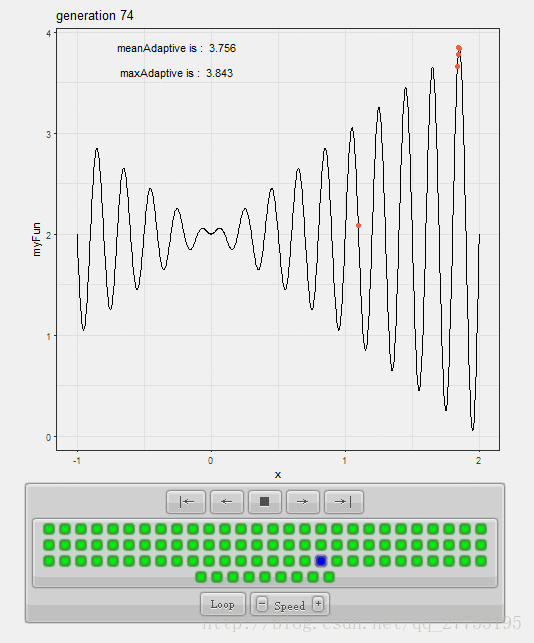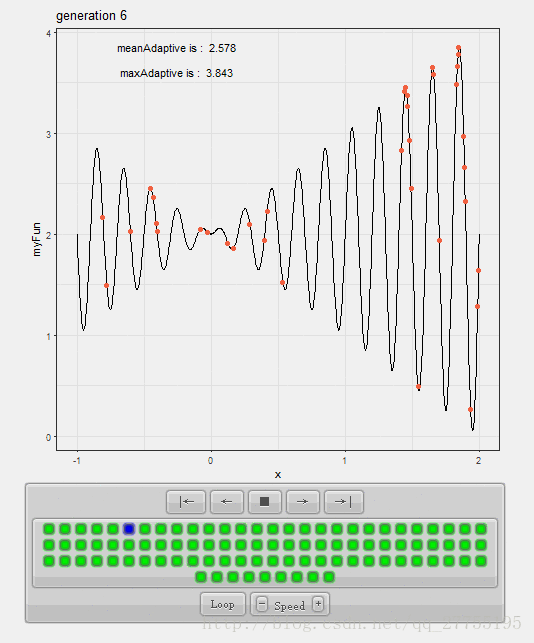
点集的收敛速度极快,并且时间花费很少,故而表现出一定的智能性。
虽然很容易陷入局部最优,但是我改进了算法,使用了将点集按fitness值递减排序+提高点集基因型的变异概率,对于解决此问题的效果反映良好。
现就遗传算法的各个概念阐述我对运用其求解问题的思想:
1、种群(Population):种群是指用遗传算法求解问题时,初始给定的多个解的集合。遗传算法的求解过程是从这个子集开始的。在此问题中,种群就是我在前面说的均匀铺开的点集。
2、个体(Individual):个体是指种群中的单个元素,它通常由一个用于描述其基本遗传结构的数据结构来表示。对于单个点,抽象成一个点类,其包含一系列的操作及数据成员。核心的数据成员是:点的x、y值(x为取值为1~2的浮点数。其中,y值还充当fitness度量),以及x值的二进制编码字符串;核心的函数成员是:根据x的二进制编码字符串更新x的值的函数,根据x的值更新x的二进制编码字符串的函数,以及根据x的值求对应的y值的函数。
3、染色体(Chromos):染色体是指对个体进行编码后所得到的编码串。其中的每1位称为基因,若干个基因构成的一个有效信息段称为基因组。在此问题中,染色体就是2中提到的二进制编码字符串。
4、适应度(Fitness)函数:适应度函数是一种用来对种群中各个个体的环境适应性进行度量的函数。在此问题中,适应度函数直接用点的y值来充当。
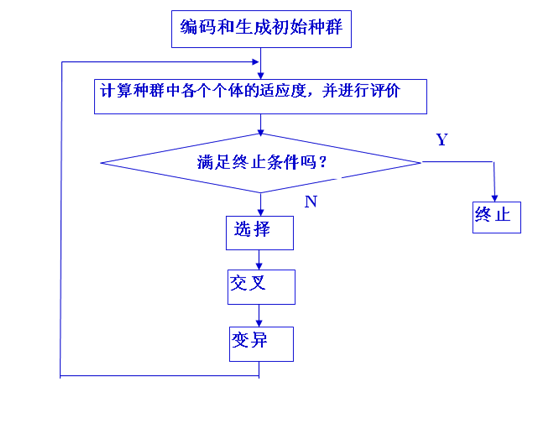
5、遗传操作(Genetic Operator):遗传操作是指作用于种群而产生新的种群的操作。标准的遗传操作包括以下3种基本形式:
(1)选择(Selection):选择表现型优秀的个体取代表现型差的个体,即实现淘汰。因为在求解时我使用的点集的点格式上限为100,所以我制定的策略是每次选择表现最优的前40个个体两两交叉,产生20个新的个体去替代表现最差的后20个个体。
(2)交叉(Crosssover):即选择两个个体的染色体的基因进行互换。在此,因为我使用的基因长度为20个字符,所以我通过调用5次随机函数生成5个位置,令这5个位置的字符进行交换。即二进制多随机点交叉。
(3)变异(Mutation):变异即随机选择个体令其染色体的基因进行改变。变异的存在是为了保留产生新的更优解的可能性,即“柳暗花明又一村”,并且在一定程度上防止点集陷入局部最优的情况。在此问题中,我使用的变异策略是:每一次迭代更新种群时,让每一个个体都有一定的相等概率随机改变其基因型中的一节。
6、迭代终止条件:从简处理,令其迭代100次就停止。实验证明,6次迭代基本上就能收敛到最优解。
流程图:
f
Basic application of Genetic Algorithm(sample source code;TZ,All Rights Reserved):
/* this code was first initiated by TZ,COI,HZAU contact email:xmb028@163.com personal website:wnm1503303791.github.io personal blogs:www.cnblogs.com/acm-icpcer/ this code has been posted on my personal blog,checking URL:www.cnblogs.com/acm-icpcer/p/8932874.html Copyright 2018/4/22 TZ. All Rights Reserved. */ //mission:求发散函数f(x)=x*sin(10*pi*x)+2在[1,2]上能取到的最大值 #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include<bitset> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<set> #include<list> #include<deque> #include<map> #include<queue> #include<ctime> using namespace std; const double PI=3.14/*15926535897932384626*/; class point { private: double x,y; public: char d_a[21];//digital x point() { d_a[20]='\0'; } double getx() { return x; } double setx(double mx) { x=mx; } double gety() { return y; } double sety(double my)//not being used { y=my; } bool renew_x()//renew x accroding to d_a { double x1=1; for(int i=2;i<20;i++) { if(d_a[i]=='1') { x1+=pow(2,-(i-1)); } else continue; } x=x1; return true; } bool renew_y()//renew y accroding to x { y=x*sin(10*PI*x)+2; return true; } bool renew_d_a()//renew d_a accroding to x { double a=x-1; d_a[0]='1'; d_a[1]='.'; for(int i=2;i<20;i++) { a=a*2; if(a>=1) { d_a[i]='1'; a-=1; } else