POLIR-Mind-Cognition-Neural Models-NLP(Neuro-Linguistic Programming) 思维逻辑层级(logical Levels)-理解+解决问题-无敌洞察力+高维思路-{精神,身份,价值,能力,行为,环境}
Neuro-Linguistic Programming-百知思维模型-NLP理解层次 能给你无敌洞察力+高维思路
https://v.douyin.com/iS74bMKr/
最重要的两种能力:
- 目标: 为 {自己|客户|公司|组织|社会|政府} 提供的
- 对社会和世界的认知与判断;
- 组织与管理能力
其他的都可以找:
- 要懂营销与市场的,招聘"市场总监",
- 要专深研究技术的,招聘"技术总监"或"科学家",
- 要通晓投资资本的,招聘“投资总监”,
- 类似的,财务、运营、行政、以及其他岗位,
全都可以招募,加以组织和管理。
POLIR-Mind-Cognition
Neural Models
认知与知识结构
-
NLP已经有二十年以上的历史,就表示"现在”有"更先进"的。
例如,NLP并没有将“社会与组织”、“世界和文化多元”包括在其理论;
再如,假设NLP决绝对正确,也只是理论,执行与实际又是另一维度;
人类社会的多元多样,
总之,学习NLP的长处。 -
首先,大多数人既有共性,也有个性,即: 认知与知识结构是有角度+高下之分;
社会劳动分工,教育分科分专业。 -
但是,并不影响人民群众"法制"上的“平等”,
一种"唯经济观点"或"唯价值度量"是按"实用主义"或"效用论"上,把"人、物、信息、关系"都"量化",甚至“金钱衡量”;
这是"不全面"的,一些场合甚至是“错误的”,例如:- "谁会用生命、自由换金钱"?当然不会。
- 中国能以资金“收购美国🇺🇸、加拿大🇨🇦或英国🇬🇧全部的土地”?Definitely Not.
- 或者美国🇺🇸的银行和资本可以“收买”全美国🇺🇸总统选举的“选票”?Absolutely Not.
美国🇺🇸作为"教科书上的资本主义国家","资本"并不能最终"收买"美国🇺🇸民众的"选票",
因此, "资本主义"并非"教科书"上传达的"印象和感知"!
或者更客观表达是"我们的教科书"在"预设立场欺骗民众". - 另一种反证法: 假设资本主义"真如"教科书上般万恶", 何以成为吸引全世界英才的"头号移民强国"?
事实上“现代经济理论”必须以“民主”、“共和”、“多元”为基础。
因为:每个人的立场、利益、理想、价值观、人性与道德观念、社会分工、组织角色、欲望、需求、家庭、社会关系、社交网络...、也不同; -
重点在用“有角度+高下之分”的“Individuals”构造一个“全面”的"Organization";
共通的部分,连接和建设好组织;
存异的部分,各展所长;
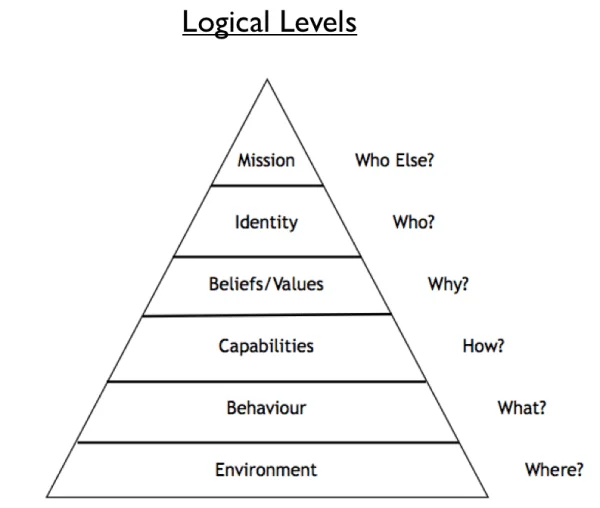
NLP(Neural Logic Levels) 思维逻辑层级
能给你无敌洞察力+高维思路
- Gregory Bertson(格雷歌理,贝特森)
- Robert B. Dilts(罗伯特,迪尔磁)
- 终于在 1991年成为理解问题和解决问题的思维模型
English Links
Neurological Levels and Logical Levels in NLP
What's NLP(Neurological levels)
In the processes of learning, change, and communication there are natural hierarchies, or logical levels.
In logical levels you have sets and subsets.
How the sets and subsets are logically set out.
- Sometimes in NLP these levels are called Neurological levels as they reflect levels of thinking.
- The function of each NLP logical level in the hierarchy is to organize the information below it.
- Changing something on a lower NLP logical level of the hierarchy could, but would not necessarily affect the levels above it.
- However… making a change at an upper level would necessarily change everything below it in order to support the higher level change.
Logical Levels of Change:
- Spirituality – Change for whom and/or what purpose?
- Identity – Does change reflect who I am?
- Values and beliefs– Why make the change?
- Capabilities and Skills- Change how?
- Behaviours – Change what?
- Environment – Where to change?
In summary, NeuroLogical Levels are made of the following "hierarchy" of neurophysological structures:
-
Spiritual :
Holographic- Individual nervous systems combining to form a larger system and deep life sustaining functions (e.g., reticular system).- Identity : Immune system and endocrine system- Nervous system as a whole, and deep life sustaining functions (e.g., reticular system).
- Beliefs & Values : Limbic and autonomic control system (e.g., heart rate, pupil dilation, etc.)
- Mission : Your long-term goals
-
Unconscious responses:
4. Capabilities : Cortical systems - Semi-conscious actions (eye movements, posture, etc.)
5. Behaviors : Motor system (pyramidal & cerebellum)-Conscious actions
6. Environment : Peripheral nervous system-Sensations and reflex reactions.
The first books formally mentioning this formulation of Logical Levels were ""Changing Beliefs with NLP" and "Beliefs: Pathways to Health and Well-Being", both published in 1990.
The Logical Levels model has continued to be developed and enriched, and has become the basis of many recent NLP processes and techniques.
My book
- "From Coach to Awakener" (2003) applies the model as a primary roadmap for the process of personal coaching.
"NLP II: The Next Generation" provides a an in-depth description of the Neurological Levels model and its relation to Set Theory, Mathematical Group Theory, hierarchical levels, Korzybski's levels of abstraction, Russell's logical types, Arthur Koestler's (also used by Ken Wilbur) notion of "holons" and "holarchy," and simple "chunking."

