OO第二次Blog作业
OO第二次博客作业
目录
前言
最近在PTA平台上发布的作业有四次题目集,一次期中考试,在超新学习通上发布了农夫过河问题及改进版,链表练习,桥接模式等实验及测试。
PTA上的四次题目集,主要考查点在于点线形类的创建,类的继承、多态性使用方法以及接口的应用,正则表达式的运用,业务类的编写。其中点线性系列题目难度较大,其他题目难度适中。
超新学习通上的农夫过河问题主要考查多态的运用,链表类练习旨在增强学生对容器类的理解,桥接模式练习主要是帮助理解认识配置文件。都具有一定难度。
期中考试有三道题,分别考查类设计,继承与多态,容器类三个方面,难度适中。
设计分析
由于题目较多,仅对于几个比较典型的编程题进行设计分析。
1.图形卡片排序游戏1
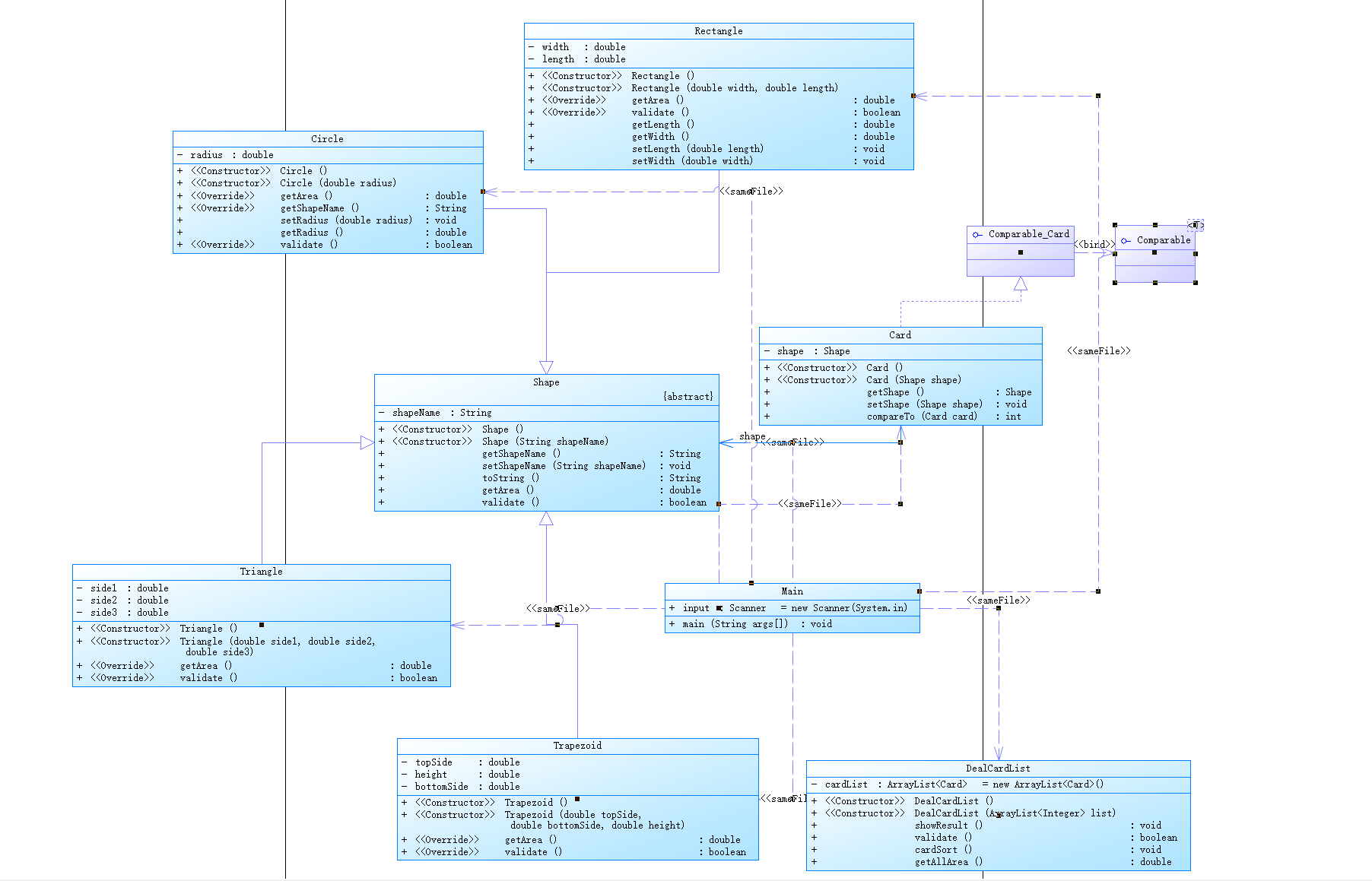
源代码如下
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.lang.Math; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; public class Main { //在Main类中定义一个静态Scanner对象,这样在其它类中如果想要使用该对象进行输入,则直接 //使用Main.input.next…即可(避免采坑) public static Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); public static void main(String[] args){ ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); int num = input.nextInt(); while(num != 0){ if(num < 0 || num > 4){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } list.add(num); num = input.nextInt(); } DealCardList dealCardList = new DealCardList(list); if(!dealCardList.validate()){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } dealCardList.showResult(); input.close(); } } class DealCardList { private ArrayList<Card> cardList=new ArrayList<Card>(); public DealCardList(){ } public DealCardList(ArrayList<Integer> list){ for (Integer in:list){ if (in==1){ Card card=new Card(new Circle(Main.input.nextDouble())); cardList.add(card); } else if(in==2){ Card card=new Card(new Rectangle(Main.input.nextDouble(),Main.input.nextDouble())); cardList.add(card); } else if (in==3){ Card card=new Card(new Triangle(Main.input.nextDouble(),Main.input.nextDouble(),Main.input.nextDouble())); cardList.add(card); } else if (in==4){ Card card=new Card(new Trapezoid(Main.input.nextDouble(),Main.input.nextDouble(),Main.input.nextDouble())); cardList.add(card); } else if (in==0){ break; } } } public void showResult() { System.out.println("The original list:"); for (Card card:cardList){ System.out.print(card.getShape().getShapeName()+":"+String.format("%.2f",card.getShape().getArea())+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("The sorted list:"); cardList.sort(Card::compareTo); for (Card card:cardList){ System.out.print(card.getShape().getShapeName()+":"+String.format("%.2f",card.getShape().getArea())+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.printf("Sum of area:"+String.format("%.2f",getAllArea())); } public boolean validate() { for (Card card:cardList){ if (card.getShape().validate()){ } else { return false; } } return true; } public void cardSort(){ } public double getAllArea(){ double sumArea=0; for (Card card:cardList){ sumArea=sumArea+card.getShape().getArea(); } return sumArea; } } class Card implements Comparable<Card>{ private Shape shape; public Card(){ } public Card(Shape shape){ this.shape=shape; } public Shape getShape() { return shape; } public void setShape(Shape shape) { this.shape = shape; } public int compareTo(Card card){ return Double.compare(card.getShape().getArea(),this.getShape().getArea()); } } abstract class Shape{ private String shapeName; public Shape(){} public Shape(String shapeName){ this.shapeName=shapeName; } public