备忘录模式
意图:
在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态。这样以后就可将该对象恢复到原先保存的状态。
适用性:
必须保存一个对象在某一个时刻的(部分)状态, 这样以后需要时它才能恢复到先前的状态。
如果一个用接口来让其它对象直接得到这些状态,将会暴露对象的实现细节并破坏对象的封装性。
代码示例
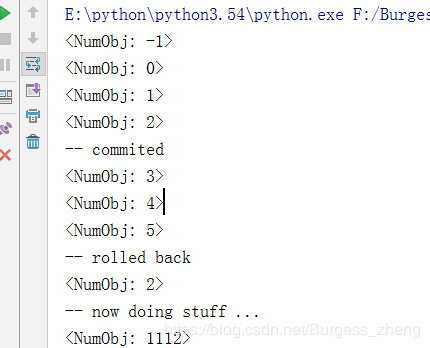
#!/usr/bin/env python #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- ''' Memento ''' import copy def Memento(obj, deep=False): state = (copy.copy, copy.deepcopy)[bool(deep)](obj.__dict__) def Restore(): obj.__dict__.clear() obj.__dict__.update(state) return Restore class Transaction: """A transaction guard. This is really just syntactic suggar arount a memento closure. """ deep = False def __init__(self, *targets): self.targets = targets self.Commit() def Commit(self): self.states = [Memento(target, self.deep) for target in self.targets] def Rollback(self): for st in self.states: st() class transactional(object): """Adds transactional semantics to methods. Methods decorated with @transactional will rollback to entry state upon exceptions. """ def __init__(self, method): self.method = method def __get__(self, obj, T): def transaction(*args, **kwargs): state = Memento(obj) try: return self.method(obj, *args, **kwargs) except: state() raise return transaction class NumObj(object): def __init__(self, value): self.value = value def __repr__(self): return '<%s: %r>' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.value) def Increment(self): self.value += 1 @transactional def DoStuff(self): self.value = 1111 # <- invalid value self.Increment() # <- will fail and rollback if __name__ == '__main__': n = NumObj(-1) print(n) t = Transaction(n) try: for i in range(3): n.Increment() print(n) t.Commit() print('-- commited') for i in range(3): n.Increment() print(n) n.value += 'x' # will fail print(n) except: t.Rollback() print('-- rolled back') print(n) print('-- now doing stuff ...') try: n.DoStuff() except: print('-> doing stuff failed!') import traceback traceback.print_exc(0) pass print(n)
执行结果