spring源码学习
spring架构
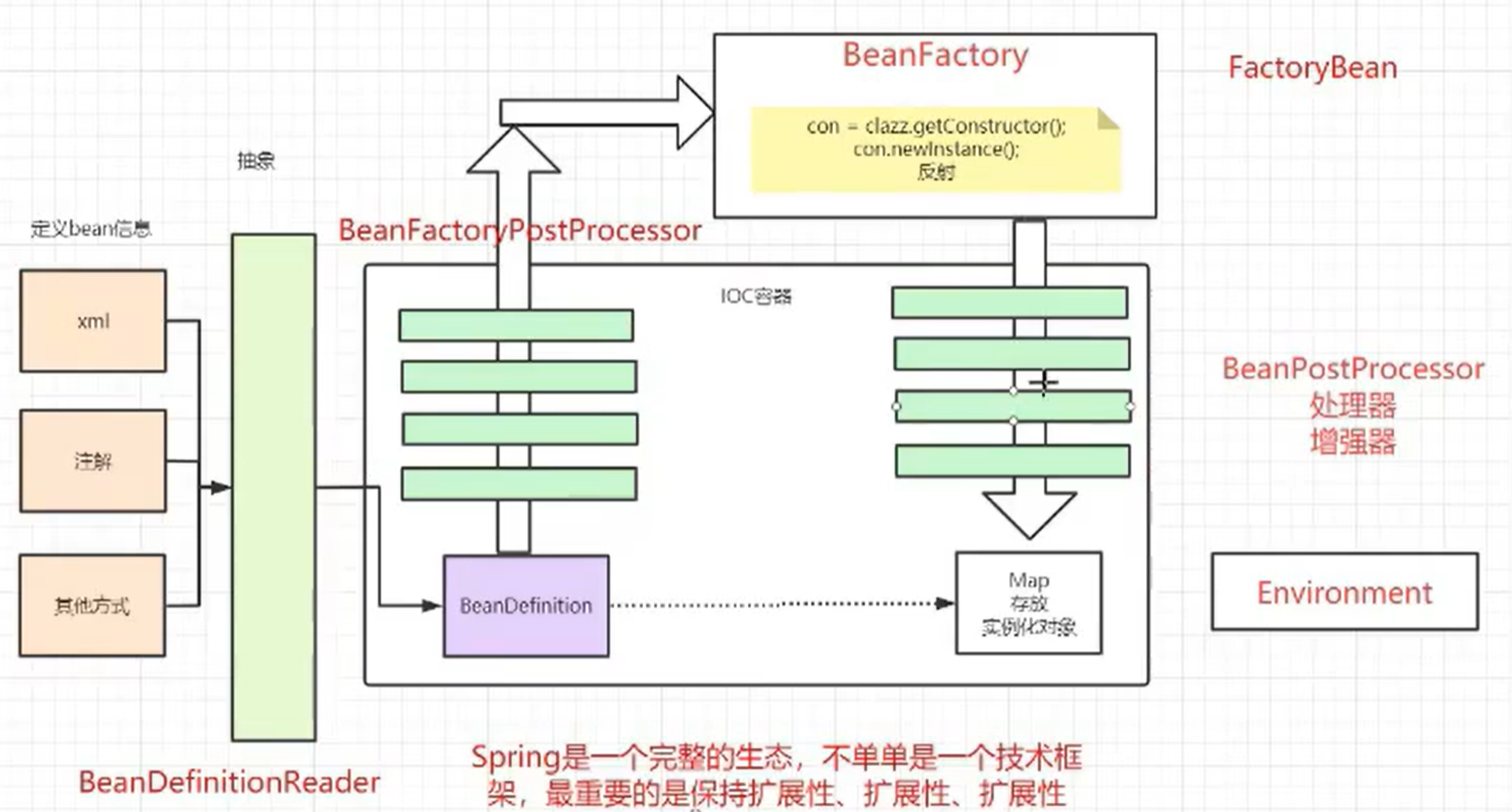
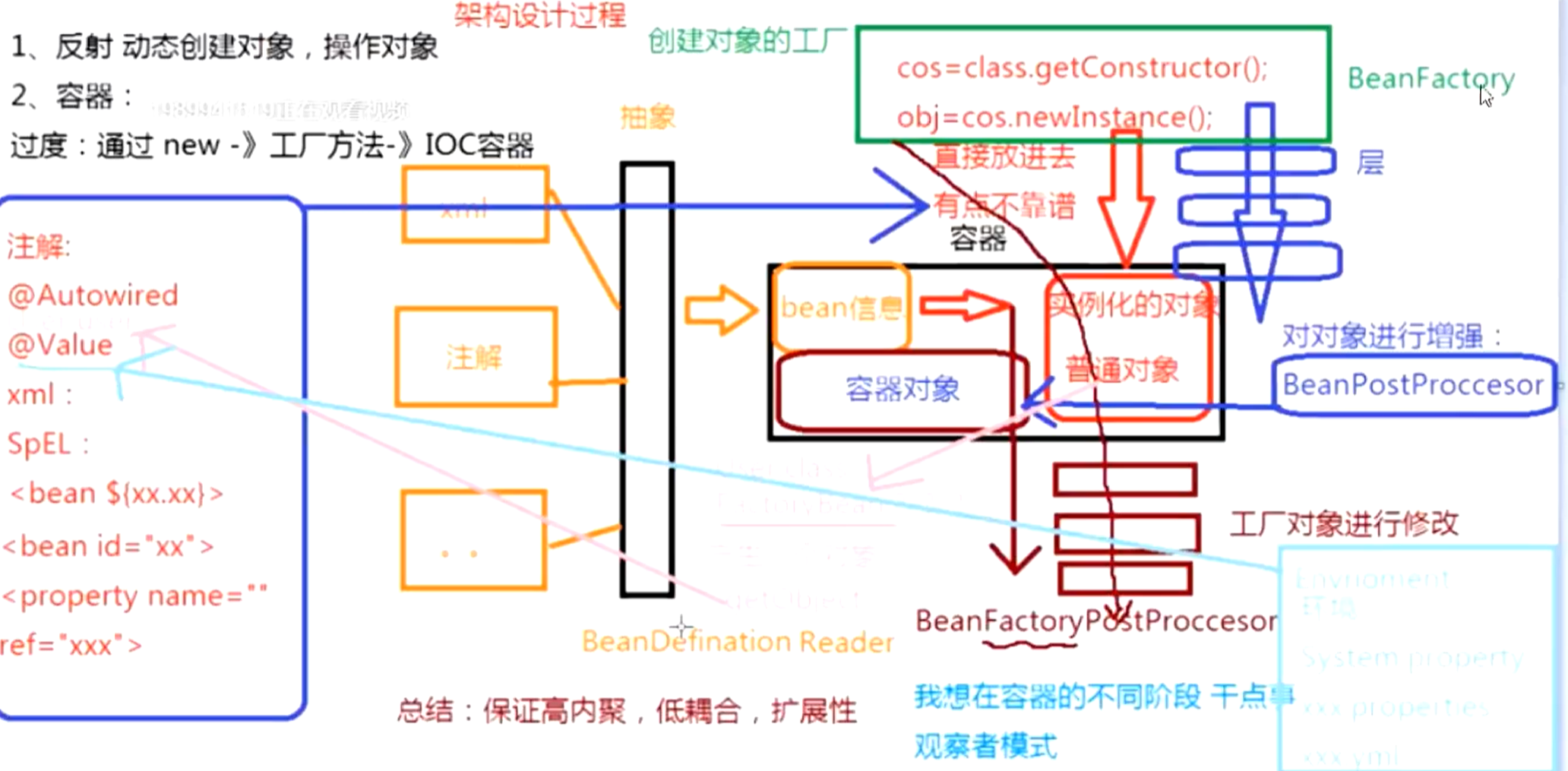
按照图中的流程,一定要自己使用idea工具配合着debug,慢慢去看里面源码,除了花费一点时间,不会很难,绝对可以理解的
spring测试用例:
maven依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
测试类:
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String gender;
}
application.xml配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--注册一个对象,spring回自动创建这个对象-->
<!--
一个bean标签就表示一个对象
id:这个对象的唯一标识
class:注册对象的完全限定名
-->
<bean id="person" class="com.biao.java8.spring.Person">
<!--使用property标签给对象的属性赋值
name:表示属性的名称
value:表示属性的值
-->
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="zhangsan"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="gender" value="男"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
启动类:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ApplicationContext:表示spring容器
//ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:表示从当前classpath路径中获取xml文件的配置
//根据spring的配置文件来获取ioc容器对象
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = context.getBean("person", Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}
先允许确保正常打印person对象无误,打上断点,进行调式,deg代码
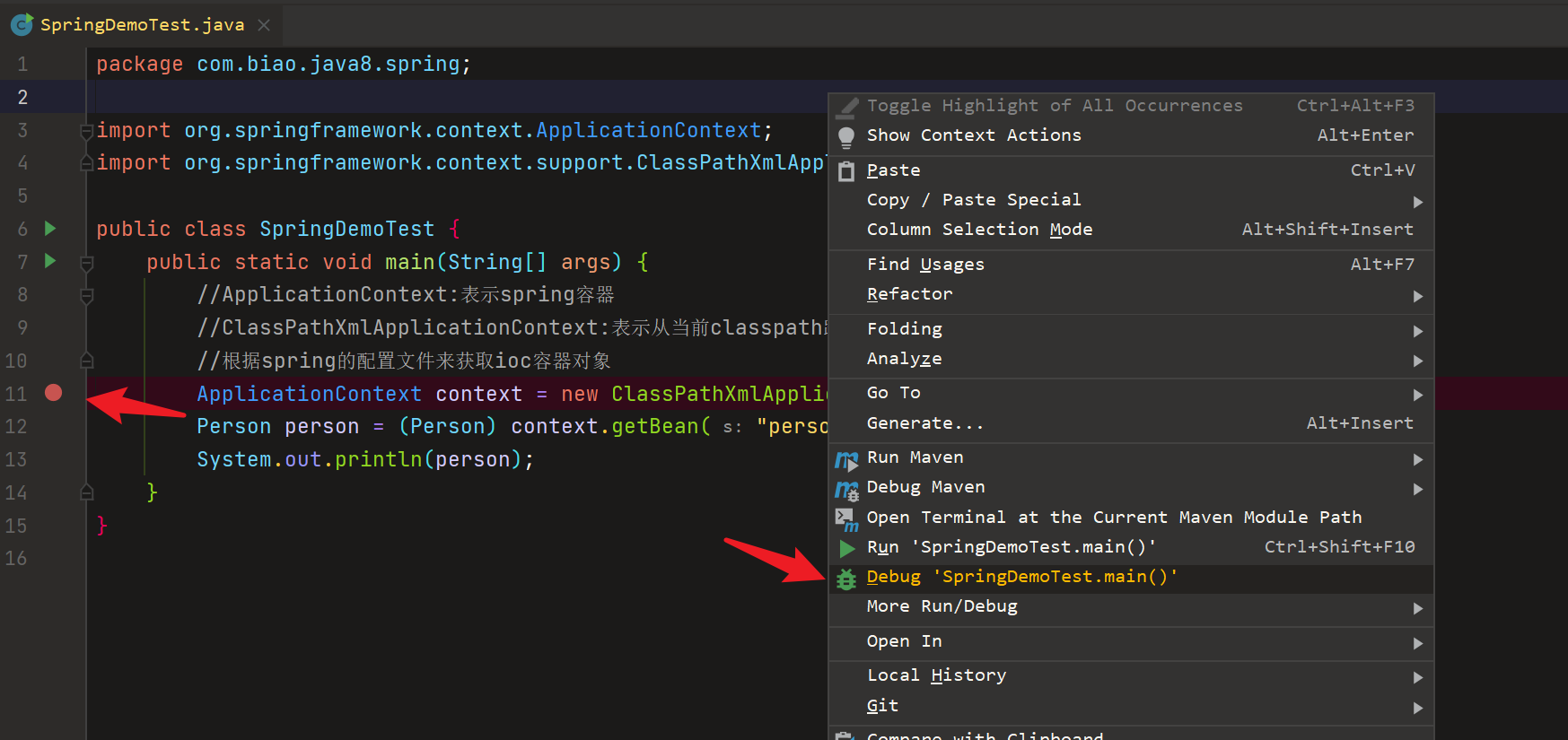
使用F7进入代码内部,这里处理了一个WebLogic 8.1应用关闭的bug,在AbstractApplicationContext类中

继续F7往下走,又回来了
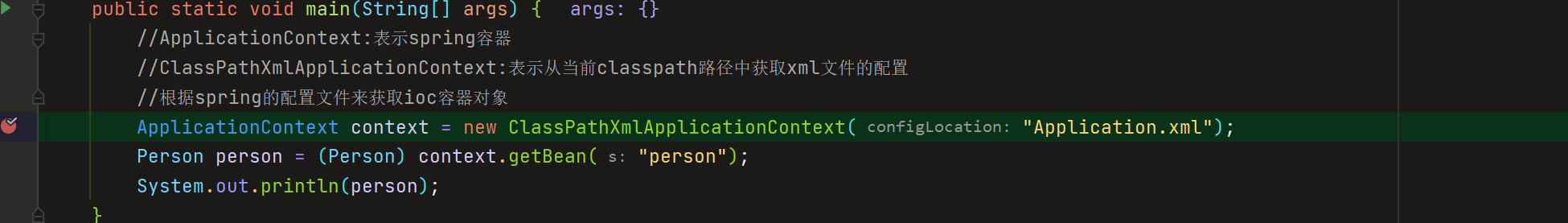
继续F7进去往下走,调用了ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的构造方法

继续F7进去往下走,在构造方法中做了一些事情
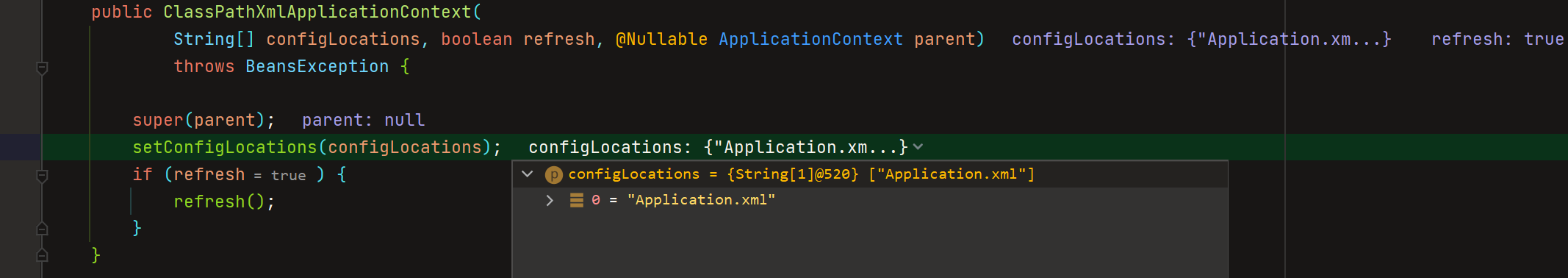
这里调用了父类的构造方法,获取到了资源处理器
获取到了配置文件application.xml,使用setConfigLocations()放到了ConfigLocations,所以后面肯定会用到
然后调用了refresh();方法,
F7进入查看这个方法,里面一共调用了13个方法
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
1、prepareRefresh();
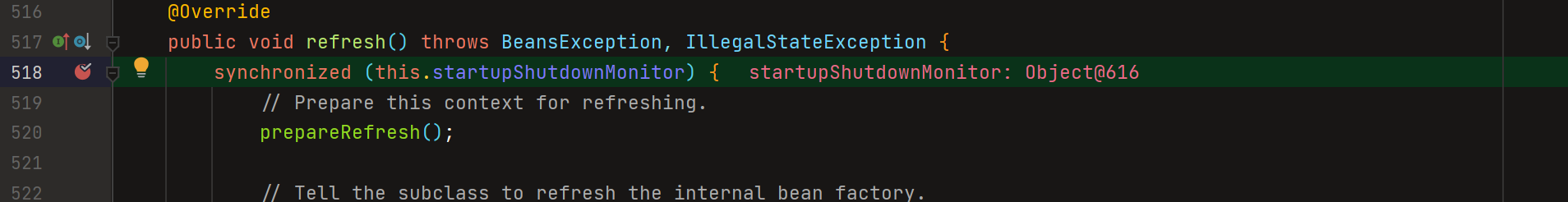
refresh()方法刚进来时候,首先有个同步操作,开启和关闭不能同事进行,然后调用了prepareRefresh();方法
使用F7进去查看prepareRefresh()方法,有些有些注释是我手动加的说明
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 设置开始时间
