C#基础
C#入门基础
目录
开发环境安装
利用visualstudio无脑安装
using System;
namespace Lesson1_练习题
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Lesson1_练习题讲解");
////打印信息后不空行
//Console.Write("");
////打印信息后空行
//Console.WriteLine("");
////检测玩家的一键输入
//Console.ReadKey();
////检测玩家的一系列输入 回车键结束
//Console.ReadLine();
//Console.WriteLine("请您输入用户名");
//Console.ReadLine();
//Console.WriteLine("请您输入年龄");
//Console.ReadLine();
//Console.WriteLine("请您输入班级");
//Console.ReadLine();
//Console.WriteLine("请问您喜欢什么运动");
//Console.ReadLine();
//Console.WriteLine("哈哈哈,好巧,我也喜欢这个运动");
Console.WriteLine("**********");
Console.WriteLine("* *");
Console.WriteLine("* *");
Console.WriteLine("* *");
Console.WriteLine("* *");
Console.WriteLine("* *");
Console.WriteLine("* *");
Console.WriteLine("* *");
Console.WriteLine("* *");
Console.WriteLine("**********");
Console.Write("**********");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("**********");
}
}
}

Console.Write("**********");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("* *");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("**********");
变量
一句话存储不同类型的数值的一个容器
变量类型
1、有符号的整型
是能存储一定范围正负数包括0的变量类型
sbyte -128-127
int -21亿-21亿
short -32768 -32767
long -900万兆900万兆
2、无符号的整型
是能存储一定范围0和正数的变量类型
byte 0-255
uint 0-42亿
ushort 0-65535
ulong 0-18百万兆
3、特殊类型
bool = true; 表示真假
char n= 'A'; 用来存储单个字符
string o="你好" 用来存储字符串
4、浮点
存储7/8位有效数字根据编译器不同有效数字也可能不一样四舍五入
float 存储7/8位有效数字根据编译器不同有效数字也可能不一样四舍五入
double 存储15-17位
加f是因为C#里默认是double类型,抛弃的数字会四舍五入
decimal 存储27-28有效数字,不建议用
变量必须先声明后使用不能没有声明直接修改
多个相同类型的变量同时声明
int a1=2,b1=2,c1=3;
练习题
Console.WriteLine("变量相关练习题");
#region 练习题1
//下面代码的输出结果是?
double num = 36.6;
//这是打印一个字符串
Console.WriteLine("num");
//打印变量容器中存储的内容
Console.WriteLine(num);
#endregion
#region 练习题2
//声明float类型变量时,为何要在数字后面加f?
float f = 1.234F;
decimal d = 1.2344545M;
#endregion
#region 练习题3
//请定义一系列变量来存储你的名字、年龄、性别、身高、体重、家庭住址等,并打印出来。
string name = "唐老狮";
Console.WriteLine("我的名字是" + name);
byte age = 18;
Console.WriteLine("我的年龄是" + age);
float height = 177.5f;
Console.WriteLine("我的身高是" + height);
float weight = 68.5f;
Console.WriteLine("我的体重是" + weight);
string address = "地球深处";
Console.WriteLine("我的家庭住址是" + address);
#endregion
#region 练习题4
//小明的数学考试成绩是80,语文的考试成绩是78,英语的考试成绩是98,请用变量描述并打印
byte shuXue = 80;
byte yuWen = 78;
byte yingYu = 98;
Console.WriteLine("我的数学成绩是:" + shuXue);
Console.WriteLine("我的语文成绩是:" + yuWen);
Console.WriteLine("我的英语成绩是:" + yingYu);
#endregion
visul studio 报错解决
显示
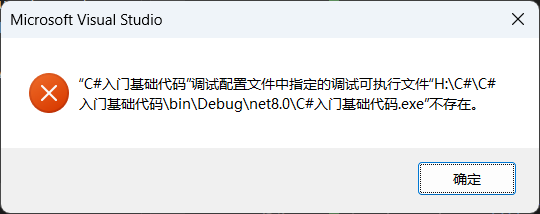
1>H:\C#\C#入门基础代码\obj\Debug\net8.0\C#入门基础代码.AssemblyInfo.cs(14,12,14,54): error CS0579: “System.Reflection.AssemblyCompanyAttribute”特性重复
1>H:\C#\C#入门基础代码\obj\Debug\net8.0\C#入门基础代码.AssemblyInfo.cs(15,12,15,60): error CS0579: “System.Reflection.AssemblyConfigurationAttribute”特性重复
1>H:\C#\C#入门基础代码\obj\Debug\net8.0\C#入门基础代码.AssemblyInfo.cs(16,12,16,58): error CS0579: “System.Reflection.AssemblyFileVersionAttribute”特性重复
1>H:\C#\C#入门基础代码\obj\Debug\net8.0\C#入门基础代码.AssemblyInfo.cs(17,12,17,67): error CS0579: “System.Reflection.AssemblyInformationalVersionAttribute”特性重复
1>H:\C#\C#入门基础代码\obj\Debug\net8.0\C#入门基础代码.AssemblyInfo.cs(18,12,18,54): error CS0579: “System.Reflection.AssemblyProductAttribute”特性重复
1>H:\C#\C#入门基础代码\obj\Debug\net8.0\C#入门基础代码.AssemblyInfo.cs(19,12,19,52): error CS0579: “System.Reflection.AssemblyTitleAttribute”特性重复
1>H:\C#\C#入门基础代码\obj\Debug\net8.0\C#入门基础代码.AssemblyInfo.cs(20,12,20,54): error CS0579: “System.Reflection.AssemblyVersionAttribute”特性重复
解决
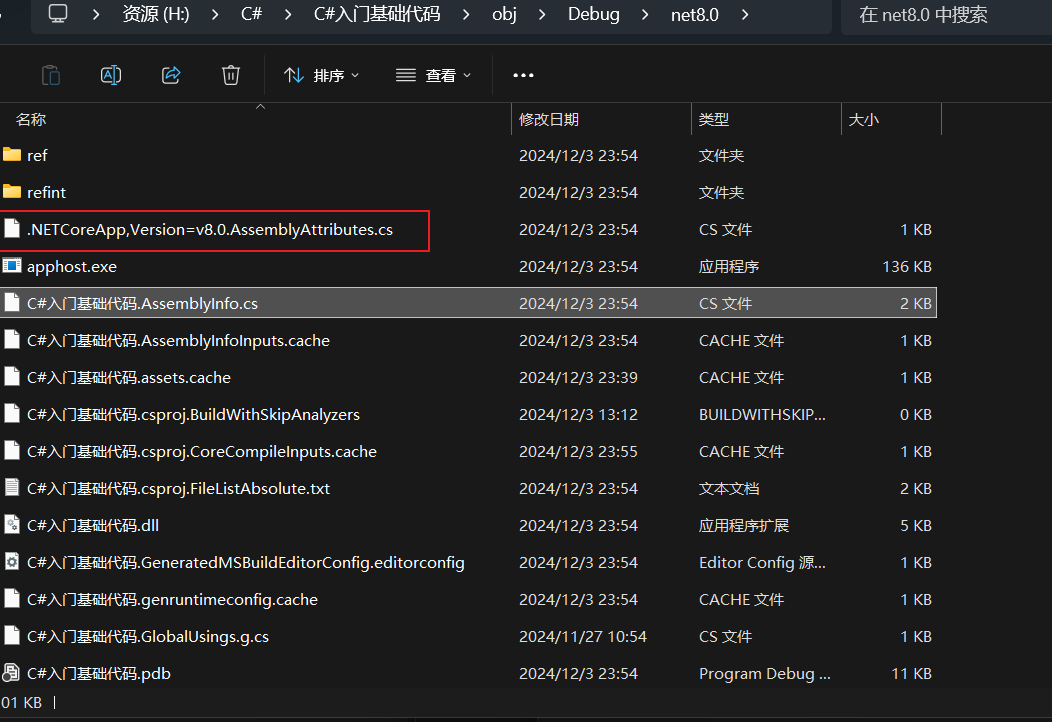
// <autogenerated />
using System;
using System.Reflection;
把下面这句话注释掉
//[assembly: global::System.Runtime.Versioning.TargetFrameworkAttribute(".NETCoreApp,Version=v8.0", FrameworkDisplayName = ".NET 8.0")]
之后重新生成解决方案就好了
变量存储空间
#region 变量存储空间
int sbytsize= sizeof(sbyte);
Console.WriteLine(sbytsize);
int intsize= sizeof(int);
Console.WriteLine(intsize);
int shortSize= sizeof(short);
Console.WriteLine(shortSize);
int Longsize= sizeof(long);
Console.WriteLine(Longsize);
//无符号
int usbytsize = sizeof(byte);
Console.WriteLine(usbytsize);
int uintsize = sizeof(uint);
Console.WriteLine(uintsize);
int ushortSize = sizeof(ushort);
Console.WriteLine(ushortSize);
int uLongsize = sizeof(ulong);
Console.WriteLine(uLongsize);
//浮点数
int floatSize = sizeof(float);
Console.WriteLine(floatSize);
int doubleSize = sizeof(double);
Console.WriteLine(doubleSize);
int decimalSize = sizeof(decimal);
Console.WriteLine(decimalSize);
//特殊类型
int boolSize = sizeof(bool);
Console.WriteLine(boolSize);
int charSize = sizeof(char);
Console.WriteLine(charSize);
// sizeof是不能够得到string类型的大小
#endregion
变量的本质
本质就是
变量的本质是2进制——>计算机中所有数据的本质都是二进制 是一堆0和1
为什么是2进制?