Six Levels(有层级高低之分)
- 精神: 使命感/期望感/责任感, 与世界的关系和看待它的方式
- 身份: 自我认知(我是谁、在哪)、自我认同(我行不行)
- 价值: 价值观、意义、信念、品质、原则、重要性排序
- 能力: 知识、技能、效率、水平、速度,做出的选择
- 行为: 行动、习惯、路线、操作步骤、流程、方法
- 环境: 个人之外的其他人、事、物、时间、地点

Neurological Levels and Logical Levels in NLP
Logical Levels
In the processes of learning, change, and communication there are natural hierarchies, or logical levels. In logical levels you have sets and subsets. How the sets and subsets are logically set out.
Sometimes in NLP these levels are called Neurological levels as they reflect levels of thinking.
The function of each NLP logical level in the hierarchy is to organize the information below it.
Changing something on a lower NLP logical level of the hierarchy could, but would not necessarily affect the levels above it.
However… making a change at an upper level would necessarily change everything below it in order to support the higher level change.
Logical Levels of Change:
- Spirituality – Change for whom and/or what purpose?
- Identity – Does change reflect who I am?
- Values and beliefs– Why make the change?
- Capabilities and Skills- Change how?
- Behaviours – Change what?
- Environment – Where to change?
They are important for understanding change from an individual, social or organisational point of view. For desgining an action plan for change.
Using Neurological levels in NLP
Neurological Level help us understand the different levels at which we experience the world,
and at which level we should work to bring a change we desire.
-
We can help others
by understandingat which level they are operatingby listening tothe language that they use. They might feel stuck in a problem because they are trying to find a solution but always operating on the same level. By helping themchangetheir thinkingtoanother level, we canbring thema new perspectivefortheir problem. -
This also applies to ourselves.
By listening tothe language used in our self-talk we candiscoverwhere** the initial problem**is being constructedandthen address itin the right way.
First and Second Order Change
First Order Change
Change occurring on the same logical level as the problem state.
Eg acting on behaviour to obtain a change in behaviour.
Change in a specific behaviour in context. Anchoring.
Second Order Change
Any change which takes place at a higher logical level than the problem state.
This allows the change to affect the system, thereby rendering the erstwhile problem harmless, irrelevant or useful.
Change in an entire category of behaviours in context. Reframing.
This subject is covered in detail at our NLP Practitioner and NLP Master Practitioner Training Courses.
Logical Types
In logial levels there are 2 dimensions, the levels and the types within the levels.
These are the types of things on a certain logical level. Eg different types of cars, within the set of cars.
This is important in order to develop flexibility in the client.
Paying attention so that you know and understand where the client is chunking.
Enables you to discover the clients true feelings.




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通