2、 JUC包下AtomicXXX类与新的同步机制:Latch Semaphore等
LongAdder
之前知道,在并发情况下,有AtomicXXX 类来解决问题,效率比Syncxxx 锁的效率高,那么如果是并发很高的情况下,LongAdder是效率更高的
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder; public class T02_AtomicVsSyncVsLongAdder { static long count2 = 0L; static AtomicLong count1 = new AtomicLong(0L); static LongAdder count3 = new LongAdder(); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Thread[] threads = new Thread[1000]; for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(() -> { for (int k = 0; k < 100000; k++) { count1.incrementAndGet(); } }); } long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (Thread t : threads) { t.start(); } for (Thread t : threads) { t.join(); }
long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); //TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10); System.out.println("Atomic: " + count1.get() + " time " + (end - start)); //----------------------------------------------------------- Object lock = new Object(); for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { for (int k = 0; k < 100000; k++) { synchronized (lock) { count2++; } } } }); } start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (Thread t : threads) { t.start(); } for (Thread t : threads) { t.join(); } end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("Sync: " + count2 + " time " + (end - start)); //---------------------------------- for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(() -> { for (int k = 0; k < 100000; k++) { count3.increment(); } }); } start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (Thread t : threads) { t.start(); } for (Thread t : threads) { t.join(); } end = System.currentTimeMillis(); //TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10); System.out.println("LongAdder: " + count1.longValue() + " time " + (end - start)); } static void microSleep(int m) { try { TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(m); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果: 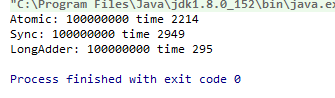
可以看到执行效率,原因:Atomic 是无锁CAS原理的操作,所以比Sync 加锁的效率高,LongAdder 是分段锁的概念。
分段锁很简单:
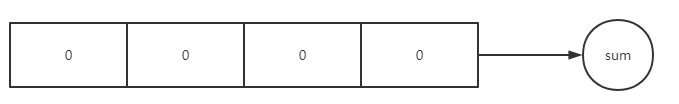
比如一个好几个线程,一个线程数组,比如4 的长度,把每个里面的每个线程执行的值全部相加后,然后加在一起汇总一个结果。
Reentrantlock
本例中由于m1锁定this,只有m1执行完毕的时候,m2才能执行
这里是复习synchronized最原始的语义,意思就是锁是可以重入的,synchronized修饰的方法可以调用synchronized修饰的方法
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class T01_ReentrantLock1 { synchronized void m1() { for(int i=0; i<10; i++) { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(i); if(i == 2) { m2(); } } } synchronized void m2() { System.out.println("m2 ..."); } public static void main(String[] args) { T01_ReentrantLock1 rl = new T01_ReentrantLock1(); new Thread(rl::m1).start(); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
结果: 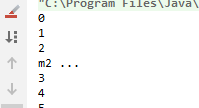
reentrantlock用于替代synchronized
使用reentrantlock可以完成同样的功能
需要注意的是,必须要必须要必须要手动释放锁(重要的事情说三遍)
使用syn锁定的话如果遇到异常,jvm会自动释放锁,但是lock必须手动释放锁,因此经常在finally中进行锁的释放
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class T02_ReentrantLock2 { Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); void m1() { try { lock.lock(); //synchronized(this) for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println(i); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } void m2() { try { lock.lock(); System.out.println("m2 ..."); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { T02_ReentrantLock2 rl = new T02_ReentrantLock2(); new Thread(rl::m1).start(); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } new Thread(rl::m2).start(); // m1 执行完以后,m2 才能执行 } }
使用reentrantlock可以进行“尝试锁定”tryLock,这样无法锁定,或者在指定时间内无法锁定,线程可以决定是否继续等待
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class T03_ReentrantLock3 { Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); void m1() { try { lock.lock(); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println(i); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } /** * 使用tryLock进行尝试锁定,不管锁定与否,方法都将继续执行 * 可以根据tryLock的返回值来判定是否锁定 * 也可以指定tryLock的时间,由于tryLock(time)抛出异常,所以要注意unclock的处理,必须放到finally中 */ void m2() { /* boolean locked = lock.tryLock(); System.out.println("m2 ..." + locked); if(locked) lock.unlock(); */ boolean locked = false; try { locked = lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 如果5 秒内拿到锁,返回true,5 秒内没拿到锁,打印下面一句话 System.out.println("m2 ..." + locked); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(locked) { lock.unlock(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { T03_ReentrantLock3 rl = new T03_ReentrantLock3(); new Thread(rl::m1).start(); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } new Thread(rl::m2).start(); } }
使用ReentrantLock还可以调用lockInterruptibly方法,可以对线程interrupt方法做出响应,