d_a[i]='0'; } return true; } }; bool y_sort(point p[]) { for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { double max=p[i].gety(); int key=i; for(int j=i+1;j<100;j++) { if(p[j].gety()>max) { max=p[j].gety(); key=j; } } point temp=p[i]; p[i]=p[key]; p[key]=temp; } return true; } //令fitness函数排名前40的个体的基因型两两交叉 ,并取代后20名,以此实现进化 bool crossgene(point p[]) { srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); point new_general[20]; int t=0; //j=0,2,4,...,,38 for(int i=0;i<20;i++) { new_general[i]=p[t]; t+=2; } t=1;//reuse the 't' variable for(int i=0;i<20;i++) { //多点随机交叉5次 for(int j=0;j<5;j++) { int position=rand()%20; if(position>=2)//从字符串第三位开始交叉 { new_general[i].d_a[position]=p[t].d_a[position]; } } t+=2;//j=1,3,5,...,39 } for(int i=0;i<20;i++) { new_general[i].renew_x(); new_general[i].renew_y(); p[i+80]=new_general[i]; } return true; } //模拟变异过程,以防止局部最优 int variation(point p[]) { srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); int flag=0; for(int i=0;i<100;i++)//每一个个体都有相同的变异概率 { if(rand()%50==1)//设置变异概率为1/50 { //假设每个个体的基因一次变异只改变一节 int position=rand()%20; if(position>=2)//从基因的第三位开始变异 { flag++; if(p[i].d_a[position]=='0') p[i].d_a[position]='1'; else p[i].d_a[position]='0'; } p[i].renew_x(); p[i].renew_y(); } } return flag; } int main() { point pset[100]; for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { pset[i].setx(1+0.01*i); pset[i].renew_y(); pset[i].renew_d_a(); //cout<<pset[i].d_a<<endl; } //present the situation before sorting /* for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { cout<<p[i].gety()<<endl; } */ y_sort(pset); //following code used to present the result after sorting /* cout<<"break testing:"<<endl; for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { cout<<pset[i].gety()<<endl; } cout<<pset[0].getx()<<endl; */ //由于不便找合适的终止条件(我证明了:不管是求一阶导数找驻点还是求二阶导数找拐点都不能找出最值点),故直接令其循环100代以求最佳结果 for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { crossgene(pset); int times=variation(pset); y_sort(pset); cout<<i<<":"<<'('<<pset[0].getx()<<','<<pset[0].gety()<<')'<<endl;//输出每代的最优个体 if(times>0) cout<<"variation happened "<<times<<" times"<<" in this general!"<<endl; } /* cout<<"finall result"<<endl; for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { cout<<pset[i].gety()<<endl; } */ cout<<"the maxium point is:"<<'('<<pset[0].getx()<<','<<pset[0].gety()<<')'<<endl; return 0; }
运行结果:
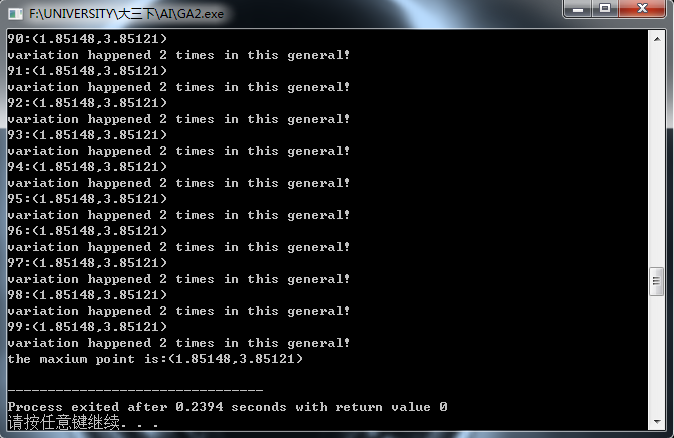
结果令人满意
tz
first posted@COI HZAU,2018/4/24
last updated@COI HZAU,2018/5/8





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY