PID算法图形 python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
class PID:
def __init__(self, P=0.2, I=0.0, D=0.0):
self.Kp = P
self.Ki = I
self.Kd = D
self.sample_time = 0.00
self.current_time = time.time()
self.last_time = self.current_time
self.clear()
def clear(self):
self.SetPoint = 0.0
self.PTerm = 0.0
self.ITerm = 0.0
self.DTerm = 0.0
self.last_error = 0.0
self.int_error = 0.0
self.windup_guard = 20.0
self.output = 0.0
def update(self, feedback_value):
error = self.SetPoint - feedback_value
self.current_time = time.time()
delta_time = self.current_time - self.last_time
delta_error = error - self.last_error
if (delta_time >= self.sample_time):
self.PTerm = self.Kp * error # 比例
self.ITerm += error * delta_time # 积分
if (self.ITerm < -self.windup_guard):
self.ITerm = -self.windup_guard
elif (self.ITerm > self.windup_guard):
self.ITerm = self.windup_guard
self.DTerm = 0.0
if delta_time > 0:
self.DTerm = delta_error / delta_time
self.last_time = self.current_time
self.last_error = error
self.output = self.PTerm + (self.Ki * self.ITerm) + (self.Kd * self.DTerm)
def setKp(self, proportional_gain):
self.Kp = proportional_gain
def setKi(self, integral_gain):
self.Ki = integral_gain
