git常用命令
下图比较形象地描述了git各区域和常用几个操作之间的关系。
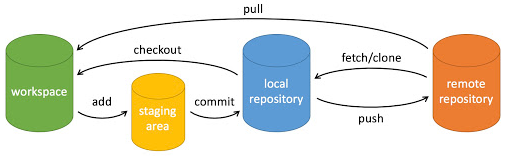
- workspace:工作区
- staging area:暂存区/缓存区
- local repository:本地仓库
- remote repository:远程仓库
1、初始化仓库
# 使用当前目录作为git仓库并初始化
git init
# 使用指定目录newRepo作为git仓库并初始化
git init newRepo
2、克隆仓库
# 下载一个项目及其整个代码历史到指定目录
git clone <仓库url> [指定目录]
# 只下载最近一次commit的默认分支代码
git clone --depth=1 <仓库url>
3、配置
# 显示当前的git配置 git config [--global|local] --list
# 编辑配置文件
git config -e [--global]
# 设置提交代码时的用户信息
git config [--global|local] user.name "gitName"
git config [--global|local] user.email "gitEmail"
4、添加|删除文件
# 添加一个或多个文件到暂存区
git add [file1] [file2] ...
# 添加指定目录(包括子目录)到暂存区
git add [dir]
# 添加当前目录下的所有文件到暂存区
git add .
# 删除工作区文件,并将这次删除放入暂存区
git rm [file1] [file2] ...
# 将文件从暂存区移除,但保留在工作区
git rm --cached [file]
# 重命名工作区文件,并将改名放入暂存区
git mv [-f] [file] [newfile]
5、提交暂存区到本地仓库
# 提交暂存区到本地仓库 git commit -m [message] # 提交暂存区的指定文件到仓库区 git commit [file1] [file2] ... -m [message] # 提交工作区自上次commit之后的变化,直接到仓库区,不需要执行git add命令 git commit -a # 提交时显示所有diff信息 git commit -v # 使用一次新的commit,替代上一次提交;如果代码没有任何新变化,则用来改写上一次commit的提交信息 git commit --amend -m [message]
# 重做上一次commit,并包括指定文件的新变化
git commit --amend [file1] [file2] ...
6、分支
# 列出所有本地分支 git branch # 列出所有远程分支 git branch -r # 列出所有本地分支和远程分支 git branch -a # 新建一个分支,但依然停留在当前分支 git branch [branch-name] # 新建一个分支,并切换到该分支 git checkout -b [branch] # 新建一个分支,指向指定commit git branch [branch] [commit] # 新建一个分支,与指定的远程分支建立追踪关系 git branch --track [branch] [remote-branch] # 切换到指定分支,并更新工作区 git checkout [branch-name] # 切换到上一个分支 git checkout - # 建立追踪关系,在现有分支与指定的远程分支之间 git branch --set-upstream [branch] [remote-branch] # 合并指定分支到当前分支 git merge [branch] # 选择一个commit,合并进当前分支 git cherry-pick [commit] # 删除分支 git branch -d [branch-name] # 删除远程分支 git push origin --delete [branch-name] git branch -dr [remote/branch]
7、标签
# 列出所有tag git tag # 新建一个tag在当前commit git tag [tag] # 新建一个tag在指定commit git tag [tag] [commit] # 删除本地tag git tag -d [tag] # 删除远程tag git push origin :refs/tags/[tagName] # 查看tag信息 git show [tag] # 提交指定tag git push [remote] [tag] # 提交所有tag git push [remote] --tags # 新建一个分支,指向某个tag git checkout -b [branch] [tag]
8、查看信息
# 显示有变更的文件 git status # 显示当前分支的版本历史 $ git log
# 查看历史记录的简洁版本
git log --oneline # 开启拓扑图查看历史记录
git log --graph
# 查找用户gitter提交的指定关键字的记录
git log --author=gitter --grep 指定关键字
# 显示commit历史,以及每次commit发生变更的文件 git log --stat # 显示某个commit之后的所有变动,每个commit占据一行 git log [tag] HEAD --pretty=format:%s # 显示过去5次提交 git log -5 --pretty --oneline # 显示所有提交过的用户,按提交次数排序 git shortlog -sn # 显示指定文件是什么人在什么时间修改过 git blame [file] # 显示暂存区和工作区的差异 git diff [file] # 显示暂存区和上一个commit的差异 git diff --cached [file] # 显示工作区与当前分支最新commit之间的差异 $ git diff HEAD # 显示两次提交之间的差异 $ git diff [first-branch]...[second-branch] # 显示某次提交的元数据和内容变化 $ git show [commit] # 显示某次提交发生变化的文件 $ git show --name-only [commit] # 显示某次提交时,某个文件的内容 git show [commit]:[filename]
9、远程同步
# 下载远程仓库的所有变动 git fetch [remote] # 显示所有远程仓库 git remote -v # 显示某个远程仓库的信息 git remote show [remote] # 增加一个新的远程仓库,并命名 git remote add [shortname] [url] # 取回远程仓库的变化,并与本地分支合并 git pull [remote] [branch] # 上传本地指定分支到远程仓库 git push [remote] [branch] # 强行推送当前分支到远程仓库,即使有冲突 git push [remote] --force # 推送所有分支到远程仓库 git push [remote] --all
10、撤销
# 恢复暂存区的指定文件到工作区 git restore --staged [file] # 恢复暂存区的所有文件到工作区 git restore --staged .
# 撤销工作区文件的修改
git restore --worktree [file] # 重置暂存区的指定文件,与上一次commit保持一致,但工作区不变 git reset [file] # 重置暂存区与工作区,与上一次commit保持一致 git reset --hard # 重置当前分支的指针为指定commit,同时重置暂存区,但工作区不变 git reset [commit] # 重置当前分支的HEAD为指定commit,同时重置暂存区和工作区,与指定commit一致 git reset --hard [commit] # 重置当前HEAD为指定commit,但保持暂存区和工作区不变 git reset --keep [commit] # 新建一个commit,用来撤销指定commit # 后者的所有变化都将被前者抵消,并且应用到当前分支 git revert [commit] 暂时将未提交的变化移除,稍后再移入 git stash git stash pop