数据传递只能通过电信号,只有开和关两种状态。所以就用0和1来表示这两种状态
计算机中的存储单位最小为bit(位),他只能表示0和1两个数字
1bit 就是1个数 要不是0要不是1
为了方便数据表示
出现一个叫byte(字节)的单位,它是由8个bit组成的存储单位。
所以我们一般说一个字节为8位
1byte = 0000 00002进制和10进制的对比
2进制和10进制之间的相互转换
十进制二进制转换

习题

变量的命名规范
#region 知识点一:必须遵守的规则
//1.不能重名
//2.不能以数字开头
//3.不能使用程序关键字命名
//4.不能有特殊符号(下划线除外)
//建议的命名规则:变量名要有含义——>用英文(拼音)表示变量的作用
//非常不建议的命名规则:用汉字命名
#endregion
#region 知识点二:常用命名规则
//驼峰命名法——首字母小写,之后单词首字母大写(变量)
string myName = "唐老狮";
string yourName = "你的名字";
string yourMotherName = "";
//帕斯卡命名法——所有单词首字母都大写(函数、类)
string MyName = "dskafj";
//潜在知识点——C#中对大小写是敏感的 是区分的
#endregion
常量
using System;
namespace Lesson5_常量
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("常量");
#region 知识点一 常量的申明
//关键字 const
//固定写法:
//const 变量类型 变量名 = 初始值;
//变量的申明
int i = 10;
//常量的申明
const int i2 = 20;
#endregion
#region 知识点二 常量的特点
//1.必须初始化
//2.不能被修改
//变量申明可以不初始化
string name;
//之后可以来修改
name = "123";
name = "345";
const string myName = "唐老狮";
//作用:申明一些常用不变的变量
//PI 3.1415926
const float PI = 3.1415926f;
Console.WriteLine(PI);
#endregion
}
}
}
转义字符
什么是转义字符
是字符串的一部分用来表示一些特殊含义的字符
using System;
namespace Lesson6_转义字符
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("转义字符");
#region 知识点一 转义字符的使用
//什么是转义字符?
//它是字符串的一部分 用来表示一些特殊含义的字符
//比如:在字符串中表现 单引号 引号 空行等等
//string str = "asld"fk";
#region 固定写法
//固定写法 \字符
//不同的 \和字符的组合 表示不同的含义
//常用转义字符
// 单引号 \'
string str = "\'哈哈哈\'";
Console.WriteLine(str);
// 双引号 \"
str = "\"哈哈哈\"";
Console.WriteLine(str);
// 换行 \n
str = "1231231\n23123123123";
Console.WriteLine(str);
// 斜杠 \\ 计算机文件路径 是要用到\符号的
str = "哈\\哈哈";
Console.WriteLine(str);
//不常用转义字符(了解)
// 制表符(空一个tab键) \t
str = "哈\t哈哈";
Console.WriteLine(str);
// 光标退格 \b
str = "123\b123";
Console.WriteLine(str);
// 空字符 \0
str = "1234\0123";
Console.WriteLine(str);
// 警报音 \a
str = "\a";
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.WriteLine("1231231231\n123123213\a\t123123");
#endregion
#endregion
#region 知识点二 取消转义字符
string str2 = @"哈哈\哈哈";
Console.WriteLine(str2);
Console.WriteLine(@"\n\\");
#endregion
}
}
}
隐式转换
类型转换就是不同变量类型之间相互转换
隐式转换基本规则->不同类型之间的自动转换;大范围装小范围
不能用小范围装大范围
有符号
long->int->short->sbyte
无符号
ulong->uint->ushort->byte
浮点数
decimal
decimal 无法用有隐式转换形式去存储double float
double->float
无符号
ushort
uint
ulong
有符号
sbyte
short
int
特殊类型不存在隐式转换
无符号装有符号(不能)
无符号装0和正数
有符号装负数0-正数
有符号的变量不能隐式转换无符号
有符号变量是可以装无符号变量前提是一定要涵盖存在隐式转换
浮点数装整数(有无符号之间)
浮点数装载任何类型的整数
decimal不能装float和double,但是可以装载任何整形
整数不能隐式存储浮点数,整数不能存储小数
bool没有办法和其他类型相互隐式转换
char 无法隐式存储其他类型的变量,可以隐式转换为整形和浮点
string 无法与其他类型进行隐式转换
// 总结 隐式转换 规则
// 高精度(大范围)装低精度(小范围)
// double ——> float ——> 整数(无符号、有符号)——>char
// decimal ——> 整数(无符号、有符号)——>char
// string 和 bool 不参与隐式转换规则的
显示转换
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace displayprograme;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 强制转换
// 将高精度的类型强制转换为低精度
// 语法 变量名=(变量类型)变量;
// 精度问题范围问题
sbyte sb = 1;
short s = 1;
int i = 1;
long l =1;
s = (short)i;
Console.WriteLine(s);
//无符号整型
byte b = 1;
uint u = 1;
ulong v = 1;
b = (byte)u;
Console.WriteLine(b);
// 无符号和有符号
uint ui2 = 1;
int i2 = -1;
ui2 = (uint)i2;
Console.WriteLine(ui2); // 强制转换要注意范围
i2 = (int)ui2;
Console.WriteLine(i2);
//浮点整型
i2 = (int)1.64f;
Console.WriteLine(i2);// 浮点转换为整型时,会直舍弃后面的小数
// char 好数值类型
i2 = 'A';
Console.WriteLine(i2);
// bool 和string不能使用括号来强制转换
#endregion
#region parse法
//把字符串类型转为对应的类型
//语法 变量类型.parse(字符串)
//字符串必须转为为对应的类型
int i4 = int.Parse("123");
//字符串必须使用能够转为对应的类型,不然报错
//int i4 = int.Parse("123.45");
// 填写字符串范围必须能够被变量存储的值
short s3 = short.Parse("123");
Console.WriteLine(s3);
Console.WriteLine(sbyte.Parse("12"));
Console.WriteLine(long.Parse("123333"));
Console.WriteLine(ushort.Parse("123333"));
Console.WriteLine(ushort.Parse("123333"));
Console.WriteLine(ushort.Parse("123333"));
Console.WriteLine(ushort.Parse("123333"));
#endregion
#region convert
//更准确的将各个类型之间进项相互转换
//语法:convert.to目标类型
//填写变量或常量必须正确
//转字符串
int a1 = Convert.ToInt32("1111");
Console.WriteLine(a1);
a1 = Convert.ToInt32(1.12f);
Console.WriteLine(a1);
//精度比括号强转好,会四舍五入
//也可以吧布尔类型强转
a1 = Convert.ToInt32(true);
Console.WriteLine(a1);
a1 = Convert.ToInt32(false);
Console.WriteLine(a1);
//每一个类型对应都有convert的用法
sbyte sb1 = Convert.ToSByte("1");
short sb2 = Convert.ToInt16("1");
int sb3 = Convert.ToInt32("1");
long sb4 = Convert.ToInt64("1");
byte sb5 = Convert.ToByte("1");
ushort sb6 = Convert.ToUInt16("1");
uint sb7 = Convert.ToUInt32("1");
ulong sb8 = Convert.ToUInt64("1");
float f5 = Convert.ToSingle("1.12");
double d5= Convert.ToDouble("1.1");
decimal d15 = Convert.ToDecimal("1.22");
bool bo5= Convert.ToBoolean("true");
char ch5= Convert.ToChar("A");
Console.WriteLine(sb1);
Console.WriteLine(sb2);
Console.WriteLine(sb3);
Console.WriteLine(sb4);
#endregion
#region 其他类型转string
//拼接打印
//变量基本知识点.toString
string str6 = 1.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(str6);
str6 = 2.ToString();
str6 = 'A'.ToString();
str6 = 2.2.ToString();
str6 = true.ToString();
#endregion
}
}
异常捕获
using System;
namespace Exceptioncatching;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 基本语法
try
{
//异常捕获的代码块放到try中
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
