Spring 学习记录2 Environment
Environment是什么
environment是什么呢....中文是环境大家都知道但是具体代表什么呢?感觉很抽象....从代码里的解释来看environment代表了profile和properties.
profile就是1组bean的定义.实际用途就是在不同环境比如测试环境和生产环境中加载不同的bean达到根据环境加载bean的用途.(因为测试环境可能有些bean是模拟的,比如接口.调用返回的报文都是自己模拟的,真实的bean在测试环境拿不到).
properties就不用说了.就是配置...
这篇文章我想分享下我对properties的学习,因为profile我感觉只要会配置就行了...可能更偏向于配置运维,而properties主要涉及到类型转化等比较复杂的东西.而我自己也写过一些conveter.所以想特别学习下.
结构
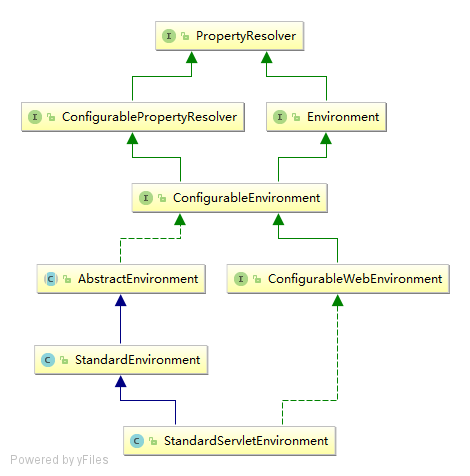
大概就是这样的结构.java web环境下一般都是StandardServletEnvironment环境,而我自己做junit测试的时候是StandardEnvironment 这里主要分析我对StandardEnvironment 的学习(子类可能也就增加了一点点其他功能吧.总的来说应该都是大同小异.估计是把servlet的环境变量也加到properties里了.)
environment的profile的功能是定义在Environment类里的

1 public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver { 2 3 /** 4 * Return the set of profiles explicitly made active for this environment. Profiles 5 * are used for creating logical groupings of bean definitions to be registered 6 * conditionally, for example based on deployment environment. Profiles can be 7 * activated by setting {@linkplain AbstractEnvironment#ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME 8 * "spring.profiles.active"} as a system property or by calling 9 * {@link ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles(String...)}. 10 * <p>If no profiles have explicitly been specified as active, then any {@linkplain 11 * #getDefaultProfiles() default profiles} will automatically be activated. 12 * @see #getDefaultProfiles 13 * @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles 14 * @see AbstractEnvironment#ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME 15 */ 16 String[] getActiveProfiles(); 17 18 /** 19 * Return the set of profiles to be active by default when no active profiles have 20 * been set explicitly. 21 * @see #getActiveProfiles 22 * @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setDefaultProfiles 23 * @see AbstractEnvironment#DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME 24 */ 25 String[] getDefaultProfiles(); 26 27 /** 28 * Return whether one or more of the given profiles is active or, in the case of no 29 * explicit active profiles, whether one or more of the given profiles is included in 30 * the set of default profiles. If a profile begins with '!' the logic is inverted, 31 * i.e. the method will return true if the given profile is <em>not</em> active. 32 * For example, <pre class="code">env.acceptsProfiles("p1", "!p2")</pre> will 33 * return {@code true} if profile 'p1' is active or 'p2' is not active. 34 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if called with zero arguments 35 * or if any profile is {@code null}, empty or whitespace-only 36 * @see #getActiveProfiles 37 * @see #getDefaultProfiles 38 */ 39 boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles); 40 41 }
而properties的功能是定义在PropertyResolver里的

1 public interface PropertyResolver { 2 3 /** 4 * Return whether the given property key is available for resolution, i.e., 5 * the value for the given key is not {@code null}. 6 */ 7 boolean containsProperty(String key); 8 9 /** 10 * Return the property value associated with the given key, or {@code null} 11 * if the key cannot be resolved. 12 * @param key the property name to resolve 13 * @see #getProperty(String, String) 14 * @see #getProperty(String, Class) 15 * @see #getRequiredProperty(String) 16 */ 17 String getProperty(String key); 18 19 /** 20 * Return the property value associated with the given key, or 21 * {@code defaultValue} if the key cannot be resolved. 22 * @param key the property name to resolve 23 * @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found 24 * @see #getRequiredProperty(String) 25 * @see #getProperty(String, Class) 26 */ 27 String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue); 28 29 /** 30 * Return the property value associated with the given key, or {@code null} 31 * if the key cannot be resolved. 