tf识别单张图片ocr(0到9的识别)- CNN方式
继上篇文章后,这次使用卷积网络做实验(上篇用的是普通2层网络)
import time
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import cv2 as cv
def generate_image(a, rnd_size=100):
image = np.zeros([28, 28], dtype=np.uint8)
cv.putText(image, str(a), (7, 21), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1.3, 255, 2, 8)
for i in range(rnd_size):
row = np.random.randint(0, 28)
col = np.random.randint(0, 28)
image[row, col] = 0
data = np.reshape(image, [1, 784])
return image, data / 255
def display_images(images):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
size = len(images)
for i in range(size):
plt.subplot(2, 5, i + 1)
plt.imshow(images[i])
plt.show()
def load_data(sess, rnd_size=100, should_display_images=False):
zero_image, zero = generate_image(0, rnd_size)
one_image, one = generate_image(1, rnd_size)
two_image, two = generate_image(2, rnd_size)
three_image, three = generate_image(3, rnd_size)
four_image, four = generate_image(4, rnd_size)
five_image, five = generate_image(5, rnd_size)
six_image, six = generate_image(6, rnd_size)
seven_image, seven = generate_image(7, rnd_size)
eight_image, eight = generate_image(8, rnd_size)
nine_image, nine = generate_image(9, rnd_size)
if should_display_images is True:
display_images(
[zero_image, one_image, two_image, three_image, four_image, five_image, six_image, seven_image, eight_image,
nine_image])
x_features = [zero, one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine]
x_features = np.array(x_features)
x_features = np.reshape(x_features, (-1,784))
y = None
y_lables = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
y = sess.run(tf.one_hot(y_lables, 10))
return x_features, y
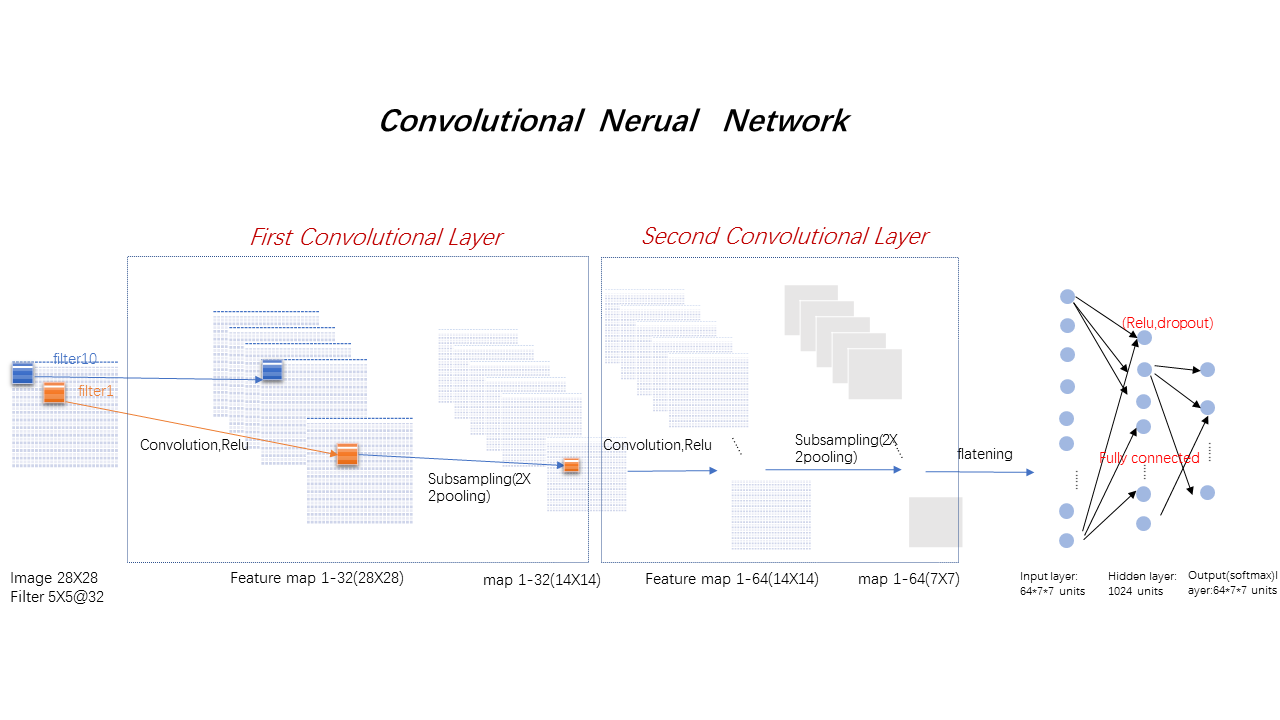
def build_network():
x = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 784], dtype=tf.float32)
y = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 10], dtype=tf.float32)
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
# convolution layer 1
conv1_w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[5, 5, 1, 32], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
conv1_bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[32], stddev=0.1))
conv1_out = tf.nn.conv2d(input=x_image, filter=conv1_w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
conv1_relu = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(conv1_out, conv1_bias))
# max pooling 1
maxpooling_1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1_relu, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# convolution layer 2
conv2_w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[5, 5, 32, 64], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
conv2_bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[64], stddev=0.1))
conv2_out = tf.nn.conv2d(input=maxpooling_1, filter=conv2_w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
conv2_relu = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(conv2_out, conv2_bias))