//如果出错了会会执行catch中的代码
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
}
finally
{
//最后执行的代码,不管有没有出错都会执行里面的代码
}
//注意:异常捕获的代码中,不需要加;在代码逻辑中去写
#endregion
#region 实践
try
{
string str = Console.ReadLine();
int i = int.Parse(str);
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入合法的内容");
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("执行完毕");
}
#endregion
}
}
算数运算符
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.Reflection;
namespace Lesson10_算数运算符
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("算数运算符");
//算数运算符 是用于 数值类型变量计算的运算符
//它的返回结果是数值
#region 知识点一:赋值符号
// =
// 关键知识点 :
// 先看右侧 再看左侧 把右侧的值赋值给左侧的变量
string myName = "唐老狮";
int myAge = 18;
float myHeight = 177.5f;
#endregion
#region 知识点二: 算数运算符
#region 加 +
// 用自己计算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
int i = 1;
// 3
i = i + 2;
Console.WriteLine(i);
// 连续运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
// 99
i = 1 + 3 + 89 + i + i;
Console.WriteLine(i);
//4
i = 1 + 2 + 1;
Console.WriteLine(i);
// 初始化时就运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
int i2 = 1 + 2 + 4 + i;
Console.WriteLine(i2);
#endregion
#region 减 -
// 用自己计算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
int j = 1;
j = j - 1;
Console.WriteLine(j);
// 连续运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
j = 1 - 2 - 3;
Console.WriteLine(j);
j = 1 - j;
Console.WriteLine(j);//5
// 初始化时就运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
int j2 = 1 - j - 0;
Console.WriteLine(j2);
#endregion
#region 乘 *
// 用自己计算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
int c = 1;
c = c * 10;
Console.WriteLine(c);
// 连续运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
c = 1 * 2 * 3;
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = 2 * c * 2;
Console.WriteLine(c);
// 初始化时就运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
int c2 = c * 2;
Console.WriteLine(c2);
#endregion
#region 除 /
// 用自己计算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
int chu = 1;
chu = 10 / chu;
Console.WriteLine(chu);
// 连续运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
// 初始化时就运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
chu = 1;
chu = 1 / 2;
Console.WriteLine(chu);
//默认的整数 是int 如果用来做除法运算 要注意 会丢失小数点后的小数
//如果你想用浮点数来存储 一定是 在运算时要有浮点数的特征
float f = 1 / 2f;
Console.WriteLine(f);
#endregion
#region 取余 %
// 用自己计算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
int y = 4;
// 4 / 3 得到余数 1
y = y % 3;
Console.WriteLine(y);
// 连续运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
y = 4 % 3 % 2;
Console.WriteLine(y);
// 初始化时就运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量
#endregion
#endregion
#region 知识点三:算数运算符的 优先级
//优先级 是指 在混合运算时的运算顺序
//乘除取余 优先级高于 加减 先算乘除取余 后算加减
// 1 + 3 + 1 + 6
int a = 1 + 2 * 3 / 2 + 1 + 2 * 3;
Console.WriteLine(a);
a = 1 + 4 % 2 * 3 / 2 + 1;
Console.WriteLine(a);
//括号可以改变优先级 优先计算括号内内容
a = 1 + 4 % (2 * 3 / 2) + 1;
Console.WriteLine(a);
//多组括号 先算最里层括号 依次往外算
a = 1 + (4 % (2 * (3 / 2))) + 1;
Console.WriteLine(a);
#endregion
#region 知识点四:算数运算符的 复合运算符
// 固定写法 运算符=
// += -= *= /= %=
//复合运算符 是用于 自己=自己进行运算
int i3 = 1;
i3 = i3 + 2;
Console.WriteLine(i3);
i3 = 1;
i3 += 2;//i3 = i3 + 2;
Console.WriteLine(i3);
i3 = 2;
i3 += 2;//4
i3 -= 2;//2
i3 /= 2;//1
i3 *= 2;//2
i3 %= 2;//0
Console.WriteLine(i3);
int i4 = 10;
// i4 += 4
i4 += 20 * 2 / 10;
Console.WriteLine(i4);
//注意:复合运算符 只能进行一种运算 不能混合运算
//i4 */-= 2;
#endregion
#region 知识点五:算术运算符的 自增减
int a2 = 1;
a2 = a2 + 1;
a2 = 1;
a2 += 1;
//自增运算符 让自己+1
a2 = 1;
a2++;//先用再加
Console.WriteLine(a2);
++a2;//先加再用
Console.WriteLine(a2);
a2 = 1;
Console.WriteLine(a2++);//1
//2
Console.WriteLine(++a2);//3
//自减运算符 让自己-1
a2 = 1;
a2--;//先用再减
--a2;//先减再用
a2 = 1;
Console.WriteLine(a2--);//1
//0
Console.WriteLine(--a2);//-1
#endregion
}
}
}
条件运算符
using System;
namespace Lesson12_条件运算符
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("条件运算符");
#region 知识点一 条件运算符
// 用于比较两个变量或常量
// 是否大于 >
// 是否小于 <
// 是否等于 ==
// 是否不等于 !=
// 是否大于等于 >=
// 是否小于等于 <=
// 条件运算符 一定存在左右两边的内容
// 左边内容 条件运算符 右边内容
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
//条件运算符 不能直接这样使用
//纯比较不用结果 那么对于我们来说 没有任何的意义
//a > b;
// 比较的结果 返回的是 一个 bool 类型的值
// true和false 如果比较的条件满足 那就返回true 不满足 就返回false
// 先算右边 再赋值给左边
bool result = a > b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = a < b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = a >= b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = a <= b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = a == b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = a != b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
#endregion
#region 知识点二 各种应用写法
//变量和变量比较
a = 5;
b = 10;
result = a < b;// true
//变量和数值(常量)比较
result = a < 10;// true
result = b > 5;// true
//数值和数值比较
result = 5 > 3;//true
result = 5 == 3; // false
result = 5 != 3; // true;
//计算结果比较
//条件运算符的 优先级 低于算数运算符
// 8 > 6
// 先计算 再比较
result = a + 3 > a - 2 + 3;// true
result = 3 + 3 < 5 - 1;//false
//左边 条件运算符 右边
#endregion
#region 知识点三 不能进行范围比较
a = 5;
//判断是否在某两个值之间
// 1 < a < 6
//在C#都不能这样写
//result = 1 < a < 6;
//要判断 一个变量是否在两个数之间 要结合 逻辑运算符的知识点
#endregion