this.closed.set(false); // 设置ioc容器的状态,closed是关闭的
this.active.set(true); // active 是true的
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
initPropertySources(); // 初始化子类扩展的一些东西
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
// 创建空的集合存放监听事件
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
2、obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 重点
obtainFreshBeanFactory();方法上面的注释说了,告诉子类刷新内部bean工厂
F7进入方法看到里面调用了2个方法,一个是刷新bean工厂,一个是获取bean工厂,主要是看refreshBeanFactory(), getBeanFactory()方法基本没做什么事
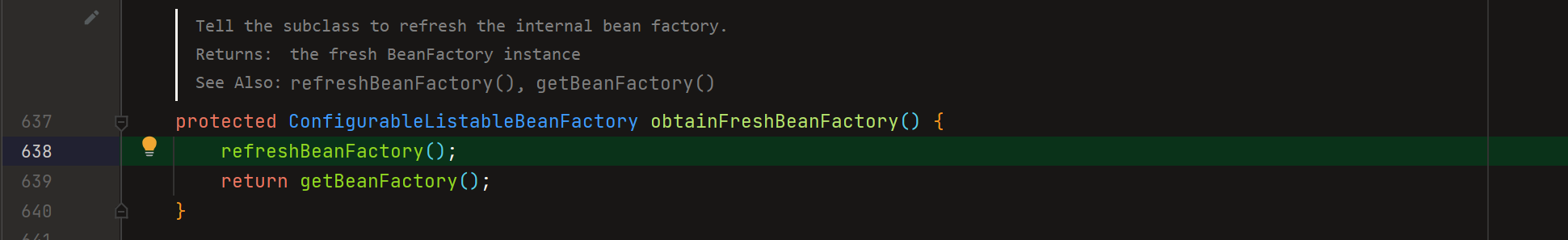
进入到refreshBeanFactory()方法里面,查看这个刷新BeanFactory的方法
/**
* This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying
* bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and
* initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle.
*/
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) { // 这里很明显是判断有没有BeanFactory
// 如果已经有BeanFactory,就给销毁掉
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); // 准备创建BeanFactory,方法在下面看
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); // 这个时候,上面一行代码已经创建好BeanFactory了,给BeanFactory存放序列化id
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); // 给BeanFactory设置自定义的功能,这个时候BeanFactory是空的,所以啥也没做
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); // 合理非常重要,把bean的值放进BeanFactory进行加载过程,看下面的loadBeanDefinitions()方法介绍
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
createBeanFactory()
createBeanFactory()方法,返回的是一个DefaultListableBeanFactory,这里最后返回的就是一个空对象,自己可以debug时候点进去看看
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {
// getInternalParentBeanFactory() 返回的是个空的,所以直接看DefaultListableBeanFactory的构造方法,调用了supper()方法,里面调用到AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory()方法
return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory构造方法调用supper,里面调用了下面代码AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory()方法