在一个线程等待锁的过程中,可以被打断,线程在请求lock并被阻塞时,
如果被interrupt,则“此线程会被唤醒并被要求处理InterruptedException”。并且如果线程已经被interrupt,再使用lockInterruptibly的时候,此线程也会被要求处理interruptedException
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class T04_ReentrantLock4 { public static void main(String[] args) { Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{ try { lock.lock(); System.out.println("t1 start"); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE); System.out.println("t1 end"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("interrupted1"); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }); t1.start(); Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{ try { //lock.lock(); lock.lockInterruptibly(); //可以对interrupt()方法做出响应 System.out.println("t2 start"); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); System.out.println("t2 end"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("interrupted2"); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }); t2.start(); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } t2.interrupt(); //打断线程2的等待 } }
ReentrantLock还可以指定为公平锁
如果不设置为公平锁,会乱序执行,公平锁会判断队列里有没有等待的线程,如果有线程了,会让排在前面的线程先执行,不会抢行
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class T05_ReentrantLock5 extends Thread { private static ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock(true); //参数为true表示为公平锁,请对比输出结果 @Override public void run() { for(int i=0; i<100; i++) { lock.lock(); try{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得锁"); }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { T05_ReentrantLock5 rl=new T05_ReentrantLock5(); Thread th1=new Thread(rl); Thread th2=new Thread(rl); th1.start(); th2.start(); } }
CountDownLatch 减法计数器
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; public class CountDownLatchDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 初始值给 6 // 减法计数器 CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6); for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { new Thread(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" go"); // 线程数量 -1 countDownLatch.countDown(); },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } // 这个方法千万别忘记,代表计数器归零,然后就可以向下执行,不然会乱的,所以这个方法写在了那个for 循环的外面 countDownLatch.await(); System.out.println("close"); // 顺序乱的话,可以自行加锁 } }
CyclicBarrier 循环屏障,满足条件触发指令,如下:循环100次,满足5 个20 ,如果循环101 或者99 次,都是模于20 模不尽的,所以会一直等待
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException; import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier; public class T07_TestCyclicBarrier { public static void main(String[] args) { //CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(20); CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(20, () -> System.out.println("满人")); /*CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(20, new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("满人,发车"); } });*/ for(int i=0; i<100; i++) { new Thread(()->{ try { barrier.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); } } }
Phaser 类似于流程控制
import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.Phaser; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class T09_TestPhaser2 { static Random r = new Random(); static MarriagePhaser phaser = new MarriagePhaser(); static void milliSleep(int milli) { // 定义一个阻塞方法 try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(milli); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { phaser.bulkRegister(7); // 一共7个人,包括新郎新娘,还有5个参加婚礼的人 for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { new Thread(new Person("p" + i)).start(); } new Thread(new Person("新郎")).start(); new Thread(new Person("新娘")).start(); } static class MarriagePhaser extends Phaser { // 继承Phaser @Override protected boolean onAdvance(int phase, int registeredParties) { switch (phase) { case 0: System.out.println("所有人到齐了!" + registeredParties); System.out.println(); return false; case 1: System.out.println("所有人吃完了!" + registeredParties); System.out.println(); return false; case 2: System.out.println("所有人离开了!" + registeredParties); System.out.println(); return false; case 3: System.out.println("婚礼结束!新郎新娘抱抱!" + registeredParties); return true; default: return true; } } } static class Person implements Runnable { // 定义4 个方法 String name; public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } public void arrive() { milliSleep(r.nextInt(1000)); System.out.printf("%s 到达现场!\n", name); phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); // 调用方法,继续往下走下一个场景 } public void eat() { milliSleep(r.nextInt(1000)); System.out.printf("%s 吃完!\n", name); phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); } public void leave() { milliSleep(r.nextInt(1000)); System.out.printf("%s 离开!\n", name); phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); } private void hug() { if(name.equals("新郎") || name.equals("新娘")) { milliSleep(r.nextInt(1000)); System.out.printf("%s 洞房!\n", name); phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); // 只有新娘新郎才可以入洞房 } else { phaser.arriveAndDeregister(); // 其他人吃完后都要走,执行注销方法 } } @Override public void run() { // 执行4 个方法 arrive(); eat(); leave(); hug(); } } }