String getShapeName() { return shapeName; } public void setShapeName(String shapeName) { this.shapeName = shapeName; } @Override public String toString() { return shapeName; } public abstract double getArea(); public abstract boolean validate(); } class Circle extends Shape{ private double radius; public Circle(){} public Circle(double radius){ this.radius=radius; super.setShapeName("Circle"); } @Override public double getArea() { return Math.PI*radius*radius; } @Override public String getShapeName() { return super.getShapeName(); } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } @Override public boolean validate() { return !(radius<=0); } } class Trapezoid extends Shape{ private double topSide; private double height; private double bottomSide; public Trapezoid(){} public Trapezoid(double topSide, double bottomSide, double height){ this.topSide = topSide; this.height = height; this.bottomSide = bottomSide; super.setShapeName("Trapezoid"); } @Override public double getArea() { return (topSide+bottomSide)*height/2; } @Override public boolean validate() { return !(topSide<=0||height<=0||bottomSide<=0); } } class Rectangle extends Shape{ private double width; private double length; public Rectangle(){} public Rectangle(double width,double length){ this.length=length; this.width=width; super.setShapeName("Rectangle"); } @Override public double getArea() { return width*length; } @Override public boolean validate() { return !(width<=0||length<=0); } public double getLength() { return length; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } } class Triangle extends Shape{ private double side1; private double side2; private double side3; public Triangle(){} public Triangle(double side1,double side2,double side3){ this.side1=side1; this.side2=side2; this.side3=side3; super.setShapeName("Triangle"); } @Override public double getArea() { double p=side1+side2+side3; p=p/2.0; //return Math.pow(p*(p-side1)+p*(p-side2)+p*(p-side3),1.0/2.0); return Math.sqrt(p*(p-side1)*(p-side2)*(p-side3)); } @Override public boolean validate() { return !(side3<=0||side2<=0||side1<+0||(side2+side1)<=side3||(side1+side3)<=side2||(side3+side2)<=side1); } }
本题要求
设计一款适合于小学生的卡片(Card)排序游戏,其规则为随机发放一些卡片给学生,卡片分为 四种形状:圆形(Circle)、矩形(Rectangle)、三角形(Triangle)及梯形(Trapezoid),并给出各种 卡片的相应参数,要求学生能够迅速求出各卡片的面积大小然后将卡片按照其面积值从大到小进行排序,同时求出所有卡片的面积之和。
输入输出示例
输入示例 1:
1 5 3 2 0
输出示例 1:
Wrong Format
输入示例 2:
4 2 1 3 0
3.2 2.5 0.4 2.3 1.4 5.6 2.3 4.2 3.5
输出示例 2:
The original list:
Trapezoid:1.14 Rectangle:3.22 Circle:98.52 Triangle:4.02
The sorted list:
Circle:98.52 Triangle:4.02 Rectangle:3.22 Trapezoid:1.14
Sum of area:106.91
输入示例 3:
4 2 1 3 0
3.2 2.5 0.4 2.3 1.4 5.6 2.3 4.2 8.4
输出示例 3:
Wrong Format
在本题中,shape类作为所有涉及图形的父类,拥有三个公有函数即shapeName的getter和sette与一个toString方法,以及两个抽象方法即用来求周长的getArea方法和检验图形的validate方法,在DealCardList类中用showResult方法打印出基本格式,用cardSort进行排序。
点线形系列
这个系列一共四道题,事实上这个系列的题目的最大难点不在于设计,而在于对错误输入的处理,在设计层面上看这道题,无非就是是不是用point类这里可能会出现差异,事实上你如果不用point类进行处理,也不会给你增加多少工作量,因为每一个判断的方法都是同样的格式,如果不用point类方法的话,上一个方法和下一个方法的区别也只是多了几个数组而已。
我们现在仅对7-2 点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算进行分析,这道题是目前为止,这个系列中的最后一道题,也是这些题里最复杂,检查点最多的题。
实现判断这些图形并不难,我们主要分析如何处理各种输入错误的情况以及容易出错的地方。
源代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Scanner; import java.lang.Math; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String arc; arc=in.nextLine(); char e =arc.charAt(0); if (arc.charAt(1)!=':'){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } arc=arc.substring(2,arc.length()); String []p1=arc.split(" "); for (int i=0;i< p1.length;i++){ String []p2=p1[i].split(","); Try(p2); } switch (e){ case '1':Void1(arc);break; case '2':Void2(arc);break; case '3':Void3(arc);break; case '4':Void4(arc);break; case '5':Void5(arc);break; default:System.out.println("Wrong Format"); }} public static void Try(String arc[]){ double sum=0; // 将数组中所有元素转化为double类型,并输出所有double类型的和以及捕获异常 for (int i = 0;i < arc.length;i ++){ try{ double d = Double.parseDouble(arc[i]); sum += d; }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } } public static void Void3(String arc) { ArrayList<Double> arrayList=new ArrayList<>(); String ak[]=arc.split(" "); if (ak.length!=4){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); System.exit(0);} double x1,x2,x3,y1,y2,y3,x4,y4,k; String p1[]=ak[0].split(","); String p2[]=ak[1].split(","); String p3[]=ak[2].split(","); String p4[]=ak[3].split(","); if (p1.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p2.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p3.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p4.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} x1=Double.parseDouble(p1[0]); y1=Double.parseDouble(p1[1]); x2=Double.parseDouble(p2[0]); y2=Double.parseDouble(p2[1]); x3=Double.parseDouble(p3[0]); y3=Double.parseDouble(p3[1]); x4=Double.parseDouble(p4[0]); y4=Double.parseDouble(p4[1]); if(x1==x2&&y1==y2||x3==x2&&y3==y2||x1==x3&&y1==y3||x1==x4&&y1==y4||x2==x4&&y2==y4||x3==x4&&y3==y4){ System.out.println("points coincide"); System.exit(0); } double a,b,c,d,e,f,a1,b1,c1,d1,e1,f1; a=K(x1,y1,x2,y2); b=K(x2,y2,x3,y3); c=K(x3,y3,x4,y4); d=K(x4,y4,x1,y1); e=K(x1,y1,x3,y3); f=K(x2,y2,x4,y4); a1=XtoX(x1,y1,x2,y2); b1=XtoX(x2,y2,x3,y3); c1=XtoX(x3,y3,x4,y4); d1=XtoX(x4,y4,x1,y1); e1=XtoX(x1,y1,x3,y3); f1=XtoX(x2,y2,x4,y4); arrayList.add(a); arrayList.add(b); arrayList.add(c); arrayList.add(d); arrayList.add(e); arrayList.add(f); HashSet hashSet=new HashSet(arrayList); arrayList.clear(); arrayList.addAll(hashSet); if(a==b||c==d||a==d||b==c){ System.out.println("not a quadrilateral"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print(JudgeOT(x1,y1,x4,y4,x3,y3,x2,y2)+" "); System.out.print(tran(a1+b1+c1+d1)+" "); System.out.println(tran((float)getArea(a1,b1,e1)+(float) getArea(c1,d1,e1))); } public static void Void1(String arc){ ArrayList<Double> arrayList=new ArrayList<>(); String ak[]=arc.split(" "); if (ak.length!=4){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); System.exit(0);} double x1,x2,x3,y1,y2,y3,x4,y4,k; String p1[]=ak[0].split(","); String p2[]=ak[1].split(","); String p3[]=ak[2].split(","); String p4[]=ak[3].split(","); if (p1.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p2.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p3.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p4.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} x1=Double.parseDouble(p1[0]); y1=Double.parseDouble(p1[1]); x2=Double.parseDouble(p2[0]); y2=Double.parseDouble(p2[1]); x3=Double.parseDouble(p3[0]); y3=Double.parseDouble(p3[1]); x4=Double.parseDouble(p4[0]); y4=Double.parseDouble(p4[1]); if(x1==x2&&y1==y2||x3==x2&&y3==y2||x1==x3&&y1==y3||x1==x4&&y1==y4||x2==x4&&y2==y4||x3==x4&&y3==y4){ System.out.println("points coincide"); System.exit(0); } double a,b,c,d,e,f; a=toInfinity(toZero(K(x1,y1,x2,y2))); b=toInfinity(toZero(K(x2,y2,x3,y3))); c=toInfinity(toZero(K(x3,y3,x4,y4))); d=toInfinity(toZero(K(x4,y4,x1,y1))); e=toInfinity(toZero(K(x1,y1,x3,y3))); f=toInfinity(toZero(K(x2,y2,x4,y4))); arrayList.add(a); arrayList.add(b); arrayList.add(c); arrayList.add(d); arrayList.add(e); arrayList.add(f); HashSet hashSet=new HashSet(arrayList); arrayList.clear(); arrayList.addAll(hashSet); if(arrayList.size()==4){ System.out.println("true true"); } else System.out.println("true false"); } public static void Void2(String arc){ ArrayList<Double> arrayList=new ArrayList<>(); String ak[]=arc.split(" "); if (ak.length!=4){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); System.exit(0);} double x1,x2,x3,y1,y2,y3,x4,y4,k; String p1[]=ak[0].split(","); String p2[]=ak[1].split(","); String p3[]=ak[2].split(","); String p4[]=ak[3].split(","); if (p1.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p2.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p3.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p4.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} x1=Double.parseDouble(p1[0]); y1=Double.parseDouble(p1[1]); x2=Double.parseDouble(p2[0]); y2=Double.parseDouble(p2[1]); x3=Double.parseDouble(p3[0]); y3=Double.parseDouble(p3[1]); x4=Double.parseDouble(p4[0]); y4=Double.parseDouble(p4[1]); if(x1==x2&&y1==y2||x3==x2&&y3==y2||x1==x3&&y1==y3||x1==x4&&y1==y4||x2==x4&&y2==y4||x3==x4&&y3==y4){ System.out.println("points coincide"); System.exit(0); } double a,b,c,d,e,f,a1,b1,c1,d1,e1,f1; a=K(x1,y1,x2,y2); b=K(x2,y2,x3,y3); c=K(x3,y3,x4,y4); d=K(x4,y4,x1,y1); e=K(x1,y1,x3,y3); f=K(x2,y2,x4,y4); a1=XtoX(x1,y1,x2,y2); b1=XtoX(x2,y2,x3,y3); c1=XtoX(x3,y3,x4,y4); d1=XtoX(x4,y4,x1,y1); e1=XtoX(x1,y1,x3,y3); f1=XtoX(x2,y2,x4,y4); arrayList.add(a); arrayList.add(b); arrayList.add(c); arrayList.add(d); arrayList.add(e); arrayList.add(f); HashSet hashSet=new HashSet(arrayList); arrayList.clear(); arrayList.addAll(hashSet); if(a==b||c==d||a==d||b==c){ System.out.println("not a quadrilateral"); System.exit(0); } if(arrayList.size()==4){ System.out.println((a1==b1&&b1==c1&&c1==d1)+" "+(a*d==-1)+" "+(a1==b1&&b1==c1&&c1==d1&&a*d==-1)); } else System.out.println("false false false"); } public static void Void4(String arc){ String ak[]=arc.split(" "); if (ak.length!=6){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); System.exit(0);} double x1,x2,x3,x4,x5,y1,y2,y3,y4,y5,k,k2; String p1[]=ak[0].split(","); String p2[]=ak[1].split(","); String p3[]=ak[2].split(","); String p4[]=ak[3].split(","); String p5[]=ak[4].split(","); String p6[]=ak[5].split(","); if (p1.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p2.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p3.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p4.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p5.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if (p6.length!=2){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0);} if(p1[0]==p2[0]&&p1[1]==p2[1]){ System.out.println("points coincide"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println("1"); } public static void Void5(String arc) { String ak[] = arc.split(" "); if (ak.length != 5) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); System.exit(0); } double x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, y1, y2, y3, y4, y5, k, k2; String p1[] = ak[0].split(","); String p2[] = ak[1].split(","); String p3[] = ak[2].split(","); String p4[] = ak[3].split(","); String p5[] = ak[4].split(","); if (p1.length != 2) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } if (p2.length != 2) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } if (p3.length != 2) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } if (p4.length != 2) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } if (p5.length != 2) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } x1 = Double.parseDouble(p1[0]); y1 = Double.parseDouble(p1[1]); x2 = Double.parseDouble(p2[0]); y2 = Double.parseDouble(p2[1]); x3 = Double.parseDouble(p3[0]); y3 = Double.parseDouble(p3[1]); x4 = Double.parseDouble(p4[0]); y4 = Double.parseDouble(p4[1]); x5 = Double.parseDouble(p5[0]); y5 = Double.parseDouble(p5[1]); double a, b, c, d, e, f, g, a1, b1, c1, d1, e1, f1,a2,a3,a4; a = K(x1, y1, x2, y2); b = K(x2, y2, x3, y3); c = K(x3, y3, x4, y4); d = K(x4, y4, x5, y5); e = K(x1, y1, x3, y3); f = K(x2, y2, x4, y4); a1 = XtoX(x1, y1, x2, y2); a2 = XtoX(x1, y1, x3, y3); a4 = XtoX(x1, y1, x4, y4); a3 = XtoX(x1, y1, x5, y5); b1 = XtoX(x2, y2, x3, y3); c1 = XtoX(x3, y3, x4, y4); d1 = XtoX(x4, y4, x5, y5); e1 = XtoX(x5, y5, x2, y2); f1 = XtoX(x3,y3,x5,y5); Line line1 = new Line(x2, y2, x3, y3); Line line2 = new Line(x3, y3, x4, y4); Line line3 = new Line(x4, y4, x5, y5); Line line4 = new Line(x5, y5, x2, y2); int t = 0; if (line1.inLine(x4, y4)) { t++; } if (line2.inLine(x5, y5)) { t++; } if (line3.inLine(x2, y2)) { t++; } if (line4.inLine(x3, y3)) { t++; } if(t==1){ System.out.println("in the triangle"); } else if(t==0){ if(judgeIn(a1,a2,a3,b1,f1,e1)||judgeIn(a4,a2,a3,c1,f1,d1)){ System.out.println("in the quadrilateral"); } else System.out.println("outof the quadrilateral"); } else System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle"); } public static boolean Ks(String x) { String w; w = "[+-]?(\\d+)(\\.\\d+)?$"; for(int i=1;i<x.length();i++){ if(x.charAt(0)=='0'&&x.length()>1&&x.charAt(1)!