C#实战附俄罗斯方块实战
C#实战
ArrayList
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Security.Principal;
namespace ArrayList数组;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 本质
/* ArrayList是一个C#封装好的类
本质是一个object类型的数组
ArrayList,*/
#endregion
#region 声明
//需要引用 命名空间using System.Collections;
ArrayList array = new ArrayList();
#endregion
#region 增删查改
array.Add(1);
array.Add("");
array.Add(true);
int v = array.Add(new object());
array.Add(new Test());
// 把另一个容器增加到另一个容器
array.AddRange(array);
//删
//指定元素
array.Remove(1);
//指定位置
array.RemoveAt(0);
array.RemoveAt(1);
//清空
//array.Clear();
// 查
Console.WriteLine(array[0]);
//查看元素是否存在
if (array.Contains("1"))
{
}
// 正向查找元素位置
//找到返回值
int index = array.IndexOf("1");
Console.WriteLine(index);
// 反向查找元素
//int index2 = array.IndexOf(true);
index = array.LastIndexOf(true);
Console.WriteLine(index);
// 改
Console.WriteLine(array[0]);
array[0] = "1";
Console.WriteLine(array[0]);
#endregion
#region 遍历
//长度
Console.WriteLine(array.Count);
// 避免产生过多垃圾
Console.WriteLine(array.Capacity);
for (int i = 0; i < array.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(array[i]);
}
foreach (var item in array)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
#endregion
#region 装箱拆箱
// ArrayList本质上可以自动扩容object数组
int i2 = 1;
array[0] = i2;// 装箱
i2 = (int)array[0];
Console.WriteLine(i2);
#endregion
}
}
Stack
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace bascicprograme;
class Test { }
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region stack本质
//stack是一个C#封装好的类
/* 它的本质是object数组,只是封装了特殊的存储规则
Stack是栈存储容器,栈是一种先进后出的数据结构
先存入的数据后取出,后存入的数据先取出*/
#endregion
#region 声明
Stack values = new Stack();
#endregion
#region 增取改查
//压栈
values.Push(1);
values.Push(true);
values.Push("1111");
values.Push(new Test());
#endregion
#region 取
//栈中不存在删除的概念
//弹栈
object v = values.Pop();
Console.WriteLine(v);
#endregion
#region 查
//1、栈无法查看指定位置元素
//只能查看栈顶内容
//2、查看元素是否存在于栈中
v = values.Peek();
Console.WriteLine(v);
#endregion
#region 改
//栈无法改变其中的元素,只能压和弹
//只能清空
//values.Clear();
#endregion
#region 遍历
Console.WriteLine(values.Count);
//foreach遍历
foreach (object item in values)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
//另一种遍历方式
//将栈转换为object数组
//遍历出来顺序也是从栈顶到栈底
object[] arr = values.ToArray();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr[i]);
}
// 循环弹栈
while (values.Count>0)
{
object o = values.Pop();
Console.WriteLine(o);
}
Console.WriteLine(values.Count);
#endregion
}
}
Queue
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace 队列;
class Test {
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 队列本质
/*queen是一个封装好的
本质也是object数组只是封装了特殊的规则
queue是对类存储容器
队列是一种新进先出的数据结构
先存入的数据先获取后存入的后获取*/
#endregion
#region 声明
Queue queue = new Queue();
#endregion
#region 增取查改
// 增
queue.Enqueue(1);
queue.Enqueue("2");
queue.Enqueue(true);
// 取
object o = queue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine(o);
Console.WriteLine(queue.Dequeue());
// 查
// 查看头部元素但不会移除
o = queue.Peek();
Console.WriteLine(o);
// 查看元素是否存在队列中
if (queue.Contains("3"))
{
Console.WriteLine("不存在");
}
// 改
//只能清空,改不了
//queue.Clear();
queue.Enqueue(1);
// 遍历
//
foreach (var item in queue)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
object[] arr = queue.ToArray();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr[i]);
}
// 循环出列
while (queue.Count>0)
{
o = queue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine(o);
}
#endregion
}
}
HashTable
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace 哈希表练习题;
//制作一个怪物管理器,提供创建怪物
//移除怪物的方法。每个怪物都有自己的唯一ID
/// <summary>
/// 怪物管理器 因为一般 管理器 都是唯一的 所以把它做成 一个单例模式的对象
/// </summary>
// 泛型单例
/*public class Singleton<T> where T : class, new()
{
// 私有静态实例
private static T instance;
// 用于线程同步的锁对象
private static readonly object lockObject = new object();
// 公共的静态属性,用于获取唯一实例
public static T Instance
{
get
{
// 双重检查锁定,提高性能
if (instance == null)
{
lock (lockObject)
{
if (instance == null)
{
instance = new T();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
}
// 具体的单例类,继承自泛型单例基类
public class MySingleton : Singleton<T>
{
// 可以在这里添加MySingleton特有的方法和属性
private MySingleton() { }
}*/
class MonsterMgr
{
private static MonsterMgr instance = new MonsterMgr();
private Hashtable monstersTable = new Hashtable();
private MonsterMgr() { }
public static MonsterMgr Instance
{
get { return instance; }
}
private int monsterId = 0;
public void AddMonster (){
Monster monster = new Monster(monsterId);
Console.WriteLine("创建了{0}的怪物",monsterId);
++monsterId;
monstersTable.Add(monster.id,monster);
}
public void RemoveMonster(int monserID)
{
if (monstersTable.ContainsKey(monserID)) {
(monstersTable[monserID] as Monster).Dead();
monstersTable.Remove(monserID);
}
}
}
class Monster
{
public int id;
public Monster(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void Dead()
{
Console.WriteLine("怪物{0}死亡",id);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MonsterMgr.Instance.AddMonster();
MonsterMgr.Instance.AddMonster();
MonsterMgr.Instance.AddMonster();
MonsterMgr.Instance.AddMonster();
MonsterMgr.Instance.AddMonster();
MonsterMgr.Instance.RemoveMonster(0);
MonsterMgr.Instance.RemoveMonster(1);
MonsterMgr.Instance.RemoveMonster(2);
}
}
泛型
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
namespace 泛型;
#region 泛型是什么
// 泛型实现了类型参数化,达到代码重用的目的
//通过类型参数化实现同一份代码操作多种类型
// 泛型相当于类型占位符
// 定义类或方法时使用替代付代表变量类型
// 当真正使用类或者方法时再具体指定类型
#endregion
#region 泛型分类
//基本语法
//class 类名<泛型占位字母>
// 泛型函数
//基本语法
//函数名 <泛型占位字母>(参数)
#endregion
class TestClass<T> {
public T Value;
}
class TestClass2<T, A, B, C> {
public T Value;
public A Value1;
public B Value5;
public C Value6;
};
interface IClass<T> {
T Value {
get; set;
}
}
// 继承
class Test : IClass<string>
{
public string Value { get; set; }
}
// 泛型方法
class TestFun {
public void Test<T> (T value) {
Console.WriteLine (value);
}
public void Test2<T>(){
T t =default (T);
Console.WriteLine (t);
}
public T Test3<T>(string V) {
return default(T);
}
public void Test<T,K,M>(T t, K k ,M m) { }
}
class TestFun<T> {
public T Value;
// 我们这个不叫泛型方法,T是泛型声明时候就制定在使用这个函数时候就不能再动态的变化了
// 没加<>不是泛型
public void Test(T t) {
}
}
// 泛型作用
/*不同类型对象相同逻辑处理就可以选择泛型
使用泛型就可以一定程度上避免装箱拆箱*/
class ArrayList<T>
{
private T[] array;
private void Add(T value) {
}
private void Clear()
{
}
private void Remove() {
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestClass<int> t = new TestClass<int>();
t.Value = 1;
Console.WriteLine(t.Value);
TestClass<String> testClass = new TestClass<String>();
testClass.Value = "555555555";
Console.WriteLine(testClass.Value);
TestClass2<int, string, float, double> testClass2 = new TestClass2<int, string, float, double>() { };
TestFun fun = new TestFun();
fun.Test<string>("123");
TestFun<int> fun2 = new TestFun<int>();
fun2.Test(11);
}
}
泛型约束
using System;
using static System.Net.Mime.MediaTypeNames;
namespace 泛型的约束;
#region 什么是泛型约束
/*让泛型的类型有一定限制
关键字where
泛型约束一共有六种
值类型 where 泛型字母:struct
引用类型 where 泛型字母:class
存在无参公共构造函数 where 泛型字母:new()
某个类本身或者其派生类 where 泛型字母:类名
某个接口派生类型 where 泛型字母:接口名
另一个泛型类型本身或者派生类型 where 泛型字母:另一个泛型字母
*/
#endregion
#region 值类型约束
class Test1<T> where T : struct
{
public T Value;
public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : struct {
}
}
class Test2<T> where T : class
{
public T Value;
public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : class
{
}
}
#endregion
#region 公共无参构造函数
class Test3<T> where T : new()
{
public T Value;
public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : new()
{
}
}
#endregion
#region 类约束
class Test4<T> where T : Test1
{
public T Value;
public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : Test1
{
}
}
class Test3 : Test1
{
}
#endregion
#region 接口约束
interface Ifly { }
class Test5 : Ifly {
}
class Test6<T> where T : Ifly
{
public T Value;
public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : Ifly
{
}
}
#endregion
#region 另一个泛型约束
//U是T的派生类
class Test7<T, U> where T : U {
public T Value;
public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : U
{
}
}
#endregion
#region 约束的组合使用
class Test8<T> where T :class,new()
{
public T Value;
public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : class, new()
{
}
}
#endregion
#region 多个泛型有约束
class Test9<T,K> where T : class, new() where K : class
{
public T Value;
public void TestFun<T,K>(T t , K k) where T : class, new() where K : class
{
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test1<int> t = new Test1<int>();