#region 知识点四 不同类型之间的比较
//不同数值类型之间 可以随意进行条件运算符比较
int i = 5;
float f = 1.2f;
double d = 12.4;
short s = 2;
byte by = 20;
uint ui = 222;
//只要是数值 就能够进行条件运算符比较 比较大于小于等于等等
result = i > f;
result = f < d;
result = i > by;
result = f > ui;
result = ui > d;
//特殊类型 char string bool 只能同类型进行 == 和 != 比较
string str = "123";
char c = 'A';
bool bo = true;
result = str == "234";//false
result = str == "123";//true
result = str != "123";//false
result = c == 'B';//false
//不仅可以和自己类型进行 == != 还可以和数值类型进行比较
//还可以和 字符类型进行大小比较
result = c > 123;
result = c > 'B';
result = bo == true;//true;
#endregion
}
}
}
逻辑运算符
using System;
namespace Lesson13_逻辑运算符
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("逻辑运算符");
//对bool类型 进行逻辑运算
#region 知识点一 逻辑与
//符号 && 并且
//规则 对两个bool值进行逻辑运算 有假则假 同真为真
bool result = true && false;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = true && true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = false && true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//bool相关的类型 bool变量 条件运算符
//逻辑运算符优先级 低于 条件运算符 算术运算
// true && true
result = 3 > 1 && 1 < 2;
Console.WriteLine(result);
int i = 3;
// 1 < i < 5;
// true && true
result = i > 1 && i < 5;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//多个逻辑与 组合运用
int i2 = 5;
// true && false && true && true
//在没有括号的情况下 从左到右 依次看即可
//有括号 先看括号内
result = i2 > 1 && i2 < 5 && i > 1 && i < 5;
Console.WriteLine(result);
#endregion
#region 知识点二 逻辑或
//符号 || 或者
//规则 对两个bool值进行逻辑运算 有真则真 同假为假
result = true || false;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = true || true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = false || true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = false || false;
Console.WriteLine(result);
// false || true
result = 3 > 10 || 3 < 5;
Console.WriteLine(result);//true
int a = 5;
int b = 11;
// true || true || false
result = a > 1 || b < 20 || a > 5;
Console.WriteLine(result);
// ? && ?
// ? || ?
// ? 可以是写死的bool变量 或者 bool值
// 还可以是 条件运算符相关
#endregion
#region 知识点三 逻辑非
//符号 !
//规则 对一个bool值进行取反 真变假 假变真
result = !true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = !false;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = !!true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//逻辑非的 优先级 较高
result = !(3 > 2);
Console.WriteLine(result);
a = 5;
result = !(a > 5);
Console.WriteLine(result);
#endregion
#region 知识点四 混合使用优先级问题
// 规则 !(逻辑非)优先级最高 &&(逻辑与)优先级高于||(逻辑或)
// 逻辑运算符优先级 低于 算数运算符 条件运算符(逻辑非除外)
bool gameOver = false;
int hp = 100;
bool isDead = false;
bool isMustOver = true;
//false || false && true || true;
//false || false || true;
result = gameOver || hp < 0 && !isDead || isMustOver;
Console.WriteLine(result);
#endregion
#region 知识点五 逻辑运算符短路规则
int i3 = 1;
// || 有真则真
// 只要 逻辑与或者逻辑或 左边满足了条件
// i3 > 0 true
// 只要 满足条件 右边的内容 对于我们来说 已经不重要
//逻辑或 有真则真 那左边只要为真了 右边就不重要
result = i3 > 0 || ++i3 >= 1;
Console.WriteLine(i3);
Console.WriteLine(result);
// false && i3 ++ > 1;抛弃后面不去计算
//逻辑与 有假则假 那左边只要为假了 右边就不重要
result = i3 < 0 && i3++ > 1;
Console.WriteLine(i3);
Console.WriteLine(result);
#endregion
}
}
}
位运算符
using System;
namespace Lesson14_位运算符
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("位运算符");
//位运算符 主要用数值类型进行计算的
//将数值转换为2进制 再进行位运算
#region 知识点一 位与 &
// 规则 连接两个数值进行位计算 将数值转为2进制
// 对位运算 有0则0
int a = 1;// 001
int b = 5;// 101
// 001
//& 101
// 001 = 1
int c = a & b;
Console.WriteLine(c);
a = 3;// 011
b = 19;// 10011
// 00011
//& 10011
// 00011
c = a & b;//3
Console.WriteLine(c);
//多个数值进行位运算 没有括号时 从左到右 依次计算
a = 1;// 001
b = 5;// 101
c = 19;//10011
// 00001
//& 00101
// 00001
//& 10011
// 00001
int d = a & b & c;
Console.WriteLine(d);
a = 1;//001
b = 2;//010
Console.WriteLine(a & b);
#endregion
#region 知识点二 位或 |
// 规则 连接两个数值进行位计算 将数值转为2进制
// 对位运算 有1则1
a = 1;//001
b = 3;//011
c = a | b;
// 001
//| 011
// 011
Console.WriteLine(c);
a = 5; // 101
b = 10;// 1010
c = 20;//10100
// 00101
//| 01010
// 01111
//| 10100
// 11111 => 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + 16 =31
Console.WriteLine(a | b | c);
#endregion
#region 知识点三 异或 ^
// 规则 连接两个数值进行位计算 将数值转为2进制
// 对位运算 相同为0 不同为1
a = 1; //001
b = 5; //101
// 001
//^101
// 100
c = a ^ b;
Console.WriteLine(c);
a = 10; // 1010
b = 11; // 1011
c = 4; // 100
// 1010
//^ 1011
// 0001
//^ 0100
// 0101 = 5
Console.WriteLine(a ^ b ^ c);
#endregion
#region 知识点四 位取反 ~
// 规则 写在数值前面 将数值转为2进制
// 对位运算 0变1 1变0
a = 5;
// 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0101
// 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1010
// 反码补码知识
c = ~a;
Console.WriteLine(c);
#endregion
#region 知识点五 左移<< 和 右移>>
// 规则 让一个数的2进制数进行左移和右移
// 左移几位 右侧加几个0
a = 5; // 101
c = a << 5;
// 1位 1010
// 2位 10100
// 3位 101000
// 4位 1010000
// 5位 10100000 = 32 + 128 = 160
Console.WriteLine(c);
// 右移几位 右侧去掉几个数
a = 5; // 101
c = a >> 2;
// 1位 10
// 2位 1
Console.WriteLine(c);
#endregion
}
}
}
三目运算符
using System;
namespace Lesson15_三目运算符
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("三目运算符");
#region 知识点一 基本语法
//套路: 3个空位 2个符号!!!
//固定语法:空位 ? 空位 : 空位;
//关键信息:bool类型 ? bool类型为真返回内容 : bool类型为假返回内容;
//三目运算符 会有返回值,这个返回值类型必须一致,并且必须使用!