public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory() {
super(); // 调用父类创建抽象工厂,中间会把所有属性的值进行填充,可以自己在这里去具体细看
// 给ignoreDependencyInterface这个集合存放下面的3个Aware
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanNameAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanFactoryAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanClassLoaderAware.class);
}
/**
* Create a new AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory with the given parent.
* @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory, or {@code null} if none
*/
public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory(@Nullable BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) {
this(); // 这个this()调用的是上面的AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory方法
setParentBeanFactory(parentBeanFactory); // 这个parentBeanFactory是空的
}
loadBeanDefinitions()
/**
* Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #initBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
*/
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader,可以自己调试进入查看做了什么
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); 给BeanDefinitionReader存放当前环境的对象
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); // 设置资源加载器,存放的是当前类的本身,是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // 这个是为了处理xml文件,可以点进去看一下,主要是获取类加载器,把资源值加载进去,然后设置到EntityResolver里面
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); // 给beanDefinitionReader进行初始化工作,主要是进行最基本的一个验证xml,这里不是太难,可以自己点进去看看
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); // 开始真正的加载过程,这里非常重要
}
loadBeanDefinitions()
/**
* Load the bean definitions with the given XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* <p>The lifecycle of the bean factory is handled by the {@link #refreshBeanFactory}
* method; hence this method is just supposed to load and/or register bean definitions.
