HDU 5492 Find a path
Find a path
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 930 Accepted Submission(s): 410
Problem Description
Frog fell into a maze. This maze is a rectangle containing ![]() rows
and
rows
and ![]() columns.
Each grid in this maze contains a number, which is called the magic value. Frog now stays at grid (1, 1), and he wants to go to grid (N, M). For each step, he can go to either the grid right to his current location or the grid below his location. Formally,
he can move from grid (x, y) to (x + 1, y) or (x, y +1), if the grid he wants to go exists.
columns.
Each grid in this maze contains a number, which is called the magic value. Frog now stays at grid (1, 1), and he wants to go to grid (N, M). For each step, he can go to either the grid right to his current location or the grid below his location. Formally,
he can move from grid (x, y) to (x + 1, y) or (x, y +1), if the grid he wants to go exists.
Frog is a perfectionist, so he'd like to find the most beautiful path. He defines the beauty of a path in the following way. Let’s denote the magic values along a path from (1, 1) to (n, m) as![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ,
and
,
and ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is
the average value of all
is
the average value of all ![]()
![]() .
The beauty of the path is
.
The beauty of the path is ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() multiplies
the variance of the values:
multiplies
the variance of the values:![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In Frog's opinion, the smaller, the better. A path with smaller beauty value is more beautiful. He asks you to help him find the most beautiful path.
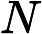 rows
and
rows
and 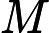 columns.
Each grid in this maze contains a number, which is called the magic value. Frog now stays at grid (1, 1), and he wants to go to grid (N, M). For each step, he can go to either the grid right to his current location or the grid below his location. Formally,
he can move from grid (x, y) to (x + 1, y) or (x, y +1), if the grid he wants to go exists.
columns.
Each grid in this maze contains a number, which is called the magic value. Frog now stays at grid (1, 1), and he wants to go to grid (N, M). For each step, he can go to either the grid right to his current location or the grid below his location. Formally,
he can move from grid (x, y) to (x + 1, y) or (x, y +1), if the grid he wants to go exists.Frog is a perfectionist, so he'd like to find the most beautiful path. He defines the beauty of a path in the following way. Let’s denote the magic values along a path from (1, 1) to (n, m) as
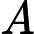
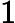
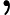
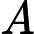
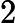
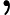

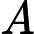
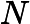
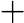
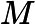

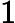 ,
and
,
and 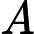
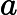
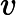
 is
the average value of all
is
the average value of all 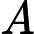
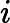 .
The beauty of the path is
.
The beauty of the path is 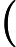
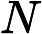

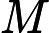

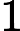
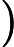 multiplies
the variance of the values:
multiplies
the variance of the values: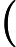
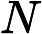

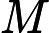

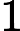
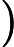
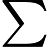
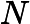
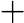
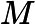

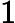
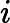

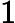
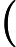
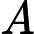
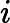

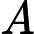
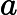
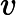

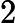
In Frog's opinion, the smaller, the better. A path with smaller beauty value is more beautiful. He asks you to help him find the most beautiful path.
Input
The first line of input contains a number ![]() indicating
the number of test cases (
indicating
the number of test cases (![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ).
).
Each test case starts with a line containing two integers![]() and
and ![]() (
(![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ).
Each of the next
).
Each of the next ![]() lines
contains
lines
contains ![]() non-negative
integers, indicating the magic values. The magic values are no greater than 30.
non-negative
integers, indicating the magic values. The magic values are no greater than 30.
 indicating
the number of test cases (
indicating
the number of test cases (

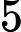
 ).
).Each test case starts with a line containing two integers
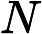 and
and 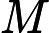 (
(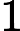

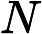
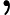
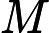

