Java实现线性阈值模型(Linear Threshold Model)
影响力传播的线性阈值模型:
网络中连接任意两个节点u,v之间的边都有权重,任意一个节点它的各个邻居节点的边的权重之和为1,即

N(v):neighbors of v.
网络中的节点分为已激活节点和未激活节点,每个节点都有一个自己的激活阈值Θ(每个节点的激活阈值可以不同,且现实情况下社交网络的各个用户的激活阈值一般不相同,有的用户活跃,阈值低,容易受人影响,而有的用户较沉默,阈值高)。未被激活的节点v受所有与之相邻且已被激活的节点u的影响。当未激活节点v与所有已被激活的邻居节点的边的权重之和达到或超过激活阈值Θ时,节点v就会被激活。
即当满足条件:
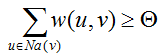
Na(v):active neighbors of v.
v被激活之后,它也会以同样的方式影响它自己的未被激活的邻居节点。这样会有越来越多的,满足激活条件的节点被激活,直到最后再也没有新的节点被激活了,激活过程才会停止。
上述过程被称为影响力传播的线性阈值模型(Linear Threshold Model),传播过程停止时最终被激活的节点的数量被称为影响力的传播范围(Influence Spread)。
无向无权图的线性阈值模型的Java实现:
public int beginDiffusionProcess(ArrayList<Node> graph,ArrayList<Integer> activeNodeIds,int lastInfSpread) { //Mark the active neighbors of each node. for(Node nd:graph) { for(Node n:nd.neighbors) { if(activeNodeIds.contains(n.nodeId)) { n.setActive(true); } } } //Determine whether each node is activated or not. for(Node nd:graph) { int activeNeighbor_Num=0; for(Node n:nd.neighbors) { if(n.isActive()) { activeNeighbor_Num++; } } if (activeNeighbor_Num/(nd.neighbors.size()*1.0)>=nd.getThreshold())//如果是带权图,这里要修改 { nd.setActive(true); activeNodeIds.add(nd.nodeId); } } //Get the influence spread of the current step. int infSpread=0; for(Node n:graph) { if(n.isActive()) { infSpread++; } } //If it converges,stop the diffusion process,else continue the next step. if(lastInfSpread==infSpread) return infSpread; else return beginDiffusionProcess(graph,activeNodeIds,infSpread); }
下面的代码调用上述方法,获取最终的Influence Spread:
public int GetInfSpread(ArrayList<Node> graph) { ArrayList<Integer> activeNodeIds=new ArrayList<Integer>();
//this.dimensions是已经被激活的种子节点,是某一个类的静态属性,类型为ArrayList<Node>,这些节点会尝试激活它们的邻居节点。 for(Node n:this.dimensions) { activeNodeIds.add(n.nodeId); } int lastInfSpread=0; return beginDiffusionProcess(graph, activeNodeIds,lastInfSpread); }
其他相关的代码:
Node.java
import java.util.ArrayList; public class Node implements Comparable<Node> { public int nodeId; public ArrayList<Node> neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>(); private boolean b_isActive = false; private double threshold = 0.0; public Node(int nodeId, double threshold) { this.nodeId = nodeId; this.threshold = threshold; } public int neighbors_num() { return this.neighbors.size(); } public void setActive(boolean isActive) { this.b_isActive = isActive; } public boolean isActive(){ return this.b_isActive; } public double getThreshold(){ return this.threshold; } // Sort nodes by (out)degree public int compareTo(Node anotherNode) { if (this.neighbors != null && anotherNode.neighbors != null) { // reverse order return anotherNode.neighbors_num() - this.neighbors_num(); // positive order // return this.neighbors_num()-anotherNode.neighbors_num(); } return 0; } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号