* @param reader the XmlBeanDefinitionReader to use
* @throws BeansException in case of bean registration errors
* @throws IOException if the required XML document isn't found
* @see #refreshBeanFactory
* @see #getConfigLocations
* @see #getResources
* @see #getResourcePatternResolver
*/
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); // 获取资源,这里是没有的,所以为空
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); // 这里是获取资源路径,就是获取到application.xml文件,想不起来的话看下面这个图,这时候肯定有值,所以进入下面判断里
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); // 开始进行整体的一个加载过程,看下面的具体代码
}
}

loadBeanDefinitions
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
int count = 0;
for (String location : locations) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(location); // 因为传的参数是数组,所以要遍历,看下面的loadBeanDefinitions具体实现代码,是又一个loadBeanDefinitions的重载方法代码
}
return count;
}
loadBeanDefinitions
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader(); // 前面已经知道了资源路径,所以在这里进行加载过来
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
// 这一行代码做了处理,把location加进去,然后获取Resources资源,自己点进去看看,调用的getResources方法在下面查看代码
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
}
getResources()
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
if (locationPattern.startsWith("classpath*:")) { // 判断传过来的是否以 classpath*: 为前缀,就是解析xml文件里的配置
return this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring("classpath*:".length())) ? this.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern) : this.findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring("classpath*:".length()));
} else {
// 判断是否是 war: 或者 */ , 都不是
int prefixEnd = locationPattern.startsWith("war:") ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1 : locationPattern.indexOf(58) + 1;
// 既然都不是,所以使用后面判断代码,当前的这个值加载回来,获取当前资源路径,把资源路径放到Resource对象里面
return this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd)) ? this.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern) : new Resource[]{this.getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
Iterator var2 = this.getProtocolResolvers().iterator();
Resource resource;
do {
if (!var2.hasNext()) {
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return this.getResourceByPath(location);
}
if (location.startsWith("classpath:")) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring("classpath:".length()), this.getClassLoader());
}
try {
URL url = new URL(location);
return (Resource)(ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url));
} catch (MalformedURLException var5) {
// 上面条件都不满足,所以会执行下面这行,通过路径返回Resource资源,点进去就可以看到处理过程了
return this.getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
ProtocolResolver protocolResolver = (ProtocolResolver)var2.next();
resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);
} while(resource == null);
return resource;
}
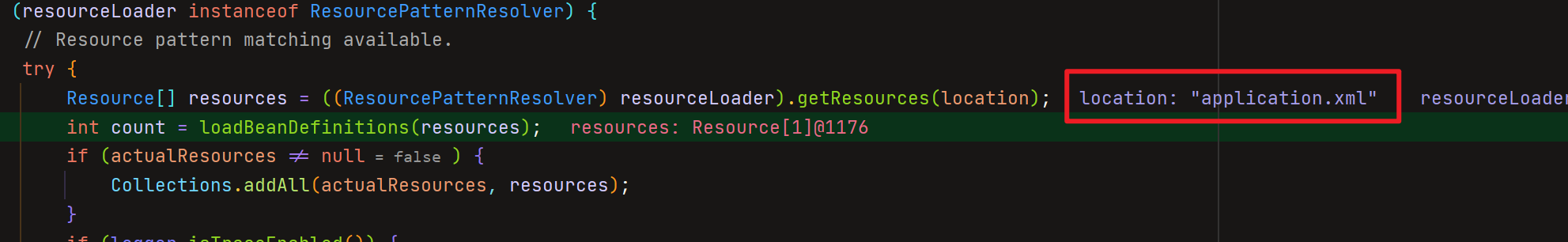
通过路径获取到resources对象后,又调用了loadBeanDefinitions()重载方法,上面执行调用时穿入的参数是字符串,现在传入的参数是资源,执行到这个方法来看下面源码
loadBeanDefinitions
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
// 现在什么都没做,所以这个里面的ThreadLocal啥也没干,currentResources是空的
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
// 把encodedResource,也就是application.xml给加入到currentResources里面
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
// 获取输入流对象,读取xml文件
try (InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
// 这里开始真正执行,跳到下面的doLoadBeanDefinitions代码去看吧
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
doLoadBeanDefinitions()
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
// 按照文档方式读取xml配置资源对象,主要是验证配置文件是否规范正确,先验证头信息,再验证其他配置信息,
// 最后得到一个DocumentBuilder对象,可以通过这个对象过去到配置文件的属性值了
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); // 具体是把xml解析一下成Document,它就是个字符串,可以自己点进去细看一下
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); // 点进去看源码,看下面代码
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count; // 这里返回的是1,因为我只有一个person对象
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
返回count为1,具体整个过程要下面的内容,到这个位置结束,就可以知道具体实现了
registerBeanDefinitions()
/**
* Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document.
* Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}.
* <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes
* {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it.
* @param doc the DOM document
* @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information)
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
* @see #setDocumentReaderClass
* @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions
*/
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 创建一个BeanDefinitionDocumentReader,这个和前面的BeanDefinitionReader是不一样的,不要搞混了
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
// getRegistry()是获取BeanFactory,.getBeanDefinitionCount 是获取注册了多少个BeanDefinition
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); // 这个时候是0个,因为还没开始注册
// 开始往里面注册,有个createReaderContext(resource),这次使用鼠标点进去,看下面的createReaderContext方法的源码
// 看完createReaderContext(resource)后发现其实就是一个赋值的操作,然后看registerBeanDefinitions的方法
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
createReaderContext:
public XmlReaderContext createReaderContext(Resource resource) {
// 查看XmlReaderContext类上面的注释,
return new XmlReaderContext(resource, this.problemReporter, this.eventListener,
// 调用的下面的getNamespaceHandlerResolver()方法
this.sourceExtractor, this, getNamespaceHandlerResolver());
}
public NamespaceHandlerResolver getNamespaceHandlerResolver() {
if (this.namespaceHandlerResolver == null) {
// 调用了下面的createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver()方法
this.namespaceHandlerResolver = createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver();
}
return this.namespaceHandlerResolver;
}
protected NamespaceHandlerResolver createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver() {
ClassLoader cl = (getResourceLoader() != null ? getResourceLoader().getClassLoader() : getBeanClassLoader());
// 点进去看DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver的源码,这个就比较好玩了
return new DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver(cl);
}
通过DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver类上面的注释可以知道,接口的默认实现,是根据映射将命名空间uri解析为实现类,包含在映射文件中。
/**
* Default implementation of the {@link NamespaceHandlerResolver} interface.