32 * @param key the property name to resolve 33 * @param targetType the expected type of the property value 34 * @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class) 35 */ 36 <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType); 37 38 /** 39 * Return the property value associated with the given key, or 40 * {@code defaultValue} if the key cannot be resolved. 41 * @param key the property name to resolve 42 * @param targetType the expected type of the property value 43 * @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found 44 * @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class) 45 */ 46 <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue); 47 48 /** 49 * Convert the property value associated with the given key to a {@code Class} 50 * of type {@code T} or {@code null} if the key cannot be resolved. 51 * @throws org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionException if class specified 52 * by property value cannot be found or loaded or if targetType is not assignable 53 * from class specified by property value 54 * @see #getProperty(String, Class) 55 */ 56 <T> Class<T> getPropertyAsClass(String key, Class<T> targetType); 57 58 /** 59 * Return the property value associated with the given key (never {@code null}). 60 * @throws IllegalStateException if the key cannot be resolved 61 * @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class) 62 */ 63 String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException; 64 65 /** 66 * Return the property value associated with the given key, converted to the given 67 * targetType (never {@code null}). 68 * @throws IllegalStateException if the given key cannot be resolved 69 */ 70 <T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException; 71 72 /** 73 * Resolve ${...} placeholders in the given text, replacing them with corresponding 74 * property values as resolved by {@link #getProperty}. Unresolvable placeholders with 75 * no default value are ignored and passed through unchanged. 76 * @param text the String to resolve 77 * @return the resolved String (never {@code null}) 78 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null} 79 * @see #resolveRequiredPlaceholders 80 * @see org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils#resolvePlaceholders(String) 81 */ 82 String resolvePlaceholders(String text); 83 84 /** 85 * Resolve ${...} placeholders in the given text, replacing them with corresponding 86 * property values as resolved by {@link #getProperty}. Unresolvable placeholders with 87 * no default value will cause an IllegalArgumentException to be thrown. 88 * @return the resolved String (never {@code null}) 89 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null} 90 * or if any placeholders are unresolvable 91 * @see org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils#resolvePlaceholders(String, boolean) 92 */ 93 String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException; 94 95 }
让我觉得很奇怪的一个地方就是既然Environment代表了profile+properties,那为什么profile相关方法要写在Environment里,而properties相关方法要写在PropertyResolver里呢...都是@since3.1为什么不再弄个ProfileResolver接口然后Environment接口继承这2个接口呢?
PropertyResolver
从前面的接口代码观察.中我觉得这个类主要就是2个作用:
1.给你1个key你要能找到它对应的value.就是解析properties.
2.在properties的基础上增加了placeholder.value中的一部分可能是占位符,要能根据key找到value同时替换占位符为实际的值.
实验1,一个小测试:
ConfigurablePropertyResolver configurablePropertyResolver; // env
1 /** 2 * getProperty直接写pro的名字 3 * resolveRequiredPlaceholders用${}替换pro 4 */ 5 @Test 6 public void testPropertiesResolver() { 7 System.out.println("a= " + configurablePropertyResolver.getProperty("a"));//a= b 8 System.out.println("${a}= " + configurablePropertyResolver.getProperty("${a}"));//${a}= null 9 System.out.println("mmp.a= " + configurablePropertyResolver.getProperty("mmp.a"));//mmp.a= 123 10 System.out.println(configurablePropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders("a=${a}"));//a=b 11 System.out.println(configurablePropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders("mmp.a=${mmp.a}"));//mmp.a=123 12 }
加载的配置文件
1 a=b 2 mmp.a=123 3 email=jyzjyz12@163.com
从这个测试中可以看出
1.加载完properties配置以后我想获得value我就只要简简单单的调用getProperty方法就行了.
