链表
链表
注意巧用这个构造器:
// 1. val
// 2. next 节点
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
甜姐说
https://tianjietalk.notion.site/01-65f94e114c84458a8d0a15a7f2777f72
相关习题
206. 反转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
92. 反转链表Ⅱ
特殊情况:
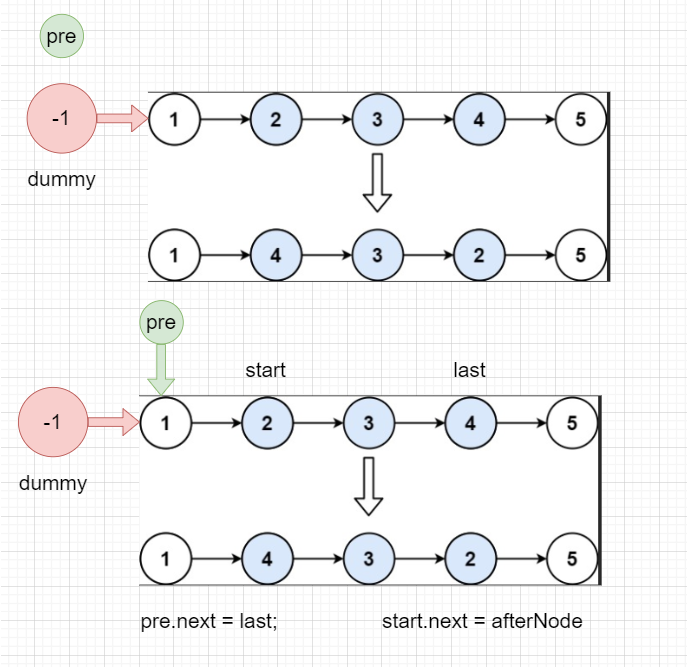
当从第一个就开始反转的时候,由于 pre 没有移动:
- 那么 pre.next = last,就相当于 dummy.next = last【因为 ListNode 是引用类型,此时就相当于 pre 指向 dummy了】
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1, head); // 巧用构造器
ListNode pre = dummyNode;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode start = pre.next;
ListNode endNode = getEndNode(start, right - left);
ListNode afterNode = endNode.next;
ListNode last = reverse(start, right - left);
pre.next = last;
start.next = afterNode;
return dummyNode.next;
}
public ListNode getEndNode(ListNode start, int count){
ListNode temp = start;
while (count > 0){
temp = temp.next;
count--;
}
return temp;
}
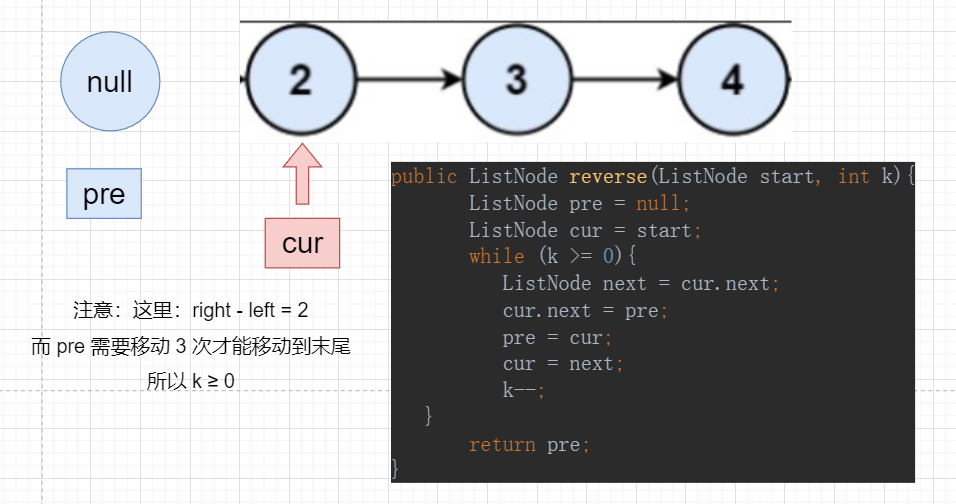
public ListNode reverse(ListNode start, int k){
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = start;
while (k >= 0){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
k--;
}
return pre;
}
}
25. K个一组反转链表
分为3步走:
- 分组
- 组内反转
- pre 指向end, start 指向 next,最后 pre 指向 start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode temp = head;
int sum = 0;
while (temp != null){
sum++;
temp = temp.next;
}
int count = sum / k;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
while (count > 0){ // 可以分为几组
ListNode start = pre.next;
ListNode end = getEndNode(start, k);
ListNode next = end.next; // 储存新的 start
ListNode last = reverse(pre.next, k);
pre.next = last;
start.next = next;
pre = start;
count--;
}
return dummy.next;
}
// 根据组内 start,得到组内 end
public ListNode getEndNode(ListNode start, int k){
ListNode temp = start;
while (k > 1){
temp = temp.next;
k--;
}
return temp;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode start, int k){
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = start;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
21. 合并2个有序链表
这里 now 是已经要的节点哦
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null && list2 == null){
return list1;
}
if (list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null){
return list1;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode start1 = list1;
ListNode start2 = list2;
if (list1.val <= list2.val){
dummy.next = list1;
start1 = start1.next;
}else {
dummy.next = list2;
start2 = start2.next;
}
// now 初始节点,逐渐互动
ListNode now = dummy.next;
while (start1 != null || start2 != null){
if (start1 == null){
now.next = start2;
now = start2;
start2 = start2.next;
continue;
}
if (start2 == null){
now.next = start1;
now = start1;
start1 = start1.next;
continue;
}
Integer val1 = start1.val;
Integer val2 = start2.val;
if (val1 <= val2){ // 我们要 start1
now.next = start1; // 1. 当前位置 指向 要的节点
now = start1; // 2. now 移动到要的节点
start1 = start1.next; // 3. 更新要的节点的位置
}else {
now.next = start2;
now = start2;
start2 = start2.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号