t.TestFun<float>(1.3f);
Test2<object> t1 = new Test2<object>();
Test2<Random> t2 = new Test2<Random>();
t2.Value = new Random();
t2.TestFun<object>(new object());
Test4<Test3> test4 = new Test4<Test3>();
Test4<Test1> test5 = new Test4<Test1>();
Test6<Ifly> t5 = new Test6<Ifly>();
t5.Value = new Test5();
Test7<Test5, Ifly> t7 = new Test7<Test5, Ifly>();
}
}
List
namespace List链表;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region List本质
//List#封装好的,本质是一个可变类型的泛型数组
//List类帮助我们实现很多方法,比如泛型数组的增删改查
#endregion
#region 声明
//需要引用命名空间
List<string> list = new List<string>();
list.Add("1");
list.Add("1");
List<int> list2 = new List<int>();
List<int> list3= new List<int>();
list2.Add(2);
list2.Add(2);
list2.Add(2);
list.AddRange(list);
list2.AddRange(list3);
// 删
list.Remove("1");
list.RemoveAt(0);
// 查
Console.WriteLine( list[0]);
if (list.Contains("1"))
{
Console.WriteLine("存在");
}
int index = list.IndexOf("1");
Console.WriteLine( index); // 找不到-1
// 改
Console.WriteLine(list[0]="333");
list.Insert(0,"9999");
Console.WriteLine(list[0]);
// 遍历
for (int i = 1; i < list.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine(list.Capacity);
#endregion
}
}
Dictionary
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
namespace Dictionary字典;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region Dictionary
/*可以将Dictionary理解为泛型的哈希table
他也是基于键的哈希代码组织起来的
键值对类型从哈希的object变为了自己可以制定的泛型*/
#endregion
#region 声明
Dictionary<int, string> directory = new Dictionary<int, string>();
#endregion
#region 增删改查
// 注意不能出现相同键
directory.Add(1,"1");
directory.Add(2,"22");
directory.Add(3,"333");
directory.Add(4,"4444");
directory.Add(5,"55555");
directory.Add(6,"666666");
// 删除
directory.Remove(1);
//清空
//directory.Clear();
//查
Console.WriteLine(directory[2]);
// 找不到不会返回空,直接报错
// 查看是否存在
if (directory.ContainsKey(1))
{
Console.WriteLine("存在");
}
if (directory.ContainsValue("22"))
{
Console.WriteLine("存在");
}
// 改
Console.WriteLine(directory[2]="5555");
//遍历
foreach (var item in directory.Keys)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
Console.WriteLine(directory[item]);
}
foreach (var item in directory.Values)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
foreach (KeyValuePair<int,string> item in directory)
{
Console.WriteLine("键"+item.Key+"值"+item.Value);
}
#endregion
}
}
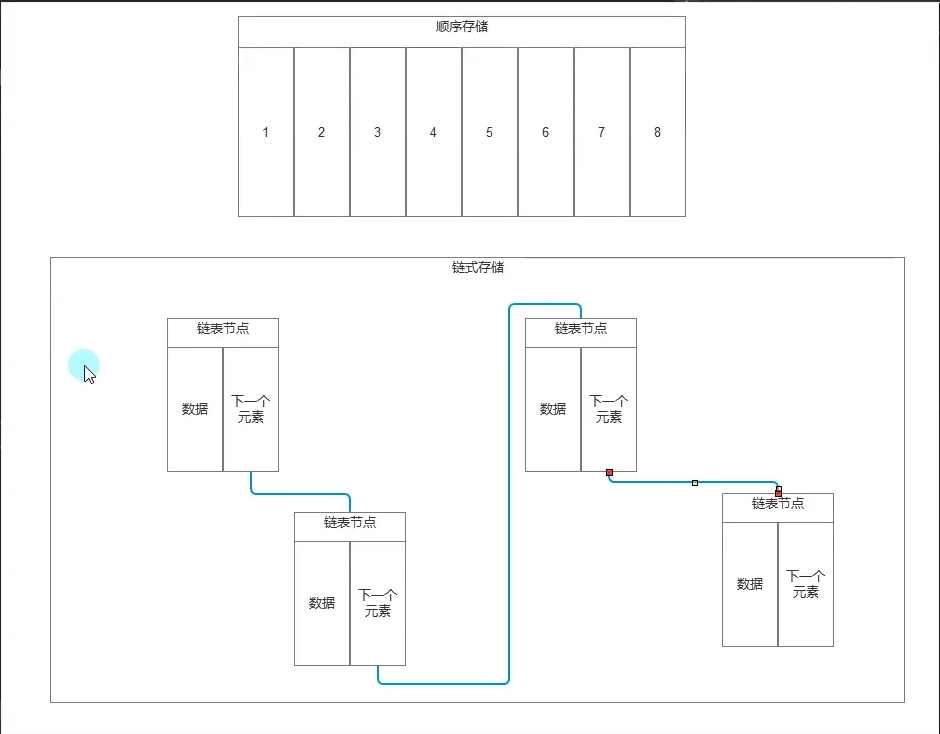
顺序存储和链式存储
using System;
namespace Lesson9_顺序存储和链式存储
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("顺序存储和链式存储");
#region 知识点一 数据结构
//数据结构
//数据结构是计算机存储、组织数据的方式(规则)
//数据结构是指相互之间存在一种或多种特定关系的数据元素的集合
//比如自定义的一个 类 也可以称为一种数据结构 自己定义的数据组合规则
//不要把数据结构想的太复杂
//简单点理解,就是人定义的 存储数据 和 表示数据之间关系 的规则而已
//常用的数据结构(前辈总结和制定的一些经典规则)
//数组、栈、队列、链表、树、图、堆、散列表
#endregion
#region 知识点二 线性表
//线性表是一种数据结构,是由n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列
//比如数组、ArrayList、Stack、Queue、链表等等
#endregion
//顺序存储和链式存储 是数据结构中两种 存储结构
#region 知识点三 顺序存储
//数组、Stack、Queue、List、ArrayList —— 顺序存储
//只是 数组、Stack、Queue的 组织规则不同而已
//顺序存储:
//用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的各个数据元素
#endregion
#region 知识点四 链式存储
//单向链表、双向链表、循环链表 —— 链式存储
//链式存储(链接存储):
//用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表中的各个数据元素
#endregion
LindedList<int> link = new LindedList<int>();
link.Add(1);
link.Add(2);
link.Add(3);
link.Add(4);
LinkedNode<int> node = link.head;
while(node != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(node.value);
node = node.nextNode;
}
link.Remove(2);
node = link.head;
while (node != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(node.value);
node = node.nextNode;
}
link.Remove(1);
node = link.head;
while (node != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(node.value);
node = node.nextNode;
}
link.Add(99);
node = link.head;
while (node != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(node.value);
node = node.nextNode;
}
}
}
#region 知识点五 自己实现一个最简单的单向链表
/// <summary>
/// 单向链表节点
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
class LinkedNode<T>
{
public T value;
//这个存储下一个元素是谁 相当于钩子
public LinkedNode<T> nextNode;
public LinkedNode(T value)
{
this.value = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 单向链表类 管理 节点 管理 添加等等
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
class LindedList<T>
{
public LinkedNode<T> head;
public LinkedNode<T> last;
public void Add(T value)
{
//添加节点 必然是new一个新的节点
LinkedNode<T> node = new LinkedNode<T>(value);
if( head == null )
{
head = node;
last = node;
}
else
{
last.nextNode = node;
last = node;
}
}
public void Remove(T value)
{
if( head == null )
{
return;
}
if( head.value.Equals(value) )
{
head = head.nextNode;
//如果头节点 被移除 发现头节点变空
//证明只有一个节点 那尾也要清空
if( head == null )
{
last = null;
}
return;
}
LinkedNode<T> node = head;
while(node.nextNode != null)
{
if( node.nextNode.value.Equals(value) )
{
//让当前找到的这个元素的 上一个节点
//指向 自己的下一个节点
node.nextNode = node.nextNode.nextNode;
break;
}
}
}
}
#endregion
#region 知识点六 顺序存储和链式存储的优缺点
//从增删查改的角度去思考
//增:链式存储 计算上 优于顺序存储 (中间插入时链式不用像顺序一样去移动位置)
//删:链式存储 计算上 优于顺序存储 (中间删除时链式不用像顺序一样去移动位置)
//查:顺序存储 使用上 优于链式存储 (数组可以直接通过下标得到元素,链式需要遍历)
//改:顺序存储 使用上 优于链式存储 (数组可以直接通过下标得到元素,链式需要遍历)
#endregion
}
LinkedList
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Lesson10_LinkedList
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("LinkedList");
#region 知识点一 LinkedList
//LinkedList是一个C#为我们封装好的类
//它的本质是一个可变类型的泛型双向链表
#endregion
#region 知识点二 申明
//需要引用命名空间
//using System.Collections.Generic
LinkedList<int> linkedList = new LinkedList<int>();
LinkedList<string> linkedList2 = new LinkedList<string>();
//链表对象 需要掌握两个类
//一个是链表本身 一个是链表节点类LinkedListNode
#endregion
#region 知识点三 增删查改
#region 增
//1.在链表尾部添加元素
linkedList.AddLast(10);
//2.在链表头部添加元素
linkedList.AddFirst(20);
//3.在某一个节点之后添加一个节点
// 要指定节点 先得得到一个节点
LinkedListNode<int> n = linkedList.Find(20);
linkedList.AddAfter(n, 15);
//4.在某一个节点之前添加一个节点
// 要指定节点 先得得到一个节点
linkedList.AddBefore(n, 11);
#endregion
#region 删
//1.移除头节点
linkedList.RemoveFirst();
//2.移除尾节点
linkedList.RemoveLast();
//3.移除指定节点
// 无法通过位置直接移除
linkedList.Remove(20);
//4.清空
linkedList.Clear();
linkedList.AddLast(1);
linkedList.AddLast(2);
linkedList.AddLast(3);
linkedList.AddLast(4);
#endregion
#region 查
//1.头节点
LinkedListNode<int> first = linkedList.First;
//2.尾节点
LinkedListNode<int> last = linkedList.Last;
//3.找到指定值的节点
// 无法直接通过下标获取中间元素
// 只有遍历查找指定位置元素
LinkedListNode<int> node = linkedList.Find(3);
Console.WriteLine(node.Value);
node = linkedList.Find(5);
//4.判断是否存在
if( linkedList.Contains(1) )
{
Console.WriteLine("链表中存在1");
}
#endregion
#region 改
//要先得再改 得到节点 再改变其中的值
Console.WriteLine(linkedList.First.Value);
linkedList.First.Value = 10;
Console.WriteLine(linkedList.First.Value);
#endregion
#endregion
#region 知识点四 遍历
//1.foreach遍历
foreach (int item in linkedList)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
//2.通过节点遍历
// 从头到尾
Console.WriteLine("&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&");
LinkedListNode<int> nowNode = linkedList.First;
while (nowNode != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(nowNode.Value);
nowNode = nowNode.Next;
}
// 从尾到头
Console.WriteLine("&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&");
nowNode = linkedList.Last;
while (nowNode != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(nowNode.Value);
nowNode = nowNode.Previous;
}
#endregion
}
}
}
泛型栈和队列
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Lesson11_泛型栈和队列
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("泛型栈和队列");
#region 知识点一 回顾数据容器
#region 变量
//无符号
//byte ushort uint ulong
//有符号
//sbyte short int long
//浮点数
//float double decimal
//特殊
//char bool string
#endregion
#region 复杂数据容器
//枚举 enum
//结构体 struct
//数组(一维、二维、交错) [] [,] [][]
//类
#endregion
#region 数据集合
//using System.Collections;
//ArrayList object数据列表
//Stack 栈 先进后出
//Queue 队列 先进先出
//Hashtable 哈希表 键值对
#endregion
#region 泛型数据集合
//using System.Collections.Generic;
//List 列表 泛型列表
//Dictionary 字典 泛型哈希表
//LinkedList 双向链表
//Statck 泛型栈
//Queue 泛型队列
#endregion
#endregion
#region 知识点二 泛型栈和队列
//命名空间:using System.Collections.Generic;
//使用上 和之前的Stack和Queue一模一样
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
Queue<object> queue = new Queue<object>();
#endregion
}
}
}
委托
using System;
namespace Lesson12_委托
{
#region 知识点一 委托是什么
//委托是 函数(方法)的容器
//可以理解为表示函数(方法)的变量类型
//用来 存储、传递函数(方法)
//委托的本质是一个类,用来定义函数(方法)的类型(返回值和参数的类型)
//不同的 函数(方法)必须对应和各自"格式"一致的委托
#endregion
#region 知识点二 基本语法
//关键字 : delegate
//语法:访问修饰符 delegate 返回值 委托名(参数列表);
//写在哪里?