2.比如在bean定义的applicationContext.XML里数据源相关的bean可能会使用占位符定义,比如datasource的username和password <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> 这里的占位符的解析也是通过propertyResolver, resolveRequiredPlaceholders方法或者resolvePlaceholders等相关placeHolder方法来完成.
上面这么多方法其实总结起来就是读取了properties文件,通过key得到value就这么简单...
实验2,再来1个测试:
1 ConfigurablePropertyResolver configurablePropertyResolver; 2 3 /** 4 * PropertyPlaceholderHelper 在进test之前就已经初始化完成了,所以修改这个placeHolderPrefix没用 5 */ 6 @Test 7 public void testConfigurablePropertyResolver() { 8 configurablePropertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix("#{"); 9 configurablePropertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix("}"); 10 System.out.println(configurablePropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders("邮箱地址=${email}")); //可以被替换 11 System.out.println(configurablePropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders("邮箱地址=#{email}"));//无效 12 }
前面测试用到了占位符.默认是${},前缀是${后缀是}......那么我们能不能换个占位符呢? 我们来做1个测试 ↑
这个实验结果似乎是不能..但是接口明明提供了setPlaceholderPrefix和suffix方法为什么会不行呢?
我们稍微跟下断点:
1 AbstractEnvironment.java 2 3 private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver = new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources); 4 5 @Override 6 public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException { 7 return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text); 8 }
env里解析placeholder是通过ConfigurablePropertyResolver 来做的.
ConfigurablePropertyResolver 里是用PropertyPlaceholderHelper strictHelper;来做的
1 @Override 2 public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException { 3 if (this.strictHelper == null) { 4 this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false); 5 } 6 return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper); 7 }
然后我再加载spring的XML配置.还没进入junit的测试方法的时候,需要加载指定目录下的bean
<context:component-scan base-package="spring">
</context:component-scan>
这样会导致strictHelper被初始化,ConfigurablePropertyResolver默认的placeholder是${}所以设置到strictHelper里的是${}.
后面进入junit的test方法以后尽管我们去修改了ConfigurablePropertyResolver的placeholder为#{}但是因为strictHelper已经被初始化过了,所以我们并不会重新初始化strictHelper.因此test方法里面修改placeholder为#{}无效.
小实验3:
从实验2种我们已经知道placeholder最终是PropertyPlaceholderHelper来解析的.那么我们是不是可以直接使用它来设置我们自己的placeholder呢?
1 /** 2 * PropertyPlaceholderHelper 替换字符串 3 */ 4 @Test 5 public void testConfigurablePropertyResolver2() { 6 PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper = new PropertyPlaceholderHelper("#((", "))"); 7 System.out.println(helper.replacePlaceholders("邮箱地址=#((email))", new PropertyPlaceholderHelper.PlaceholderResolver() { //邮箱地址=jyzjyz12@163.com 8 @Override 9 public String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholderName) { 10 return configurablePropertyResolver.getProperty(placeholderName); 11 } 12 })); 13 }
这里我们新建了1个placeholder是#(())的helper..用它去解析#((email)).....从这个实验中我们大概可以观察到.PropertyPlaceholderHelper 得到#((email))这个字符串以后通过匹配前缀和后缀剥离字符串以后肯定会得到email.然后通过email这个key去environment(或者他的委托类的时候)的properties里去getProperties得到对应的value.