* Resolves namespace URIs to implementation classes based on the mappings
* contained in mapping file.
*
* <p>By default, this implementation looks for the mapping file at
* {@code META-INF/spring.handlers}, but this can be changed using the
* {@link #DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver(ClassLoader, String)} constructor.
*
* @author Rob Harrop
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.0
* @see NamespaceHandler
* @see DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader
*/
public class DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver implements NamespaceHandlerResolver {
/**
* The location to look for the mapping files. Can be present in multiple JAR files.
*/
// 看这个"META-INF/spring.handlers"的值,
public static final String DEFAULT_HANDLER_MAPPINGS_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.handlers";
。。。。。。
在这个META-INF/spring.handlers路径下找一找对应的spring.handlers文件里面都有很多对应的处理器,这些处理器就这么通过文件给拿过来的
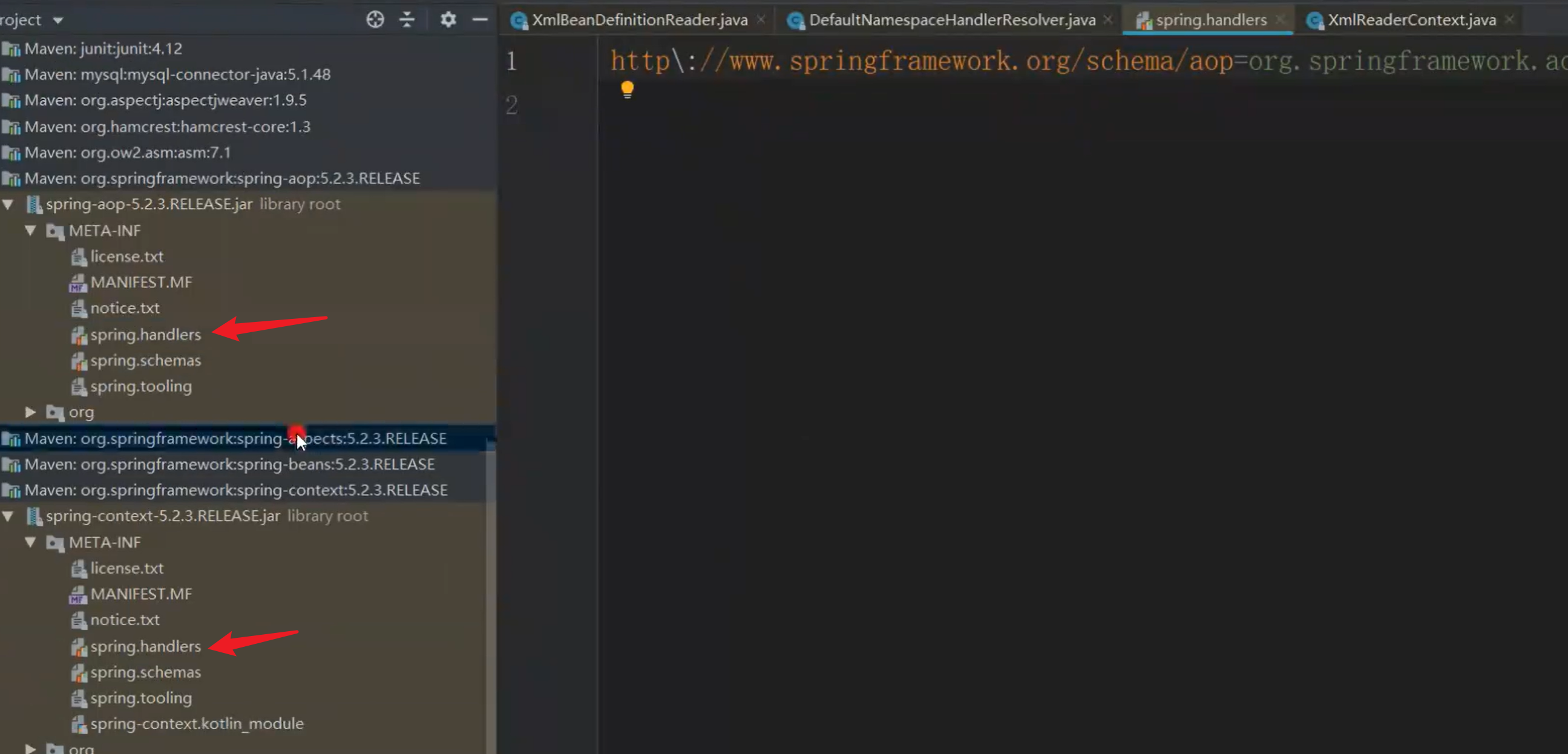
这些就对应的xml配置文件里面的命名空间,所以xml文件的格式为什么要有固定的正确格式,不是白写的
registerBeanDefinitions:
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
// doc.getDocumentElement()是获取到xml文件里的父级标签
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(doc.getDocumentElement()); // 所有带do的方法都是实际干活的方法,所以这个挺重要,看下面代码
}
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
// 开始赋值,这时候可以点进去看到 new了一个 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate,其实就是得到xml配置文件里对应的标签的值,如下图
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { // 判断是否是默认的命名空间
// PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE = "profile",PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE的值就是"profile",想想springboot时候,通过它来设置使用对应的环境切换,dev啦,sit啦
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
// 这里是同于空的,所以进不到这个判断里
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
// We cannot use Profiles.of(...) since profile expressions are not supported
// in XML config. See SPR-12458 for details.
