并查集【合并 Union、查询 Find】
并查集(Disjoint-set data structure):不交集数据结构
处理一些不交集(Disjoint sets,一系列没有重复元素的集合)和合并与查询
1. 并查集支持的操作
1.1 查询
查询某个元素属于哪个集合,通常返回集内的一个 ”代表元素“。===> 为了判断2个元素是否在同一集合中
1.2 合并
将2个集合合并成一个
1.3 添加
添加一个新集合,其中有一个新元素
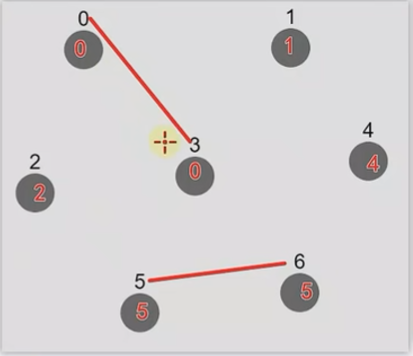
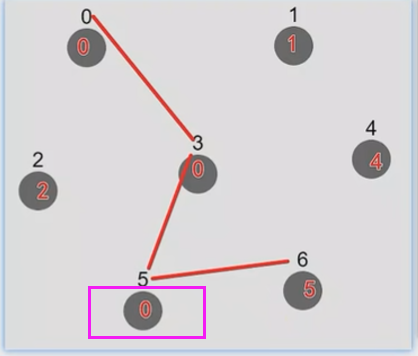
Union方法:让2个原本不相交的集合,让其相交 ===> 在这2个集合中选出一个新的老大
- 原来 0 是集合1的老大,5是集合2的老大
- 现在我们指定0为最终的新老大,那么原来的5就得改成0了
现在要建立 0 --> 5 的联系,这时注意:我们不能直接将 3 指向 5,而是先找到 3 的老大 0 ,让0 去指向 5
习题
297. We are a Team
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {
static int[] arr;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt(); // n 个人
int m = in.nextInt(); // m 条消息
if (n < 1 || n >= 100000 || m < 1 || m >= 100000){
System.out.println("NULL");
return;
}
arr = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
int c = in.nextInt();
if (!isValid(a, b, c, n)){
System.out.println("da pian zi");
continue;
}
if (c == 0){
union(a, b);
continue;
}
if (find(a) == find(b)){
System.out.println("we are a team");
continue;
}
System.out.println("we are not a team");
}
}
public static int find(int x){
if (x == arr[x]){
return x;
}
return arr[x] = find(arr[x]);
}
public static void union(int x, int y){
int f1 = find(x);
int f2 = find(y);
if (f1 != f2){
arr[f2] = f1;
}
}
public static boolean isValid(int a, int b, int c, int n){
if (c != 1 && c != 0){
return false;
}
if (a < 1 || a > n){
return false;
}
if (b < 1 || b > n){
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
231. 图像物体的边界【解像素1是否联通的并查集求解 ===> 双重循环】
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {
static int[][] arr;
static int[] temp;
static int[][] offsets = {{0, 1}, {1, 1}, {1, 0}, {1, -1}, {0, -1}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 0}, {-1, 1}};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int row = in.nextInt();
int col = in.nextInt();
arr = new int[row][col];
int res = 0;
List<Dir> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
arr[i][j] = in.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] == 5){
for (int[] offset : offsets) {
int x = i + offset[0];
int y = j + offset[1];
if (x >= 0 && x < row && y >= 0 && y < col && arr[x][y] == 1){
list.add(new Dir(x, y));
res++;
}
}
}
}
}
temp = new int[res];
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
temp[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Dir dir1 = list.get(i);
for (int j = i + 1; j < list.size(); j++) {
Dir dir2 = list.get(j);
if (union(dir1.x, dir1.y, dir2.x, dir2.y, i, j)){
res--;
}
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
public static int find(int x){
if (x == temp[x]){
return x;
}
return find(temp[x]);
}
public static boolean union(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int order1, int order2){
if (Math.abs(x1 - x2) <= 1 && Math.abs(y1 - y2) <= 1){
int f1 = find(order1);
int f2 = find(order2);
if (f1 != f2){
temp[f2] = f1;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
class Dir{
int x;
int y;
public Dir(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号