def setKd(self, derivative_gain):
self.Kd = derivative_gain
def setWindup(self, windup):
self.windup_guard = windup
def setSampleTime(self, sample_time):
self.sample_time = sample_time
import time
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use("TkAgg")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.interpolate import make_interp_spline
def test_pid(P=0.2, I=0.0, D=0.0, L=100):
pid = PID(P, I, D)
pid.SetPoint = 0.0
pid.setSampleTime(0.01)
END = L
feedback = 0
feedback_list = []
time_list = []
setpoint_list = []
for i in range(1, END):
pid.update(feedback)
output = pid.output
# print(output)
if pid.SetPoint > 0:
feedback += output # (output - (1/i))控制系统的函数
if 9 <= i <= 40:
pid.SetPoint = 1
elif i > 40:
pid.SetPoint = 0.5
time.sleep(0.01)
feedback_list.append(feedback)
setpoint_list.append(pid.SetPoint)
time_list.append(i)
time_sm = np.array(time_list)
time_smooth = np.linspace(time_sm.min(), time_sm.max(), 300)
feedback_smooth = make_interp_spline(time_list, feedback_list)(time_smooth)
plt.figure(0)
plt.plot(time_smooth, feedback_smooth)
plt.plot(time_list, setpoint_list)
plt.xlabel('time (s)')
plt.ylabel('PID (PV)')
plt.title('TEST PID {}/{}/{}'.format(P, I, D))
plt.xlim((0, L))
plt.ylim((-0.5, 2))