我们来稍微跟一下断点:
当我们调用env的resolveRequiredPlaceholders或者类的其他处理placeholder方法的时候,其实都是通过env内部的PropertyResolver去处理的.就是说env实现了PropertyResolver接口.但是他自己不处理,委托其他类来处理
1 AbstractEnvironment.java 2 3 private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver = new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources); 4 @Override 5 public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException { 6 return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text); 7 }
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver是用PropertyPlaceholderHelper来处理,这里分为2步,第一步是helper.replacePlaceholders得到剥离了placeholder的key.第二步是通过内部类的resplvePlaceholder方法调用getPropertyAsRawString方法输入key得到value
AbstractPropertyResolver.java @Override public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException { if (this.strictHelper == null) { this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false); } return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper); }
private String doResolvePlaceholders(String text, PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper) { return helper.replacePlaceholders(text, new PropertyPlaceholderHelper.PlaceholderResolver() { @Override public String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholderName) { return getPropertyAsRawString(placeholderName); } }); }
PropertyPlaceholderHelper来处理的时候会一层一层剥离placeholder,因为placeholder可能有N层.
1 /** 2 * Replaces all placeholders of format {@code ${name}} with the value returned 3 * from the supplied {@link PlaceholderResolver}. 4 * @param value the value containing the placeholders to be replaced 5 * @param placeholderResolver the {@code PlaceholderResolver} to use for replacement 6 * @return the supplied value with placeholders replaced inline 7 */ 8 public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) { 9 Assert.notNull(value, "'value' must not be null"); 10 return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, new HashSet<String>()); 11 } 12 13 protected String parseStringValue( 14 String strVal, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) { 15 16 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(strVal); 17 18 int startIndex = strVal.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix); 19 while (startIndex != -1) { 20 int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex); 21 if (endIndex != -1) { 22 String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex); 23 String originalPlaceholder = placeholder; 24 if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) { 25 throw new IllegalArgumentException( 26 "Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions"); 27 } 28 // Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key. 29 placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders); 30 // Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key... 31 String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder); 32 if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) { 33 int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator); 34 if (separatorIndex != -1) { 35 String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex); 36 String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length()); 37 propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder); 38 if (propVal == null) { 39 propVal = defaultValue; 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 if (propVal != null) { 44 // Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the 45 // previously resolved placeholder value. 46 propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders); 47 result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal); 48 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 49 logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'"); 50 } 51 startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length()); 52 } 53 else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) { 54 // Proceed with unprocessed value. 55 startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length()); 56 } 57 else { 58 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" + 59 placeholder + "'" + " in string value \"" + strVal + "\""); 60 } 61 visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder); 62 } 63 else { 64 startIndex = -1; 65 } 66 } 67 68 return result.toString(); 69 }
29行是个递归调用如果我穿的是${email},29行做完返回的就是email...得到了placeholder中的key以后我们就需要通过内部类PropertyPlaceholderHelper.PlaceholderResolver中的getPropertyAsRawString(placeholderName);去通过key得到value.
这个时候的getPropertyAsRawString(placeholderName);中的placeholderName是email.
这个方法其实就是简单的调用getProperty方法
1 @Override 2 protected String getPropertyAsRawString(String key) { 3 return getProperty(key, String.class, false); 4 }
这样就能获得value了.
小结
小结一下environment解决properties和placeholder的方法.
1.如果是properties.直接通过内部PropertySourcesPropertyResolver的getProperty解决
2.如果是placeholder.通过env内部PropertySourcesPropertyResolver相应的resolveRequiredPlaceholders方法(或者其他placeholder方法)来解决.
2.1.这些方法内部会使用helper来解析placeholder....
2.2.PropertyPlaceholderHelper的replacePlaceholders递归调用parseStringValue方法来来剥离placeholder得到key返回给env的PropertySourcesPropertyResolver........
2.3.PropertySourcesPropertyResolver再得到key以后就和查找properties一样了.
所以placeholder相比properties,就是多了一步解析placeholder得到key.利用了PropertyPlaceholderHelper来处理placeholder.
以上便是Environment做为PropertyResolver的用途与原理.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号