#endregion
#region 知识点二 具体使用
string str = false ? "条件为真" : "条件为假";
Console.WriteLine(str);
int a = 5;
str = a < 1 ? "a大于1" : "a不满条件";
Console.WriteLine(str);
int i = a > 1 ? 123 : 234;
//第一个空位 始终是结果为bool类型的表达式 bool变量 条件表达式 逻辑运算符表达式
//第二三个空位 什么表达式都可以 只要保证他们的结果类型是一致的
bool b = a > 1 ? a > 6 : !false;
#endregion
}
}
}
三目运算符练习题
using System;
namespace Lesson15_练习题
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("三目运算符练习题");
#region 练习题一
//比较两个数的大小,求出最大的。
//int a = 10;
//int b = 15;
//string str = a >= b ? "较大数是a" + a : "较大的数是b" + b;
//Console.WriteLine(str);
//try
//{
// Console.WriteLine("请分别输入两个数比较大小");
// string str = Console.ReadLine();
// int a = int.Parse(str);
// str = Console.ReadLine();
// int b = int.Parse(str);
// str = a >= b ? "较大的数是" + a : "较大的数是" + b;
// Console.WriteLine(str);
//}
//catch
//{
// Console.WriteLine("请输入数字");
//}
#endregion
#region 练习题二
////提示用户输入一个姓名,然后再控制台输出姓名,只要输入的不是帅哥,就显示美女。
//Console.WriteLine("请输入一个姓名");
//string name = Console.ReadLine();
//string str2 = name == "帅哥" ? name : "美女";
//Console.WriteLine(str2);
#endregion
#region 练习题三
//依次输入学生的姓名,C#语言的成绩,Unity的成绩,
//两门成绩都大于等于90分,才能毕业,请输出最后的结果。
//try
//{
// Console.WriteLine("请输入姓名");
// string yourName = Console.ReadLine();
// Console.WriteLine("请输入C#成绩");
// int csharp = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
// Console.WriteLine("请输入Unity成绩");
// int unity = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
// //string result = csharp + unity >= 90 ? "顺利毕业" : "请再学一次!";
// Console.WriteLine(csharp + unity >= 90 ? "顺利毕业" : "请再学一次!");
//}
//catch
//{
// Console.WriteLine("成绩只能输入整数");
//}
#endregion
#region 练习题四
//要求用户输入一个年份,然后判断是不是闰年?
//闰年判断条件:
//年份能被400整除(2000)
//或者
//年份能被4整除,但是不能被100整除(2008)
try
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入一个年份,用来判断是不是闰年");
int year = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
//string result = year % 400 == 0 || year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 ? "闰年" : "不是闰年";
Console.WriteLine(year % 400 == 0 || year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 ? "闰年" : "不是闰年");
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("年份要是整数");
}
#endregion
}
}
}
条件分支语句
using System;
namespace Lesson16_条件分支语句_if
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("条件分支语句");
#region 知识点一 作用
//让顺序执行的代码 产生分支
//if语句是第一个 可以让我们的程序 产生逻辑变化的 语句
#endregion
#region 知识点二 if语句
//作用: 满足条件时 多执行一些代码
//语法:
// if( bool类型值 ) // bool类型相关:bool变量 条件运算符表达式 逻辑运算符表达式
// {
// 满足条件要执行的代码 写在if代码块中;
// }
// 注意:
// 1.if语句的语法部分, 不需要写分号
// 2.if语句可以嵌套使用
if( false )
{
Console.WriteLine("进入了if语句代码块,执行其中的代码逻辑");
Console.WriteLine("进入了if语句代码块,执行其中的代码逻辑");
Console.WriteLine("进入了if语句代码块,执行其中的代码逻辑");
}
Console.WriteLine("if语句外的代码");
int a = 1;
if( a > 0 && a < 5)
{
Console.WriteLine("a在0到5之间");
}
string name = "唐老狮";
string passWord = "666";
if( name == "唐老狮" && passWord == "666" )
{
Console.WriteLine("登录成功");
}
//嵌套使用
if( name == "唐老狮" )
{
Console.WriteLine("用户名验证成功");
if( passWord == "666" )
{
Console.WriteLine("密码验证成功");
//可以无限嵌套
}
//可以无限嵌套
}
#endregion
#region 知识点三 if...else语句
// 作用:产生两条分支 十字路 满足条件做什么 不满足条件做什么
//语法:
// if( bool类型值 )
// {
// 满足条件执行的代码;
// }
// else
// {
// 不满足条件执行的代码:
// }
// 注意:
// 1.if ...else 语句 语法部分 不需要写分号
// 2.if ...else 语句 可以嵌套
if( false )
{
Console.WriteLine("满足if条件 做什么");
if( true )
{
if (true)
{
}
else
{
}
}
else
{
if (true)
{
}
else
{
}
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("不满足if条件 做什么");
if (true)
{
}
else
{
}
}
//其它的使用和if的使用时一样
// 嵌套使用 也是和if语句 一样的
#endregion
#region 知识点四 if...else if...else 语句
//作用:产生n条分支 多条道路选择 最先满足其中的一个条件 就做什么
// 语法:
// if( bool类型值 )
// {
// 满足条件执行的代码;
// }
// else if( bool类型值 )
// {
// 满足条件执行的代码;
// }
// ...中间可以有n个 else if语句代码块
// else
// {
// 不满足条件执行的代码:
// }
// 注意:
// 1. 和前面两个是一样的 不需要写分号
// 2. 是可以嵌套的
// 3. else 是可以省略的
// 4. 注意 条件判断 从上到下执行 满足了第一个后 之后的都不会执行了
int a3 = 6;
if (a3 >= 10)
{
Console.WriteLine("a大于等于10");
}
else if( a3 > 5 && a3 < 10 )
{
Console.WriteLine("a在6和9之间");
}
else if( a3 >= 0 && a3 <= 5 )
{
Console.WriteLine("a在0和5之间");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("a小于0");
}
//if语句相关 if if..else if...else if...else
// else if 和 else 是组合套餐 根据实际情况选择使用
#endregion
}
}
}
switch语句
using System;
namespace Lesson17_条件分支语句_switch
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("switch语句");
#region 知识点一 作用
//让顺序执行的代码 产生分支
#endregion
#region 知识点二 基本语法
//switch(变量)
//{
// // 变量 == 常量 执行 case和 break之间的代码
// case 常量:
// 满足条件执行的代码逻辑;
// break;
// case 常量:
// 满足条件执行的代码逻辑;
// break;
// case 可以有无数个
// default:
// 如果上面case的条件都不满足 就会执行 default中的代码
// break;
//}
// 注意: 常量!! 只能写一个值 不能去写一个范围 不能写条件运算符啊 逻辑运算符啊
// switch 只判断变量是否等于某一个固定值!!!!
int a = 3;
int a2 = 3;
switch (a)
{
//这个条件一定是常量
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("a等于1");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("a等于2");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("a等于3");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("什么条件都不满足,执行default中的内容");
break;
}
float f = 1.4f;
//它一般是配合枚举使用
switch (f)
{
case 1.5f:
Console.WriteLine("f等于1.5");
break;
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("f等于1.5");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("f什么条件都不满足,执行default中的内容");
break;
}
#endregion
#region 知识点三 default可省略
string str = "123";
switch (str)
{
case "123":
Console.WriteLine("等于123");
break;
case "234":
Console.WriteLine("等于234");
break;
}
#endregion
#region 知识点四 可自定义常量
char c = 'A';
//1.必须初始化 2.不能修改
const char c2 = 'A';
switch (c)
{
case c2:
Console.WriteLine("c等于A");
break;
default:
break;
}
#endregion
#region 知识点五 贯穿
//作用:满足某些条件时 做的事情是一样的 就可以使用贯穿
int aa = 1;
switch (aa)
{
// 不写case后面配对的break 就叫做贯穿
// 满足 1 3 4 2其中一个条件 就会执行 之后的代码
case 1:
case 3:
case 4:
case 2:
// case和break之间可以写n句语句
// 并且可以嵌套使用
Console.WriteLine("是个数字");
Console.WriteLine("是个数字");
Console.WriteLine("是个数字");
Console.WriteLine("是个数字");
Console.WriteLine("是个数字");
Console.WriteLine("是个数字");
Console.WriteLine("是个数字");
if( aa == 1 )
{
switch(aa)
{
default:
break;
}
}
else
{
}
break;
default:
break;
}
#endregion
}
}
}
While循环
using System;
namespace Lesson18_循环语句_while
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("while语句");
#region 知识点一 作用
// 让顺序执行的代码 可以不停的循环执行某一代码块的内容
// 条件分支语句 是 让代码产生分支
// 循环语句 是 让代码可以被重复执行
#endregion
#region 知识点二 语法相关
// bool类型变量 条件运算符 逻辑运算符
//while(bool类型的值)
//{
// //当满足条件时 就会执行while语句块中的内容
// //......