//可以申明在namespace和class语句块中
//更多的写在namespace中
//简单记忆委托语法 就是 函数申明语法前面加一个delegate关键字
#endregion
#region 知识点三 定义自定义委托
//访问修饰默认不写 为public 在别的命名空间中也能使用
//private 其它命名空间就不能用了
//一般使用public
//申明了一个可以用来存储无参无返回值函数的容器
//这里只是定义了规则 并没有使用
delegate void MyFun();
//委托规则的申明 是不能重名(同一语句块中)
//表示用来装载或传递 返回值为int 有一个int参数的函数的 委托 容器规则
public delegate int MyFun2(int a);
//委托是支持 泛型的 可以让返回值和参数 可变 更方便我们的使用
delegate T MyFun3<T, K>(T v, K k);
#endregion
#region 知识点四 使用定义好的委托
//委托变量是函数的容器
//委托常用在:
//1.作为类的成员
//2.作为函数的参数
class Test
{
public MyFun fun;
public MyFun2 fun2;
public Action action;
public void TestFun( MyFun fun, MyFun2 fun2 )
{
//先处理一些别的逻辑 当这些逻辑处理完了 再执行传入的函数
int i = 1;
i *= 2;
i += 2;
//fun();
//fun2(i);
//this.fun = fun;
//this.fun2 = fun2;
}
#region 增
public void AddFun(MyFun fun, MyFun2 fun2)
{
this.fun += fun;
this.fun2 += fun2;
}
#endregion
#region 删
public void RemoveFun(MyFun fun, MyFun2 fun2)
{
//this.fun = this.fun - fun;
this.fun -= fun;
this.fun2 -= fun2;
}
#endregion
}
#endregion
#region 知识点五 委托变量可以存储多个函数(多播委托)
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("委托");
//专门用来装载 函数的 容器
MyFun f = new MyFun(Fun);
Console.WriteLine("1");
Console.WriteLine("2");
Console.WriteLine("3");
Console.WriteLine("4");
Console.WriteLine("5");
f.Invoke();
MyFun f2 = Fun;
Console.WriteLine("1");
Console.WriteLine("2");
Console.WriteLine("3");
Console.WriteLine("4");
Console.WriteLine("5");
f2();
MyFun2 f3 = Fun2;
Console.WriteLine(f3(1));
MyFun2 f4 = new MyFun2(Fun2);
Console.WriteLine(f4.Invoke(3));
Test t = new Test();
t.TestFun(Fun, Fun2);
Console.WriteLine("***************");
//如何用委托存储多个函数
MyFun ff = null;
//ff = ff + Fun;
ff += Fun;
ff += Fun3;
ff();
//从容器中移除指定的函数
ff -= Fun;
//多减 不会报错 无非就是不处理而已
ff -= Fun;
ff();
//清空容器
ff = null;
if( ff != null )
{
ff();
}
#region 知识点六 系统定义好的委托
//使用系统自带委托 需要引用using System;
//无参无返回值
Action action = Fun;
action += Fun3;
action();
//可以指定返回值类型的 泛型委托
Func<string> funcString = Fun4;
Func<int> funcInt = Fun5;
//可以传n个参数的 系统提供了 1到16个参数的委托 直接用就行了
Action<int, string> action2 = Fun6;
//可以穿n个参数的 并且有返回值的 系统也提供了 16个委托
Func<int, int> func2 = Fun2;
#endregion
}
static void Fun()
{
Console.WriteLine("张三做什么");
}
static void Fun3()
{
Console.WriteLine("李四做什么");
}
static string Fun4()
{
return "";
}
static int Fun5()
{
return 1;
}
static void Fun6(int i, string s)
{
}
static int Fun2(int value)
{
return value;
}
}
//总结
//简单理解 委托 就是装载、传递函数的容器而已
//可以用委托变量 来存储函数或者传递函数的
//系统其实已经提供了很多委托给我们用
//Action:没有返回值,参数提供了 0~16个委托给我们用
//Func:有返回值,参数提供了 0~16个委托给我们用
}
练习题
using System;
namespace Lesson12_练习题
{
#region 练习题一
//一家三口,妈妈做饭,爸爸妈妈和孩子都要吃饭
//用委托模拟做饭——>开饭——>吃饭的过程
abstract class Person
{
public abstract void Eat();
}
class Mother : Person
{
public Action beginEat;
public override void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("妈妈吃饭");
}
public void DoFood()
{
Console.WriteLine("妈妈做饭");
Console.WriteLine("妈妈做饭做好了");
//执行委托函数
if(beginEat != null)
{
beginEat();
}
}
}
class Father:Person
{
public override void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("爸爸吃饭");
}
}
class Son:Person
{
public override void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("孩子吃饭");
}
}
#endregion
#region 练习题二
//怪物死亡后,玩家要加10块钱,界面要更新数据
//成就要累加怪物击杀数,请用委托来模拟实现这些功能
//只用写核心逻辑表现这个过程,不用写的太复杂
class Monster
{
//当怪物死亡时 把自己作为参数传出去
public Action<Monster> deadDoSomthing;
//怪物成员变量 特征 价值多少钱
public int money = 10;
public void Dead()
{
Console.WriteLine("怪物死亡");
if(deadDoSomthing != null)
{
deadDoSomthing(this);
}
//一般情况下 委托关联的函数 有加 就有减(或者直接清空)
deadDoSomthing = null;
}
}
class Player
{
private int myMoney = 0;
public void MonsterDeadDoSomthing(Monster m)
{
myMoney += m.money;
Console.WriteLine("现在有{0}元钱", myMoney);
}
}
class Panel
{
private int nowShowMoney = 0;
public void MonsterDeadDo(Monster m)
{
nowShowMoney += m.money;
Console.WriteLine("当前面板显示{0}元钱", nowShowMoney);
}
}
class CJ
{
private int nowKillMonsterNum = 0;
public void MonsterDeadDo(Monster m)
{
nowKillMonsterNum += 1;
Console.WriteLine("当前击杀了{0}怪物", nowKillMonsterNum);
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("委托练习题");
Mother m = new Mother();
Father f = new Father();
Son s = new Son();
//告诉妈妈 一会做好了 我要吃
m.beginEat += f.Eat;
m.beginEat += s.Eat;
m.beginEat += m.Eat;
//做饭
m.DoFood();
Monster monster = new Monster();
Player p = new Player();
Panel panel = new Panel();
CJ cj = new CJ();
monster.deadDoSomthing += p.MonsterDeadDoSomthing;
monster.deadDoSomthing += panel.MonsterDeadDo;
monster.deadDoSomthing += cj.MonsterDeadDo;
monster.Dead();
monster.Dead();
Monster monster2 = new Monster();
monster2.deadDoSomthing += p.MonsterDeadDoSomthing;
monster2.deadDoSomthing += panel.MonsterDeadDo;
monster2.deadDoSomthing += cj.MonsterDeadDo;
monster2.Dead();
}
}
}
事件
using System;
namespace Lesson13_事件
{
#region 知识点一 事件是什么
//事件是基于委托的存在
//事件是委托的安全包裹
//让委托的使用更具有安全性
//事件 是一种特殊的变量类型
#endregion
#region 知识点二 事件的使用
//申明语法:
//访问修饰符 event 委托类型 事件名;
//事件的使用:
//1.事件是作为 成员变量存在于类中
//2.委托怎么用 事件就怎么用
//事件相对于委托的区别:
//1.不能在类外部 赋值
//2.不能再类外部 调用
//注意:
//它只能作为成员存在于类和接口以及结构体中
class Test
{
//委托成员变量 用于存储 函数的
public Action myFun;
//事件成员变量 用于存储 函数的
public event Action myEvent;
public Test()
{
//事件的使用和委托 一模一样 只是有些 细微的区别
myFun = TestFun;
myFun += TestFun;
myFun -= TestFun;
myFun();
myFun.Invoke();
myFun = null;
myEvent = TestFun;
myEvent += TestFun;
myEvent -= TestFun;
myEvent();
myEvent.Invoke();
myEvent = null;
}
public void DoEvent()
{
if(myEvent != null)
{
myEvent();
}
}
public void TestFun()
{
Console.WriteLine("123");
}
}
#endregion
#region 知识点三 为什么有事件
//1.防止外部随意置空委托
//2.防止外部随意调用委托
//3.事件相当于对委托进行了一次封装 让其更加安全
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("事件");
Test t = new Test();
//委托可以在外部赋值
t.myFun = null;
t.myFun = TestFun;
t.myFun = t.myFun + TestFun;
t.myFun += TestFun;
//事件是不能再外部赋值的
//t.myEvent = null;
//t.myEvent = TestFun;
//虽然不能直接赋值 但是可以 加减 去添加移除记录的函数
t.myEvent += TestFun;
t.myEvent -= TestFun;
//委托是可以在外部调用的
t.myFun();
t.myFun.Invoke();
//事件不能再外部调用
//t.myEvent();
//只能在类的内部去封装 调用
t.DoEvent();
Action a = TestFun;
//事件 是不能作为临时变量在函数中使用的
//event Action ae = TestFun;
}
static void TestFun()
{
}
}
//总结
//事件和委托的区别
//事件和委托的使用基本是一模一样的
//事件就是特殊的委托
//主要区别:
//1.事件不能再外部使用赋值=符号,只能使用+ - 委托 哪里都能用
//2.事件 不能再外部执行 委托哪里都能执行
//3.事件 不能作为 函数中的临时变量的 委托可以
}
匿名函数
using System;
namespace Lesson14_匿名函数
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("匿名函数");
#region 知识点一 什么是匿名函数
//顾名思义,就是没有名字的函数
//匿名函数的使用主要是配合委托和事件进行使用
//脱离委托和事件 是不会使用匿名函数的
#endregion
#region 知识点二 基本语法
//delegate (参数列表)
//{
// //函数逻辑
//};
//何时使用?
//1.函数中传递委托参数时
//2.委托或事件赋值时
#endregion
#region 知识点三 使用
//1.无参无返回
//这样申明匿名函数 只是在申明函数而已 还没有调用
//真正调用它的时候 是这个委托容器啥时候调用 就什么时候调用这个匿名函数
Action a = delegate ()
{
Console.WriteLine("匿名函数逻辑");
};
a();
//2.有参
Action<int, string> b = delegate (int a, string b)
{
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.WriteLine(b);
};
b(100, "123");
//3.有返回值
Func<string> c = delegate ()
{
return "123123";
};
Console.WriteLine(c());
//4.一般情况会作为函数参数传递 或者 作为函数返回值
Test t = new Test();
Action ac = delegate ()
{
Console.WriteLine("随参数传入的匿名函数逻辑");
};
t.Dosomthing(50, ac);
// 参数传递
t.Dosomthing(100, delegate ()
{
Console.WriteLine("随参数传入的匿名函数逻辑");
});
// 返回值
Action ac2 = t.GetFun();
ac2();
//一步到位 直接调用返回的 委托函数
t.GetFun()();
#endregion
#region 知识点四 匿名函数的缺点
//添加到委托或事件容器中后 不记录 无法单独移除
Action ac3 = delegate ()
{
Console.WriteLine("匿名函数一");
};
ac3 += delegate ()
{
Console.WriteLine("匿名函数二");
};
ac3();
//因为匿名函数没有名字 所以没有办法指定移除某一个匿名函数
//此匿名函数 非彼匿名函数 不能通过看逻辑是否一样 就证明是一个
//ac3 -= delegate ()
//{
// Console.WriteLine("匿名函数一");
//};
ac3 = null;
//ac3();
#endregion
}
static void TestFun()
{
}
}
class Test
{
public Action action;
//作为参数传递时
public void Dosomthing(int a, Action fun)
{
Console.WriteLine(a);
fun();
}
//作为返回值
public Action GetFun()
{
return delegate() {
Console.WriteLine("函数内部返回的一个匿名函数逻辑");
};
}
public void TestTTTT()
{
}
}
//总结
//匿名函数 就是没有名字的函数
//固定写法
//delegate(参数列表){}
//主要是在 委托传递和存储时 为了方便可以直接使用倪敏该函数
//缺点是 没有办法指定移除
}
Lambad表达式
using System;
namespace Lesson15_lambad表达式
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("lambad表达式");
#region 知识点一 什么是lambad表达式
//可以将lambad表达式 理解为匿名函数的简写
//它除了写法不同外
//使用上和匿名函数一模一样
//都是和委托或者事件 配合使用的
#endregion
#region 知识点二 lambad表达式语法
//匿名函数
//delegate (参数列表)
//{
//};
//lambad表达式
//(参数列表) =>
//{
// //函数体
//};
#endregion
#region 知识点三 使用
//1.无参无返回
Action a = () =>
{
Console.WriteLine("无参无返回值的lambad表达式");
};
a();
//2.有参
Action<int> a2 = (int value) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("有参数Lambad表达式{0}", value);
};
a2(100);
//3.甚至参数类型都可以省略 参数类型和委托或事件容器一致
Action<int> a3 = (value) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("省略参数类型的写法{0}", value);
};
a3(200);
//4.有返回值
Func<string, int> a4 = (value) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("有返回值有参数的那么大表达式{0}", value);