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root); // 这里什么都没做,可以点进去看看是个空的,没有具体的实现,所以就是让我们自己去扩展的
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); // 这里是个核心,开始去解析BeanDefinitions了,看下面的源码
postProcessXml(root); // 这里也是空的,没有具体的实现,让自己去扩展用的
this.delegate = parent;
}
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate类:
BeanDefinitions()
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
// 获取beans里面所有标签
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
// 判断当前的一行是不是Element,这里要对应你写的xml配置文件,命名空间完后的内容
if (node instanceof Element) { // 如果这一行不为换行或注释,就会进来
Element ele = (Element) node;
// 这些都在for循环当中,也就是在循环遍历每一行,看是否是默认beans标签里面的子标签
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { // 判断是否属于默认的,也就是<beans 标签里面的
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); // 我的xml配置文件里写的就是bean标签,所以就进来了,看下面的parseDefaultElement()方法代码
}
else { // 如果这一行不是属于<beans 标签里面的,是其他定义的,就会到下面
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
parseDefaultElement()方法:这个里面就比较熟悉了
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) { // 判断是否是import标签
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) { // 判断是否是alias标签
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { // 判断是否是bean标签,很显然是,就执行下面方法
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate); // 看下面的方法源码
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
processBeanDefinition()
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 调用了parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele),可以看下源码,最后调了parseBeanDefinitionElement()方法,看下面方法源码图
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
parseBeanDefinitionElement():
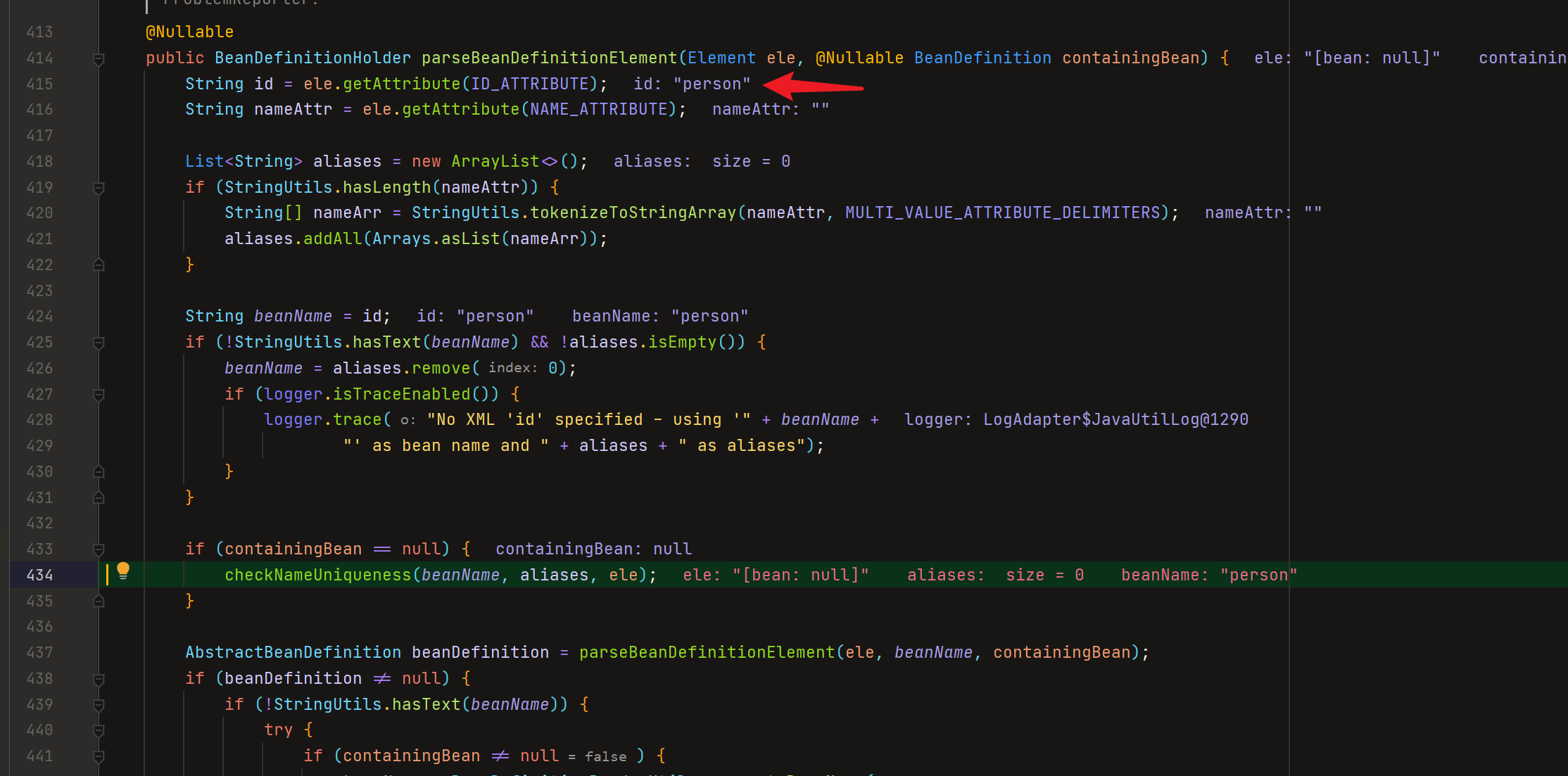
可以看到通过bean标签获取到了具体的属性值,因为containingBean是空的,所以又调用了checkNameUniqueness()方法,其实里面就是验证bean属性值的唯一性
parseBeanDefinitionElement()方法的源码:
@Nullable
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
// 开始执行parseBeanDefinitionElement方法,看下面方法的源代码吧。。
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) { // 这里beanName是person属性值,所以不会进入这个判断
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.
// This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
// 返回一个BeanDefinitionHolder的对象
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}
parseBeanDefinitionElement():
@Nullable
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
try {
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
// 这个方法解析判断是否是单例singleton的,是否是scope的等等,很多判断,可以自己点进去看看
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
// 这些方法都是在解析xml配置文件里的标签
parseMetaElements(ele, bd); // meta
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); // lookup-method
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); // replaced-method
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd); // constructor-arg
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd); // property
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd); // qualifier
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd; // 设置完以后返回
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}
看到这里,以上就是doLoadBeanDefinitions()方法的实现了
然后就可以一直往上返回了,以上就是obtainFreshBeanFactory()大概的一个具体实现了
3、prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
这些方法不算太难,可以自己点进去看每个方法功能实现
主要就是往beanFactory里面注入一些属性或对象的值,方便以后调用
/**
* Configure the factory's standard context characteristics,
* such as the context's ClassLoader and post-processors.