// //......
// //......
// //......
// //当代码逻辑执行完 会回到while循环开头
// //再次进行条件判断
//}
//Console.WriteLine("主代码逻辑");
//死循环
//就不停的执行循环中的逻辑 "直到死为止"
//死循环只有在目前我们学习 控制台程序时 会频繁使用
//之后进入 Unity过后 基本不会使用死循环
//1.可能因为内存问题 造成程序崩溃 闪退
//2.造成程序卡死
//while(true)
//{
// Console.WriteLine("**************");
// Console.WriteLine("请玩家输入用户名密码");
// Console.ReadLine();
//}
//计算一个为0的整形变量 让他只能累加1 不停的加到10为止
//int i = 0;
////bool类型的值 还可以用逻辑运算符 && || ! 条件运算符 算术运算结合运算
//while(i < 10)
//{
// ++i;
//}
//Console.WriteLine(i);
#endregion
#region 知识点三 嵌套使用
// 不仅可以嵌套 if switch 还可以嵌套 while
//int a = 0;
//int b = 0;
//while(a < 10)
//{
// ++a;
// while( b < 10)
// {
// ++b;
// }
//}
//a = 0;
//b = 0;
//while( a < 10)
//{
// ++a;
// if( b < 10 )
// {
// ++b;
// }
//}
//int a2 = 0;
//while( a2 < 10 )
//{
// ++a2;
// //每次从外层循环进来是
// //b2和上一次的b2有没有关系 是不是一个变量
// //切忌 没有关系
// int b2 = 0;
// ++b2;
//}
#endregion
#region 知识点四 流程控制关键词
//作用 : 控制循环逻辑的关键词
// break:跳出循环
while(true)
{
Console.WriteLine("break之前的代码");
break;
Console.WriteLine("break之后的代码");
}
Console.WriteLine("循环外的代码");
int i = 0;
while(true)
{
++i;
Console.WriteLine(i);
if ( i == 10 )
{
break;
}
}
Console.WriteLine(i);
// continue:回到循环开始 继续执行
//while (true)
//{
// Console.WriteLine("continue前的代码");
// continue;
// Console.WriteLine("continue后的代码");
//}
//Console.WriteLine("循环外的代码");
//打印1到20之间的 奇数
int index = 0;
while(index < 20)
{
++index;
//什么样的数是奇数
//不能被2整除的数 ——> %
if (index % 2 == 0)
{
continue;
}
Console.WriteLine(index);
}
//注意:break和continue主要是和循环配合使用的 和if语句没关
// break在switch中的作用 和 while循环中的作用有异曲同工之妙
//while(true)
//{
// int a = 1;
// switch(a)
// {
// default:
// continue;
// break;
// }
// Console.WriteLine("11111");
//}
#endregion
}
}
}
for循环
using System;
namespace Lesson20_循环语句_for
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("for循环");
#region 知识点一 基本语法
//for( /*初始表达式*/; /*条件表达式*/; /*增量表达式*/ )
//{
// //循环代码逻辑;
//}
// 第一个空(初始表达式): 一般声明一个临时变量,用来计数用
// 第二个空(条件表达式): 表明进入循环的条件 一个bool类型的结果(bool变量 条件运算符 逻辑运算符 算术运算符)
// 第三个空(增量表达式): 用第一个空中的变量 进行 自增减运算
// 第一次进入循环时 才会调用 第一个空中的代码
// 每次进入循环之前 都会判断第二个空中的条件 满足才会进入循环逻辑
for( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
//执行完循环语句块中的逻辑后
//最后执行第三个空中的代码
}
for( int i = 10; i >= 0; i-- )
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
//每个空位 可以按照规则进行书写
//第一个空位 就是申明变量 所以可以连续申明
//第二个空位 就是进入条件 只要是bool结果的表达式 都可以
//第三个空位 就是执行一次循环逻辑过后要做的事情 做啥都行
//for( int i = 0, j = 0; i < 10 && j < 0; ++i, j = j + 1)
//{
//}
#endregion
#region 知识点二 支持嵌套
//for( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
//{
// for( int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
// {
// Console.WriteLine(i + "_" + j);
// }
// while(true)
// {
// }
// if(true)
// {
// }
// do
// {
// } while (true);
//}
#endregion
#region 知识点三 特殊写法
//for循环 这三个空位 可以都空着 可以根据需求去填写
// for循环可以写死循环
//for( ; ; )
//{
// Console.WriteLine("for循环的死循环");
//}
//int k = 0;
//for(; k < 10; )
//{
// ++k;//k++, k += 1;
//}
//for( k = 0; ; ++k )
//{
// if( k >= 10 )
// {
// break;
// }
//}
#endregion
#region 知识点四 对比while循环
//for循环 一般用来可以准确得到 一个范围中的所有数
for( int i = 0; i < 10; ++i )
{
}
int j = 0;
while(j < 10)
{
//......................
++j;
}
#endregion
}
}
}
for循环练习题
using System;
namespace Lesson20_练习题
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("for循环练习题");
#region 练习题一
//输出1到100之间的整数(包含本身)
//for(int i = 1; i <= 100; ++i)
//{
// Console.WriteLine(i);
//}
#endregion
#region 练习题二
//求1~100之间所有偶数的和
//int sum = 0;
//for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
//{
// //判断是否是偶数 是否能整除2
// if( i % 2 == 0 )
// {
// sum += i;
// }
//}
//for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 2)
//{
// sum += i;
//}
//Console.WriteLine(sum);
#endregion
#region 练习题三
//找出100~999之间的水仙花数
//例如:153 = 1 * 1 * 1 + 5 * 5 * 5 + 3 * 3 * 3 这个数就是水仙花数
//int bai, shi, ge;
//for (int i = 100; i <= 999; i++)
//{
// //判断 每一位 的立方加起来 是不是等于自己
// //得到每一位 百位 十位 个位
// bai = i / 100;
// shi = i % 100 / 10;
// ge = i % 10;
// //是否满足水仙花数条件
// if( bai * bai * bai + shi * shi * shi + ge * ge * ge == i )
// {
// Console.WriteLine(i);
// }
//}
#endregion
#region 练习题四
//在控制台上输出九九乘法表
//for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++)
//{
// //1 1 X 1 = 1 空行
// //2 1 X 2 = 2 2 X 2 = 4 空行
// //3 1 X 3 = 3 2 X 3 = 6 3 X 3 = 9 空行
// for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
// {
// Console.Write("{0}X{1}={2} ", j, i, i * j);
// }
// Console.WriteLine();
//}
#endregion
#region 练习题五
//在控制台上输出如下10 * 10的空心星型方阵
//**********
//* *
//* *
//* *
//* *
//* *
//* *
//* *
//* *
//**********
//行
//for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
//{
// //列
// for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
// {
// //列 如果是 第1行和最后1行 那么 内层列循环 都打印星号
// // 按照 **********的规则打印
// if( j == 0 || j == 9 )
// {
// Console.Write("*");
// }
// //否则 就是 按照* *的规则打印
// else
// {
// if (i == 0 || i == 9)
// {
// Console.Write("*");
// }
// else
// {
// Console.Write(" ");
// }
// }
// }
// Console.WriteLine();
//}
#endregion
#region 练习题六
//在控制台上输出如下10 * 10的三角形方阵
//* 1 1
//** 2 2
//*** 3 3
//**** 4 4
//*****
//******
//*******
//********
//*********
//**********
//行
//for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
//{
// //列
// //**********
// for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
// {
// Console.Write("*");
// }
// Console.WriteLine();
//}
#endregion
#region 练习题七
//在控制台上输出如下10行的三角形方阵
// * 1 1 -> 2i - 1 9 10 - i
// *** 2 3 -> 2i - 1 8 10 - i