return 1;
};
Console.WriteLine(a4("123123"));
//其它传参使用等和匿名函数一样
//缺点也是和匿名函数一样的
#endregion
Test t = new Test();
t.DoSomthing();
}
}
#region 知识点四 闭包
//内层的函数可以引用包含在它外层的函数的变量
//即使外层函数的执行已经终止
//注意:
//该变量提供的值并非变量创建时的值,而是在父函数范围内的最终值。
class Test
{
public event Action action;
public Test()
{
int value = 10;
//这里就形成了闭包
//因为 当构造函数执行完毕时 其中申明的临时变量value的声明周期被改变了
action = () =>
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
//此index 非彼index
int index = i;
action += () =>
{
Console.WriteLine(index);
};
}
}
public void DoSomthing()
{
action();
}
}
#endregion
//总结
//匿名函数的特殊写法 就是 lambad表达式
//固定写法 就是 (参数列表)=>{}
//参数列表 可以直接省略参数类型
//主要在 委托传递和存储时 为了方便可以直接使用匿名函数或者lambad表达式
//缺点:无法指定移除
}
List排序
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis;
namespace Lesson16_List排序
{
class Item : IComparable<Item>
{
public int money;
public Item(int money)
{
this.money = money;
}
public int CompareTo(Item other)
{
//返回值的含义
//小于0:
//放在传入对象的前面
//等于0:
//保持当前的位置不变
//大于0:
//放在传入对象的后面
//可以简单理解 传入对象的位置 就是0
//如果你的返回为负数 就放在它的左边 也就前面
//如果你返回正数 就放在它的右边 也就是后面
if( this.money > other.money )
{
return -1;
}
else
{
return 1;
}
}
}
class ShopItem
{
public int id;
public ShopItem(int id)
{
this.id = id;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("List排序");
#region 知识点一 List自带排序方法
List<int> list = new List<int>();
list.Add(3);
list.Add(2);
list.Add(6);
list.Add(1);
list.Add(4);
list.Add(5);
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
//list提供了排序方法
list.Sort();
Console.WriteLine("**************");
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
//ArrayList中也有Sort排序方法
#endregion
#region 知识点二 自定义类的排序
List<Item> itemList = new List<Item>();
itemList.Add(new Item(45));
itemList.Add(new Item(10));
itemList.Add(new Item(99));
itemList.Add(new Item(24));
itemList.Add(new Item(100));
itemList.Add(new Item(12));
//排序方法
itemList.Sort();
for (int i = 0; i < itemList.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(itemList[i].money);
}
#endregion
#region 知识点三 通过委托函数进行排序
List<ShopItem> shopItems = new List<ShopItem>();
shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(2));
shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(1));
shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(4));
shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(3));
shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(6));
shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(5));
//shopItems.Sort(SortShopItem);
//匿名函数
//shopItems.Sort(delegate (ShopItem a, ShopItem b)
//{
// if (a.id > b.id)
// {
// return -1;
// }
// else
// {
// return 1;
// }
//});
//lambad表达式 配合 三目运算符的 完美呈现
shopItems.Sort((a, b) =>{ return a.id > b.id ? 1 : -1;});
Console.WriteLine("*********************");
for (int i = 0; i < shopItems.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(shopItems[i].id);
}
#endregion
}
static int SortShopItem( ShopItem a, ShopItem b )
{
//传入的两个对象 为列表中的两个对象
//进行两两的比较 用左边的和右边的条件 比较
//返回值规则 和之前一样 0做标准 负数在左(前) 正数在右(后)
if (a.id > b.id)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
return 1;
}
}
}
//总结
//系统自带的变量(int,float,double.....) 一般都可以直接Sort
//自定义类SOrt有两种方式
//1.继承接口 IComparable
//2.在Sort中传入委托函数
}
协变逆变
using System;
namespace Lesson17_协变逆变
{
#region 知识点一 什么是协变逆变
//协变:
//和谐的变化,自然的变化
//因为 里氏替换原则 父类可以装子类
//所以 子类变父类
//比如 string 变成 object
//感受是和谐的
//逆变:
//逆常规的变化,不正常的变化
//因为 里氏替换原则 父类可以装子类 但是子类不能装父类
//所以 父类变子类
//比如 object 变成 string
//感受是不和谐的
//协变和逆变是用来修饰泛型的
//协变:out
//逆变:in
//用于在泛型中 修饰 泛型字母的
//只有泛型接口和泛型委托能使用
#endregion
#region 知识点二 作用
//1.返回值 和 参数
//用out修饰的泛型 只能作为返回值
delegate T TestOut<out T>();
//用in修饰的泛型 只能作为参数
delegate void TestIn<in T>(T t);
//2.结合里氏替换原则理解
class Father
{
}
class Son:Father
{
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("协变逆变");
#region 知识点二 作用(结合里氏替换原则理解)
//协变 父类总是能被子类替换
// 看起来 就是 son ——> father
TestOut<Son> os = () =>
{
return new Son();
};
TestOut<Father> of = os;
Father f = of();//实际上 返回的 是os里面装的函数 返回的是Son
//逆变 父类总是能被子类替换
//看起来像是 father——>son 明明是传父类 但是你传子类 不和谐的
TestIn<Father> iF = (value) =>
{
};
TestIn<Son> iS = iF;
iS(new Son());//实际上 调用的是 iF
#endregion
}
}
//总结
//协变 out
//逆变 in
//用来修饰 泛型替代符的 只能修饰接口和委托中的泛型
//作用两点
//1.out修饰的泛型类型 只能作为返回值类型 in修饰的泛型类型 只能作为 参数类型
//2.遵循里氏替换原则的 用out和in修饰的 泛型委托 可以相互装载(有父子关系的泛型)
// 协变 父类泛型委托装子类泛型委托 逆变 子类泛型委托装父类泛型委托
}
多线程
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace Lesson18_多线程
{
class Program
{
static bool isRuning = true;
static object obj = new object();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("多线程");
#region 知识点一 了解线程前先了解进程
//进程(Process)是计算机中的程序关于某数据集合上的一次运行活动
//是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位,是操作系统结构的基础
//说人话:打开一个应用程序就是在操作系统上开启了一个进程
//进程之间可以相互独立运行,互不干扰
//进程之间也可以相互访问、操作
#endregion
#region 知识点二 什么是线程
//操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位。
//它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位
//一条线程指的是进程中一个单一顺序的控制流,一个进程中可以并发多个线程
//我们目前写的程序 都在主线程中
//简单理解线程:
//就是代码从上到下运行的一条“管道”
#endregion
#region 知识点三 什么是多线程
//我们可以通过代码 开启新的线程
//可以同时运行代码的多条“管道” 就叫多线程
#endregion
#region 知识点四 语法相关
//线程类 Thread
//需要引用命名空间 using System.Threading;
//1.申明一个新的线程
// 注意 线程执行的代码 需要封装到一个函数中
// 新线程 将要执行的代码逻辑 被封装到了一个函数语句块中
Thread t = new Thread(NewThreadLogic);
//2.启动线程
t.Start();
//3.设置为后台线程
//当前台线程都结束了的时候,整个程序也就结束了,即使还有后台线程正在运行
//后台线程不会防止应用程序的进程被终止掉
//如果不设置为后台线程 可能导致进程无法正常关闭
t.IsBackground = true;
//4.关闭释放一个线程
//如果开启的线程中不是死循环 是能够结束的逻辑 那么 不用刻意的去关闭它
//如果是死循环 想要中止这个线程 有两种方式
//4.1-死循环中bool标识
//Console.ReadKey();
//isRuning = false;
//Console.ReadKey();
//4.2-通过线程提供的方法(注意在.Net core版本中无法中止 会报错)
//中止线程
//try
//{
// t.Abort();
// t = null;
//}
//catch
//{
//}
//5.线程休眠
//让线程休眠多少毫秒 1s = 1000毫秒
//在哪个线程里执行 就休眠哪个线程
//Thread.Sleep(1000);
#endregion
#region 知识点五 线程之间共享数据
//多个线程使用的内存是共享的,都属于该应用程序(进程)
//所以要注意 当多线程 同时操作同一片内存区域时可能会出问题
//可以通过加锁的形式避免问题
//lock
//当我们在多个线程当中想要访问同样的东西 进行逻辑处理时
//为了避免不必要的逻辑顺序执行的差错
//lock(引用类型对象)
while(true)
{
lock(obj)
{
Console.SetCursorPosition(0, 0);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.Write("●");
}
}
#endregion
#region 知识点六 多线程对于我们的意义
//可以用多线程专门处理一些复杂耗时的逻辑
//比如 寻路、网络通信等等
#endregion
}
static void NewThreadLogic()
{
//新开线程 执行的代码逻辑 在该函数语句块中
while(isRuning)
{
//Thread.Sleep(1000);
//Console.WriteLine("新开线程代码逻辑");
lock(obj)
{
Console.SetCursorPosition(10, 5);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.Write("■");
}
}
}
}
//总结
//多线程是多个可以同时执行代码逻辑的“管道”
//可以通过代码开启多线程,用多线程处理一些复杂的可能影响主线程流畅度的逻辑
//关键字 Thread
}
预处理
//定义一个符号
#define Unity4
#define Unity5
#define Unity2017
#define Unity2019
//取消定义一个符号
#undef Unity4
#define IOS
#define Android
#define PC
using System;
namespace Lesson19_预处理器指令
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("预处理器指令");
#region 知识点一 什么是编译器
//编译器是一种翻译程序
//它用于将源语言程序翻译为目标语言程序
//源语言程序:某种程序设计语言写成的,比如C#、C、C++、Java等语言写的程序
//目标语言程序:二进制数表示的伪机器代码写的程序
#endregion
#region 知识点二 什么是预处理器指令
//预处理器指令 指导编译器 在实际编译开始之前对信息进行预处理
//预处理器指令 都是以#开始
//预处理器指令不是语句,所以它们不以分号;结束
//目前我们经常用到的 折叠代码块 就是预处理器指令
#endregion
#region 知识点三 常见的预处理器指令
//1
//#define
//定义一个符号,类似一个没有值的变量
//#undef
//取消define定义的符号,让其失效
//两者都是写在脚本文件最前面
//一般配合 if指令使用 或配合特性
//2
//#if
//#elif
//#else
//#endif
//和if语句规则一样,一般配合#define定义的符号使用
//用于告诉编译器进行编译代码的流程控制
//如果发现有Unity4这个符号 那么其中包含的代码 就会被编译器翻译
//可以通过 逻辑或 和 逻辑与 进行多种符号的组合判断
#if Unity4
Console.WriteLine("版本为Unity4");
#elif Unity2017 && IOS
Console.WriteLine("版本为Unity2017");
//#warning 这个版本 不合法
//#error 这个版本不准执行
#else
Console.WriteLine("其它版本");
#endif
//3
//#warning
//#error
//告诉编译器
//是报警告还是报错误
//一般还是配合if使用
#endregion
}
}
//总结
//预处理器指令
//可以让代码还没有编译之前就可以进行一些预处理判断
//在Unity中会用来进行一些平台或者版本的判断
//决定不同的版本或者不同的平台使用不同的代码逻辑
}
反射
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Threading;
namespace Lesson20_反射
{
#region 知识点回顾
//编译器是一种翻译程序
//它用于将源语言程序翻译为目标语言程序
//源语言程序:某种程序设计语言写成的,比如C#、C、C++、Java等语言写的程序
//目标语言程序:二进制数表示的伪机器代码写的程序
#endregion
#region 知识点一 什么是程序集
//程序集是经由编译器编译得到的,供进一步编译执行的那个中间产物
//在WINDOWS系统中,它一般表现为后缀为·dll(库文件)或者是·exe(可执行文件)的格式
//说人话:
//程序集就是我们写的一个代码集合,我们现在写的所有代码
//最终都会被编译器翻译为一个程序集供别人使用
//比如一个代码库文件(dll)或者一个可执行文件(exe)
#endregion
#region 知识点二 元数据
//元数据就是用来描述数据的数据
//这个概念不仅仅用于程序上,在别的领域也有元数据
//说人话:
//程序中的类,类中的函数、变量等等信息就是 程序的 元数据
//有关程序以及类型的数据被称为 元数据,它们保存在程序集中
#endregion
#region 知识点三 反射的概念
//程序正在运行时,可以查看其它程序集或者自身的元数据。
//一个运行的程序查看本身或者其它程序的元数据的行为就叫做反射
//说人话:
//在程序运行时,通过反射可以得到其它程序集或者自己程序集代码的各种信息
//类,函数,变量,对象等等,实例化它们,执行它们,操作它们
#endregion
#region 知识点四 反射的作用
//因为反射可以在程序编译后获得信息,所以它提高了程序的拓展性和灵活性
//1.程序运行时得到所有元数据,包括元数据的特性
//2.程序运行时,实例化对象,操作对象
//3.程序运行时创建新对象,用这些对象执行任务
#endregion
class Test
{
private int i = 1;
public int j = 0;
public string str = "123";
public Test()
{
}
public Test(int i)
{
this.i = i;
}
public Test( int i, string str ):this(i)
{
this.str = str;
}
public void Speak()
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("反射");
#region 知识点五 语法相关
#region Type
//Type(类的信息类)
//它是反射功能的基础!