plt.grid(True)
# plt.show()
plt.savefig('./images/TEST PID {}-{}-{}.jpg'.format(P, I, D))
plt.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_pid(1.2, 1.0, 0.001, L=50)
test_pid(1.2, 1.0, 0, L=50)
test_pid(1.2, 0, 0, L=50)
test_pid(0.8, 1.0, 0.001, L=50)
test_pid(0.8, 1.0, 0, L=50)
test_pid(0.8, 0, 0, L=50)
test_pid(0.2, 0.0, 0.001, L=50)
test_pid(0.2, 0.0, 0, L=50)
test_pid(0.2, 0, 0, L=50)
test_pid(0.8, 0, 0.001, L=50)
test_pid(1.2, 0, 0.001, L=50)
test_pid(0.7, 0.8, 0.001, L=50)
test_pid(0.8, L=50)


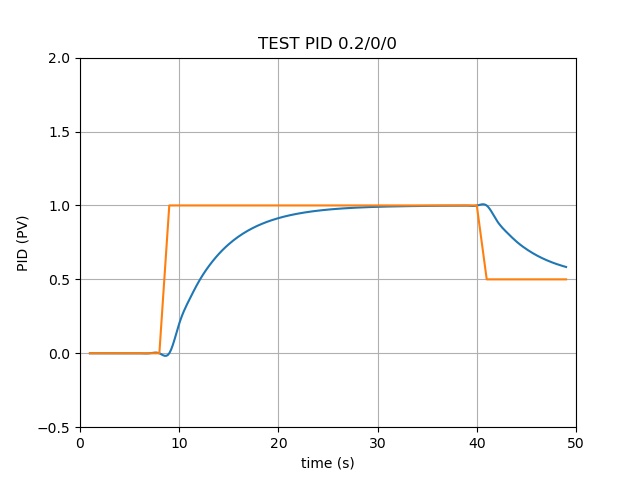

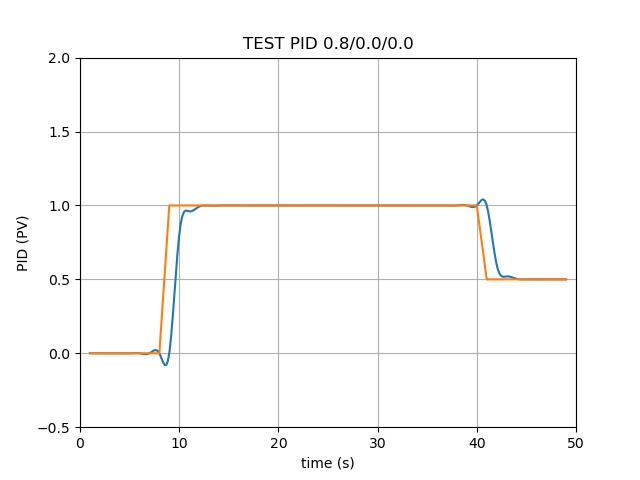
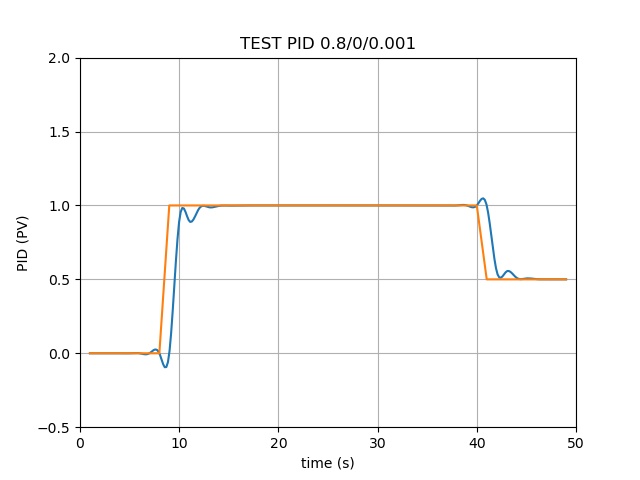
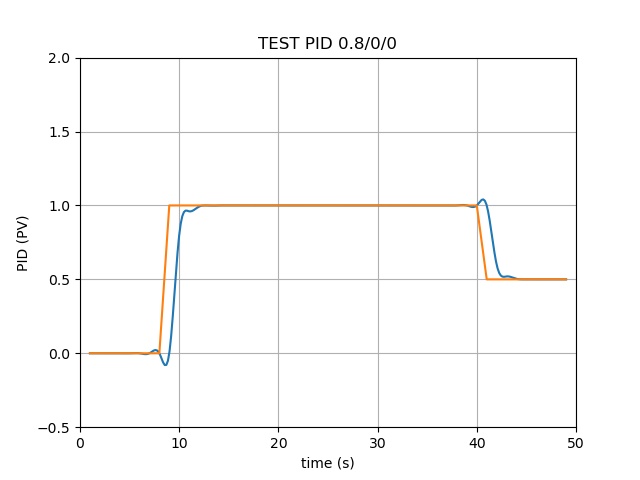
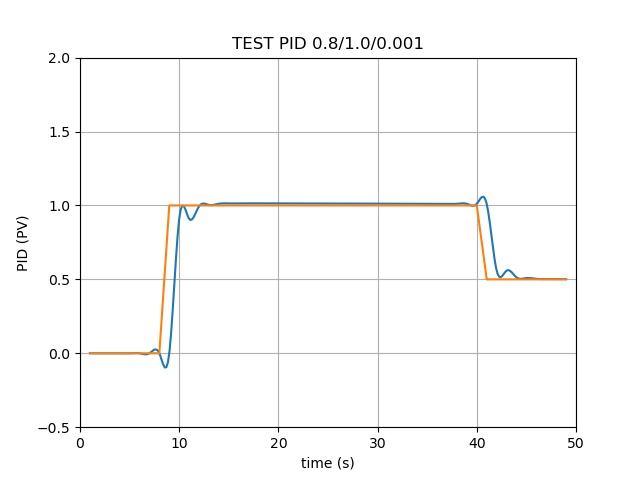
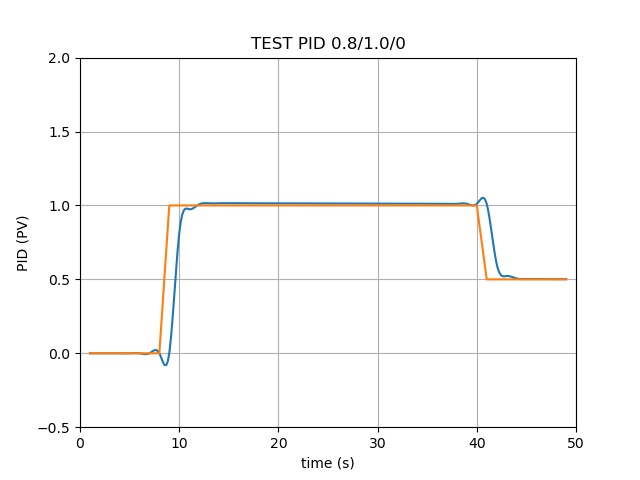
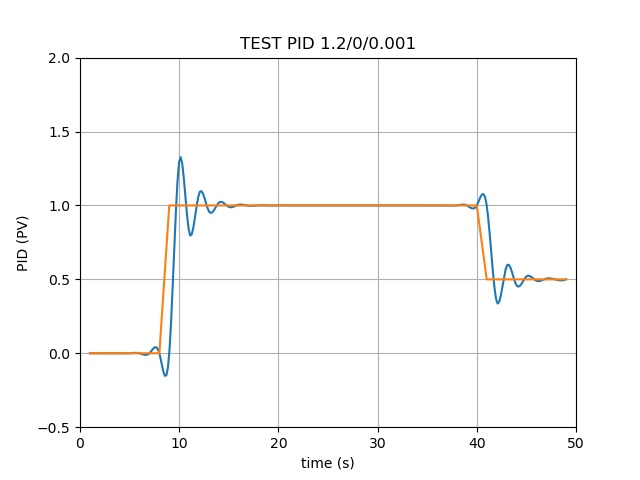



模拟了电动机电压的输出:
- 从0秒开始到第9秒,要求输出电压为0V;
- 从第10秒开始到第40秒,要求输出电压为1V;
- 从第41秒开始到第50秒,要求输出电压为0.5V
橘黄色线代表上述需求(理想输出电压)
绿色线为PID算法输出带反馈积分的输出电压
看得到P(比例)部分 是一个最重要的参数、I(积分)部分能让两条线完全重合(可能过于理想,有待验证)、D(微分)部分会对电压产生微调的上下波动影响
PID算法的参数看来是能够影响元器件寿命的
自省推动进步,视野决定未来。
心怀远大理想。
为了家庭幸福而努力。
商业合作请看此处:https://www.magicube.ai
心怀远大理想。
为了家庭幸福而努力。
商业合作请看此处:https://www.magicube.ai



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号