// ***** 3 5 7 10 - i
// ******* 4 7 6 10 - i
// ********* 5 9 5
// *********** 6 11 4
// ************* 7 13 3
// *************** 8 15 2
// ***************** 9 17 1
//******************* 10 19 0 10 - i
//行
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
//打印空格的列
for (int k = 1; k <= 10 - i; k++)
{
Console.Write(" ");
}
//打印星号的列
for (int j = 1; j <= 2*i-1; j++)
{
Console.Write("*");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
#endregion
}
}
}
控制台
using System;
namespace 必备知识点_控制台相关
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("控制台相关");
#region 知识点一 复习 输入输出
//输出
//Console.WriteLine("123123");//光标空行
//Console.Write("123123123123");//不空行
//输入
//string str = Console.ReadLine();
//如果在ReadKey(true)不会把输入的内容显示在控制台上
//char c = Console.ReadKey(true).KeyChar;
//Console.WriteLine(c);
#endregion
#region 知识点二 控制台其它方法
//1.清空
Console.Clear();
//2.设置控制台大小
// 窗口大小 缓冲区大小
// 注意:
//1.先设置窗口大小,再设置缓冲区大小
//2.缓冲区的大小不能小于窗口的大小
//3.窗口的大小不能大于控制台的最大尺寸
//窗口大小
Console.SetWindowSize(100, 50);
//缓冲区大小 (可打印内容区域的宽高 )
Console.SetBufferSize(1000, 1000);
//3.设置光标的位置
//控制台左上角为原点0 0 右侧是X轴正方向 下方是Y轴正方向 它是一个平面二维坐标系
//注意:
//1.边界问题
//2.横纵距离单位不同 1y = 2x 视觉上的
Console.SetCursorPosition(10, 5);
Console.WriteLine("123123");
//4.设置颜色相关
//文字颜色设置
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.WriteLine("123123123");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
//背景颜色设置
//Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
//重置背景颜色过后 需要Clear一次 才能把整个背景颜色改变
//Console.Clear();
//5.光标显隐
Console.CursorVisible = false;
//6.关闭控制台
Environment.Exit(0);
#endregion
}
}
}
随机数
using System;
namespace 必备知识点_随机数
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("随机数");
#region 知识点一 产生随机数对象
//固定写法
// Random 随机数变量名 = new Random();
Random r = new Random();
#endregion
#region 知识点二 生成随机数
int i = r.Next(); //生成一个非负数的随机数
Console.WriteLine(i);
i = r.Next(100); // 生成一个 0~99的随机数 左边始终是0 左包含 右边是100 右不包含
Console.WriteLine(i);
i = r.Next(5, 100); // 生成一个 5到99的随机数 左包含 右不包含
Console.WriteLine(i);
#endregion
}
}
}
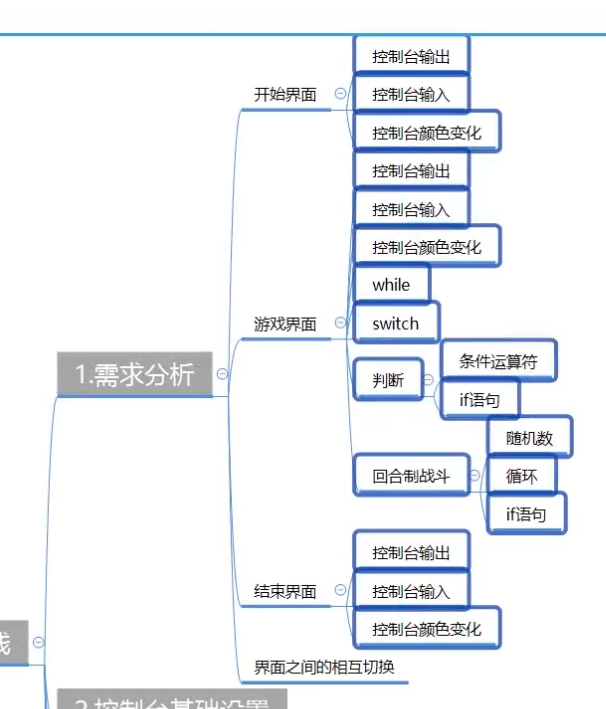
一个简单的小项目
需求分析
using System;
namespace 入门实践
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 1 控制台基础设置
//隐藏光标
Console.CursorVisible = false;
//通过两个变量来存储 舞台的大小
int w = 50;
int h = 30;
//设置舞台(控制台)的大小
Console.SetWindowSize(w, h);
Console.SetBufferSize(w, h);
#endregion
#region 2 多个场景
//当前所在场景的编号
int nowSceneID = 1;
#region 9 结束场景相关
//结束场景显示的 文字提示内容
string gameOverInfo = "";
#endregion
while (true)
{
//不同的场景ID 进行不同的逻辑处理
switch (nowSceneID)
{
//开始场景
case 1:
Console.Clear();
#region 3 开始场景逻辑
Console.SetCursorPosition(w / 2 - 7, 8);
Console.Write("唐老狮营救公主");
//当前选项的编号
int nowSelIndex = 0;
//因为要输入 我们可以构造一个 开始界面自己的 死循环
//专门用来处理 开始场景相关的逻辑
while (true)
{
//用一个标识 来处理 想要在while循环内部的switch逻辑执行时 希望退出外层while循环时
// 改变标识即可
bool isQuitWhile = false;
// 显示 内容
//先设置光标位置 再显示内容
Console.SetCursorPosition(w / 2 - 4, 13);
//根据当前选择的编号 来决定 是否变色
Console.ForegroundColor = nowSelIndex == 0 ? ConsoleColor.Red : ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write("开始游戏");
Console.SetCursorPosition(w / 2 - 4, 15);
Console.ForegroundColor = nowSelIndex == 1 ? ConsoleColor.Red : ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write("退出游戏");
// 检测 输入
// 检测玩家 输入的一个键内容 并且不会再控制台上显示输入的内容
char input = Console.ReadKey(true).KeyChar;
switch (input)
{
case 'W':
case 'w':
--nowSelIndex;
if (nowSelIndex < 0)
{
nowSelIndex = 0;
}
break;
case 'S':
case 's':
++nowSelIndex;
if (nowSelIndex > 1)
{
nowSelIndex = 1;
}
break;
case 'J':
case 'j':
if (nowSelIndex == 0)
{
//1.改变当前选择的场景ID
nowSceneID = 2;
//2.要退出 内层while循环
isQuitWhile = true;
}
else
{
//关闭控制台
Environment.Exit(0);
}
break;
}
if (isQuitWhile)
{
break;
}
}
#endregion
break;
//游戏场景
case 2:
Console.Clear();
#region 4 不变的红墙
//设置颜色为红色
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
//画墙
//上方墙
for (int i = 0; i < w; i += 2)
{
//上方墙
Console.SetCursorPosition(i, 0);
Console.Write("■");
//下方墙
Console.SetCursorPosition(i, h - 1);
Console.Write("■");
//中间墙
Console.SetCursorPosition(i, h - 6);
Console.Write("■");
}
//左边的墙
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
{
//左边的墙
Console.SetCursorPosition(0, i);
Console.Write("■");
//右边的墙
Console.SetCursorPosition(w - 2, i);
Console.Write("■");
}
#endregion
#region 5 boss属性相关
int bossX = 24;
int bossY = 15;
int bossAtkMin = 7;
int bossAtkMax = 13;
int bossHp = 100;
string bossIcon = "■";
//申明一个 颜色变量
ConsoleColor bossColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
#endregion
#region 6 玩家属性相关
int playerX = 4;
int playerY = 5;
int playerAtkMin = 8;
int playerAtkMax = 12;
int playerHp = 100;
string playerIcon = "●";
ConsoleColor playerColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
//玩家输入的内容 外面申明 节约性能
char playerInput;
#endregion
#region 8 公主相关
int princessX = 24;
int princessY = 5;
string princessIcon = "★";
ConsoleColor princessColor = ConsoleColor.Blue;
#endregion
#region 7 玩家战斗相关
//战斗状态
bool isFight = false;
//作用是 从while循环内部的switch 改变标识 用来跳出外层的while循环
bool isOver = false;
#endregion
//游戏场景的死循环 专门用来 检测 玩家输入相关循环
while (true)
{
#region 5 boss属性相关
//boss活着时才绘制
if (bossHp > 0)
{
//绘制boss图标
Console.SetCursorPosition(bossX, bossY);
Console.ForegroundColor = bossColor;
Console.Write(bossIcon);
}
#endregion
#region 8 公主相关
else
{
Console.SetCursorPosition(princessX, princessY);
Console.ForegroundColor = princessColor;
Console.Write(princessIcon);
}
#endregion
#region 6 玩家移动相关
//画出玩家