# max pooling 2
maxpooling_2 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2_relu, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# fc-1
w_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[7*7*64, 1024], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[1024]))
h_pool2 = tf.reshape(maxpooling_2, [-1, 7*7*64])
output_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(h_pool2, w_fc1), b_fc1))
# dropout
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
h2 = tf.nn.dropout(output_fc1, keep_prob=keep_prob)
# fc-2
w_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[1024, 10], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[10]))
y_conv = tf.add(tf.matmul(output_fc1, w_fc2), b_fc2)
cross_loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=y_conv, labels=y)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_loss)
step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.05).minimize(loss)
# accuracy
acc_mat = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
acc = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(acc_mat, tf.float32))
prediction = tf.argmax(y_conv, 1)
tf.summary.scalar("accuracy", acc)
tf.summary.image('testing', x_image, max_outputs = 10)
return x, y, step, acc, acc_mat, prediction, keep_prob
def train():
x, y, step, acc, acc_mat, prediction, keep_prob = build_network()
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
summary_merged = tf.summary.merge_all() #必须放在初始化的后面,否则报错
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs'+str(time.time()), sess.graph)
for i in range(50):
x_features, y_lables = load_data(sess)
_, summary_ = sess.run([step, summary_merged], feed_dict={x: x_features, y: y_lables, keep_prob: 0.5})
writer.add_summary(summary_, i)
if (i + 1) % 5 == 0:
curr_acc = sess.run(acc, feed_dict={x: x_features, y: y_lables, keep_prob: 1.0})
print("current test Accuracy : %f" % (curr_acc))
saver.save(sess, "./checkpoint/tf_mnist.model", global_step=50)
writer.close()
print('*************************')
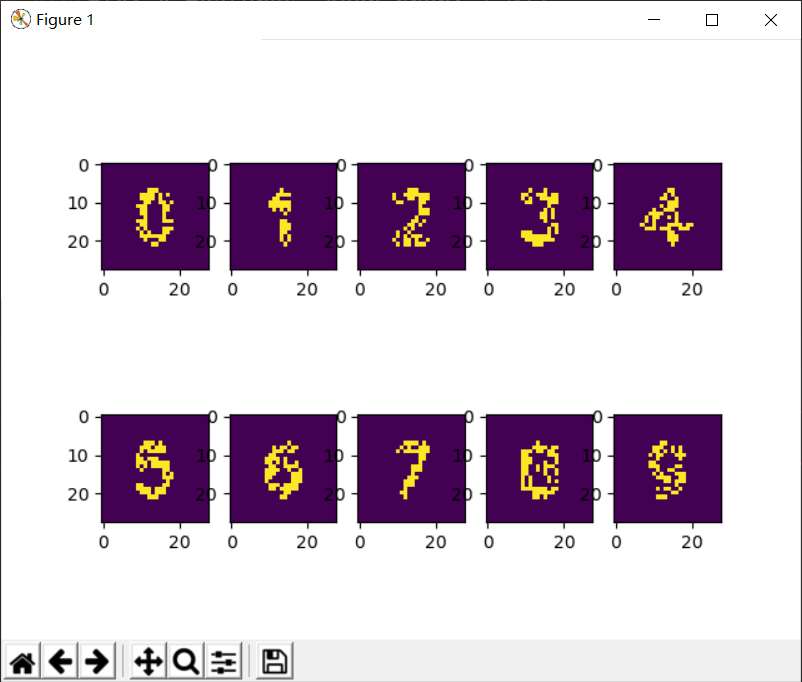
x_features, y_labels = load_data(sess, 300, should_display_images=True)
pred_ys = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x: x_features, keep_prob: 1.0})
print('图片识别结果:', pred_ys)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
current test Accuracy : 4.000000 current test Accuracy : 7.000000 current test Accuracy : 7.000000 current test Accuracy : 10.000000 current test Accuracy : 8.000000 current test Accuracy : 10.000000 current test Accuracy : 10.000000 current test Accuracy : 10.000000 current test Accuracy : 10.000000 current test Accuracy : 10.000000 ************************* 图片识别结果: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
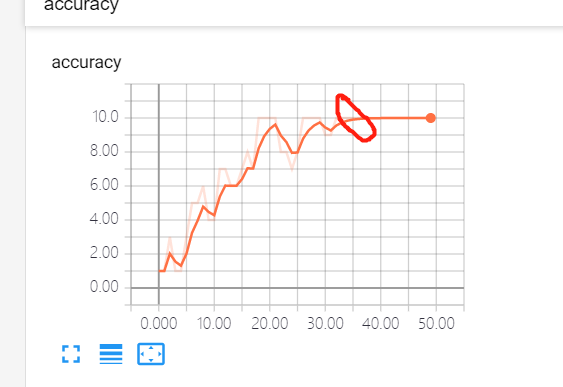
我们可以看到,在用卷积网络做训练时,大概35此迭代就实现了正确率达到了10张图片全部识别正确,但是普通2层全连接网络需要花费大概400次迭代才能达到100%正确率
自省推动进步,视野决定未来。
心怀远大理想。
为了家庭幸福而努力。
商业合作请看此处:https://www.magicube.ai
心怀远大理想。
为了家庭幸福而努力。
商业合作请看此处:https://www.magicube.ai



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号