//它是访问元数据的主要方式。
//使用 Type 的成员获取有关类型声明的信息
//有关类型的成员(如构造函数、方法、字段、属性和类的事件)
#region 获取Type
//1.万物之父object中的 GetType()可以获取对象的Type
int a = 42;
Type type = a.GetType();
Console.WriteLine(type);
//2.通过typeof关键字 传入类名 也可以得到对象的Type
Type type2 = typeof(int);
Console.WriteLine(type2);
//3.通过类的名字 也可以获取类型
// 注意 类名必须包含命名空间 不然找不到
Type type3 = Type.GetType("System.Int32");
Console.WriteLine(type3);
#endregion
#region 得到类的程序集信息
//可以通过Type可以得到类型所在程序集信息
Console.WriteLine(type.Assembly);
Console.WriteLine(type2.Assembly);
Console.WriteLine(type3.Assembly);
#endregion
#region 获取类中的所有公共成员
//首先得到Type
Type t = typeof(Test);
//然后得到所有公共成员
//需要引用命名空间 using System.Reflection;
MemberInfo[] infos = t.GetMembers();
for (int i = 0; i < infos.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(infos[i]);
}
#endregion
#region 获取类的公共构造函数并调用
//1.获取所有构造函数
ConstructorInfo[] ctors = t.GetConstructors();
for (int i = 0; i < ctors.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(ctors[i]);
}
//2.获取其中一个构造函数 并执行
//得构造函数传入 Type数组 数组中内容按顺序是参数类型
//执行构造函数传入 object数组 表示按顺序传入的参数
// 2-1得到无参构造
ConstructorInfo info = t.GetConstructor(new Type[0]);
//执行无参构造 无参构造 没有参数 传null
Test obj = info.Invoke(null) as Test;
Console.WriteLine(obj.j);
// 2-2得到有参构造
ConstructorInfo info2 = t.GetConstructor(new Type[] { typeof(int) });
obj = info2.Invoke(new object[] { 2 }) as Test;
Console.WriteLine(obj.str);
ConstructorInfo info3 = t.GetConstructor(new Type[] { typeof(int), typeof(string) });
obj = info3.Invoke(new object[] { 4, "444444" }) as Test;
Console.WriteLine(obj.str);
#endregion
#region 获取类的公共成员变量
//1.得到所有成员变量
FieldInfo[] fieldInfos = t.GetFields();
for (int i = 0; i < fieldInfos.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(fieldInfos[i]);
}
//2.得到指定名称的公共成员变量
FieldInfo infoJ = t.GetField("j");
Console.WriteLine(infoJ);
//3.通过反射获取和设置对象的值
Test test = new Test();
test.j = 99;
test.str = "2222";
// 3-1通过反射 获取对象的某个变量的值
Console.WriteLine(infoJ.GetValue(test));
// 3-2通过反射 设置指定对象的某个变量的值
infoJ.SetValue(test, 100);
Console.WriteLine(infoJ.GetValue(test));
#endregion
#region 获取类的公共成员方法
//通过Type类中的 GetMethod方法 得到类中的方法
//MethodInfo 是方法的反射信息
Type strType = typeof(string);
MethodInfo[] methods = strType.GetMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < methods.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(methods[i]);
}
//1.如果存在方法重载 用Type数组表示参数类型
MethodInfo subStr = strType.GetMethod("Substring",
new Type[] { typeof(int), typeof(int) });
//2.调用该方法
//注意:如果是静态方法 Invoke中的第一个参数传null即可
string str = "Hello,World!";
//第一个参数 相当于 是哪个对象要执行这个成员方法
object result = subStr.Invoke(str, new object[] { 7, 5 });
Console.WriteLine(result);
#endregion
#region 其它
//Type;
//得枚举
//GetEnumName
//GetEnumNames
//得事件
//GetEvent
//GetEvents
//得接口
//GetInterface
//GetInterfaces
//得属性
//GetProperty
//GetPropertys
//等等
#endregion
#endregion
#region Assembly
//程序集类
//主要用来加载其它程序集,加载后
//才能用Type来使用其它程序集中的信息
//如果想要使用不是自己程序集中的内容 需要先加载程序集
//比如 dll文件(库文件)
//简单的把库文件看成一种代码仓库,它提供给使用者一些可以直接拿来用的变量、函数或类
//三种加载程序集的函数
//一般用来加载在同一文件下的其它程序集
//Assembly asembly2 = Assembly.Load("程序集名称");
//一般用来加载不在同一文件下的其它程序集
//Assembly asembly = Assembly.LoadFrom("包含程序集清单的文件的名称或路径");
//Assembly asembly3 = Assembly.LoadFile("要加载的文件的完全限定路径");
//1.先加载一个指定程序集
Assembly asembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\Users\MECHREVO\Desktop\CSharp进阶教学\Lesson18_练习题\bin\Debug\netcoreapp3.1\Lesson18_练习题");
Type[] types = asembly.GetTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < types.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(types[i]);
}
//2.再加载程序集中的一个类对象 之后才能使用反射
Type icon = asembly.GetType("Lesson18_练习题.Icon");
MemberInfo[] members = icon.GetMembers();
for (int i = 0; i < members.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(members[i]);
}
//通过反射 实例化一个 icon对象
//首先得到枚举Type 来得到可以传入的参数
Type moveDir = asembly.GetType("Lesson18_练习题.E_MoveDir");
FieldInfo right = moveDir.GetField("Right");
//直接实例化对象
object iconObj = Activator.CreateInstance(icon, 10, 5, right.GetValue(null));
//得到对象中的方法 通过反射
MethodInfo move = icon.GetMethod("Move");
MethodInfo draw = icon.GetMethod("Draw");
MethodInfo clear = icon.GetMethod("Clear");
Console.Clear();
while(true)
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
clear.Invoke(iconObj, null);
move.Invoke(iconObj, null);
draw.Invoke(iconObj, null);
}
//3.类库工程创建
#endregion
#region Activator
//用于快速实例化对象的类
//用于将Type对象快捷实例化为对象
//先得到Type
//然后 快速实例化一个对象
Type testType = typeof(Test);
//1.无参构造
Test testObj = Activator.CreateInstance(testType) as Test;
Console.WriteLine(testObj.str);
//2.有参数构造
testObj = Activator.CreateInstance(testType, 99) as Test;
Console.WriteLine(testObj.j);
testObj = Activator.CreateInstance(testType, 55, "111222") as Test;
Console.WriteLine(testObj.j);
#endregion
#endregion
}
}
//总结
//反射
//在程序运行时,通过反射可以得到其他程序集或者自己的程序集代码的各种信息
//类、函数、变量、对象等等,实例化他们,执行他们,操作他们
//关键类
//Type
//Assembly
//Activator
//对于我们的意义
//在初中级阶段 基本不会使用反射
//所以目前对于大家来说,了解反射可以做什么就行
//很长时间内都不会用到反射相关知识点
//为什么要学反射
//为了之后学习Unity引擎的基本工作原理做铺垫
//Unity引起的基本工作机制 就是建立在反射的基础上
}
练习题
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace Lesson20_练习题
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("反射练习题");
#region 练习题
//新建一个类库工程
//有一个Player类,有姓名,血量,攻击力,防御力,位置等信息
//有一个无参构造函数
//再新建一个控制台工程
//通过反射的形式使用类库工程生成的dll程序集
//实例化一个Player对象
//加载类库生成的 程序集 dll库文件
Assembly assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\Users\MECHREVO\Desktop\CSharp进阶教学\测试\bin\Debug\测试");
Type[] types = assembly.GetTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < types.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(types[i]);
}
Type player = assembly.GetType("MrTang.Player");
object obj = Activator.CreateInstance(player);
Console.WriteLine(obj);
#endregion
}
}
}
特性
#define Fun
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace Lesson21_特性
{
#region 知识点一 特性是什么
//特性是一种允许我们向程序的程序集添加元数据的语言结构
//它是用于保存程序结构信息的某种特殊类型的类
//特性提供功能强大的方法以将声明信息与 C# 代码(类型、方法、属性等)相关联。
//特性与程序实体关联后,即可在运行时使用反射查询特性信息
//特性的目的是告诉编译器把程序结构的某组元数据嵌入程序集中
//它可以放置在几乎所有的声明中(类、变量、函数等等申明)
//说人话:
//特性本质是个类
//我们可以利用特性类为元数据添加额外信息
//比如一个类、成员变量、成员方法等等为他们添加更多的额外信息
//之后可以通过反射来获取这些额外信息
#endregion
#region 知识点二 自定义特性
//继承特性基类 Attribute
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Field, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = false)]
class MyCustomAttribute : Attribute
{
//特性中的成员 一般根据需求来写
public string info;
public MyCustomAttribute(string info)
{
this.info = info;
}
public void TestFun()
{
Console.WriteLine("特性的方法");
}
}
#endregion
#region 知识点三 特性的使用
//基本语法:
//[特性名(参数列表)]
//本质上 就是在调用特性类的构造函数
//写在哪里?
//类、函数、变量上一行,表示他们具有该特性信息
[MyCustom("这个是我自己写的一个用于计算的类")]
[MyCustom("这个是我自己写的一个用于计算的类")]
class MyClass
{
[MyCustom("这是一个成员变量")]
public int value;
//[MyCustom("这是一个用于计算加法的函数")]
//public void TestFun( [MyCustom("函数参数")]int a )
//{
//}
public void TestFun(int a)
{
}
}
#endregion
#region 知识点四 限制自定义特性的使用范围
//通过为特性类 加特性 限制其使用范围
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Struct, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = true)]
//参数一:AttributeTargets —— 特性能够用在哪些地方
//参数二:AllowMultiple —— 是否允许多个特性实例用在同一个目标上
//参数三:Inherited —— 特性是否能被派生类和重写成员继承
public class MyCustom2Attribute : Attribute
{
}
#endregion
#region 知识点五 系统自带特性——过时特性
//过时特性
//Obsolete
//用于提示用户 使用的方法等成员已经过时 建议使用新方法
//一般加在函数前的特性
class TestClass
{
//参数一:调用过时方法时 提示的内容
//参数二:true-使用该方法时会报错 false-使用该方法时直接警告
[Obsolete("OldSpeak方法已经过时了,请使用Speak方法", false)]
public void OldSpeak(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
public void Speak()
{
}
public void SpeakCaller(string str, [CallerFilePath]string fileName = "",
[CallerLineNumber]int line = 0, [CallerMemberName]string target = "")
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.WriteLine(fileName);
Console.WriteLine(line);
Console.WriteLine(target);
}
}
#endregion
#region 知识点六 系统自带特性——调用者信息特性
//哪个文件调用?
//CallerFilePath特性
//哪一行调用?
//CallerLineNumber特性
//哪个函数调用?
//CallerMemberName特性
//需要引用命名空间 using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
//一般作为函数参数的特性
#endregion
#region 知识点七 系统自带特性——条件编译特性
//条件编译特性
//Conditional
//它会和预处理指令 #define配合使用
//需要引用命名空间using System.Diagnostics;
//主要可以用在一些调试代码上
//有时想执行有时不想执行的代码
#endregion
#region 知识点八 系统自带特性——外部Dll包函数特性
//DllImport
//用来标记非.Net(C#)的函数,表明该函数在一个外部的DLL中定义。
//一般用来调用 C或者C++的Dll包写好的方法
//需要引用命名空间 using System.Runtime.InteropServices
#endregion
class Program
{
[DllImport("Test.dll")]
public static extern int Add(int a, int b);
[Conditional("Fun")]
static void Fun()
{
Console.WriteLine("Fun执行");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("特性");
#region 特性的使用
MyClass mc = new MyClass();
Type t = mc.GetType();
//t = typeof(MyClass);
//t = Type.GetType("Lesson21_特性.MyClass");
//判断是否使用了某个特性
//参数一:特性的类型
//参数二:代表是否搜索继承链(属性和事件忽略此参数)
if( t.IsDefined(typeof(MyCustomAttribute), false) )
{
Console.WriteLine("该类型应用了MyCustom特性");
}
//获取Type元数据中的所有特性
object[] array = t.GetCustomAttributes(true);
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
if( array[i] is MyCustomAttribute )
{
Console.WriteLine((array[i] as MyCustomAttribute).info);
(array[i] as MyCustomAttribute).TestFun();
}
}
TestClass tc = new TestClass();
tc.OldSpeak("123");
tc.Speak();
tc.SpeakCaller("123123123123123");
Fun();
#endregion
}
}
//总结:
//特性是用于 为元数据再添加更多的额外信息(变量、方法等等)
//我们可以通过反射获取这些额外的数据 来进行一些特殊的处理
//自定义特性——继承Attribute类
// 系统自带特性:过时特性
// 为什么要学习特性
// Unity引擎中很多地方都用到了特性来进行一些特殊处理
}
习题
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace Lesson21_练习题
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("特性练习题");
#region 练习题
//为反射练习题中的Player对象
//随便为其中一个成员变量加一个自定义特性
//同样实现反射练习题中的要求
//但是当在设置加了自定义特性的成员变量时,在控制台中打印一句
//非法操作,随意修改XXX成员
Assembly assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\Users\MECHREVO\Desktop\CSharp进阶教学\测试\bin\Debug\测试");
Type[] types = assembly.GetTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < types.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(types[i]);
}
//得type
Type playerType = assembly.GetType("MrTang.Player");
//实例化
object playerObj = Activator.CreateInstance(playerType);
Console.WriteLine(playerObj);
FieldInfo[] fields = playerType.GetFields();
for (int i = 0; i < fields.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(fields[i]);
}
//首先要得到我们自定特性的Type
Type attribute = assembly.GetType("MrTang.MyCustomAttribute");
//赋值名字
FieldInfo fildStr = playerType.GetField("name");
//得到的特性如果不为空 就证明有
if(fildStr.GetCustomAttribute(attribute) != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("非法操作,随意修改name成员");
}
else
{
//检测是否被自定义特性修饰 如果是 就不能修改 而是提示
fildStr.SetValue(playerObj, "123123");
}
#endregion
}
}
}
迭代器
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace Lesson22_迭代器
{
#region 知识点一 迭代器是什么
//迭代器(iterator)有时又称光标(cursor)
//是程序设计的软件设计模式
//迭代器模式提供一个方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各个元素
//而又不暴露其内部的标识
//在表现效果上看
//是可以在容器对象(例如链表或数组)上遍历访问的接口
//设计人员无需关心容器对象的内存分配的实现细节
//可以用foreach遍历的类,都是实现了迭代器的
#endregion
#region 知识点二 标准迭代器的实现方法
//关键接口:IEnumerator,IEnumerable
//命名空间:using System.Collections;
//可以通过同时继承IEnumerable和IEnumerator实现其中的方法
class CustomList : IEnumerable, IEnumerator
{
private int[] list;
//从-1开始的光标 用于表示 数据得到了哪个位置
private int position = -1;
public CustomList()
{
list = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
}
#region IEnumerable
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
Reset();
return this;
}
#endregion
public object Current
{
get
{
return list[position];
}
}
public bool MoveNext()
{
//移动光标
++position;
//是否溢出 溢出就不合法
return position < list.Length;
}
//reset是重置光标位置 一般写在获取 IEnumerator对象这个函数中
//用于第一次重置光标位置
public void Reset()
{
position = -1;
}
}
#endregion
#region 知识点三 用yield return 语法糖实现迭代器
//yield return 是C#提供给我们的语法糖
//所谓语法糖,也称糖衣语法
//主要作用就是将复杂逻辑简单化,可以增加程序的可读性
//从而减少程序代码出错的机会
//关键接口:IEnumerable
//命名空间:using System.Collections;
//让想要通过foreach遍历的自定义类实现接口中的方法GetEnumerator即可
class CustomList2 : IEnumerable
{
private int[] list;
public CustomList2()
{
list = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
for (int i = 0; i < list.Length; i++)
{
//yield关键字 配合迭代器使用
//可以理解为 暂时返回 保留当前的状态
//一会还会在回来
//C#的语法糖
yield return list[i];
}
//yield return list[0];
//yield return list[1];
//yield return list[2];
//yield return list[3];
//yield return list[4];
//yield return list[5];
//yield return list[6];
//yield return list[7];
}
}
#endregion
#region 知识点四 用yield return 语法糖为泛型类实现迭代器
class CustomList<T> : IEnumerable
{
private T[] array;
public CustomList(params T[] array)
{
this.array = array;
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
yield return array[i];
}
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("迭代器");
CustomList list = new CustomList();
//foreach本质
//1.先获取in后面这个对象的 IEnumerator
// 会调用对象其中的GetEnumerator方法 来获取
//2.执行得到这个IEnumerator对象中的 MoveNext方法
//3.只要MoveNext方法的返回值时true 就会去得到Current
// 然后复制给 item
//foreach (int item in list)
//{
// Console.WriteLine(item);
//}
//foreach (int item in list)
//{
// Console.WriteLine(item);
//}
CustomList<string> list2 = new CustomList<string>("123","321","333","555");
foreach (string item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
foreach (string item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}
}
//总结:
//迭代器就是可以让我们在外部直接通过foreach遍历对象中元素而不需要了解其结构
//主要的两种方式
//1.传统方式 继承两个接口 实现里面的方法
//2.用语法糖 yield return 去返回内容 只需要继承一个接口即可
习题
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace Lesson22_练习题
{
#region 练习题
//请为一个自定义类
//用两种方法让其可以被foreach遍历
class CustomList : IEnumerable
{
private int[] list;
public CustomList()
{
list = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
for (int i = 0; i < list.Length; i++)
{
yield return list[i];
}
}
}
class CustomList2 : IEnumerable, IEnumerator
{
private string[] list;
private int position = -1;
public CustomList2()
{
list = new string[] { "123", "321", "666", "7777" };
}
public object Current
{
get
{
return list[position];
}
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
Reset();
return this;
}
public bool MoveNext()
{
++position;
return position < list.Length;
}
public void Reset()
{
position = -1;
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("迭代器练习题");
z
CustomList list = new CustomList();
foreach (int item in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
CustomList2 list2 = new CustomList2();
foreach (string item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
foreach (string item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}
}
特殊语法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Lesson23_特殊语法
{
class Person
{
private int money;
public bool sex;
public string Name
{
get => "唐老狮";
set => sex = true;
}
public int Age
{
get;
set;
}
public Person(int money)
{
this.money = money;
}
public int Add(int x, int y) => x + y;
public void Speak(string str) => Console.WriteLine(str);
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("特殊语法");
#region 知识点一 var隐式类型
//var是一种特殊的变量类型
//它可以用来表示任意类型的变量
//注意:
//1.var不能作为类的成员 只能用于临时变量申明时
// 也就是 一般写在函数语句块中
//2.var必须初始化
var i = 5;
var s = "123";
var array = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
var list = new List<int>();
#endregion
#region 知识点二 设置对象初始值
//申明对象时
//可以通过直接写大括号的形式初始化公共成员变量和属性
Person p = new Person(100) { sex = true, Age = 18, Name = "唐老狮" };
Person p2 = new Person(200) { Age = 18 };
#endregion
#region 知识点三 设置集合初始值
//申明集合对象时
//也可以通过大括号 直接初始化内部属性
int[] array2 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
List<int> listInt = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
List<Person> listPerson = new List<Person>() {
new Person(200),
new Person(100){Age = 10},
new Person(1){sex = true, Name = "唐老狮"}
};
Dictionary<int, string> dic = new Dictionary<int, string>()
{
{ 1, "123" },
{ 2, "222"}
};
#endregion
#region 知识点四 匿名类型
//var 变量可以申明为自定义的匿名类型
var v = new { age = 10, money = 11, name = "小明" };
Console.WriteLine(v.age);
Console.WriteLine(v.name);
#endregion
#region 知识点五 可空类型
//1.值类型是不能赋值为 空的
//int c = null;
//2.申明时 在值类型后面加? 可以赋值为空
int? c = 3;
//3.判断是否为空
if( c.HasValue )
{
Console.WriteLine(c);
Console.WriteLine(c.Value);
}
//4.安全获取可空类型值
int? value = null;
// 4-1.如果为空 默认返回值类型的默认值
Console.WriteLine(value.GetValueOrDefault());
// 4-2.也可以指定一个默认值
Console.WriteLine(value.GetValueOrDefault(100));
float? f = null;
double? d = null;
object o = null;
if( o != null )
{
Console.WriteLine(o.ToString());
}
//相当于是一种语法糖 能够帮助我们自动去判断o是否为空
//如果是null就不会执行tostring也不会报错
Console.WriteLine(o?.ToString());
int[] arrryInt = null;
Console.WriteLine(arrryInt?[0]);
Action action = null;
//if (action != null)
//{
// action();
//}
action?.Invoke();
#endregion
#region 知识点六 空合并操作符
// 空合并操作符 ??
// 左边值 ?? 右边值
// 如果左边值为null 就返回右边值 否则返回左边值
// 只要是可以为null的类型都能用
int? intV = null;
//int intI = intV == null ? 100 : intV.Value;
int intI = intV ?? 100;
Console.WriteLine(intI);
string str = null;
str = str ?? "hahah";
Console.WriteLine(str);
#endregion
#region 知识点七 内插字符串
//关键符号:$
//用$来构造字符串,让字符串中可以拼接变量
string name = "唐老狮";
int age = 18;
Console.WriteLine($"好好学习,{name},年龄:{age}");
#endregion
#region 知识点八 单句逻辑简略写法
//当循环或者if语句中只有 一句代码时 大括号可以省略
if (true)
Console.WriteLine("123123");
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
Console.WriteLine(j);
while (true)
Console.WriteLine("123123");
#endregion
}
}
}
值和引用
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Lesson24_值和引用
{
class Test
{
public static int TestI = 0;
int b = 0;
string str = "123";
TestStrict ts = new TestStrict();
public void Fun()
{
b = 1;
}
}
struct TestStrict
{
public Test t;
public int i;
}
class Program
{
static int b;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("值和引用");
#region 知识回顾
//值类型
//无符号:byte,ushort,uint,ulong
//有符号:sbyte,short,int,long
//浮点数:float,double,decimal
//特殊:char,bool
//枚举:enum
//结构体:struct
//引用类型
//string
//数组
//class
//interface
//委托
//值类型和引用类型的本质区别
//值的具体内容存在栈内存上
//引用的具体内容存在堆内存上
#endregion
#region 问题一 如何判断 值类型和引用类型
//F12进到类型的内部去查看
//是class就是引用
//是struct就是值
int i = 12;
string str = "123";
#endregion
#region 问题二 语句块
//命名空间
// ↓
//类、接口、结构体
// ↓
//函数、属性、索引器、运算符重载等(类、接口、结构体)
// ↓
//条件分支、循环
//上层语句块:类、结构体
//中层语句块:函数
//底层的语句块: 条件分支 循环等
//我们的逻辑代码写在哪里?
//函数、条件分支、循环-中底层语句块中
//我们的变量可以申明在哪里?
//上、中、底都能申明变量
//上层语句块中:成员变量
//中、底层语句块中:临时变量
#endregion
#region 问题三 变量的生命周期
//编程时大部分都是 临时变量
//在中底层申明的临时变量(函数、条件分支、循环语句块等)
//语句块执行结束
//没有被记录的对象将被回收或变成垃圾
//值类型:被系统自动回收
//引用类型:栈上用于存地址的房间被系统自动回收,堆中具体内容变成垃圾,待下次GC回收
int i2 = 1;
string str2 = "123";
//{
// int b = 1;
//}
//Console.WriteLine(b);
//while(true)
//{
// int index = 1;
//}
//想要不被回收或者不变垃圾
//必须将其记录下来
//如何记录?