Console.SetCursorPosition(playerX, playerY);
Console.ForegroundColor = playerColor;
Console.Write(playerIcon);
//得到玩家输入
playerInput = Console.ReadKey(true).KeyChar;
#endregion
//战斗状态处理什么逻辑
if (isFight)
{
#region 7 玩家战斗相关
//如果是战斗状态 你做什么
//只会处理J键
if (playerInput == 'J' || playerInput == 'j')
{
//在这判断 玩家或者怪物 是否死亡 如果死亡了 继续之后的流程
if (playerHp <= 0)
{
//游戏结束
//输掉了 应该直接显示 我们的 游戏结束界面
nowSceneID = 3;
gameOverInfo = "游戏失败";
break;
}
else if (bossHp <= 0)
{
//去营救公主
//boss擦除
Console.SetCursorPosition(bossX, bossY);
Console.Write(" ");
isFight = false;
}
else
{
//去处理按J键打架
// 玩家打怪物
Random r = new Random();
//得到随机攻击了
int atk = r.Next(playerAtkMin, playerAtkMax);
//血量减对应的攻击力
bossHp -= atk;
//打印信息
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
//先擦除这一行 上次显示的内容
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 4);
Console.Write(" ");
//再来写新的信息
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 4);
Console.Write("你对boss造成了{0}点伤害,boss剩余血量为{1}", atk, bossHp);
// 怪物打玩家
if (bossHp > 0)
{
//得到随机攻击了
atk = r.Next(bossAtkMin, bossAtkMax);
playerHp -= atk;
//打印信息
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
//先擦除这一行 上次显示的内容
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.Write(" ");
//再来写新的信息
//boss如果把玩家打死了 做什么
if (playerHp <= 0)
{
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.Write("很遗憾,你未能通过boss的试炼,战败了");
}
else
{
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.Write("boss对你造成了{0}点伤害,你的剩余血量为{1}", atk, playerHp);
}
}
else
{
//擦除之前的战斗信息
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 5);
Console.Write(" ");
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 4);
Console.Write(" ");
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.Write(" ");
//显示恭喜胜利的信息
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 5);
Console.Write("你战胜了boss,快去营救公主");
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 4);
Console.Write("前往公主身边按J键继续");
}
}
}
#endregion
}
//非战斗状态处理什么逻辑
else
{
#region 6 玩家移动相关
//擦除
Console.SetCursorPosition(playerX, playerY);
Console.Write(" ");
//改位置
switch (playerInput)
{
case 'W':
case 'w':
--playerY;
if (playerY < 1)
{
playerY = 1;
}
//位置如果和boss重合了 并且boss没有死
else if (playerX == bossX && playerY == bossY && bossHp > 0)
{
//拉回去
++playerY;
}
else if ( playerX == princessX && playerY == princessY && bossHp <= 0 )
{
//拉回去
++playerY;
}
break;
case 'A':
case 'a':
playerX -= 2;
if (playerX < 2)
{
playerX = 2;
}
else if (playerX == bossX && playerY == bossY && bossHp > 0)
{
//拉回去
playerX += 2;
}
else if (playerX == princessX && playerY == princessY && bossHp <= 0)
{
//拉回去
playerX += 2;
}
break;
case 'S':
case 's':
++playerY;
if (playerY > h - 7)
{
playerY = h - 7;
}
else if (playerX == bossX && playerY == bossY && bossHp > 0)
{
//拉回去
--playerY;
}
else if (playerX == princessX && playerY == princessY && bossHp <= 0)
{
//拉回去
--playerY;
}
break;
case 'D':
case 'd':
playerX += 2;
if (playerX > w - 4)
{
playerX = w - 4;
}
else if (playerX == bossX && playerY == bossY && bossHp > 0)
{
//拉回去
playerX -= 2;
}
else if (playerX == princessX && playerY == princessY && bossHp <= 0)
{
//拉回去
playerX -= 2;
}
break;
case 'J':
case 'j':
#region 7 玩家战斗相关
//开始战斗
//要让玩家不能再移动
//下方能够显示信息
if ((playerX == bossX && playerY == bossY - 1 ||
playerX == bossX && playerY == bossY + 1 ||
playerX == bossX - 2 && playerY == bossY ||
playerX == bossX + 2 && playerY == bossY) && bossHp > 0)
{
isFight = true;
//可以开始战斗
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 5);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write("开始和Boss战斗了,按J键继续");
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 4);
Console.Write("玩家当前血量为{0}", playerHp);
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.Write("boss当前血量为{0}", bossHp);
}
#endregion
#region 8 公主相关
//判断是否在公主身边按J键
else if ((playerX == princessX && playerY == princessY - 1 ||
playerX == princessX && playerY == princessY + 1 ||
playerX == princessX - 2 && playerY == princessY ||
playerX == princessX + 2 && playerY == princessY) && bossHp <= 0)
{
//改变 场景ID
nowSceneID = 3;
gameOverInfo = "游戏通关";
//跳出 游戏界面的while循环 回到主循环
isOver = true;
}
#endregion
break;
}
#endregion
}
#region 8 公主相关
//外层while循环逻辑
if (isOver)
{
//就是和while配对
break;
}
#endregion
}
break;
//结束场景
case 3:
Console.Clear();
#region 9 结束场景逻辑
//标题的显示
Console.SetCursorPosition(w / 2 - 4, 5);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write("GameOver");
//可变内容的显示 根据失败或者 成功显示的内容不一样
Console.SetCursorPosition(w / 2 - 4, 7);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.Write(gameOverInfo);
int nowSelEndIndex = 0;
while (true)
{
bool isQuitEndWhile = false;
Console.SetCursorPosition(w / 2 - 6, 9);
Console.ForegroundColor = nowSelEndIndex == 0 ? ConsoleColor.Red : ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write("回到开始界面");
Console.SetCursorPosition(w / 2 - 4, 11);
Console.ForegroundColor = nowSelEndIndex == 1 ? ConsoleColor.Red : ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write("退出游戏");
char input = Console.ReadKey(true).KeyChar;
switch (input)
{
case 'W':
case 'w':
--nowSelEndIndex;
if (nowSelEndIndex < 0)
{
nowSelEndIndex = 0;
}
break;
case 'S':
case 's':
++nowSelEndIndex;
if (nowSelEndIndex > 1)
{
nowSelEndIndex = 1;
}
break;
case 'J':
case 'j':
if (nowSelEndIndex == 0)
{
nowSceneID = 1;
isQuitEndWhile = true;
}
else
{
Environment.Exit(0);
}
break;
}
//为了 从switch中跳出上一层的 while循环 加的标识
if (isQuitEndWhile)
{
break;
}
}
#endregion
break;
}
}
#endregion
}
}
}