='.') return false; } if(x.matches(w)) return true; else return false; } public static boolean YesTangle(double x1,double x2,double x3){ if (x1+x2<=x3||x1+x3<=x2||x2+x3<=x1){ return false; } else { return true; } } public static double XtoX(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){ double X; X=(x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2); X=Math.pow(X,1.0/2); return toInfinity(toZero(X)); } public static double getArea(double side1,double side2,double side3) { double p=side1+side2+side3; p=p/2.0; //return Math.pow(p*(p-side1)+p*(p-side2)+p*(p-side3),1.0/2.0); return Math.sqrt(p*(p-side1)*(p-side2)*(p-side3)); } public static String tran(double x) { String str_d = String.valueOf(x); str_d = str_d.substring(str_d.indexOf(".") + 1); int len = str_d.length(); len = len > 3 ? 3 : len; String out = String.format("%." + len + "f", x); return out; } public static double sort(double a,double b,double c){ double max=a; if(b>a){ max=b; } if (c>max){ max=c; } return max; } public static double K(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){ return toInfinity(toZero((y1 - y2) / (x1 - x2))); } public static double toZero(double x){ if(Math.abs(x)<0.000001){ return 0; } else return x; } public static double toInfinity(double x){ if(Math.abs(x)==Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY){ return Math.abs(x); } else return x; } public static boolean JudgeOT(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3, double x4, double y4) { double z1, z2, z3, z4; z1 = (x4-x1)*(y2-y1)-(y4-y1)*(x2-x1); z2 = (x1-x2)*(y3-y2)-(y1-y2)*(x3-x2); z3 = (x2-x3)*(y4-y3)-(y2-y3)*(x4-x3); z4 = (x3-x4)*(y1-y4)-(y3-y4)*(x1-x4); return z1*z2*z3*z4>0; } public static String getFourArea(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3, double x4, double y4){ double X,Y; X=(x1*y2+x2*y3+x3*y1-x1*y3+x2*y1+x3*y2)/2; Y=(x1*y3+x3*y4+x4*y1-x1*y4+x3*y1+x4*y3)/2; return tran(X+Y); } public static boolean judgeIn(double s1,double s2,double s3,double x,double y,double z){ if(getArea(s1,s2,x)+getArea(s2,s3,y)+getArea(s3,s1,z)<=getArea(x,y,z)){ return true; } else return false; } } class Line{ public double x1,x2,y1,y2,k,c; public Line(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){ this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; this.x2 = x2; this.y2 = y2; k=(y1-y2)/(x1-x2); c=y2-k*x2; } public boolean inLine(double x,double y){ if(y-k*x==c){ return true; } else { return false; } } }
1.INFINITY与0处理
在计算斜率的时候难免会出现直线的斜率无穷大的情况,但是对于直线垂直于X轴的情况,却会出现两种不同的斜率INFINITY 和-INFINITY,这是因为虽然分母为零,但是分子可以是正,也可能为负。因为我在代码中用hashset来清除重复的数据,因此要把INFINITY统一,因此我用
public static double toInfinity(double x){
if(Math.abs(x)==Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY){
return Math.abs(x);
}
else
return x;
}
这个方法对所有的INFINITY情况进行了取绝对值的处理。同时,对所有趋近于0的函数,为防止出现-0.0与0.0同时存在,也采用了类似方法进行处理,对绝对值小于0.000001的值返回0。
2.小数位数处理
题目中有要求,将小数后超过三位的部分进行四舍五入,只留3位,对小数点后不足三位的数不做处理,因此,我在处理方法中通过三元运算符来判断小数位数,用格式化处理来进行四舍五入即返回字符串。
public static String tran(double x) {
String str_d = String.valueOf(x);
str_d = str_d.substring(str_d.indexOf(".") + 1);
int len = str_d.length();
len = len > 3 ? 3 : len;
String out = String.format("%." + len + "f", x);
return out;
}
3.Wrong format错误格式输入处理
为处理这种错误情况我使用了正则表达式对格式错误进行处理。
public static boolean Ks(String x) {
String w;
w = "[+-]?(\\d+)(\\.\\d+)?$";
for(int i=1;i<x.length();i++){
if(x.charAt(0)=='0'&&x.length()>1&&x.charAt(1)!='.')