//在更高层级记录或者
//使用静态全局变量记录
b = 0;
if(true)
{
b = 1;
}
int c = 10;
Test.TestI = c;
//Game g = new Game();
//while(true)
//{
//}
#endregion
#region 问题四 结构体中的值和引用
//结构体本身是值类型
//前提:该结构体没有做为其它类的成员
//在结构体中的值,栈中存储值具体的内容
//在结构体中的引用,堆中存储引用具体的内容
//引用类型始终存储在堆中
//真正通过结构体使用其中引用类型时只是顺藤摸瓜
TestStrict ts = new TestStrict();
#endregion
#region 问题五 类中的值和引用
//类本身是引用类型
//在类中的值,堆中存储具体的值
//在类中的引用,堆中存储具体的值
//值类型跟着大哥走,引用类型一根筋
Test t = new Test();
#endregion
#region 问题六 数组中的存储规则
//数组本身是引用类型
//值类型数组,堆中房间存具体内容
//引用类型数组,堆中房间存地址
int[] arrayInt = new int[5];
object[] objs = new object[5];
#endregion
#region 问题七 结构体继承接口
//利用里氏替换原则,用接口容器装载结构体存在装箱拆箱
TestStruct obj1 = new TestStruct();
obj1.Value = 1;
Console.WriteLine(obj1.Value);
TestStruct obj2 = obj1;
obj2.Value = 2;
Console.WriteLine(obj1.Value);
Console.WriteLine(obj2.Value);
ITest iObj1 = obj1;//装箱 value 1
ITest iObj2 = iObj1;
iObj2.Value = 99;
Console.WriteLine(iObj1.Value);
Console.WriteLine(iObj2.Value);
TestStruct obj3 = (TestStruct)iObj1;//拆箱
#endregion
}
}
interface ITest
{
int Value
{
get;
set;
}
}
struct TestStruct : ITest
{
int value;
public int Value
{
get
{
return value;
}
set
{
this.value = value;
}
}
}
}
俄罗斯方块实战
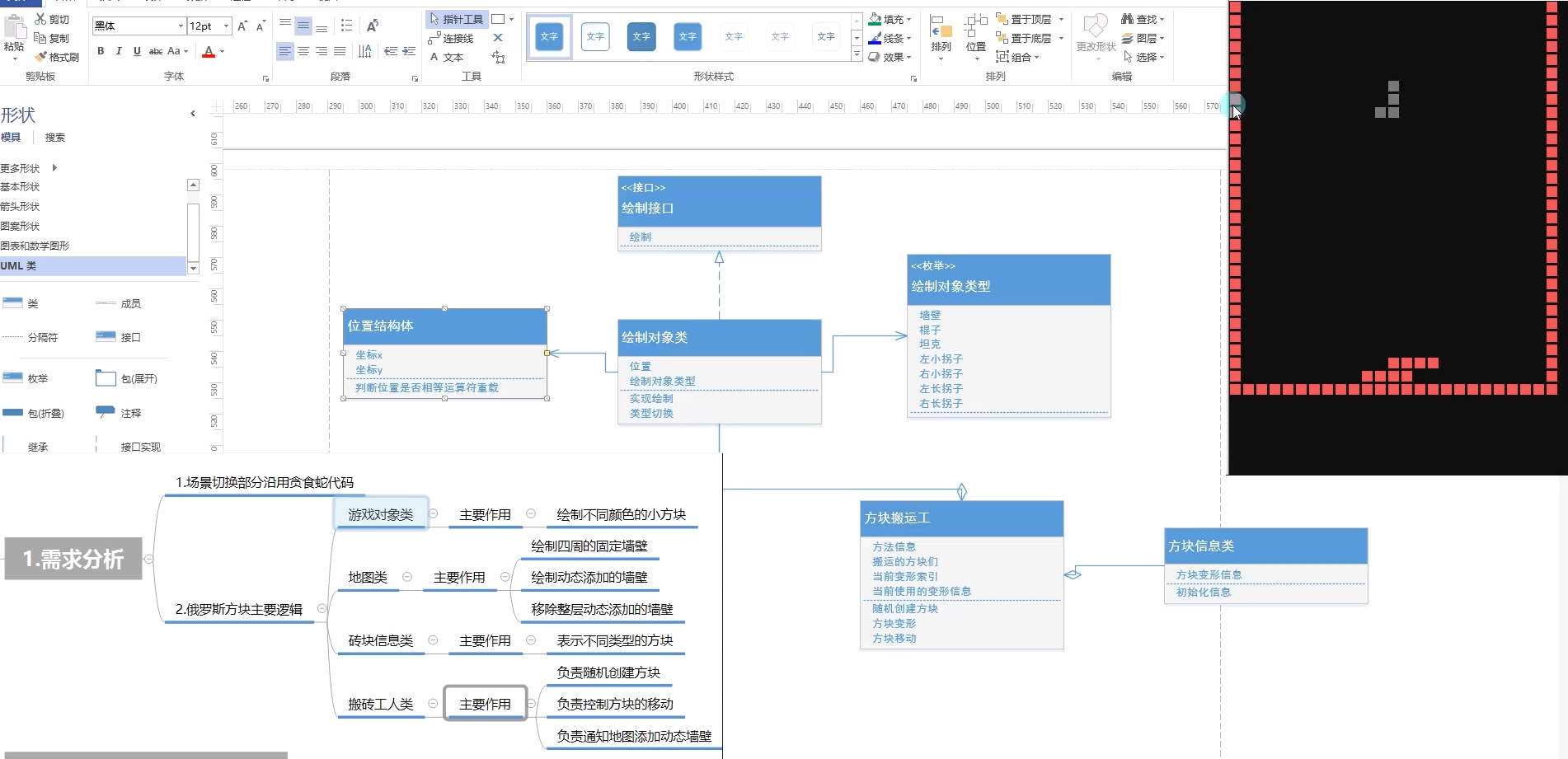
需求分析
开始场景结束场景复用贪吃蛇
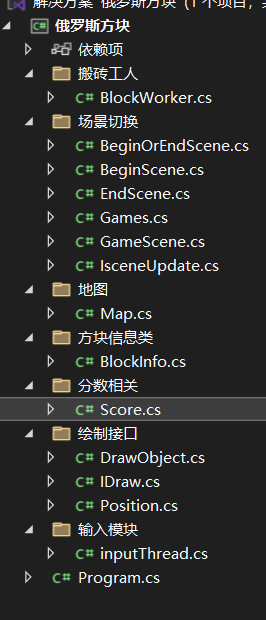
项目文件
BeginOrEndScene
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using 俄罗斯方块;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
abstract class BeginOrEndScene : IsceneUpdate
{
protected int nowSelIndex = 0;
protected string strTitle;
protected string StrOne;
public abstract void EnterJDoSomthing();
public void Update()
{
// 开始或结束游戏逻辑
//选择当前选项,监听键盘输入
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
// 显示标题
Console.SetCursorPosition(Game.w/2-strTitle.Length,5);
Console.Write(strTitle);
Console.SetCursorPosition(Game.w / 2 - StrOne.Length, 8);
Console.ForegroundColor = nowSelIndex==0?ConsoleColor.Red:ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write(StrOne);
Console.SetCursorPosition(Game.w / 2 -4, 10);
Console.ForegroundColor = nowSelIndex == 1 ? ConsoleColor.Red : ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write("结束游戏");
switch (Console.ReadKey(true).Key)
{
case ConsoleKey.W:
--nowSelIndex;
if (nowSelIndex <0)
{
nowSelIndex = 0;
}
break;
case ConsoleKey.A:
++nowSelIndex;
if (nowSelIndex >1)
{
nowSelIndex = 1;
}
break;
case ConsoleKey.S:
++nowSelIndex;
if (nowSelIndex > 1)
{
nowSelIndex = 1;
}
break;
case ConsoleKey.D:
--nowSelIndex;
if (nowSelIndex < 0)
{
nowSelIndex = 0;
}
break;
case ConsoleKey.J:
EnterJDoSomthing();
break;
}
// 显示下方选项
// 检测输入
}
}
}
BeginScene
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
internal class BeginScene : BeginOrEndScene
{
public BeginScene() {
strTitle = "俄罗斯方块";
StrOne = "开始游戏";
}
public override void EnterJDoSomthing()
{
// 按J键做什么
if (nowSelIndex == 0)
{
Game.ChangeScene(E_SceneType.Game);
}
else {
Environment.Exit(0);
}
}
}
}
EndScene
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
internal class EndScene : BeginOrEndScene
{
public EndScene() {
strTitle = "结束游戏";
StrOne = "回到开始界面";
}
public override void EnterJDoSomthing()
{
// 按J键做什么
if (nowSelIndex == 0)
{
Game.ChangeScene(E_SceneType.Begin);
}
else
{
Environment.Exit(0);
}
}
}
}
Games
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
enum E_SceneType
{
/// <summary>
/// 开始
/// </summary>
Begin,
/// <summary>
/// 游戏
/// </summary>
Game,
/// <summary>
/// 结束
/// </summary>
End
}
class Game
{
public const int w = 50;
public const int h = 35;
public static IsceneUpdate nowSecene;
public Game()
{
Console.CursorVisible = false;
Console.SetWindowSize(w, h);
Console.SetBufferSize(w, h);
ChangeScene(E_SceneType.Begin);
}
public void Start() {
while (true)
{
if (nowSecene != null)
{
nowSecene.Update();
}
}
}
public static void ChangeScene(E_SceneType type)
{
// 切场景之前把上一个场景绘制清理
Console.Clear();
switch (type)
{
case E_SceneType.Begin:
nowSecene = new BeginScene();
break;
case E_SceneType.Game:
nowSecene = new GameScene();
break;
case E_SceneType.End:
nowSecene = new EndScene();
break;
}
}
}
}
GameScene
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
class GameScene : IsceneUpdate
{
Map map;
BlockWorker blockWorker;
Score Score;
//Thread inputThread;
//public bool isRunning = true;
public GameScene()
{
map = new Map(this);
blockWorker = new BlockWorker();
Score = new Score(this);
// 添加输入时间监听
inputThread.Instance.inputEvent += CheckInputThread;
//inputThread = new Thread(CheckInputThread);
//inputThread.IsBackground = true;
//inputThread.Start();
}
private void CheckInputThread()
{
//while (isRunning)
//{
if (Console.KeyAvailable)
{
lock (blockWorker)
{
switch (Console.ReadKey(true).Key)
{
case ConsoleKey.LeftArrow:
if (blockWorker.IsChange(E_Change_Type.left, map))
{
blockWorker.Change(E_Change_Type.left);
}
break;
case ConsoleKey.RightArrow:
if (blockWorker.IsChange(E_Change_Type.right, map))
{
blockWorker.Change(E_Change_Type.right);
}
break;
case ConsoleKey.A:
if (blockWorker.IsMoveRL(E_Change_Type.left, map))
{
blockWorker.MoveRl(E_Change_Type.left);
}
break;
case ConsoleKey.D:
if (blockWorker.IsMoveRL(E_Change_Type.right, map))
{
blockWorker.MoveRl(E_Change_Type.right);
}
break;
case ConsoleKey.S:
if (blockWorker.IsAutoMove(map))
{
blockWorker.AutoMoveDown();
}
break;
}
//Score.ScoreLine = map.updateScore();
//Score.ScoreNum = map.GetScore();
}
}
}
public void StopThread()
{
// 移除事件监听
inputThread.Instance.inputEvent-=CheckInputThread;
}
public void Update()
{
lock (blockWorker)
{
/* Console.ReadKey(true);
Game.ChangeScene(E_SceneType.End);*/
map.IDraw();
blockWorker.IDraw();
if (blockWorker.IsAutoMove(map))
{
blockWorker.AutoMoveDown();
}
//Score.DrawScore(0, 0);
if (map.cleared)
{
Score.DrawScore(map.GetScore(),map.updateScore());
map.cleared = false;
}
}
// 线程休眠
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
//
}
}
IsceneUpdate.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
// 场景更新接口
internal interface IsceneUpdate
{
void Update();
}
}
Map
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
internal class Map:IDraw
{
// 固定墙壁
private List<DrawObject> walls = new List<DrawObject>();
// 动态墙壁
public List<DrawObject> dynamicWalls = new List<DrawObject>();
private GameScene nowGameScene;
// 记录垮掉的行次数
public int ScoreCount;
public int Score;
// 快速得到地图边界
public int w;
public int h;
// 跨层
//记录有多少方块
private int[] recordInfo;
// 重载无参构造初始化固定墙壁
public Map(GameScene scene) {
this.nowGameScene = scene;
h= Game.h-6;
// 代表每行计数的初始化,默认都为0
recordInfo = new int[h];
// 动态墙壁的宽容量
w = 0;
// 横向
for (int i = 0; i < Game.w; i+=2)
{
walls.Add(new DrawObject(E_DrawType.wall, i, Game.h - 6));
walls.Add(new DrawObject(E_DrawType.wall, i, Game.h-1));
++w;
}
w -= 2;
// 纵向
for (int i = 0; i < Game.h; i += 1)
{
walls.Add(new DrawObject(E_DrawType.wall, 0, i));
walls.Add(new DrawObject(E_DrawType.wall, Game.w-2,i));
}
}
public void IDraw()
{
// 绘制固定墙壁
for (int i = 0; i < walls.Count; i++)
{
walls[i].Draw();
}
// 绘制动态墙壁
for (int i = 0; i < dynamicWalls.Count; i++)
{
dynamicWalls[i].Draw();
}
}
// 清除动态墙壁
public void ClearDraw() {
for (int i = 0; i < dynamicWalls.Count; i++)
{
dynamicWalls[i].ClearDraw();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 提供给外部动态添加方块的函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="walls"></param>
public void AddWall(List<DrawObject> walls)
{
for (int i = 0; i < walls.Count; i++)
{
walls[i].ChangType(E_DrawType.wall);
dynamicWalls.Add(walls[i]);
// 在动态墙壁添加出发现位置满了就结束
if (walls[i].Position.y <= 0)
{
// 关闭输入线程
this.nowGameScene.StopThread();
Game.ChangeScene(E_SceneType.End);
return;
}
// 添加动态墙壁计数
//根据索引来得到行
recordInfo[h - 1 - walls[i].Position.y] += 1;
}
// 先把之前的动态小方块擦掉
ClearDraw();
CheckClear();
IDraw();
}
public bool cleared = false;
public void CheckClear()
{
// 添加一个待移除记录列表
List<DrawObject> tmpClearList = new List<DrawObject>();
//要选择记录行中有多少个方块的容器
//数组
//判断这个一行是否满(方块)
//遍历数组 检测数组里面存的数
//是不是w-2
for (int i = 0; i < recordInfo.Length; i++)
{
// 满足条件才证明满了
if (recordInfo[i] == w)
{
// 这一行的虽有小方块移除
for (int j = 0; j < dynamicWalls.Count; j++)
{
//当前动态方块y计算在那一行,如果行号和当前所以一直就证明应该移除
if (i == (h - dynamicWalls[j].Position.y-1))
{
// 移除
// 添加一个移除记录列表
tmpClearList.Add(dynamicWalls[j]);
}
//要这一行上的所有小方块下移一个单位
else if ((h - dynamicWalls[j].Position.y - 1)>i)
{
++dynamicWalls[j].Position.y;
}
}
//移除待移除的小方块
for (int j = 0; j < tmpClearList.Count; j++)
{
dynamicWalls.Remove(tmpClearList[j]);
}
//记录小方块的数量数组从上到下迁移
for (int j = i; j < recordInfo.Length-1; j++)
{
recordInfo[j] = recordInfo[j + 1];
}
// 置空最顶的计数
recordInfo[recordInfo.Length - 1] = 0;
// 垮掉一行ScoreTime+1
// 垮掉一行后,再次从头判断一次
cleared =true;
CheckClear();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
BlockInfo
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块.方块信息类
{
internal class BlockInfo
{
// 方块信息坐标
private List<Position[]> list;
public BlockInfo(E_DrawType type) {
//list 初始化才能装东西
list = new List<Position[]>();
switch (type)
{
case E_DrawType.Cube:
// list添加形状信息
list.Add(new Position[3] {
new Position(2,0),
new Position(0,1),
new Position(2,1)
});
break;
case E_DrawType.Line:
list.Add(new Position[3] {
new Position(0, -1),
new Position(0, 1),
new Position(0, 2),
});
list.Add(new Position[3] {
new Position(-4, 0),
new Position(-2, 0),
new Position(2, 0),
});
list.Add(new Position[3] {
new Position(0, -2),
new Position(0, -1),
new Position(0, 1),
});
list.Add(new Position[3] {
new Position(-2, 0),
new Position(2, 0),
new Position(4, 0),
});
break;
case E_DrawType.Tank:
list.Add(new Position[3] {
new Position(-2, 0),
new Position(2, 0),
new Position(0, 1),
});
list.Add(new Position[3] {
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(-2,0),
new Position(0,1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3] {
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(-2,0),
new Position(2,0)
});
list.Add(new Position[3] {
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(2,0),
new Position(0,1)
});
break;
case E_DrawType.Left_Ladder:
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(2,0),
new Position(2,1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(2,0),
new Position(0,1),
new Position(-2,1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(-2,-1),
new Position(-2,0),
new Position(0,1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(2,-1),
new Position(-2,0)
});
break;
case E_DrawType.Right_Ladder:
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(-2,0),
new Position(-2,1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(-2,-1),
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(2,0)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(2,-1),
new Position(2,0),
new Position(0,1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(0,1),
new Position(2,1),
new Position(-2,0)
});
break;
case E_DrawType.Left_Long_Ladder:
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(-2,-1),
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(0,1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(2,-1),
new Position(-2,0),
new Position(2,0)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(2,1),