* @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure
*/
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
// beanFactory是刚上个方法创建的DefaultListableBeanFactory,然后把类加载器设置进去
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
// 设置SPEL表达式解析器
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
// 存放一个资源编辑器,一般很少用
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
// 加入一个增强器,就是实例化对象前的一个增强操作
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 把之前的一些ignoreDependency()方法执行的都给加进来
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
// 必须要注入进入的bean对象
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
// 又有一个addBeanPostProcessor,一个广播器
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { // 是否包含loadTimeWeaver属性值
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) { // 是否包含environment属性值,没有的话把它放进来
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { // 是否包含systemProperties属性,没有的话也给放进来
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
4、postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
发现postProcessBeanFactory()的方法是空的,所以留给子类实现,可以让我们自己去扩展实现一些东西
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for registering special
* BeanPostProcessors etc in certain ApplicationContext implementations.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
*/
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}
5、invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 最核心的就是调用了invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,看下面源码,这个方法有点多
// getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()返回的是空的,所以可以先不用看
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); // 存放已经执行过的processe,避免重复执行
// 判断是否是BeanDefinitionRegistry的子类,看下图,DefaultListableBeanFactory就是BeanDefinitionRegistry的子类
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
// 定义两个集合,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类,可以自己看下关系图
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 这个是空的,所以就不会进入循环
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 进入看getBeanNamesForType源码,在下面有
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { // 为空的,进不到循环里
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { // 主要是判断类型是否匹配
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); // 往集合里添加,上面定义的集合
// 执行上面postProcessorNames循环里是否有对应添加到currentRegistryProcessors的BeanDefinition
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // 上面一行代码执行完后,给清掉
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 这里开始和上面一段代码很像
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// 上面等于经历了3次过滤
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
// 这两个方法挺麻烦的
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 定义3个集合
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { // 开始在循环里做判断
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { // 分配判断是否是3种PostProcessor
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 这个还是自己点进去看了大概的逻辑,不难
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 有orderedPostProcessors的话,添加进order的集合
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 这个不难,自己大概看一下
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
getBeanNamesForType()
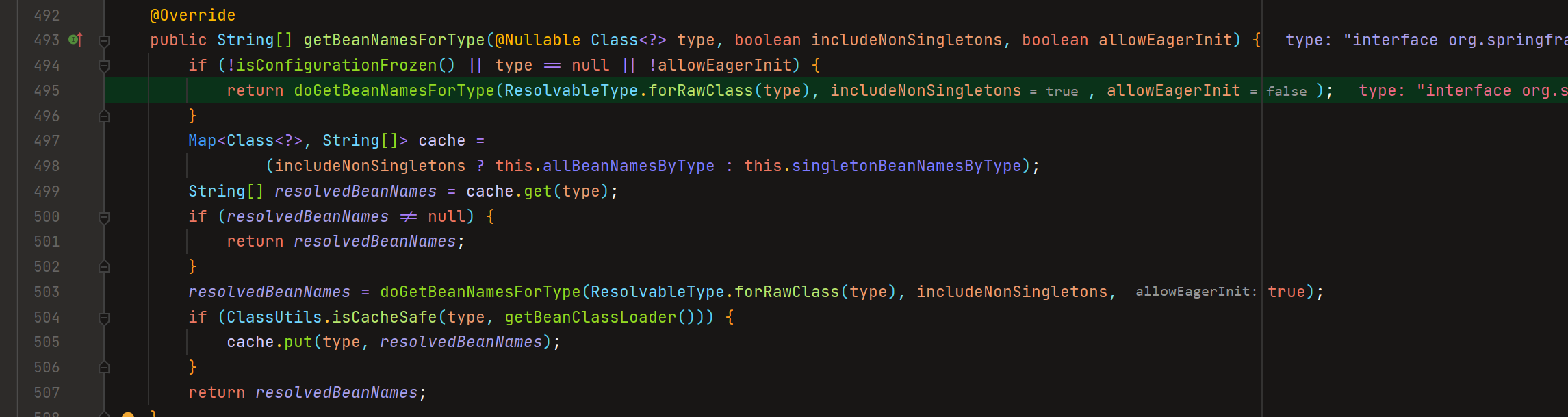
看这个doGetBeanNamesForType的方法代码吧
private String[] doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
// Check all bean definitions.
for (String beanName : this.beanDefinitionNames) { // 取出bean对象名称
// Only consider bean as eligible if the bean name is not defined as alias for some other bean.
if (!isAlias(beanName)) { // 如果不是别名的话
try {
// 获取合并本地的BeanDefinition?点进入看下可以知道,返回了一个从根上来的BeanDefinition,不用过于仔细看,太多了,知道就行
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// Only check bean definition if it is complete.得到RootBeanDefinition后,进入到判断里了
if (!mbd.isAbstract() && (allowEagerInit ||
(mbd.hasBeanClass() || !mbd.isLazyInit() || isAllowEagerClassLoading()) &&
!requiresEagerInitForType(mbd.getFactoryBeanName()))) {
boolean isFactoryBean = isFactoryBean(beanName, mbd); // 显然不是FactoryBean对象
BeanDefinitionHolder dbd = mbd.getDecoratedDefinition();
boolean matchFound = false;
boolean allowFactoryBeanInit = (allowEagerInit || containsSingleton(beanName));
boolean isNonLazyDecorated = (dbd != null && !mbd.isLazyInit());
if (!isFactoryBean) {
if (includeNonSingletons || isSingleton(beanName, mbd, dbd)) {
// 判断类型是否是匹配的,显然不是
matchFound = isTypeMatch(beanName, type, allowFactoryBeanInit);
}
}
else {
if (includeNonSingletons || isNonLazyDecorated ||
(allowFactoryBeanInit && isSingleton(beanName, mbd, dbd))) {
matchFound = isTypeMatch(beanName, type, allowFactoryBeanInit);
}
if (!matchFound) {
// In case of FactoryBean, try to match FactoryBean instance itself next.
beanName = FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName;
matchFound = isTypeMatch(beanName, type, allowFactoryBeanInit);
}
}
if (matchFound) { // matchFound为false
result.add(beanName);
}
}
}
catch (CannotLoadBeanClassException | BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
if (allowEagerInit) {
throw ex;
}
// Probably a placeholder: let's ignore it for type matching purposes.
LogMessage message = (ex instanceof CannotLoadBeanClassException ?
LogMessage.format("Ignoring bean class loading failure for bean '%s'", beanName) :
LogMessage.format("Ignoring unresolvable metadata in bean definition '%s'", beanName));
logger.trace(message, ex);
// Register exception, in case the bean was accidentally unresolvable.
onSuppressedException(ex);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Bean definition got removed while we were iterating -> ignore.
}
}
}
// Check manually registered singletons too.
for (String beanName : this.manualSingletonNames) { // 这些循环里面的判断都进不去,直接跳到最后返回
try {
// In case of FactoryBean, match object created by FactoryBean.
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
if ((includeNonSingletons || isSingleton(beanName)) && isTypeMatch(beanName, type)) {
result.add(beanName);
// Match found for this bean: do not match FactoryBean itself anymore.
continue;
}
// In case of FactoryBean, try to match FactoryBean itself next.
beanName = FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName;
}
// Match raw bean instance (might be raw FactoryBean).
if (isTypeMatch(beanName, type)) {
result.add(beanName);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Shouldn't happen - probably a result of circular reference resolution...
logger.trace(LogMessage.format(
"Failed to check manually registered singleton with name '%s'", beanName), ex);
}
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(result);
}
返回到getBeanNamesForType方法里面的doGetBeanNamesForType调用,这一行也是返回的,返回到了上面代码里的
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法里面的beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType()调用
6、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);

registerBeanPostProcessors里面又调用了registerBeanPostProcessors,看这个调用的方法代码
registerBeanPostProcessors()
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // 完成一个加入其他操作的功能,aop的思想
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 定义了4个集合,然后循环遍历,判断给不同集合放值
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
// 最后完成注册进去
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
7、initMessageSource();
这个方法比较简单,主要完成国际化的消息通知
protected void initMessageSource() {
// 获取BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) { // 是否包含"messageSource"
this.messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class);
// Make MessageSource aware of parent MessageSource.
if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) {
HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource;
if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) {
// Only set parent context as parent MessageSource if no parent MessageSource
// registered already.
hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
else { // 跳到这个分支
// Use empty MessageSource to be able to accept getMessage calls.
DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource(); // 创建新的messageSource
dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource()); // 添加到父类messageSource
this.messageSource = dms;
beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource); // 注册成singleton对象
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
}
8、initApplicationEventMulticaster();
初始化事件监听器
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); // 获取beanFactory
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { // 是否包含applicationEventMulticaster
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else { // 不包含,走下面
// 创建一个新的
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
// 注册事件监听器
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
9、onRefresh();
发现里面什么都没做,那就是留给子类做具体实现的
/**
* Template method which can be overridden to add context-specific refresh work.
* Called on initialization of special beans, before instantiation of singletons.
* <p>This implementation is empty.
* @throws BeansException in case of errors
* @see #refresh()
*/
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
10、registerListeners();
上面使用了initApplicationEventMulticaster()方法,所以这时候要注册一些事件监听器
这里因为只有一个bean对象person对象,别的啥也没有,所以这个方法等于没执行
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
11、finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
实例化所有单例对象,这个方法很重要
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
// 是否包含conversionService对象,这时候没有
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) { // 这里判断没有的话,就给加进来
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) { // 为空,所以没有进来循环
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null); // 设置空的临时加载器
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration(); // 不允许更改bean的元素
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); // 这里很重要,开始进行实例化所有的单例对象,看下面源码
}
preInstantiateSingletons()
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames); // 把bean的名称拿过来
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); // 这个方法前面很早时候有遇到过
// 判断不是抽象的、懒加载的,是单例的
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { // 不是FactoryBean,所以这里不会进来
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else { // 跳到这里来
getBean(beanName); // 这里方法是个难点,看下图,调用了doGetBean方法
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) { // 循环遍历所有bean对象,这里不是很难
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
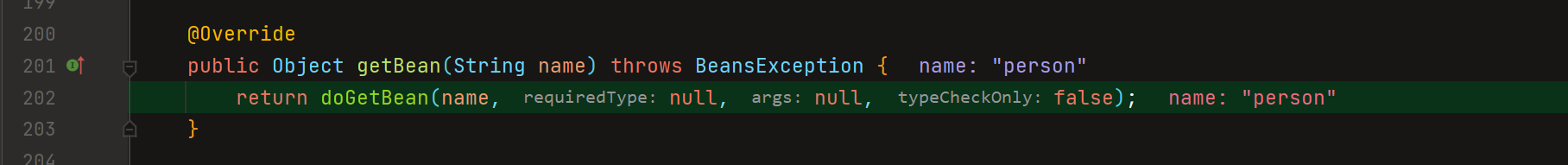
这个doGetBean方法实在太长了,自己debug时候看看吧
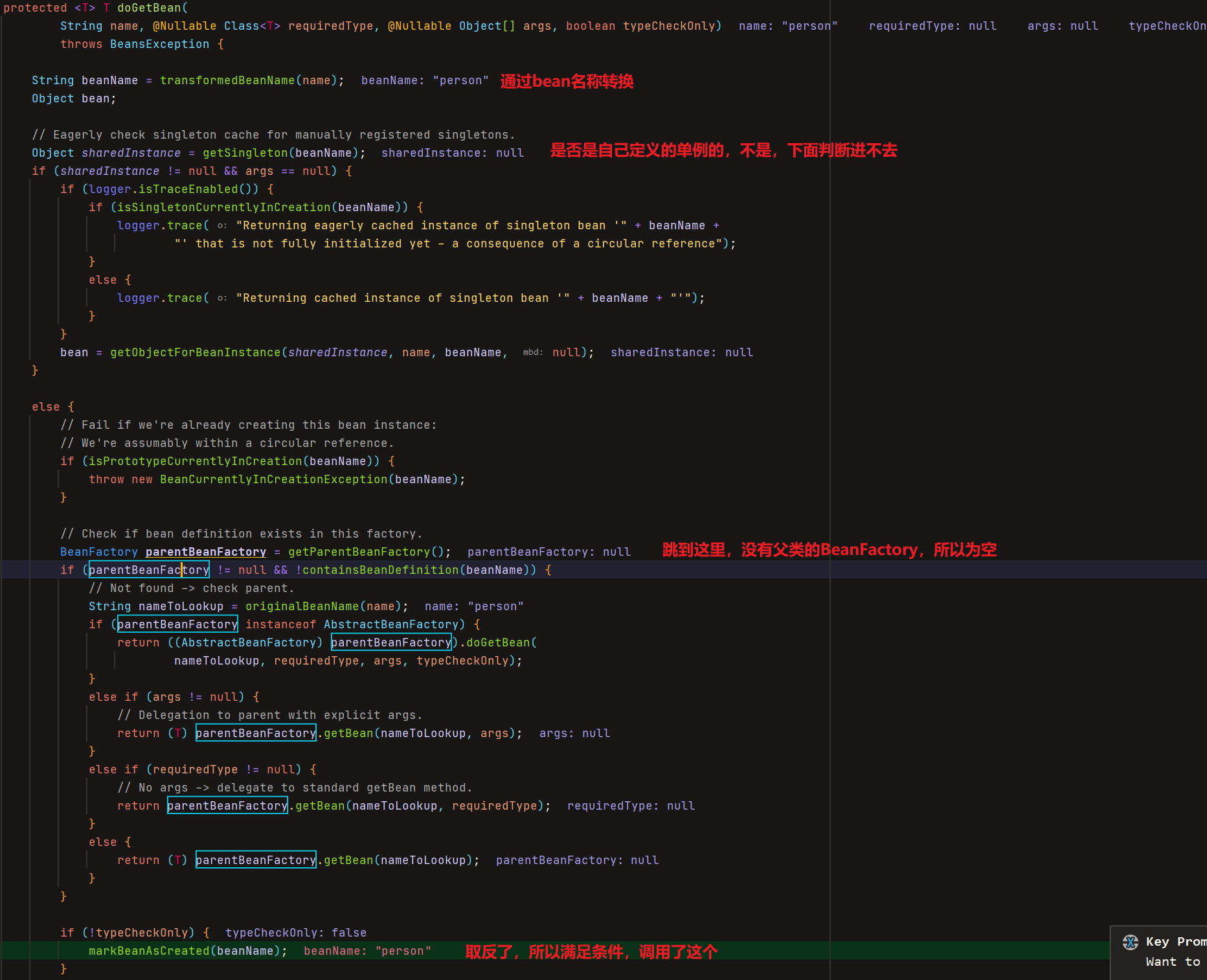
下面还有方法的其他代码,太多了,自己好好看看吧
里面有个createBean()方法,调用的doCreateBean方法,里面使用了反射
12、finishRefresh();
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
clearResourceCaches(); // 清楚缓存
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor(); // 初始化生命周期操作
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(); // 刷新生命周期
// Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)); // 刷新对应的事件
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this); // 注册ApplicationContext
}
13、resetCommonCaches();
重置公共缓存


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号