Java EE学习笔记(四)
Spring的数据库开发
1、Spring JDBC
1)、Spring JDBC模块的作用:Spring的JDBC模块负责数据库资源管理和错误处理,大大简化了开发人员对数据库的操作,使得开发人员可以从繁琐的数据库操作中解脱出来,从而将更多的精力投入到编写业务逻辑当中。 (只要由new实例就可以用IOC实现,只要有setter方法就可以用DI实现)
2)、Spring JdbcTemplate的解析:
a)、JdbcTemplate类是Spring JDBC的核心类。
b)、JdbcTemplate类的继承结构具体如下图所示:
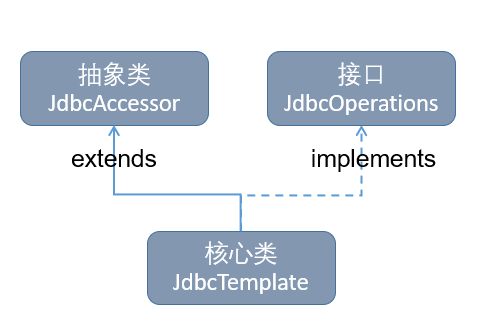
c)、DataSource(连接池,也称数据源):其主要功能是获取数据库连接,还可以引入对数据库连接的缓冲池和分布式事务的支持,它可以作为访问数据库资源的标准接口。
d)、SQLExceptionTranslator:该接口负责对SQLException进行转译工作。通过必要的设置获取SQLExceptionTranslator中的方法,可以使JdbcTemplate在需要处理SQLException时,委托SQLExceptionTranslator的实现类来完成相关的转译工作。
e)、JdbcOperations接口定义了在JdbcTemplate类中可以使用的操作集合,包括添加、修改、查询和删除等操作。
3)、Spring JDBC的配置
a)、Spring JDBC模块主要由4个包组成,分别是core(核心包)、dataSource(数据源包)、object(对象包)和support(支持包)。
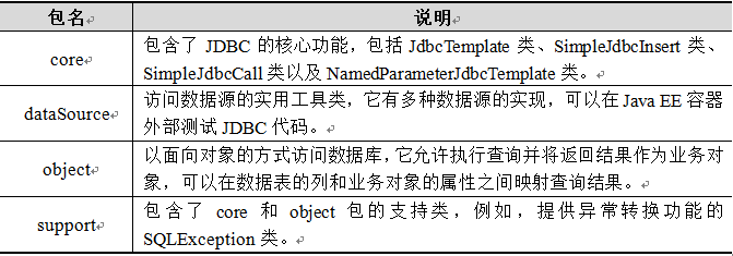
b)、从上表可以看出,Spring对数据库的操作都封装在了这几个包中,而想要使用Spring JDBC,就需要对其进行配置,配置模板如下:
1 <!--1、配置数据源--> 2 <bean id="dataSourceID" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> 3 <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> 4 <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring"/> 5 <property name="username" value="root"/> 6 <property name="password" value="****"/> 7 </bean> 8 9 <!--配置JDBC模板--> 10 <bean id="jdbcTemplateID" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> 11 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSourceID"/> <!--注入数据源--> 12 </bean> 13 14 <!--配置需要实例化的Bean--> 15 <bean id="xxx" class="Xxx"> 16 <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplateID"/> <!--注入JDBC模板--> 17 </bean>
c)、关于上述示例dataSource配置中的4个属性说明,如下表所示:
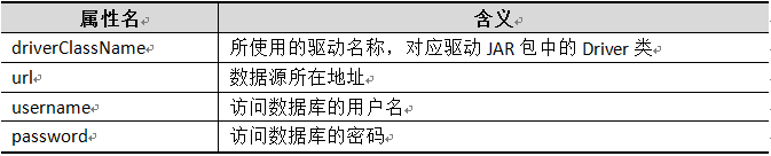
上表中的属性值在实际配置时,需要根据数据库类型和设置进行相应配置。
2、Spring JdbcTemplate的常用方法
1)、在JdbcTemplate核心类中,提供了大量的更新和查询数据库的方法:
a)、execute(String sql)方法可用于执行sql语句;
b)、update()用于执行插入、更新和删除操作;
c)、query()用于执行数据查询操作。