ReadWriteLock 读写锁,就是共享锁(读锁) 和 排他锁(写锁)
读的时候,允许其他线程也去读,但是如果其他线程这时候要写入,是不允许的,一直要等着
import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; public class T10_TestReadWriteLock { static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private static int value; // 读写锁使用 static ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); static Lock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock(); static Lock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock(); public static void read(Lock lock) { try { lock.lock(); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("read over!"); //模拟读取操作 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void write(Lock lock, int v) { try { lock.lock(); Thread.sleep(1000); value = v; System.out.println("write over!"); //模拟写操作 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // 如果使用Runnable 加锁的话,过程中是不允许其他线程读或写的,所以大概需要20秒时间 //Runnable readR = ()-> read(lock); //Runnable writeR = ()->write(lock, new Random().nextInt()); // 如果使用读写锁,同一时间允许其他线程读,所以也就1秒的时间,但写锁还是要阻塞1秒的 Runnable readR = ()-> read(readLock); Runnable writeR = ()->write(writeLock, new Random().nextInt()); for(int i=0; i<18; i++) { new Thread(readR).start(); } for(int i=0; i<2; i++) { new Thread(writeR).start(); } } }
Semaphore 信号量,可以限流,最多只有几个线程 同时执行,默认是非公平的,会有一个队列
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; public class T11_TestSemaphore { public static void main(String[] args) { //Semaphore s = new Semaphore(2);
// 允许两个线程同时执行
Semaphore s = new Semaphore(2, true); //允许一个线程 同时执行 //Semaphore s = new Semaphore(1); new Thread(()->{ try { s.acquire(); // 得到 System.out.println("T1 running..."); Thread.sleep(200); System.out.println("T1 running..."); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { s.release(); // 释放 } }).start(); new Thread(()->{ try { s.acquire(); System.out.println("T2 running..."); Thread.sleep(200); System.out.println("T2 running..."); s.release(); // 释放 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); } }
测试2:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; public class T08_Semaphore { // 添加volatile,使t2能够得到通知 volatile List lists = new ArrayList(); public void add(Object o) { lists.add(o); } public int size() { return lists.size(); } static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null; public static void main(String[] args) { T08_Semaphore c = new T08_Semaphore(); Semaphore s = new Semaphore(1); t1 = new Thread(() -> { try { s.acquire(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { c.add(new Object()); System.out.println("add " + i); } s.release(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 让t2线程插入执行 try { t2.start(); t2.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // t1线程继续执行 try { s.acquire(); for (int i = 5; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println(i); } s.release(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "t1"); t2 = new Thread(() -> { try { s.acquire(); System.out.println("t2 结束"); s.release(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "t2"); //t2.start(); t1.start(); } }
Exchanger 交换器,线程之间交互数据用的,只有2 个线程交互,不然会阻塞
import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger; public class T12_TestExchanger { static Exchanger<String> exchanger = new Exchanger<>(); public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(()->{ String s = "T1"; try { s = exchanger.exchange(s); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + s); }, "t1").start(); new Thread(()->{ String s = "T2"; try { s = exchanger.exchange(s); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + s); }, "t2").start(); } }
LockSupport 线程停止 与 释放,unpark 可以在park 方法前面提前不让线程停止,也可以在后面再解开
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport; public class T13_TestLockSupport { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t = new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println(i); if(i == 5) { LockSupport.park(); } try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); t.start(); LockSupport.unpark(t); /*try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(8); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("after 8 senconds!"); LockSupport.unpark(t);*/ } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号