return false;
}
if(x.matches(w))
return true;
else
return false;
}
最后还有一些图形的错误处理,这个用一些数学知识就可以处理。
期中考试
三道题属于循序渐进的,基本上是从基础题不断提高难度。
第一道题属于基础题,考查了基本的类设计。
第二题考查了类继承,与第一题一样较基础。
第三题点线面问题再重构(容器类),由于本人对泛型的使用并不熟练,所以在Arraylist<>的括号中没有加入内容,而是使用了一个Object类进行存储,然后在Main函数中进行集合元素的类型转换。题目源代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ GeometryObject geometryObject=new GeometryObject(); geometryObject.add(); for(Object obj:geometryObject.getArrayList()){ Element element=null; element= (Element) obj; element.display(); } }} class Line extends Element{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line(Point point1,Point point2,String color){ this.point1=point1; this.point2=point2; this.color=color; } public String format(double value) { return String.format("%.2f", value).toString(); } public double distance(Point point1,Point point2){ double x1,x2,y1,y2,X; x1=point1.getX(); x2=point2.getX(); y1=point1.getY(); y2=point2.getY(); X=(x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2); X=Math.pow(X,1.0/2); return X; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public void display(){ System.out.println("The line's color is:" +color+"\n"+ "The line's begin point's Coordinate is:\n" + point1 +"\n"+ "The line's end point's Coordinate is:\n" + point2 +"\n"+ "The line's length is:"+format(distance(point1,point2))); } } class Point extends Element{ private double x; private double y; public Point(double x,double y){ this.x=x; this.y=y; } public void check(){ if(x<=0||x>200||y<=0||y>=200){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } @Override public String toString() { return "("+format(x)+","+format(y)+")"; } public void display(){ System.out.println(this); } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getX() { return x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } public String format(double value) { return String.format("%.2f", value).toString(); } } abstract class Element{ abstract void display(); } class Plane extends Element{ private String color; public Plane(String color){ this.color=color; } @Override void display() { System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+color); } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } } class GeometryObject { private ArrayList<Element> arrayList=new ArrayList<>(); public void add(){ Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); int choice; choice = input.nextInt(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list Point point=new Point(input.nextDouble(),input.nextDouble()); point.check(); arrayList.add(point); break; case 2://insert Line object into list Point point1=new Point(input.nextDouble(),input.nextDouble()); Point point2=new Point(input.nextDouble(),input.nextDouble()); point2.check(); point1.check(); Line line=new Line(point1,point2,input.next()); arrayList.add(line); break; case 3://insert Plane object into list Plane plane=new Plane(input.next()); arrayList.add(plane); break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list int index = input.nextInt(); if(index>0&&index<=arrayList.size()) remove(index); break; default: add(); } choice = input.nextInt(); } } public void remove(int index){ arrayList.remove(index-1); } public ArrayList getArrayList() { return arrayList; } }
链表练习
链表练习有单链表练习和双链表练习两次作业,由于双链表是在单链表基础上改进而来,这里我们对双链表类进行分析。
首先是添加元素和删减元素,我在addSome()方法和remove()方法中使用的是首插法,即从头节点开始遍历,在遍历到下标位置时通过前后节点的首尾点的修改达到增删的目的。
其次,在链表类所要求的增删改查等方法中,为了方便调用,我写了两个方法分别用来调用节点以及节点的值。
踩坑心得
- 在点线面第四题中遇到了一个问题,在输出小数时小数点后无法省去多余的0,使用的解决办法是将得到的double数据类型进行float强制类型转换处理。
- 判断点是否在四边形内我使用的是用面积判断,即用四个三角形的面积加起来是否大于四边形面积来判断。
改进建议
在点线面系列题目的代码中可以使用Point类来存储点。
总结
Java路漫漫,FX下一站。