2)、execute()的使用:
a)、src->applicationContext.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> 6 7 <!-- 1、配置数据源 --> 8 <bean id="dataSourceID" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> 9 10 <!--1.1、数据库驱动 --> 11 <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> 12 13 <!--1.2、连接数据库的url(即数据库所在地址) --> 14 <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring" /> 15 16 <!--1.3、连接数据库的用户名 --> 17 <property name="username" value="root" /> 18 19 <!--1.4、连接数据库的密码 --> 20 <property name="password" value="******" /> 21 </bean> 22 23 <!-- 2、配置JDBC模板,并且注入数据源 --> 24 <bean id="jdbcTemplateID" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> 25 26 <!-- 2.1、默认必须使用数据源 --> 27 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSourceID" /> 28 </bean> 29 30 <!--3、定义id为accountDaoID的Bean,即配置DAO层--> 31 <bean id="accountDaoID" class="com.itheima.jdbc.AccountDaoImpl"> 32 33 <!-- 3.1、将jdbcTemplate注入到accountDao类实例中 --> 34 <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplateID" /> 35 </bean> 36 37 </beans>
b)、src->com.itheima.jdbc
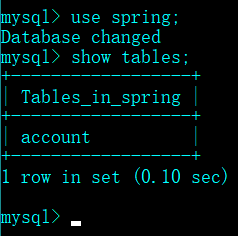
①JdbcTemplateTest.java
1 package com.itheima.jdbc; 2 import java.util.List; 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 6 import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; 7 8 public class JdbcTemplateTest { 9 /** 10 * 使用execute()方法建表 11 */ 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 14 // 1、加载配置文件 15 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 16 17 // 2、获取JdbcTemplate实例 18 JdbcTemplate jdTemplate = (JdbcTemplate) applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplateID"); 19 20 // 3、使用该实例的execute()方法执行SQL语句,创建用户账户管理表account 21 jdTemplate.execute("create table account(" + 22 "id int primary key auto_increment," + 23 "username varchar(50)," + 24 "balance double)"); 25 System.out.println("账户表account创建成功!"); 26 } 27 }
②运行结果:

3)、update()的使用
a)、update()方法可以完成插入、更新和删除数据的操作。在JdbcTemplate类中,提供了一系列的update()方法,其常用方法下表所示:
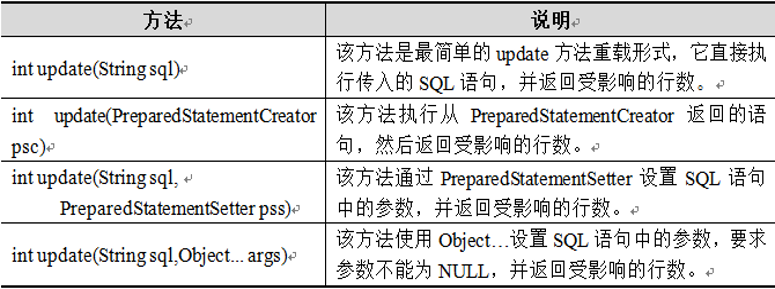
b)、src->com.itheima.jdbc
①普通账户类:Account.java
1 package com.itheima.jdbc; 2 3 public class Account { // 账户的信息 4 5 private Integer id; // 账户id 6 private String username; // 用户名 7 private Double balance; // 账户余额 8 9 public Integer getId() { 10 return id; 11 } 12 13 public void setId(Integer id) { 14 this.id = id; 15 } 16 17 public String getUsername() { 18 return username; 19 } 20 21 public void setUsername(String username) { 22 this.username = username; 23 } 24 25 public Double getBalance() { 26 return balance; 27 } 28 29 public void setBalance(Double balance) { 30 this.balance = balance; 31 } 32 33 public String toString() { 34 return "Account [id=" + id + ", " + "username=" + username + ", balance=" + balance + "]."; 35 } 36 }
②用户接口类:AccountDao.java
1 package com.itheima.jdbc; 2 3 import java.util.List; 4 5 public interface AccountDao { // 创建接口 6 7 // 添加 8 public int addAccount(Account account); 9 10 // 更新 11 public int updateAccount(Account account); 12 13 // 删除 14 public int deleteAccount(int id); 15 16 // 通过id查询 17 public Account findAccountById(int id); 18 19 // 查询所有账户 20 public List<Account> findAllAccount(); 21 }
③用户接口实现类:AccountDaoImpl.java
1 package com.itheima.jdbc; 2 import java.util.List; 3 import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper; 4 import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; 5 import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper; 6 7 public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { // 数据访问层DAO 8 9 // 1、声明JdbcTemplate属性及其setter方法 10 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; 11 12 public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { // 由Spring容器注入JBDC模板来操作mysql 13 this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; 14 } 15 16 // 2、添加账户 17 public int addAccount(Account account) { 18 19 // 2.1、定义SQL 20 String sql = "insert into account(username,balance) value(?,?)"; 21 22 // 2.2、定义数组来存放SQL语句中的参数 23 Object[] obj = new Object[] { account.getUsername(), account.getBalance() }; 24 25 // 2.3、执行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数 26 int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql, obj); 27 return num; 28 } 29 30 // 3、更新账户 31 public int updateAccount(Account account) { 32 33 // 3.1、定义SQL 34 String sql = "update account set username=?,balance=? where id = ?"; 35 36 // 3.2、定义数组来存放SQL语句中的参数 37 Object[] params = new Object[] { account.getUsername(), account.getBalance(), account.getId() }; 38 39 /* 40 * 3.3、执行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数 41 * 第1个参数:sql操作语句 42 * 第2个参数: 43 */ 44 int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql, params); 45 return num; 46 } 47 48 // 4、删除账户 49 public int deleteAccount(int id) { 50 51 // 4.1、定义SQL 52 String sql = "delete from account where id = ? "; 53 54 // 4.2、执行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数 55 int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql, id); 56 return num; 57 } 58 59 // 5、通过id查询账户数据信息 60 public Account findAccountById(int id) { 61 62 //5.1、定义SQL语句 63 String sql = "select * from account where id = ?"; 64 65 // 5.2、创建一个新的BeanPropertyRowMapper对象 66 RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class); 67 68 // 5.3、将id绑定到SQL语句中,并通过RowMapper返回一个Object类型的单行记录 69 return this.jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, id); 70 } 71 72 // 6、查询所有账户信息 73 public List<Account> findAllAccount() { 74 75 // 6.1、定义SQL语句 76 String sql = "select * from account"; 77 78 // 6.2、创建一个新的BeanPropertyRowMapper对象 79 RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class); 80 81 // 6.3、执行静态的SQL查询,并通过RowMapper返回结果 82 return this.jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rowMapper); 83 } 84 }
④测试类:JdbcTemplate中添加一个测试方法addAccountTest(),用于添加用户信息:
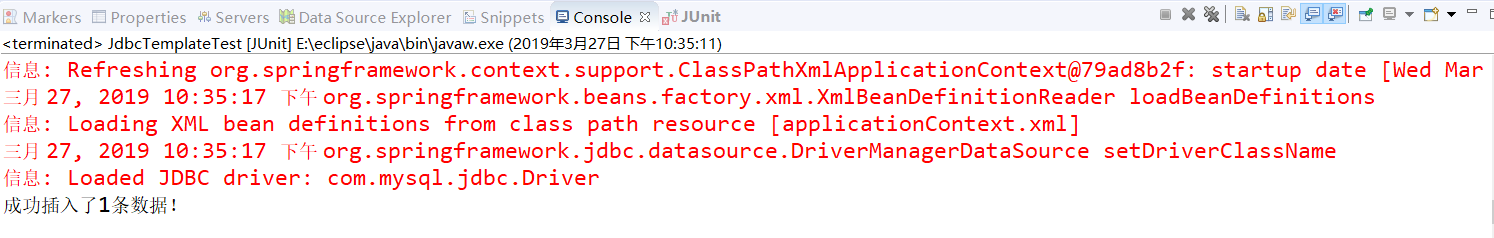
1 @Test 2 public void addAccountTest() { 3 4 // 1、加载配置文件 5 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 6 7 // 2、获取AccountDao的Bena实例AccountDaoID 8 AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) applicationContext.getBean("accountDaoID"); 9 10 // 3、创建Account对象,并向Account对象中添加数据 11 Account account = new Account(); 12 account.setUsername("joy"); 13 account.setBalance(100.00); 14 15 // 4、执行addAccount()方法,并获取返回结果 16 int num = accountDao.addAccount(account); 17 if (num > 0) { 18 System.out.println("成功插入了" + num + "条数据!"); 19 } else { 20 System.out.println("插入操作执行失败!"); 21 } 22 }
⑤运行结果:

⑥测试类:JdbcTemplate中添加一个测试方法updateAccountTest(),用于更新用户信息:
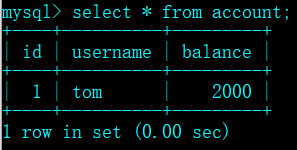
1 @Test 2 public void updateAccountTest() { 3 4 // 1、加载配置文件 5 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 6 7 // 2、获取AccountDao的Bean实例accountDaoID 8 AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) applicationContext.getBean("accountDaoID"); 9 10 // 3、创建Account对象,并向Account对象中添加数据 11 Account account = new Account(); 12 account.setId(1); 13 account.setUsername("tom"); 14 account.setBalance(2000.00); 15 16 // 4、执行updateAccount()方法,并获取返回结果 17 int num = accountDao.updateAccount(account); 18 if (num > 0) { 19 System.out.println("成功修改了" + num + "条数据!"); 20 } else { 21 System.out.println("修改操作执行失败!"); 22 } 23 }
⑦运行结果:

⑧测试类:JdbcTemplate中添加一个测试方法deleteAccountTest(),用于删除用户信息:
1 @Test 2 public void deleteAccountTest() { 3 4 // 1、加载配置文件 5 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 6 7 // 2、获取AccountDao的Bean实例accountDaoID 8 AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) applicationContext.getBean("accountDaoID"); 9 10 // 3、执行deleteAccount()方法,并获取返回结果 11 int num = accountDao.deleteAccount(1); 12 if (num > 0) { 13 System.out.println("成功删除了" + num + "条数据!"); 14 } else { 15 System.out.println("删除操作执行失败!"); 16 } 17 }
⑨运行结果:

![]()
4)、query()的使用
a)、JdbcTemplate类中还提供了大量的query()方法来处理各种对数据库表的查询操作。其中,常用的几个query()方法如下表所示:
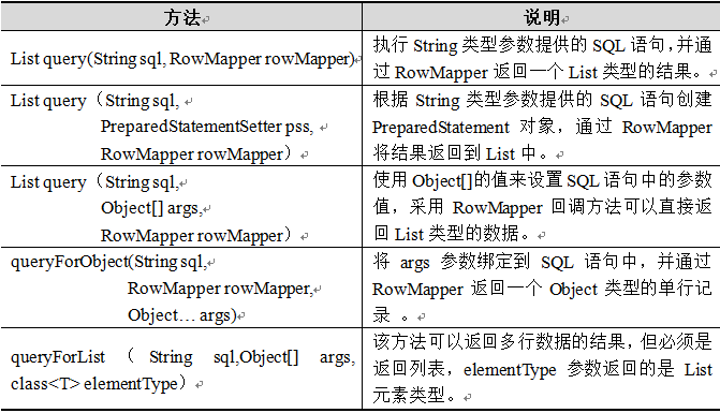
b)、向数据表account中插入几条数据:

①测试类JdbcTemplate中添加一个测试方法findAccountByIdTest(),用于查找用户id的信息:
1 @Test 2 public void findAccountByIdTest() { 3 4 // 1、加载配置文件 5 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 6 7 // 2、获取AccountDao的Bean实例accountDaoID 8 AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) applicationContext.getBean("accountDaoID"); 9 10 // 3、执行findAccountById()方法 11 Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(1); 12 System.out.println(account); 13 }
②运行结果:

③测试类JdbcTemplate中添加一个测试方法findAllAccountTest(),用于查找所有用户的信息:
1 @Test 2 public void findAllAccountTest() { 3 4 // 1、加载配置文件 5 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 6 7 // 2、获取AccountDao实例 8 AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) applicationContext.getBean("accountDaoID"); 9 10 // 3、执行findAllAccount()方法,获取Account对象的集合 11 List<Account> account = accountDao.findAllAccount(); 12 13 // 4、循环输出集合中的对象 14 for (Account act : account) { 15 System.out.println(act); 16 } 17 }
④运行结果:

个人总结:
如何管理用户的数据库?首先应单独写一个类来存储用户的所有信息;其次“管理员”创建实现操作用户的接口类(拥有的操作方法)以及对应的接口实现类,其中接口实现类要注入JdbcTemplate属性和它的setter方法,因为用JdbcTemplate管理数据库起来很方便,并且要实现对用户的增删查改的具体方法;然后测试操作时,首先都要加载配置文件,因为这些都由Spring容器来管理,然后获取容器中管理用户的Bean实例,若要对用户信息进行增加或更新,则要先new一个普通用户的实例,向这个实例中传入需要操作的数据,最后通过Bean实例去调用相应的操作用户的方法即可。