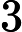
 ).
Each of the next
).
Each of the next 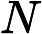 lines
contains
lines
contains 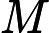 non-negative
integers, indicating the magic values. The magic values are no greater than 30.
non-negative
integers, indicating the magic values. The magic values are no greater than 30.
Output
For each test case, output a single line consisting of “Case #X: Y”. ![]() is
the test case number starting from 1.
is
the test case number starting from 1. ![]() is
the minimum beauty value.
is
the minimum beauty value.
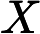 is
the test case number starting from 1.
is
the test case number starting from 1. 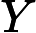 is
the minimum beauty value.
is
the minimum beauty value.
Sample Input
1
2 2
1 2
3 4
Sample Output
Case #1: 14
Source
这个是合肥网络赛的一道题目,知道是dp但是当时没做出来
题目大体意思是有m*n的棋盘 从左上角走到右下角 求路径上经过的数字的方差最小
当时想的是 f[i][j][k]表示走到i,j 和为k的时候的最小值
其实就差一步就过了
当时想的是 要统计出来 经过i,j走到m,n可行的取值k
因为担心有一种情况 从1,1 经过i,j 到达 m,n 路径上的数字的和取不到k 但是用k当作和求方差导致错误
其实这种情况是不存在的
如果把平均值ave看作变量 x1,x2,...,xn看作常数
写出来方差的公式
整理一下发现是关于ave的二次方程
当ave=(x1+x2+...+xn)/n时取最小值
所以不会出现 用不是路径和的k得到更小的值
所以枚举k 直接做就行
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int f[31][31];
int s[31][31];
int m,n,x,y;
int t;
int ans;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&t);
for(int it=1;it<=t;it++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
scanf("%d",&s[i][j]);
int w=(m+n-1);
ans=0x3f3f3f3f;
for(int lim=0;lim<=w*30;lim++)
{
memset(f,0x3f,sizeof(f));
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(i==1 &&j==1)
f[i][j]=(w*s[i][j]-lim)*(w*s[i][j]-lim);
if(i>1)
f[i][j]=min(f[i][j],f[i-1][j]+(w*s[i][j]-lim)*(w*s[i][j]-lim));
if(j>1)
f[i][j]=min(f[i][j],f[i][j-1]+(w*s[i][j]-lim)*(w*s[i][j]-lim));
}
ans=min(ans,f[m][n]);
}
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",it,ans/w);
}
return 0;
}
http://blog.csdn.net/queuelovestack/article/details/48768275
我摘抄过来
/************************************************************************************
首先,因为公式涉及权值的平均数,不妨将其化简一下
N+M-1的值是固定的,所以只跟和
有关
又因为Ai的值是不超过30的,而N+M-1个Ai相加最多不超过1800,故我们可以用个三维dp来解此题,dp[i][j][k]表示从点(1,1)到点(i,j)的值为k时,
的值是dp[i][j][k],那么我们最后只需求出min((M+N-1)dp[i][j][k]-k*k)即可
代码如下
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int f[31][31][61*30+1];
int s[31][31];
int t,m,n;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&t);
for(int it=1;it<=t;it++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&s[i][j]);
for(int k=0;k<=(m+n-1)*30;k++)
f[i][j][k]=1e8;
}
f[1][1][s[1][1]]=s[1][1]*s[1][1];
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
for(int k=0;k<=(m+n-1)*30;k++)
{
if(i==1 && j==1 &&k==s[i][j])
f[i][j][k]=s[i][j]*s[i][j];
if(k>=s[i][j])
{
if(i>1)
f[i][j][k]=min(f[i][j][k],f[i-1][j][k-s[i][j]]+s[i][j]*s[i][j]);
if(j>1)
f[i][j][k]=min(f[i][j][k],f[i][j-1][k-s[i][j]]+s[i][j]*s[i][j]);
}
}
int ans=1e9;
int temp=(m+n-1);
for(int k=0;k<=temp*30;k++)
if(f[m][n][k]!=1e8)
ans=min(ans,temp*f[m][n][k]-k*k);
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",it,ans);
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号