new Position(0,1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(2,0),
new Position(-2,0),
new Position(-2,1)
});
break;
case E_DrawType.Right_Long_Ladder:
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(0,1),
new Position(2,-1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(2,0),
new Position(-2,0),
new Position(2,1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(0,-1),
new Position(-2,1),
new Position(0,1)
});
list.Add(new Position[3]{
new Position(-2,-1),
new Position(-2,0),
new Position(2,0)
});
break;
default:
break;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 提供给外部啊根据索引位置快速获取位置偏移信息
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Position[] this[int index]
{
get {
if (index < 0)
{
return list[0];
}
else if (index >= list.Count)
{
return list[list.Count - 1];
}
else
return list[index];
}
}
public int Count { get => list.Count; }
}
}
Score.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
// 画出得分
internal class Score : Map
{
protected String SumScoreName;
protected String ScoreLineName;
public int ScoreNum;
public int ScoreLine;
int ScoreInit = 0;
int LineInit = 0;
public Score(GameScene scene) : base(scene)
{
// 显示得分位置,地图边界在map里面
SumScoreName = "分数:";
ScoreLineName = "行数:";
#region 计算得分
// 消除一行得分+10,行数+1
#endregion
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, Game.h - 4);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.Write(SumScoreName);
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, Game.h - 3);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.Write(ScoreLineName);
// 初始化分数0
Console.SetCursorPosition(7, Game.h - 4);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write(ScoreInit);
Console.SetCursorPosition(7, Game.h - 3);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write(LineInit);
}
public void DrawScore(int ScoreNum, int ScoreLine)
{
// 显示实际得分
Console.SetCursorPosition(7, Game.h - 4);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write(ScoreNum);
Console.SetCursorPosition(7, Game.h - 3);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write(ScoreLine);
}
public int updateScore()
{
return ++ScoreCount;
}
public int GetScore()
{
return Score += 10;
}
// 判断是否消除一行
public void Isclear()
{
DrawScore(GetScore(), updateScore());
}
}
}
BlockWorker
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis;
using System.Linq;
using System.Numerics;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using 俄罗斯方块.方块信息类;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
enum E_Change_Type
{
left,
right,
}
internal class BlockWorker : IDraw
{
// 方块们
private List<DrawObject> blocks;
// 记录各个方块的信息
private Dictionary<E_DrawType, BlockInfo> blockInfoDict;
private BlockInfo nowBlockInfo;
// 当前形态索引
private int nowInfoIndex;
public BlockWorker()
{
// 初始化撞开信息
blockInfoDict = new Dictionary<E_DrawType, BlockInfo>()
{
{ E_DrawType.Cube ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Cube)},
{ E_DrawType.Line ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Line)},
{ E_DrawType.Tank ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Tank)},
{ E_DrawType.Left_Ladder ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Left_Ladder)},
{ E_DrawType.Right_Ladder ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Right_Ladder)},
{ E_DrawType.Left_Long_Ladder ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Left_Long_Ladder)},
{ E_DrawType.Right_Long_Ladder ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Right_Long_Ladder)},
};
// 随机方块
RandomCratBlock();
}
public void IDraw()
{
for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++)
{
blocks[i].Draw();
}
}
public void RandomCratBlock()
{
// 随机方块的类型
Random r = new Random();
E_DrawType type = (E_DrawType)r.Next(1, 8);
// 每次创建一个砖块其实就是创建4个小方形
blocks = new List<DrawObject>()
{
new DrawObject(type),
new DrawObject(type),
new DrawObject(type),
new DrawObject(type),
};
// 初始化方块的位置
blocks[0].Position = new Position(24, -5);
// 把方块信息存起来
nowBlockInfo = blockInfoDict[type];
// 随机形态
nowInfoIndex = r.Next(0, nowBlockInfo.Count);
// 取出一种形态坐标信息
Position[] positions = nowBlockInfo[nowInfoIndex];
for (int i = 0; i < positions.Length; i++)
{
// 取出来的pos相对原点方块的坐标
blocks[i + 1].Position = blocks[0].Position + positions[i];
}
}
#region 变形相关
// 清除
public void ClearDraw()
{
for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++)
{
blocks[i].ClearDraw();
}
}
public void Change(E_Change_Type type)
{
// 变之前擦除
ClearDraw();
switch (type)
{
case E_Change_Type.left:
--nowInfoIndex;
if (nowInfoIndex < 0)
{
nowInfoIndex = nowBlockInfo.Count - 1;
}
break;
case E_Change_Type.right:
++nowInfoIndex;
if (nowInfoIndex >= nowBlockInfo.Count)
{
nowInfoIndex = 0;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
// 得到索引目的是得到对应形态的位置偏移信息
//用于设置另外三个小方块
Position[] positions = nowBlockInfo[nowInfoIndex];
for (int i = 0; i < positions.Length; i++)
{
// 取出来的pos相对原点方块的坐标
blocks[i + 1].Position = blocks[0].Position + positions[i];
}
// 变之后再绘制
IDraw();
}
public bool IsChange(E_Change_Type type, Map map)
{
int nowIndex = nowInfoIndex;
switch (type)
{
case E_Change_Type.left:
--nowIndex;
if (nowIndex < 0)
{
nowIndex = nowBlockInfo.Count - 1;
}
break;
case E_Change_Type.right:
++nowIndex;
if (nowIndex >= nowBlockInfo.Count)
{
nowIndex = 0;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
// 通过临时索引判断是否超出边界
Position[] Nowpositions = nowBlockInfo[nowIndex];
// 判断是否超出地图边界
Position tempPostion;
for (int i = 0; i < Nowpositions.Length; i++)
{
// 判断左右边界和下边界
tempPostion = blocks[0].Position + Nowpositions[i];
if (tempPostion.x < 2 || tempPostion.x >= Game.w - 2 || tempPostion.y >= map.h)
{
return false;
}
}
// 判断是否和地图上的动态方块重合
for (int i = 0; i < Nowpositions.Length; i++)
{
tempPostion = blocks[0].Position + Nowpositions[i];
for (int j = 0; j < map.dynamicWalls.Count; j++)
{
if (tempPostion == map.dynamicWalls[j].Position)
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
#endregion
#region 方块左右移动
/// <summary>
/// 方块左右移动函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="type"></param>
public void MoveRl(E_Change_Type type)
{
// 动之前得到坐标擦除
ClearDraw();
// 根据传入的类型,决定左右移动
// 左 x-2,y0,右x+2,y0
Position movePosition = new Position(type == E_Change_Type.left ? -2 : 2, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++)
{
blocks[i].Position += movePosition;
}
IDraw();
}
// 判断是否可以移动
public bool IsMoveRL(E_Change_Type type, Map map)
{
// 判断左右边界重合
// 得到左右的偏移位置
Position movePosition = new Position(type == E_Change_Type.left ? -2 : 2, 0);
// 动过之后结果不能直接改小方块的位置
Position position;
for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++)
{
position = blocks[i].Position + movePosition;
if (position.x < 2 || position.x >= Game.w - 2)
{
return false;
}
}
// 要不要和动态方块重合
for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++)
{
position = blocks[i].Position + movePosition;
for (int j = 0; j < map.dynamicWalls.Count; j++)
{
if (position == map.dynamicWalls[j].Position)
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
#endregion
#region 自动向下移动
/// <summary>
/// 自动移动
/// </summary>
public void AutoMoveDown()
{
ClearDraw();
Position downMove = new Position(0, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++)
{
blocks[i].Position += downMove;
//blocks[i].Position.y += 1;
}
IDraw();
}
public bool IsAutoMove(Map map)
{
// 用临时变量存储下一次移动的位置用于重合判断
Position position;
Position downMove = new Position(0, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++)
{
position = blocks[i].Position + downMove;
if (position.y >= map.h)
{
// 停下
map.AddWall(blocks);
// 随机创建新的方块
RandomCratBlock();
return false;
}
}
// 动态方块
for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++)
{
position = blocks[i].Position + downMove;
for (int j = 0; j < map.dynamicWalls.Count; j++)
{
if (position == map.dynamicWalls[j].Position)
{
// 停下
map.AddWall(blocks);
// 随机创建新的方块
RandomCratBlock();
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
#endregion
}
}
DrawObject
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
/// <summary>
/// 绘制方块
/// </summary>
enum E_DrawType
{
/// <summary>
/// 墙壁
/// </summary>
wall,
/// <summary>
/// 正方形
/// </summary>
Cube,
/// <summary>
/// 长的
/// </summary>
Line,
/// <summary>
/// 坦克
/// </summary>
Tank,
/// <summary>
/// 左
/// </summary>
Left_Ladder,
/// <summary>
/// 右
/// </summary>
Right_Ladder,
/// <summary>
/// 左长
/// </summary>
Left_Long_Ladder,
/// <summary>
/// 右长
/// </summary>
Right_Long_Ladder,
}
internal class DrawObject : IDraw
{
public Position Position;
public E_DrawType type;
public DrawObject(E_DrawType type)
{
this.type = type;
}
public DrawObject(E_DrawType type, int x, int y) : this(type)
{
this.Position = new Position(x, y);
}
public void Draw()
{
if (Position.y<0)
{
return;
}
Console.SetCursorPosition(Position.x, Position.y);
switch (type)
{
case E_DrawType.wall:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
break;
case E_DrawType.Cube:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
break;
case E_DrawType.Line:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Blue;
break;
case E_DrawType.Tank:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
break;
case E_DrawType.Left_Ladder:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.DarkGray;
break;
case E_DrawType.Right_Ladder:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.DarkGray;
break;
case E_DrawType.Left_Long_Ladder:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray;
break;
case E_DrawType.Right_Long_Ladder:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray;
break;
default:
break;
}
Console.Write("卐");
}
public void ClearDraw()
{
if (Position.y<0)
{
return;
}
Console.SetCursorPosition(Position.x, Position.y);
Console.Write(" ");
}
/// <summary>
/// 切换方块类型,搬砖掉落到墙壁上转为墙壁
/// </summary>
public void ChangType(E_DrawType type)
{
this.type = type;
}
void IDraw.IDraw()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}
IDraw
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
internal interface IDraw
{
void IDraw();
}
}
Position
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
internal class Position
{
public int x;
public int y;
public Position(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public static bool operator ==(Position p1, Position p2) {
if (p1.x== p2.x&&p1.y==p2.y)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static bool operator !=(Position p1, Position p2)
{
if (p1.x == p2.x && p1.y == p2.y)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static Position operator +(Position p1, Position p2)
{
Position position = new Position(p1.x+p2.x,p1.y+p2.y);
return position;
}
}
}
inputThread
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{
internal class inputThread
{
Thread inputThead;
public event Action inputEvent;
private static inputThread instance = new inputThread();
public static inputThread Instance
{
get { return instance; }
}
private inputThread()
{
inputThead = new Thread(InputCheck);
inputThead.IsBackground = true;
inputThead.Start();
}
public void InputCheck() {
while (true)
{
inputEvent?.Invoke();
}
}
// 线程
}
}
显示清除最后





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号