【C++】二叉树的构建、前序遍历、中序遍历
写在前面:本博客为本人原创,严禁任何形式的转载!本博客只允许放在博客园(.cnblogs.com),如果您在其他网站看到这篇博文,请通过下面这个唯一的合法链接转到原文!
本博客全网唯一合法URL:https://www.cnblogs.com/acm-icpcer/p/10404776.html
按前序遍历次序构建二叉树:
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<fstream> using namespace std; struct tnode { char data; tnode *l,*r; }; class tree { public: tnode *root; tree() { //root=NULL; } tnode* getroot() { return this->root; } bool build(tnode * & root,char *input,int & index) { if(index>=strlen(input)) { return false; } if(input[index]=='#') { root=NULL; index++; } else { root=new tnode; root->data=input[index]; index++; build(root->l,input,index); build(root->r,input,index); } } bool pre_display(tnode *t,fstream &f); }; /* bool tree::build() { root->data='a'; root->l=new tnode(); root->l->data='c'; root->r=new tnode(); root->r->data='b'; return true; } */ /* bool tree::build(tnode * & root,char *input,int & index) { if(index>=strlen(input)) { return false; } if(input[index]=='#') { root=NULL; index++; } else { root=new tnode; root->data=input[index]; index++; build(root->l,input,index); build(root->r,input,index); } } */ bool tree::pre_display(tnode *t,fstream &f) { if(t!=NULL) { f<<t->data<<endl; cout<<t->data<<' '; pre_display(t->l,f); pre_display(t->r,f); } return true; } /* void preOrder(tnode * & root,char *input,int & index) { if(index>=strlen(input)) { return ; } if(input[index]=='#') { root=NULL; index++; } else { root=new tnode; root->data=input[index]; index++; preOrder(root->l,input,index); preOrder(root->r,input,index); } } */ //this function is not belongs to the tree class,writing for test purpose void inOrder(tnode * root) { if(root==NULL) { return ; } inOrder(root->l); cout<<root->data<<" "; inOrder(root->r); } int main() { fstream f("result.txt", ios::out); char buffer[256]; memset(buffer,'\0',strlen(buffer)); tree *mt=new tree(); while(scanf("%s",&buffer)) { int index=0; //cout<<mt->getroot()<<endl<<mt->root<<endl; if(mt->build(mt->root,buffer,index)) { inOrder(mt->getroot()); cout<<endl; mt->pre_display(mt->getroot(),f); } } f.close(); return 0; }
代码运行说明:
手动按照前序输入字符串,每个字符代表一个节点,对于空节点则输入‘#’,程序会输出前序遍历结果和秩序遍历结果。
例如,对于二层满二叉树,输入前序遍历为:ab##c##
输出为:
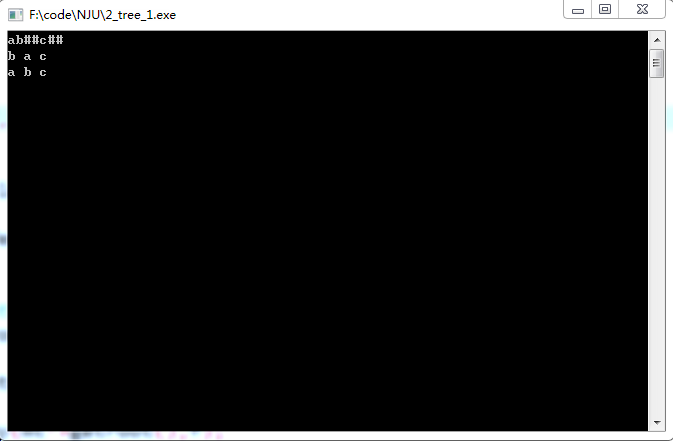
第一行结果为中序遍历,第二行结果为前序遍历。
按行序遍历构建二叉树:
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; const int M=1024; struct node{ char data; node *l; node *r; }; void build(node * & root,char *input,int index) { if(index>=strlen(input)) return ; if(input[index]=='#') root=NULL; else { root=new node(); root->data=input[index]; build(root->l,input,(index+1)*2-1); build(root->r,input,(index+1)*2); } } void pre_display(node *root) { if(root==NULL) return ; cout<<root->data<<" "; pre_display(root->l); pre_display(root->r); } void in_display(node *root) { if(root==NULL) return ; in_display(root->l); cout<<root->data<<" "; in_display(root->r); } int main() { node *tree1=new node(); char data[M]; memset(data,'\0',sizeof(data)); while(scanf("%s",data)) { build(tree1,data,0); pre_display(tree1); cout<<endl; in_display(tree1); } return 0; }

第一行结果为中序遍历,第二行结果为前序遍历。
tz@HZAU
2019/2/20


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号